Signs of tetany!!!
“Trousseau sign of malignancy, Trousseau sign of latent tetany, Trousseau–Lallemand bodie”
French internist Armand Trousseau (1801–1867)
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/
“Trousseau sign of malignancy, Trousseau sign of latent tetany, Trousseau–Lallemand bodie”
French internist Armand Trousseau (1801–1867)
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/

Definition
Tetanus
- it is different disease w/ different pathology
Tetanic contractions (physiologic tetanus)
- broad range of muscle contraction types
Tetany
- a type of tetanic contraction
2/
Tetanus
- it is different disease w/ different pathology
Tetanic contractions (physiologic tetanus)
- broad range of muscle contraction types
Tetany
- a type of tetanic contraction
2/
Clinical manifestations of tetany
“spasm and tonic contractions of the skeletal muscles, principally the distal muscles of the extremities”
3/
“spasm and tonic contractions of the skeletal muscles, principally the distal muscles of the extremities”
3/
Pathophysiology
- more easily obtained if the patient first hyperventilates for a few minutes (latent tetany)
4/
- more easily obtained if the patient first hyperventilates for a few minutes (latent tetany)
4/

Chvostek’s sign
“tapping over the facial nerve causes a twitch”
Hyperexcitability of the motor nerves
2 points of stimulation
-Chvostek: just below zygomatic process of temporal bone, in front of ear
-Schultz: midway between the zygomatic arch and the angle of the mouth
5/
“tapping over the facial nerve causes a twitch”
Hyperexcitability of the motor nerves
2 points of stimulation
-Chvostek: just below zygomatic process of temporal bone, in front of ear
-Schultz: midway between the zygomatic arch and the angle of the mouth
5/

Conditions associated w/ Chvostek sign
- tetany
- CST lesion (hyperreflexia)
- children w/ epilepsy
- neonatal period disappearing w/ aging
Limitation
- crude indicator of neuro-muscular irritability and an unreliable indicator of hypocalcemia
6/
- tetany
- CST lesion (hyperreflexia)
- children w/ epilepsy
- neonatal period disappearing w/ aging
Limitation
- crude indicator of neuro-muscular irritability and an unreliable indicator of hypocalcemia
6/
Chvostek’s sign
via: NEJM
7/
via: NEJM
7/
Chvostek’s sign
via: Ivan Paredes
8/
via: Ivan Paredes
8/
Trousseau’s sign
“compression of the arm by manual pressure cause contraction of the muscles of the hand”
Ischemia increases nerve excitability & spontaneous discharges
Obstetrician’s/accoucheur’s hand, main d’accoucheur
Similar pressure around thigh will cause pedal spasm
9/
“compression of the arm by manual pressure cause contraction of the muscles of the hand”
Ischemia increases nerve excitability & spontaneous discharges
Obstetrician’s/accoucheur’s hand, main d’accoucheur
Similar pressure around thigh will cause pedal spasm
9/
Phases
First, paresthesia progress centripetally
Second, finger twitching
Third, contraction
- there may be a latent period of 1/2 to 4 minutes
- 20 mmHg over their systolic blood pressure for 3 minutes
10/
First, paresthesia progress centripetally
Second, finger twitching
Third, contraction
- there may be a latent period of 1/2 to 4 minutes
- 20 mmHg over their systolic blood pressure for 3 minutes
10/
Limitations
- sometimes positive in hysterical subjects
- workers whose hands are held in a semi-tetanic position for some hours daily
11/
- sometimes positive in hysterical subjects
- workers whose hands are held in a semi-tetanic position for some hours daily
11/
Trousseau’s sign
via: NEJM
12/
via: NEJM
12/
Trousseau’s sign
via: Doams BD
13/
via: Doams BD
13/
Clinical significance
a. Sensitivity for latent tetany
- Trousseau (94%) vs Chvostek (29%)
b. Healthy individuals
- 4% of healthy individuals have Trousseau
14/
a. Sensitivity for latent tetany
- Trousseau (94%) vs Chvostek (29%)
b. Healthy individuals
- 4% of healthy individuals have Trousseau
14/
Hyperventilation test
Elicitation: hyperventilate at rate of 55-60/min for 3 min. Sitting upright, with hands placed loosely on knees
Response: if no tetanic manifestation develops, tetany is ruled out
Disadvantages: disturbing symptoms after hyperventilation
15/
Elicitation: hyperventilate at rate of 55-60/min for 3 min. Sitting upright, with hands placed loosely on knees
Response: if no tetanic manifestation develops, tetany is ruled out
Disadvantages: disturbing symptoms after hyperventilation
15/

Hyperventilation test
via: Sanjoy Ray
16/
via: Sanjoy Ray
16/
Trousseau-von Bonsdorff test
(tourniquet&hyperventillation)
a. sitting up, hands placed on knees
b. tourniquet for 4 min
c. if no cramp appear, tourniquet is removed
d. hyperventilate at the rate of 40 breaths/min
d. test is stopped at 75sec/sooner if carpel cramp appears
17/
(tourniquet&hyperventillation)
a. sitting up, hands placed on knees
b. tourniquet for 4 min
c. if no cramp appear, tourniquet is removed
d. hyperventilate at the rate of 40 breaths/min
d. test is stopped at 75sec/sooner if carpel cramp appears
17/
Pool-Schlesinger sign
Pool/arm phenomenon
- abduct&elevate patient's arm w/ his forearm extended
- brachial plexus tension
Schlesinger/leg phenomenon
- flex patient's extended leg at the hip
- sciatic nerve tension
18/
Pool/arm phenomenon
- abduct&elevate patient's arm w/ his forearm extended
- brachial plexus tension
Schlesinger/leg phenomenon
- flex patient's extended leg at the hip
- sciatic nerve tension
18/

Peroneal (Lust phenomenon)
Elicit: tap over the common peroneal nerve (lateral neck of the fibula with the patient's knee
relaxed and slightly flexed)
Response: dorsiflexion and abduction of the foot
19/
Elicit: tap over the common peroneal nerve (lateral neck of the fibula with the patient's knee
relaxed and slightly flexed)
Response: dorsiflexion and abduction of the foot
19/

Escherich's sign
Elicit: percussion of the inner surface of the lips/tongue
Response: contractions of the lips, masseters, and tongue
20/
Elicit: percussion of the inner surface of the lips/tongue
Response: contractions of the lips, masseters, and tongue
20/
Hochsinger’s sign
Elicit: pressure on inner aspect of biceps muscle
Response: spasm and contraction of the hand (variant of Trousseau sign)
21/
Elicit: pressure on inner aspect of biceps muscle
Response: spasm and contraction of the hand (variant of Trousseau sign)
21/
Kashida thermic
Elicit: application of either hot or cold irritants
Response: hyperesthesias and spasms
22/
Elicit: application of either hot or cold irritants
Response: hyperesthesias and spasms
22/
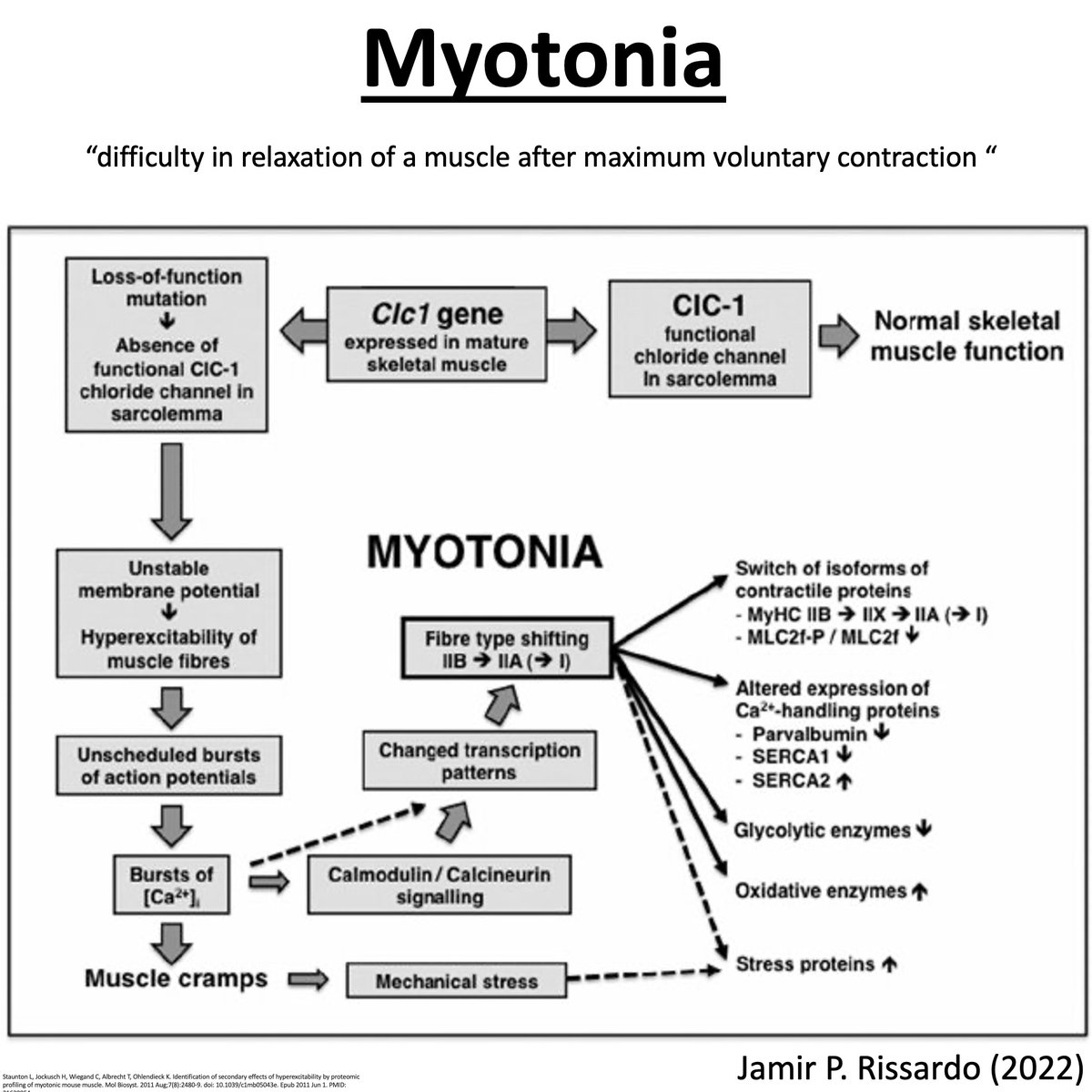
Schultze’s sign
Elicit: mechanical stimulation of protruded tongue
Response: transient depression or dampling at the site of stimulation (similar to myotonia)
23/
Elicit: mechanical stimulation of protruded tongue
Response: transient depression or dampling at the site of stimulation (similar to myotonia)
23/
NeuroTeach - Content
The blog contains all the threads and videos.
neuronland.blogspot.com/2022/11/neurot…
Have a great day!
25/
The blog contains all the threads and videos.
neuronland.blogspot.com/2022/11/neurot…
Have a great day!
25/
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh