Drifts!!!
French neurologist Jean Alexandre Barré (1880–1967)
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/
French neurologist Jean Alexandre Barré (1880–1967)
#MedTwitter #neurotwitter #EndNeurophobia #tweetorials
1/
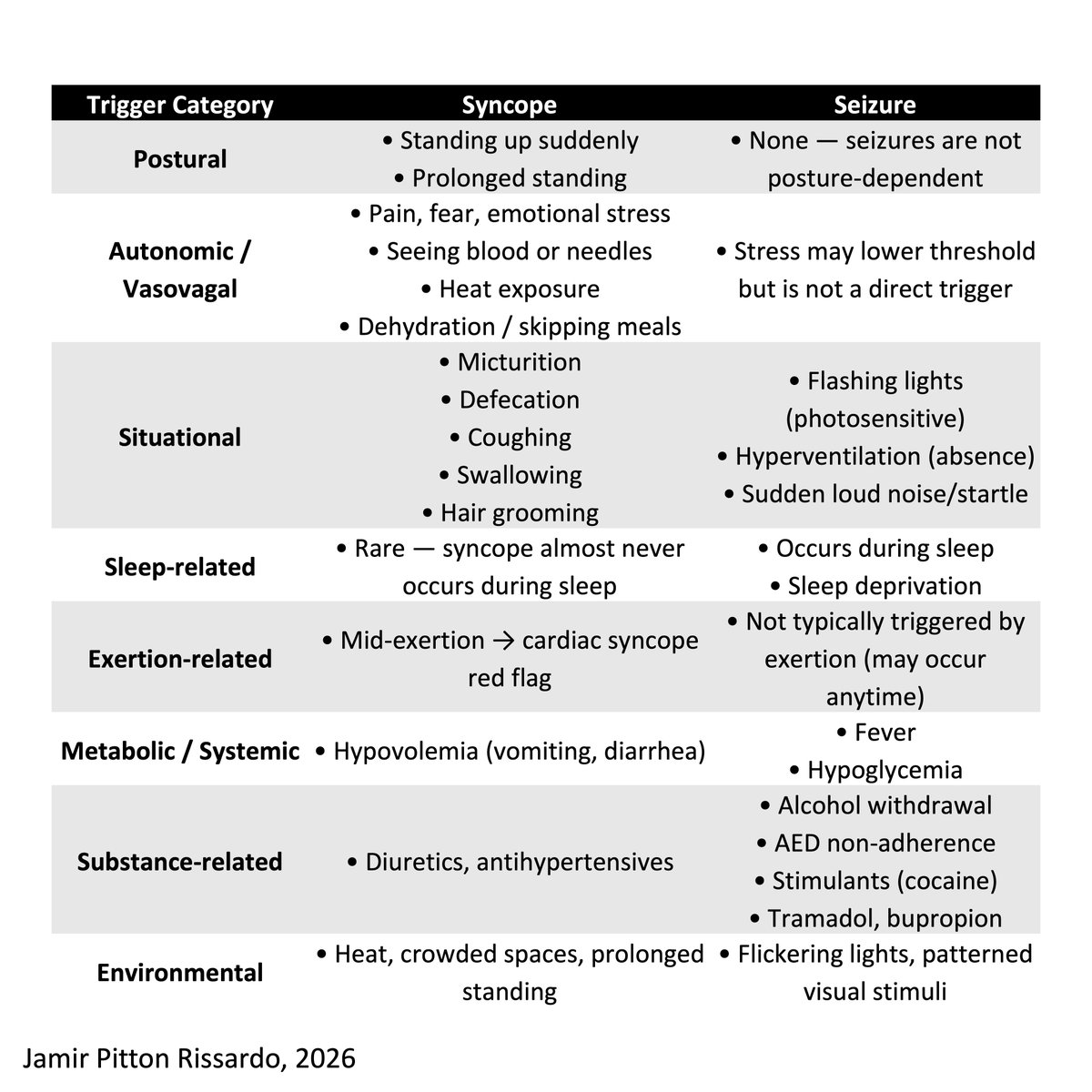
The four types of drift
“pronator, cerebellar, parietal, and functional”
- pronator drift (pyramidal drift) was the 1st to be described
- Dr. Barre was the 1st to report it
2/
“pronator, cerebellar, parietal, and functional”
- pronator drift (pyramidal drift) was the 1st to be described
- Dr. Barre was the 1st to report it
2/
Pronator drift (Barre’s sign)
progress from distal to proximal
1st downward arm drift
2nd forearm pronation
3rd flexion of the wrist and elbow
3/
progress from distal to proximal
1st downward arm drift
2nd forearm pronation
3rd flexion of the wrist and elbow
3/

Pronator drift – assessment
"patient extends both arms upright in the supinated position and hold them at shoulder height for at least 10 sec (patient should be asked to keep eyes open initially and later test again with eyes closed)"
via: daihocyduoc
4/
"patient extends both arms upright in the supinated position and hold them at shoulder height for at least 10 sec (patient should be asked to keep eyes open initially and later test again with eyes closed)"
via: daihocyduoc
4/
Response
“the examiner can simple wait for the response or hasten the process by tapping on the patient’s palms or having the patient turn the head back and forth, or both”
5/
“the examiner can simple wait for the response or hasten the process by tapping on the patient’s palms or having the patient turn the head back and forth, or both”
5/

Pronator drift development
The stronger muscles of the upper limbs are "pronators, biceps, and internal rotators of the shoulder"
6/
The stronger muscles of the upper limbs are "pronators, biceps, and internal rotators of the shoulder"
6/

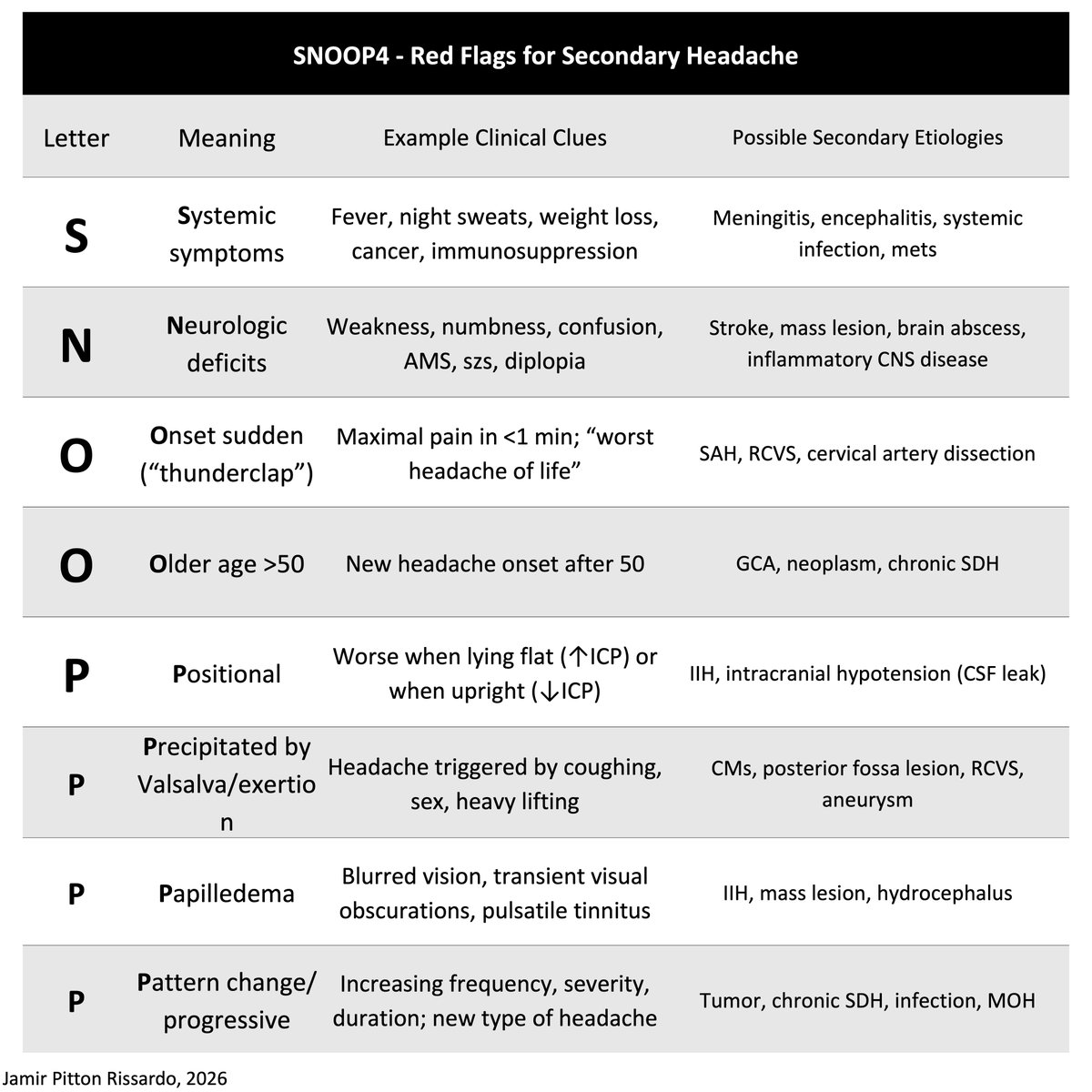
Clinical significance
a. can detect subtle upper motor neuron lesion which goes unrecognized by routine motor examination
b. included in initial examination of stroke
c. if only one motor test could be done in a patient – the best single test would be to examine the drift
7/
a. can detect subtle upper motor neuron lesion which goes unrecognized by routine motor examination
b. included in initial examination of stroke
c. if only one motor test could be done in a patient – the best single test would be to examine the drift
7/
Mechanism
Why pronator drift occurs when eyes are closed?
Why pronator overcomes supinator in pyramidal lesion?
8/
Why pronator drift occurs when eyes are closed?
Why pronator overcomes supinator in pyramidal lesion?
8/

Pronator drift
via: NEJM
9/
via: NEJM
9/
Pronator drift
via: Dr. Sourya Acharya
10/
via: Dr. Sourya Acharya
10/
Pronator drift
via: intmedrocks
11/
via: intmedrocks
11/
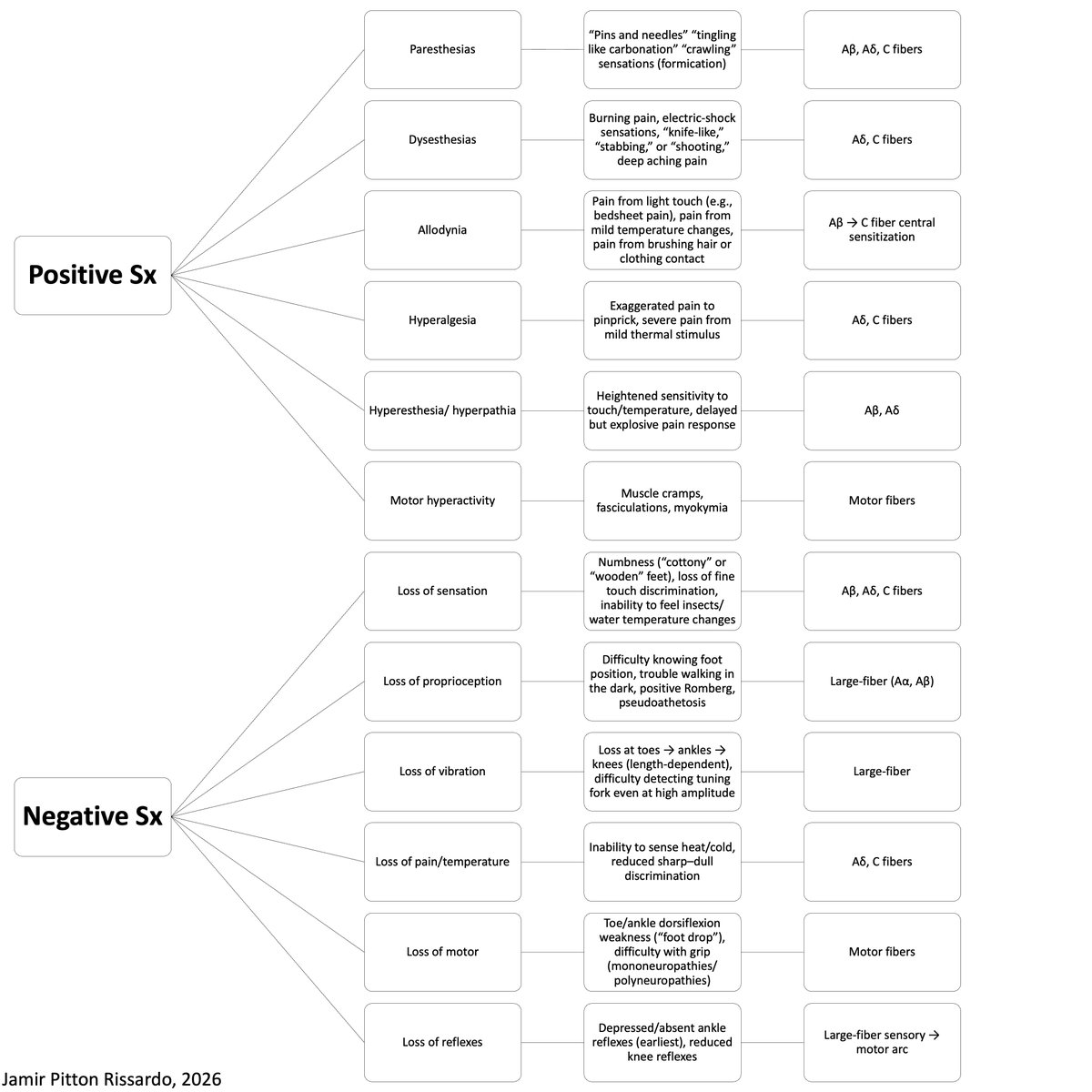
Drifts
Pronator(+) w/ eyes open: motor deficit
Pronator(+) w/ eyes closed: sensory deficit (post column)
Out: cerebellar
Updrift (rising arm overhead w/o pt awareness): parietal lobe lesion (loss of position sense)
Drift w/o pronation: functional upper limb paresis
12/
Pronator(+) w/ eyes open: motor deficit
Pronator(+) w/ eyes closed: sensory deficit (post column)
Out: cerebellar
Updrift (rising arm overhead w/o pt awareness): parietal lobe lesion (loss of position sense)
Drift w/o pronation: functional upper limb paresis
12/
Cerebellar drift
“drifts mainly outward, either at same level, rising, sinking”
- accentuated by raise&lower arms or tapping wrists
- ipsilateral
13/
“drifts mainly outward, either at same level, rising, sinking”
- accentuated by raise&lower arms or tapping wrists
- ipsilateral
13/
Parietal drift
i) can be ‘out, up or rarely downward’
ii) parieto-occipital lesion out&upward
iii) parieto-temporal lesion up but NOT outward
- contralateral lesion
- Brodmann area relation
14/
i) can be ‘out, up or rarely downward’
ii) parieto-occipital lesion out&upward
iii) parieto-temporal lesion up but NOT outward
- contralateral lesion
- Brodmann area relation
14/

Leg drift
“patient lies supine with the hips and knees flexed, the knees forming an angle of about 45 degrees”
-positive, heel will gradually slide downward, knee slowly extends, and the hip goes into extension, external rotation, and abduction
- no clear localization
17/
“patient lies supine with the hips and knees flexed, the knees forming an angle of about 45 degrees”
-positive, heel will gradually slide downward, knee slowly extends, and the hip goes into extension, external rotation, and abduction
- no clear localization
17/
NeuroTeach - Content
The blog contains all the threads and videos.
neuronland.blogspot.com/2022/11/neurot…
Have a great day!
The blog contains all the threads and videos.
neuronland.blogspot.com/2022/11/neurot…
Have a great day!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh