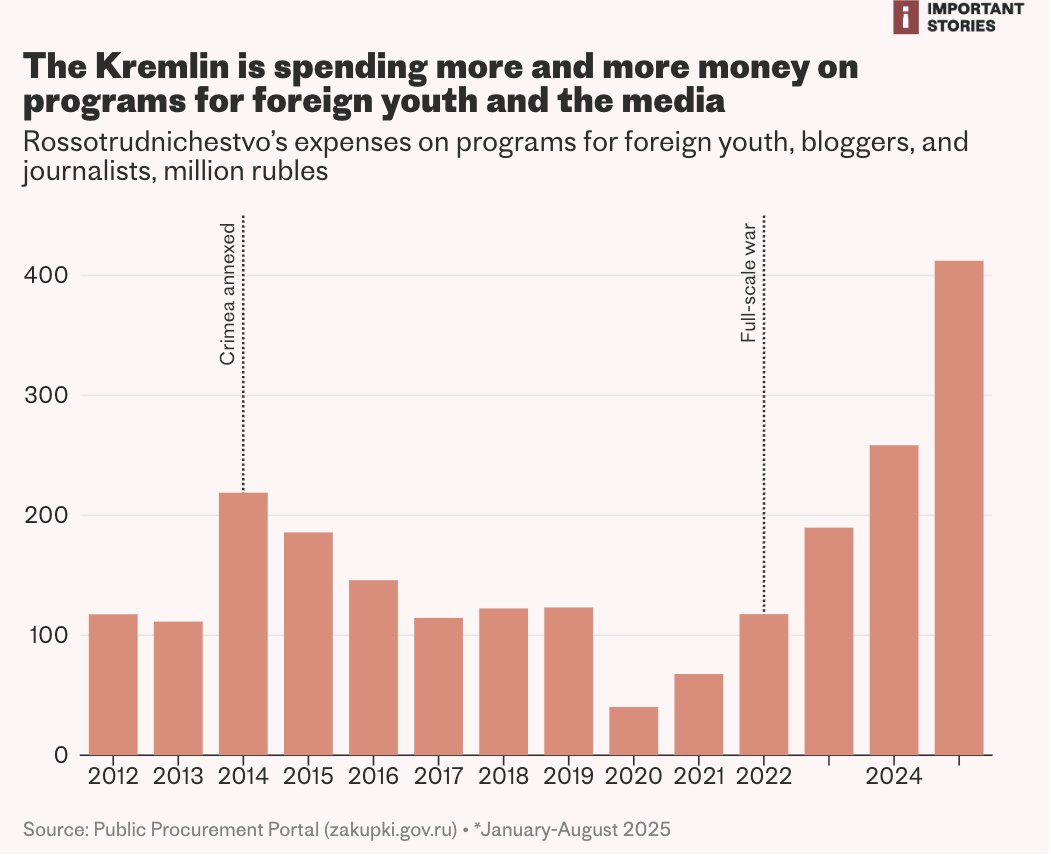
In today's #vatnik soup I'm going to talk about conspiracy theories and the people who believe in them. These theories are an explanation for an event that's orchestrated by powerful and often hidden groups.
1/15
1/15

Conspiracy theories are often political and they're even more often explained with insufficient evidence.
Douglas & Sutton (2011) concluded that belief in conspiracies correlates with lower analytical thinking, low intelligence, paranoia and Machiavellianism.
2/15
Douglas & Sutton (2011) concluded that belief in conspiracies correlates with lower analytical thinking, low intelligence, paranoia and Machiavellianism.
2/15

2022 meta-analysis by Stasielowicz
supports this, adding that conspiracy theorists often believe in pseudoscience, are narcissistic or religious/spiritual and have relatively low cognitive ability. Douglas et al. (2017) stated that conspiracy theories correlate strongly ... 3/15
supports this, adding that conspiracy theorists often believe in pseudoscience, are narcissistic or religious/spiritual and have relatively low cognitive ability. Douglas et al. (2017) stated that conspiracy theories correlate strongly ... 3/15

...with two emotions: anxiety and disenfranchisement (the feeling of being deprived of a privilege).
A 2017 paper by van Prooijen, Douglas & De Inocencio also found correlation between conspiracy theorists and a phenomenon called "apophenia" or "illusory pattern perception".4/15
A 2017 paper by van Prooijen, Douglas & De Inocencio also found correlation between conspiracy theorists and a phenomenon called "apophenia" or "illusory pattern perception".4/15

It is a tendency to find connections between unrelated things. We often try to find patterns in order to explain the surrounding world to ourselves, but these people go WAY beyond, finding patterns everywhere. 5/15 

Good examples of pattern seeking is the constant search for the number 666 or decoding QAnon codes and cryptic messages. However, many cognitive scientists consider conspiracy theorizing to be a nonpathological and may just be our innate drive to gossip. 6/15 

Conspiracy theories that spread virally can have grave consequences: AIDS denialism through conspiracy theories led to over 300 000 AIDS deaths in South Africa, QAnon led to the US Capitol attack, and conspiracy theories regarding GMO food led to serious famine in Zambia. 7/15 

Many terrorists, including Anders Breivik and Timothy McVeigh
were also strongly influenced by conspiracy theories. 8/15
were also strongly influenced by conspiracy theories. 8/15

Conspiracy theories used to be limited to fringe communities like zines, early Bulletin Board Systems or small social groups, but Internet and especially social media brought them to mainstream. 9/15
Social media algorithms prioritize user engagement over user safety, thus providing conspiracy theory rabbit holes to keep the users on these platforms. They are then
spread further by troll farms and foreign state actors in order to polarize and agitate.
10/15
spread further by troll farms and foreign state actors in order to polarize and agitate.
10/15
In 2020 poll by NPR/Ipsos, 17% of the US population believed in QAnon and 37% were "not sure" if it's real or not. The number for mass shooting hoaxes was 12%/27%, and for moon landing conspiracy theory 8%/20%.
11/15
11/15

Michael Barkun has divided conspiracy theories into three distinct categories: event (e.g. Kennedy assasination or 9/11), systemic (Freemasons, WEF, etc.) or superconspiracy (e.g. QAnon,
Icke's "Son of the Godhead" or Hubbard's "Xenu").
12/15
Icke's "Son of the Godhead" or Hubbard's "Xenu").
12/15

The problem with arguing with conspiracy theorists is that their theories can't be falsified and are reinforced by arguments that are also false. Also, both evidence against the theory and the absence of such evidence are re-interpreted as evidence of its truth.
13/15
13/15
Successful propaganda and disinfo campaigns have also lowered people's trust towards mainstream media and the state, and conspiracy theorists often mock and criticize these establishments.
14/15
14/15
Today's conspiracy theories are much more powerful and dangerous tools as they can spread fast and wide via the web. For example QAnon has spread around the world, and there are sects for example in Japan, Finland, Russia, Australia and Brazil.
15/15
15/15

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh