
Every Bitcoiner should understand this graph.
Without it, #Bitcoin would be impossible.
Elliptic Curves thread:
Without it, #Bitcoin would be impossible.
Elliptic Curves thread:

Elliptic curve cryptography is a type of cryptography that uses elliptic curves to create mathematically linked public & private keys.
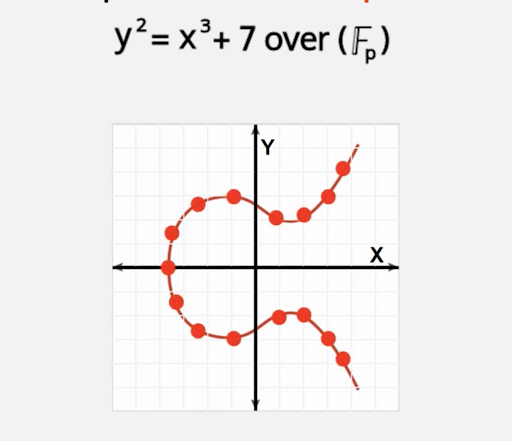
Bitcoin uses a curve called secp256k1, which is defined by the equation y^2=x^3+7.
The points along this curve are used to derive the values of public & private keys.
The points along this curve are used to derive the values of public & private keys.
Public-key cryptography is useful because it satisfies two conditions:
1. It is computationally impossible to derive a private key from its public key.
2. It is possible to prove ownership of a given private/public key pair without revealing any useful information about the private key in the process.
2. It is possible to prove ownership of a given private/public key pair without revealing any useful information about the private key in the process.
How is this accomplished?
Bitcoin takes advantage of the Discrete Log Problem to create irreversible, one-way mathematical functions.
Bitcoin takes advantage of the Discrete Log Problem to create irreversible, one-way mathematical functions.
To summarize the Discrete Log Problem without getting into the math:
Making a smoothie is easy, but compiling the ingredients back into their original form is very hard.
Making a smoothie is easy, but compiling the ingredients back into their original form is very hard.

In the same way, we can only ever get the public key from a private key but not the other way around.
If the public key is the smoothie, the private key is the ingredients.
This “trap door” mechanism ensures that your private key is secure.
If the public key is the smoothie, the private key is the ingredients.
This “trap door” mechanism ensures that your private key is secure.
To get an idea of the leverage involved here, there are 2^256 combinations of public and private keys.
That number is larger than the number of atoms in the observable universe.
To guess a private key is highly statistically unlikely.
That number is larger than the number of atoms in the observable universe.
To guess a private key is highly statistically unlikely.
So how does Bitcoin use the secp256k1 curve to generate public & private keys?
To create a public & private key pair using secp256k1 we can start with a random point on the curve, “k”.
“k” is our private key.
To create a public & private key pair using secp256k1 we can start with a random point on the curve, “k”.
“k” is our private key.
Bitcoin’s algorithm specifies a generator point “G” which is the same for all keypairs.
The generator point is just a single point on the secp256k1 curve.
The generator point is just a single point on the secp256k1 curve.
If we multiply the point “k” (our random number) by the generator point “G”, we end up with a new point “P” - our public key.
Thanks to the Discrete Log Problem, the math involved only allows us to calculate from private keys (“k”) to public keys (“P”), and not the other way around.
In other words, dividing the public key “P” by the generator point “G” cannot yield the private key “k”.
In other words, dividing the public key “P” by the generator point “G” cannot yield the private key “k”.
We’ve now created a public key “P” which is linked to the private key “k”, but cannot be used to derive the private key “k”.
With Elliptic Curves, Bitcoin can provide the same security profile as other encryption methods like RSA, but with a much smaller footprint.
This is essential because BTC is a p2p network that requires small packets.
This is essential because BTC is a p2p network that requires small packets.

TLDR;
Bitcoin uses Elliptic Curves to calculate public & private keys.
It's computationally impossible to derive a private key from its public key.
It's possible to prove ownership of a given private/public key pair without leaking any useful information about the private key.
Bitcoin uses Elliptic Curves to calculate public & private keys.
It's computationally impossible to derive a private key from its public key.
It's possible to prove ownership of a given private/public key pair without leaking any useful information about the private key.
This was undoubtedly a simplified explanation of Elliptic Curves, but we hoped you learned something new.
Bear markets are for learning!
Be sure to follow us @LN_Capital for more.
Bear markets are for learning!
Be sure to follow us @LN_Capital for more.
If you haven't already, check out Torq, a financial management tool for your Lightning node. You can find it on @umbrel and @BtcpayServer, or you can download it directly from us. Stay tuned for updates!
github.com/lncapital/torq
github.com/lncapital/torq
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh










