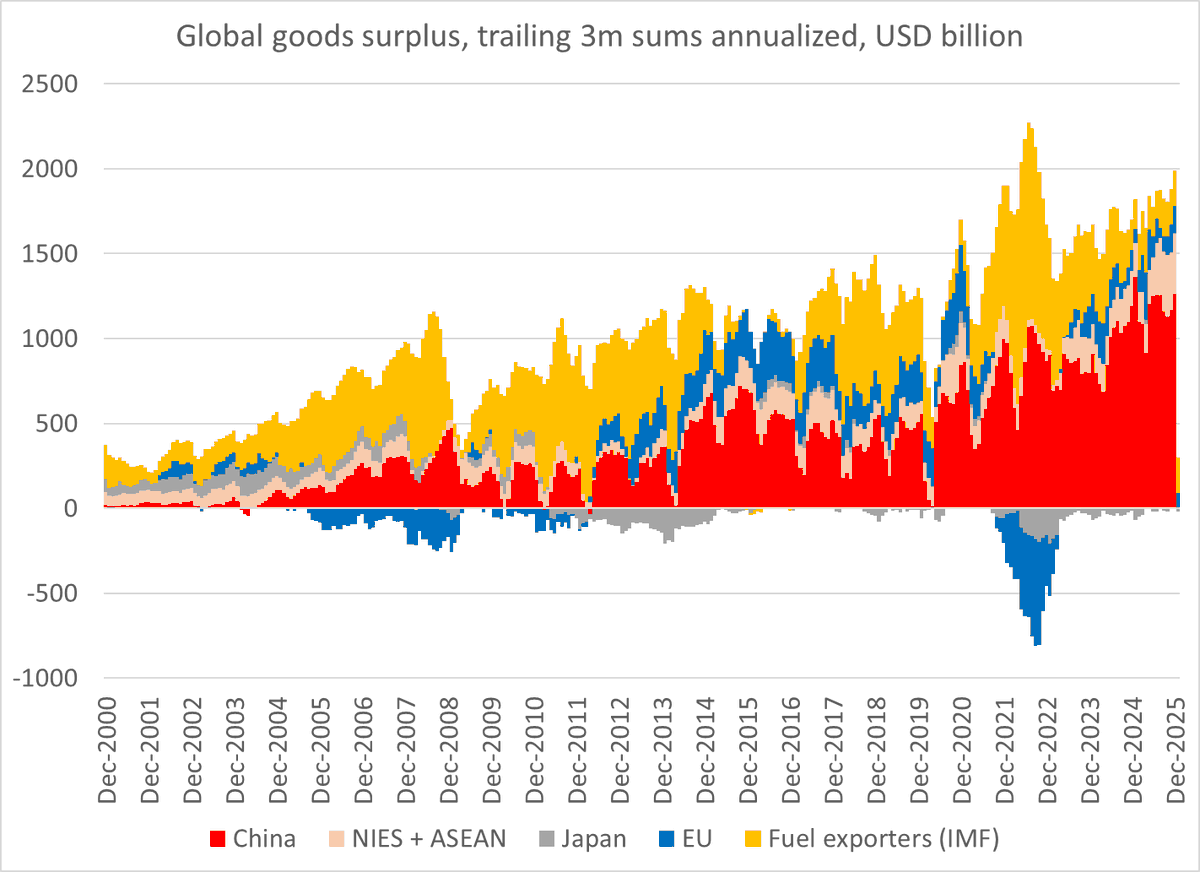
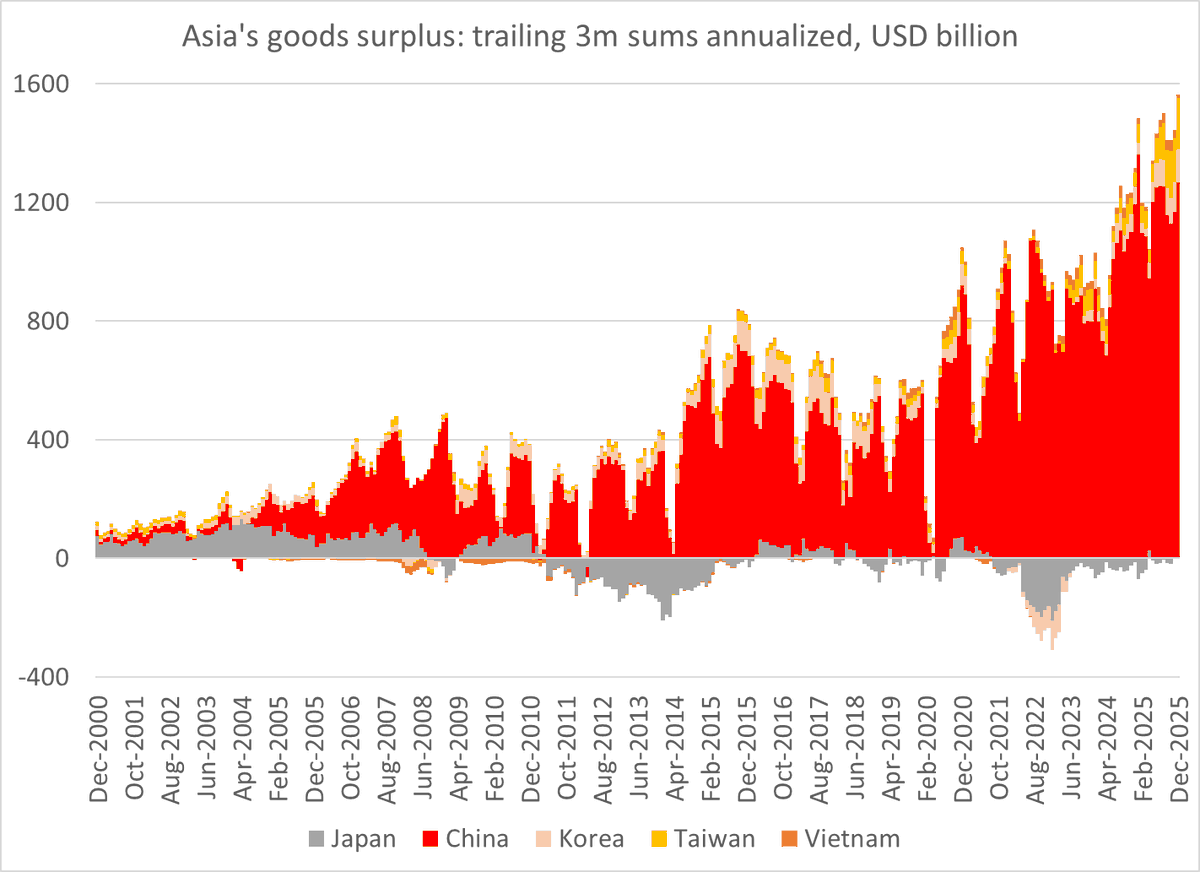
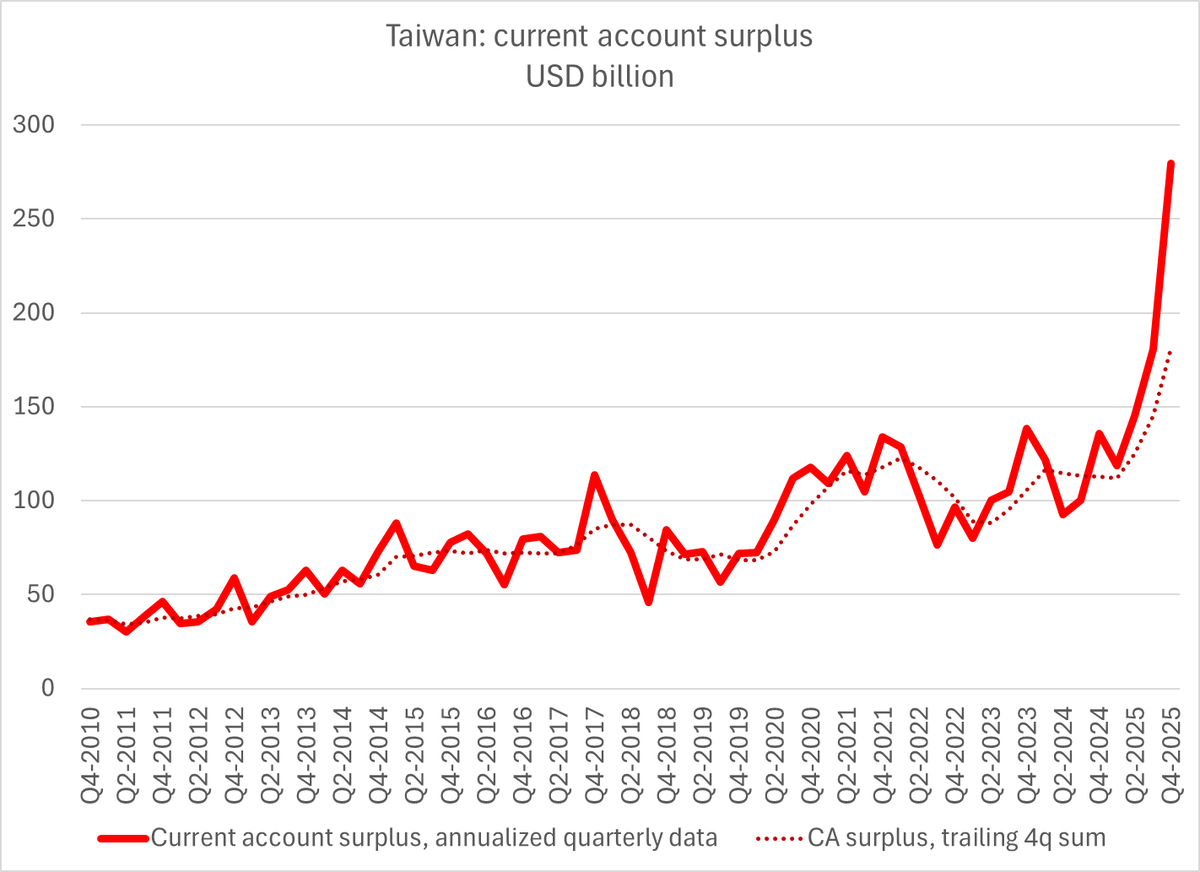
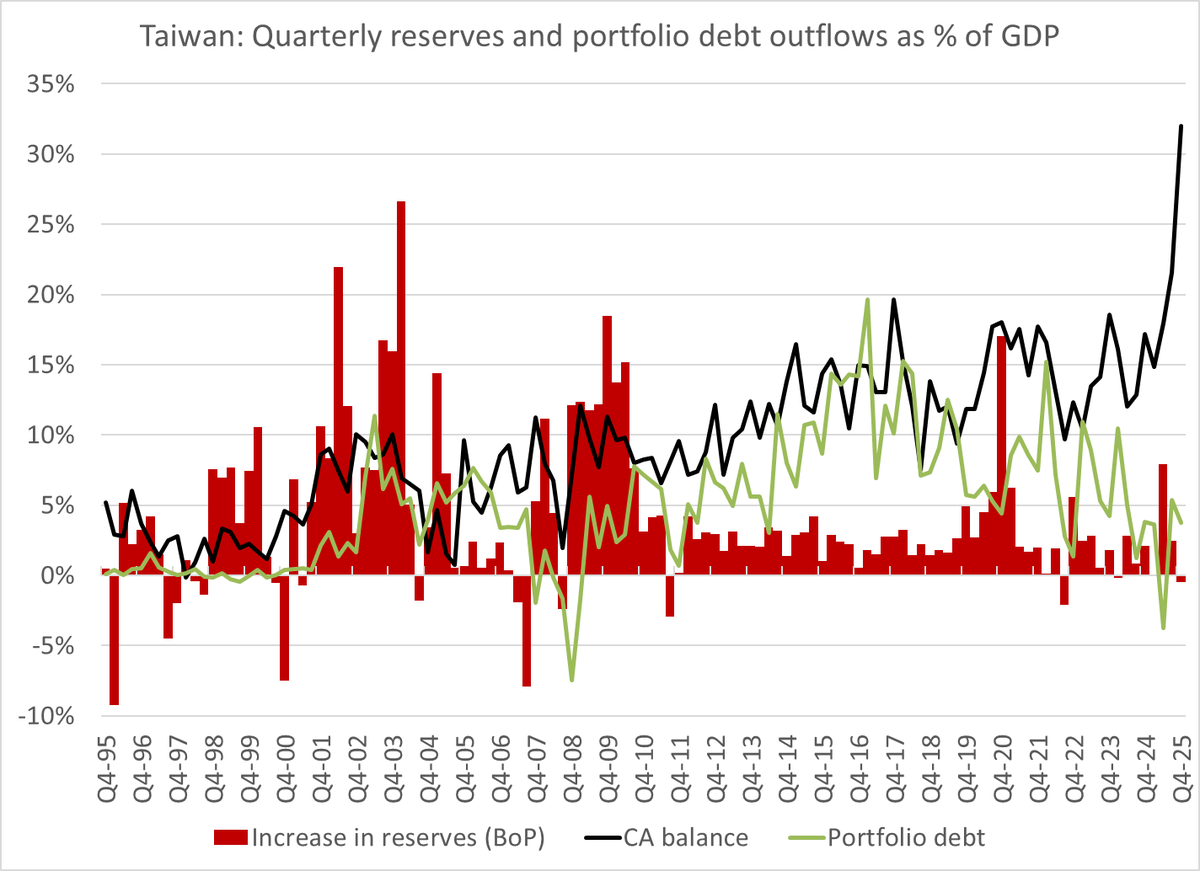
Turkey looked to be heading toward trouble in the summer of 2022: it was selling reserves to cover a growing current account deficit.
But Erdogan pulled a rabbit or two out of the hat in the H2 2022; reserves are now rising even with the persistent external deficit.
1/x
But Erdogan pulled a rabbit or two out of the hat in the H2 2022; reserves are now rising even with the persistent external deficit.
1/x

To be sure, Turkey's balance of payments doesn't look healthy --
There hasn't been any real demand for Turkey's government debt for a while (especially the TL bonds, but recent FX issue largely offset earlier maturities)
2/
There hasn't been any real demand for Turkey's government debt for a while (especially the TL bonds, but recent FX issue largely offset earlier maturities)
2/

And the banks understandable don't want to rollover costly long-term (often 1 year + 1 day) loans -- they have more domestic deposits than they need in any case.
3/
3/

Rather the bulk of the inflow -- setting "errors" aside -- has come from potentially risky short-term deposits (and a reduction in the banks' external liquidity buffer, which is part of the "net" deposit flow)
5/
5/

Zooming in a bit, the recent rebound in reserves has mostly come from:
-- the Rosatom loan (the yellow bar)
-- CBRT swaps + cross border deposits (from geopolitical friends of Turkey)
-- renewed Eurobond issuance (some likely to Turkish banks)
6/
-- the Rosatom loan (the yellow bar)
-- CBRT swaps + cross border deposits (from geopolitical friends of Turkey)
-- renewed Eurobond issuance (some likely to Turkish banks)
6/

But the CBRT's reserves have been increasing faster than its external debt -- there isn't any imminent risk that Turkey is going to run out.
(of course, having $70b in reserves/ $20b in illiquid currencies isn't great if you have $30b or so in external debt)
7/
(of course, having $70b in reserves/ $20b in illiquid currencies isn't great if you have $30b or so in external debt)
7/

The November reverse increase though was a bit bigger than can be explained by the eurobond issue.
As this chart illustrates Turkey's banks also ran down their stock of offshore deposits (more than covering external debt repayment)
(Chart sums flows to infer stocks)
8/
As this chart illustrates Turkey's banks also ran down their stock of offshore deposits (more than covering external debt repayment)
(Chart sums flows to infer stocks)
8/

Turkey still isn't in a great place. I wouldn't want to manage an economy when the central banks net fx position is negative by any measure. And the end December reserves dipped a bit.
But Ergogan's geo-financial strategy has bought Turkey a bit of time.
9/9
But Ergogan's geo-financial strategy has bought Turkey a bit of time.
9/9

p.s. the chart above nets out illiquid reserves from the swaps with Qatar and the UAE to try to estimate liquid reserve assets. I also netted out the PBOC swap as I am not sure that the CBRT's CNY are usable, but I don't have a strong view on that specific adjustment.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh