
Hailey Lujan - Psychological Operations Specialist - US Army | LinkedIn
Hailey Lujan
Psychological Operations Specialist at US Army
US ArmyJohn F. Kennedy Special Warfare Center and School linkedin.com/in/hailey-luja…
Hailey Lujan
Psychological Operations Specialist at US Army
US ArmyJohn F. Kennedy Special Warfare Center and School linkedin.com/in/hailey-luja…
The command originated in 1950, when the U.S. Army developed the Psychological Warfare (PSYWAR) Division of the Army General School at Fort Riley, Kansas. The U.S. Army Psychological Warfare Center and School, which included operational tactical units and a school under the same
umbrella, moved to Fort Bragg in 1952. The center was proposed by the Army's then-Psychological Warfare Chief, Robert A. McClure, to provide doctrinal support and training for both psychological and unconventional warfare.
Born in Mattoon, Illinois, Robert A. McClure graduated
Born in Mattoon, Illinois, Robert A. McClure graduated

from the Kentucky Military Institute in 1915. He initially joined the Philippine Constabulary before joining the regular army in 1917.
In 1941 he served as military attaché to the American Embassy in London before being appointed by general Dwight D. Eisenhower to chief of
In 1941 he served as military attaché to the American Embassy in London before being appointed by general Dwight D. Eisenhower to chief of
intelligence for the European theater of operations in 1942.
After the invasion of Korea in 1950, beginning the Korean War, the Office of the Chief of Psychological Warfare was formed in Washington, D.C., headed by McClure. During his tenure, the Psychological Warfare Center was
After the invasion of Korea in 1950, beginning the Korean War, the Office of the Chief of Psychological Warfare was formed in Washington, D.C., headed by McClure. During his tenure, the Psychological Warfare Center was
established at Fort Bragg, North Carolina which centralized the newly formed Psychological Warfare School and 10th Special Forces Group at a single location.
In 1952, McClure was assigned to Iran as chief of three U.S. Military Missions, where he played a role in the 1953 d'état
In 1952, McClure was assigned to Iran as chief of three U.S. Military Missions, where he played a role in the 1953 d'état
and formed a close relationship with the Shah.
The Shah went on to become a dominant figure in OPEC.
In 1949, Venezuela and Iran took the earliest steps in the direction of OPEC, by inviting Iraq, Kuwait and Saudi Arabia to improve communication among petroleum-exporting
The Shah went on to become a dominant figure in OPEC.
In 1949, Venezuela and Iran took the earliest steps in the direction of OPEC, by inviting Iraq, Kuwait and Saudi Arabia to improve communication among petroleum-exporting
nations as the world recovered from World War II. At the time, some of the world's largest oil fields were just entering production in the Middle East. The United States had established the Interstate Oil Compact Commission to join the Texas Railroad Commission in limiting
overproduction.
On December 3, 1934, Oklahoma Governor-elect E. W. Marland met with the governors of Kansas and Texas to discuss an interstate compact. This led to the drafting of the Interstate Compact to Conserve Oil and Gas, which was ratified by Congress on August 27, 1935.
On December 3, 1934, Oklahoma Governor-elect E. W. Marland met with the governors of Kansas and Texas to discuss an interstate compact. This led to the drafting of the Interstate Compact to Conserve Oil and Gas, which was ratified by Congress on August 27, 1935.
Marland was educated in private schools, he did collegiate and law studies on an accelerated schedule, earning his LL.B. from the University of Michigan Law School at the age of 19 in 1893.
Marland first founded the 101 Ranch Oil Company. Marland was successful in
Marland first founded the 101 Ranch Oil Company. Marland was successful in
reestablishing his fortune and, by 1920, it was estimated at $85,000,000. That year he founded the Marland Oil Company in Ponca City (it was incorporated in Delaware on October 8, 1920) and served as its president. In 1928, the Marland Oil Company was taken over in a hostile bid
process by J. P. Morgan, Jr. and was merged with Continental Oil and Transportation Company (CONOCO).
The "Continental Oil and Transportation Company" was founded by Isaac Elder Blake in 1875. Based in Ogden, Utah, the company distributed oil, kerosene, benzene, and other
The "Continental Oil and Transportation Company" was founded by Isaac Elder Blake in 1875. Based in Ogden, Utah, the company distributed oil, kerosene, benzene, and other
products in the western United States. Continental Oil Company was acquired by Standard Oil Company in 1884 and was spun off from Standard Oil during the Standard Oil divestiture in 1911.
Dan Moran, who succeeded Marland founder E. W. Marland as president of Marland Oil in 1928,
Dan Moran, who succeeded Marland founder E. W. Marland as president of Marland Oil in 1928,
became the first president of the merged Conoco.
In 1981 Conoco became a subsidiary of former rival DuPont.
In 1981, cash rich and wanting to diversify, Seagram Company Ltd. engineered a takeover of Conoco. Although Seagram acquired a 32.2% stake in Conoco, DuPont was brought
In 1981 Conoco became a subsidiary of former rival DuPont.
In 1981, cash rich and wanting to diversify, Seagram Company Ltd. engineered a takeover of Conoco. Although Seagram acquired a 32.2% stake in Conoco, DuPont was brought
in as a white knight by the oil company and entered the bidding war. Mobil Corporation, the nation's second-largest oil company at the time, also joined the bid, and borrowed $5 billion to bid for Cocono. In the end, Seagram and Mobil lost out in the Conoco bidding war. In
exchange for its stake in Conoco Inc, Seagram became a 24.3% owner of DuPont.
In 1995, Conoco Inc. was awarded a contract by Iran to develop a huge offshore oilfield in the Persian Gulf. It was the first energy agreement involving Iran and the United States since Washington
In 1995, Conoco Inc. was awarded a contract by Iran to develop a huge offshore oilfield in the Persian Gulf. It was the first energy agreement involving Iran and the United States since Washington
severed relations with Tehran in 1980. The contract was signed after three years of negotiations. However, the company dropped the plan after the White House announced that President Bill Clinton would issue a directive blocking all such transactions on grounds of national
security.
On May 10, 2006, Richard Armitage, former deputy-secretary of the U.S. State Department, was elected to the board of directors of the ConocoPhillips oil company.
Ryan Lance serves as the chairman and chief executive officer of ConocoPhillips.
Thomas Bertram "Bert"
On May 10, 2006, Richard Armitage, former deputy-secretary of the U.S. State Department, was elected to the board of directors of the ConocoPhillips oil company.
Ryan Lance serves as the chairman and chief executive officer of ConocoPhillips.
Thomas Bertram "Bert"
Lance (June 3, 1931 – August 15, 2013) was an American businessman who served as director of the Office of Management and Budget under President Jimmy Carter in 1977.
Lance was implicated in the Bank of Credit and Commerce International (BCCI) scandal of the 1980s and early
Lance was implicated in the Bank of Credit and Commerce International (BCCI) scandal of the 1980s and early
1990s. He was involved in deals with notable BCCI luminaries Agha Hasan Abedi, Mochtar Riady, and Ghaith Pharaon and with BCCI's largest borrower, Ponnapula Sanjeeva Prasad, and joined with Arkansas-based power investor Jackson Stephens in facilitating BCCI's takeover of
Financial General Bankshares. Lance and Stephens made millions in the wake of BCCI's collapse.
1962 – Jackson Stephens became a member of the Augusta National Golf Club, the host of the annual Masters tournament. Later became the club's chairman from 1991-98.
Also known as
1962 – Jackson Stephens became a member of the Augusta National Golf Club, the host of the annual Masters tournament. Later became the club's chairman from 1991-98.
Also known as
the "Eisenhower Pine," a loblolly pine was located on the 17th hole, about 210 yards from the Masters tee. President Dwight D. Eisenhower, an Augusta National member, hit the tree so many times that, at a 1956 club meeting, he proposed that it be cut down. Not wanting to offend 

the president, the club's chairman, Clifford Roberts, immediately adjourned the meeting rather than reject the request.
During the Second World War American general Dwight D. Eisenhower established a military headquarters at 20 Grosvenor Square, and during this time the square
During the Second World War American general Dwight D. Eisenhower established a military headquarters at 20 Grosvenor Square, and during this time the square
was nicknamed "Eisenhower Platz".
The former United States Embassy of 1938–1960 on the square was purchased by the Canadian government and renamed Macdonald House.
The next chancery, also on the square, was designed by Finnish American modernist architect Eero Saarinen and
The former United States Embassy of 1938–1960 on the square was purchased by the Canadian government and renamed Macdonald House.
The next chancery, also on the square, was designed by Finnish American modernist architect Eero Saarinen and
constructed in the late 1950s, opening in 1960. The United States paid only a symbolic peppercorn rent to the Duke of Westminster for use of the land.
Hugh Richard Arthur Grosvenor, 2nd Duke of Westminster, GCVO, DSO (familiarly "Bendor"; 19 March 1879 – 19 July 1953) was a
Hugh Richard Arthur Grosvenor, 2nd Duke of Westminster, GCVO, DSO (familiarly "Bendor"; 19 March 1879 – 19 July 1953) was a

British landowner and one of the wealthiest men in the world.
From his childhood and during his adult life he was known within family circles as "Bendor", which was also the name of the racehorse Bend Or owned by his grandfather the first Duke, which won The Derby in 1880, the
From his childhood and during his adult life he was known within family circles as "Bendor", which was also the name of the racehorse Bend Or owned by his grandfather the first Duke, which won The Derby in 1880, the
year following his grandson's birth.
In Monte Carlo in 1923, Bendor was introduced to Coco Chanel by Vera Bate Lombardi. The duke lavished Chanel with extravagant jewels, costly art and a home in London's prestigious Mayfair district. His bend her over affair with Chanel lasted
In Monte Carlo in 1923, Bendor was introduced to Coco Chanel by Vera Bate Lombardi. The duke lavished Chanel with extravagant jewels, costly art and a home in London's prestigious Mayfair district. His bend her over affair with Chanel lasted
ten years.
Bend her like Bendor purchased a home for Chanel in London's prestigious Mayfair district, and in 1927 gave her a parcel of land on the French Riviera at Roquebrune-Cap-Martin where Chanel built her villa, La Pausa.
La Pausa was sold by Chanel to the Hungarian
Bend her like Bendor purchased a home for Chanel in London's prestigious Mayfair district, and in 1927 gave her a parcel of land on the French Riviera at Roquebrune-Cap-Martin where Chanel built her villa, La Pausa.
La Pausa was sold by Chanel to the Hungarian
publisher Emery Reves. The former British Prime Minister Winston Churchill spent roughly a third of each year at La Pausa from 1956 to 1958 with Reves and his wife, Wendy, and wrote and edited part of his History of the English Speaking Peoples there.
In 1941, Reves published I
In 1941, Reves published I
Paid Hitler (1941), by Fritz Thyssen, writing that he considered German steel magnate Thyssen to be "one of the men most responsible for the rise of Hitler and for the seeking of power by the National Socialists in Germany", and attributing Hitler's rise in part to the support
of leading industrialists.
I paid Hitler, which Reves published under the name Fritz Thyssen, is one of the most cited but most inaccurate sources on the relationship between high finance and Nazism. This book had actually been written by Reves (based on the stenographs of the
I paid Hitler, which Reves published under the name Fritz Thyssen, is one of the most cited but most inaccurate sources on the relationship between high finance and Nazism. This book had actually been written by Reves (based on the stenographs of the
interviews Thyssen and Reves had had in France in the spring of 1940) and only a small number of chapters had been reviewed and approved by Thyssen.
In 1944, Reves was the publishing agent of Jan Karski's book Story of a Secret State.
Karski traveled to the United States, where
In 1944, Reves was the publishing agent of Jan Karski's book Story of a Secret State.
Karski traveled to the United States, where
on 28 July 1943 he met with President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the Oval Office, the first eyewitness to tell Roosevelt of the situation in Poland and the Jewish Holocaust.
Karski met with many other government and civic leaders in the United States, including Supreme Court
Karski met with many other government and civic leaders in the United States, including Supreme Court
Justice Felix Frankfurter, Cordell Hull, William Joseph Donovan, and Rabbi Stephen Wise.
Karski's accounts of the problems of stateless people and their vulnerability to murder helped inspire the formation of the War Refugee Board, changing US governmental policy from neutrality
Karski's accounts of the problems of stateless people and their vulnerability to murder helped inspire the formation of the War Refugee Board, changing US governmental policy from neutrality
to support for war refugees and civilians in Europe, and after the war, inspiring the creation of the Office of High Commissioner for Refugees.
At the war's end, Karski remained in the United States in Washington, D.C. He began graduate studies at Georgetown University,
At the war's end, Karski remained in the United States in Washington, D.C. He began graduate studies at Georgetown University,
receiving his Ph.D. in 1952. In 1954, Karski became a naturalized citizen of the United States.
Karski taught Eastern European affairs, comparative government, and international affairs at Georgetown University for 40 years.
Story of a Secret State (later republished under
Karski taught Eastern European affairs, comparative government, and international affairs at Georgetown University for 40 years.
Story of a Secret State (later republished under

longer, titles, Courier from Poland: The Story of a Secret State and Story of a Secret State: My Report to the World) is a 1944 book by Polish resistance Home Army courier Jan Karski.
Although Karski was the main author, and the sole credited author of the work, he closely
Although Karski was the main author, and the sole credited author of the work, he closely
collaborated with bilingual translator Krystyna Sokołowska (who translated his Polish manuscript to English) and the final script was copyedited by William Poster.
The Home Army absorbed most of the other Polish partisans and underground forces. Its allegiance was to the Polish
The Home Army absorbed most of the other Polish partisans and underground forces. Its allegiance was to the Polish
government-in-exile in London, and it constituted the armed wing of what came to be known as the Polish Underground State.
One of Sikorski's political goals was the creation of a Central and Eastern European federation, starting with the Polish-Czechoslovakian confederation.
One of Sikorski's political goals was the creation of a Central and Eastern European federation, starting with the Polish-Czechoslovakian confederation.
He saw such an organization as necessary if smaller states were to stand up to traditional German and Russian imperialism. That concept, although ultimately futile, gained some traction around that time, as Sikorski and Edvard Beneš from the Czechoslovak government-in-exile,
signed an agreement declaring the intent to pursue closer cooperation on 10 November 1940.
Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union ("Operation Barbarossa") in June 1941, Sikorski opened negotiations with the Soviet ambassador to London, Ivan Maisky, to re-establish
Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union ("Operation Barbarossa") in June 1941, Sikorski opened negotiations with the Soviet ambassador to London, Ivan Maisky, to re-establish
diplomatic relations between Poland and the Soviet Union, which had been broken off after the Soviet invasion of Poland in September 1939.
In 1943 the fragile relations between the Soviet Union and the Polish government-in-exile finally reached their breaking point when, on
In 1943 the fragile relations between the Soviet Union and the Polish government-in-exile finally reached their breaking point when, on
13 April, the Germans announced via the Katyn Commission the discovery of the bodies of 20,000 Polish officers who had been murdered by the Soviets and buried in Katyn Forest, near Smolensk, Russia. Stalin claimed that the atrocity had been carried out by the Germans, while
Nazi propaganda orchestrated by Joseph Goebbels successfully exploited the Katyn massacre to drive a wedge between Poland, the Western Allies and the Soviet Union.
The massacre was initiated in NKVD chief Lavrentiy Beria.
After the war, Beria organised the communist takeover of
The massacre was initiated in NKVD chief Lavrentiy Beria.
After the war, Beria organised the communist takeover of

the state institutions in central and eastern Europe. His ruthlessness in his duties and skill at producing results culminated in his success in overseeing the Soviet atomic bomb project.
Pavel Fyodorovich Batitsky served in the Red Army from 1924 and was commander-in-chief
Pavel Fyodorovich Batitsky served in the Red Army from 1924 and was commander-in-chief

of the Air Defense Forces from 1966 to 1978. Following the death of Joseph Stalin in 1953, he was chosen to execute Lavrentiy Beria, the former head of the NKVD.
From September 1939 to December 1940, Batitsky was in China as Chief of Staff of Soviet military advisers at the
From September 1939 to December 1940, Batitsky was in China as Chief of Staff of Soviet military advisers at the
headquarters of Chiang Kai-shek.
In 1939 Muslim leaders Isa Yusuf Alptekin and Ma Fuliang were sent by Chiang to several Middle Eastern countries, including Egypt, Turkey, and Syria, to gain support for the Chinese War against Japan, and to express his support for Muslims.
In 1939 Muslim leaders Isa Yusuf Alptekin and Ma Fuliang were sent by Chiang to several Middle Eastern countries, including Egypt, Turkey, and Syria, to gain support for the Chinese War against Japan, and to express his support for Muslims.
Alptekin asked Ma Bufang on whether Chiang Kai-shek and the Chinese government would allow an independent Islamic state in southern Xinjiang to counter the Communists and the Soviet-backed Second East Turkestan Republic, but Ma Bufang did not bother with this request. Instead,
Ma fled in an American CIA airplane with several million dollars in gold as the Chinese Communist army approached Qinghai. Ma then fled to the Kuomintang-controlled island of Taiwan, then to Egypt.
Isa Yusuf Alptekin was the father of Erkin Alptekin.
In 1971, due to his
Isa Yusuf Alptekin was the father of Erkin Alptekin.
In 1971, due to his
father's connections, Erkin Alptekin got a job at Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty (RFE/RL) in Munich. He worked as a "Senior Policy Advisor" and directed the Uyghur Division until 1979, when Uyghur-language broadcasts were discontinued for a lack of an audience under RFE/RL
jurisdiction.
Concurrently in the 1970s and 1980s, the CIA looked to connect to Uyghur separatists and found Alptekin a suitable match because of his leadership in various Uyghur organizations and his tenure at RFE. He became an adviser to the CIA and retired his RFE/RL post in
Concurrently in the 1970s and 1980s, the CIA looked to connect to Uyghur separatists and found Alptekin a suitable match because of his leadership in various Uyghur organizations and his tenure at RFE. He became an adviser to the CIA and retired his RFE/RL post in
1995 as it moved to Prague in the Czech Republic.
Blinken Open Society Archives (abbreviated as Blinken OSA) was founded by George Soros in 1995, and opened in 1996 as a department of the Central European University. Originally called simply Open Society Archives (OSA), in 2015
Blinken Open Society Archives (abbreviated as Blinken OSA) was founded by George Soros in 1995, and opened in 1996 as a department of the Central European University. Originally called simply Open Society Archives (OSA), in 2015
it was renamed Vera and Donald Blinken Open Society Archives after receiving a major donation from the couple.
The original core of Blinken OSA’s holdings is the former archives of the Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty Research Institute, previously based in Munich and New York.
The original core of Blinken OSA’s holdings is the former archives of the Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty Research Institute, previously based in Munich and New York.
The Special Library collections include the London-based Wiener Library's Testaments to the Holocaust collections on the history of Nazism and the European Jews.
Alfred Wiener, a German Jew who worked for the Centralverein deutscher Staatsbürger jüdischen Glaubens (Central
Alfred Wiener, a German Jew who worked for the Centralverein deutscher Staatsbürger jüdischen Glaubens (Central
Association of German Citizens of Jewish Faith), a Jewish civil rights group, spent years documenting the rise of antisemitism.
Wiener and his family fled to Amsterdam where he, together with Dr. David Cohen of Amsterdam University, founded the Jewish Central
Wiener and his family fled to Amsterdam where he, together with Dr. David Cohen of Amsterdam University, founded the Jewish Central
Information Office (JCIO).
Cohen was a prominent Dutch Jew who founded the Committee for Jewish Refugees at the same time; the Committee used the work of the JCIO for its publications, and provided some financial support to the JCIO.
Following Kristallnacht in November 1938, a
Cohen was a prominent Dutch Jew who founded the Committee for Jewish Refugees at the same time; the Committee used the work of the JCIO for its publications, and provided some financial support to the JCIO.
Following Kristallnacht in November 1938, a
Kindertransport was organized to move children - without their parents - to countries outside of the German Reich. In the Netherlands, Truus Wijsmuller-Meijer negotiated an agreement with the Dutch government to accept 1500 children who were en route to Great Britain and other
countries.
Geertruida Wijsmuller-Meijer, known as 'Truus' to her family, was born in the city of Alkmaar. She was the firstborn child of Jacob Meijer, who worked in a drug store, and Hendrika Boer, a self-employed dressmaker.
On 17 November 1938, she took her first group of
Geertruida Wijsmuller-Meijer, known as 'Truus' to her family, was born in the city of Alkmaar. She was the firstborn child of Jacob Meijer, who worked in a drug store, and Hendrika Boer, a self-employed dressmaker.
On 17 November 1938, she took her first group of

6 children from the crowded waiting room of the Dutch consulate to the train. But customs attempted to remove them from the train. Wijsmuller however had noticed that the Dutch Princess Juliana was on the coupe next to her. "Children, comb your hair and wash your hands" and she 

threatened to take the six of them to the princess. After which customs backed down.
Princess Juliana and Prince Bernhard celebrate their engagement announcement in Amsterdam
Prince Bernhard studied law and worked as an executive secretary at the Paris office of IG Farben. In
Princess Juliana and Prince Bernhard celebrate their engagement announcement in Amsterdam
Prince Bernhard studied law and worked as an executive secretary at the Paris office of IG Farben. In

1937 he married Princess Juliana of the Netherlands and was immediately given the title Prince of the Netherlands with the style of Royal Highness.
Bernhard helped found the World Wildlife Fund (WWF, later renamed World Wide Fund for Nature), becoming its first president in
Bernhard helped found the World Wildlife Fund (WWF, later renamed World Wide Fund for Nature), becoming its first president in
1961. In 1970, along with Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh and other associates, he established the WWF's financial endowment "The 1001: A Nature Trust". In 1954, he was a co-founder of the international Bilderberg Group, which has met annually since then to discuss corporate
globalisation and other issues concerning Europe and North America. He was forced to step down from both groups after being involved in the Lockheed Bribery Scandal in 1976.
Prince Bernhard was a member of the "Reiter-SS", a mounted unit of the SS and had joined the Nazi party
Prince Bernhard was a member of the "Reiter-SS", a mounted unit of the SS and had joined the Nazi party
before the war. He later also joined the National Socialist Motor Corps.
In England, Prince Bernhard asked to work in British Intelligence. The War Admiralty, and later General Eisenhower's Allied Command offices, did not trust him enough to allow him access to sensitive
In England, Prince Bernhard asked to work in British Intelligence. The War Admiralty, and later General Eisenhower's Allied Command offices, did not trust him enough to allow him access to sensitive
intelligence information.
On the recommendation of Bernhard's friend and admirer King George VI, however, who was also of German aristocratic descent through his mother Mary of Teck and his great-grandfather Prince Albert, and after Bernhard was personally screened by British
On the recommendation of Bernhard's friend and admirer King George VI, however, who was also of German aristocratic descent through his mother Mary of Teck and his great-grandfather Prince Albert, and after Bernhard was personally screened by British
intelligence officer Ian Fleming at the behest of Winston Churchill.
With his global contacts having been approached by the secretive Polish diplomat, Józef Retinger, in May 1954 Bernhard was a major figure in organising a meeting at the Bilderberg Hotel in the Netherlands for
With his global contacts having been approached by the secretive Polish diplomat, Józef Retinger, in May 1954 Bernhard was a major figure in organising a meeting at the Bilderberg Hotel in the Netherlands for
the business elite and intellectuals of the Western World to discuss the economic problems in the face of what they characterised as the growing threat from Communism.
After the outbreak of World War II, Retinger was principal adviser to the Polish government-in-exile.
After the outbreak of World War II, Retinger was principal adviser to the Polish government-in-exile.
Retinger's brother, Juliusz, taught physiological chemistry at the University of Chicago and University of Wilno.
Retinger developed a close friendship with his older Polish compatriot, the already well established novelist, Joseph Conrad.
The year 1890 marked Conrad's first
Retinger developed a close friendship with his older Polish compatriot, the already well established novelist, Joseph Conrad.
The year 1890 marked Conrad's first
return to Poland, where he would visit his uncle and other relatives and acquaintances. His visit took place while he was waiting to proceed to the Congo Free State, having been hired by Albert Thys, deputy director of the Société Anonyme Belge pour le Commerce du Haut-Congo.
Conrad's association with the Belgian company, on the Congo River, would inspire his novella, Heart of Darkness.
Created in 1906, the UMHK was founded as a joint venture of the Belgian Compagnie du Katanga, the Belgian Comité Spécial du Katanga and the British Tanganyika
Created in 1906, the UMHK was founded as a joint venture of the Belgian Compagnie du Katanga, the Belgian Comité Spécial du Katanga and the British Tanganyika
Concessions. The Compagnie du Katanga was a subsidiary of the Compagnie du Congo pour le Commerce et l'Industrie (CCCI), which was controlled by the countrhy's largest conglomerate, the Société Générale de Belgique.
By the start of World War II, the Société Générale controlled
By the start of World War II, the Société Générale controlled
70% of the Congolese economy.
The Société générale was originally founded as an investment bank by William I of the Netherlands in 1822 when Belgium was under Dutch rule.
William I (Willem Frederik, Prince of Orange-Nassau; 24 August 1772 – 12 December 1843) was a Prince of
The Société générale was originally founded as an investment bank by William I of the Netherlands in 1822 when Belgium was under Dutch rule.
William I (Willem Frederik, Prince of Orange-Nassau; 24 August 1772 – 12 December 1843) was a Prince of

Orange, the King of the Netherlands and Grand Duke of Luxembourg.
Feeling threatened by Napoleon, who had escaped from Elba, William proclaimed the Netherlands a kingdom on 16 March 1815 at the urging of the powers gathered at the Congress of Vienna. His son, the future king
Feeling threatened by Napoleon, who had escaped from Elba, William proclaimed the Netherlands a kingdom on 16 March 1815 at the urging of the powers gathered at the Congress of Vienna. His son, the future king
William II, fought as a commander at the Battle of Waterloo.
In 1819, William II was blackmailed over what Minister of Justice Van Maanen termed in a letter his "shameful and unnatural lusts": presumably bisexuality. Separately, his signing the constitutional reform of 1848, twitter.com/i/web/status/1…
In 1819, William II was blackmailed over what Minister of Justice Van Maanen termed in a letter his "shameful and unnatural lusts": presumably bisexuality. Separately, his signing the constitutional reform of 1848, twitter.com/i/web/status/1…

enabling a parliamentary democracy, may have been partly influenced by blackmail. He may also have gone balls deep with a dandy by the name of Pereira.
William II died on 17 March 1849 and was succeeded by his son William III.
William3 married his cousin Sophie of Württemberg
William II died on 17 March 1849 and was succeeded by his son William III.
William3 married his cousin Sophie of Württemberg
in 1839 and they had three sons, William, Maurice, and Alexander, all of whom predeceased him. After Sophie's death in 1877 he married Emma of Waldeck and Pyrmont in 1879 and they had one daughter Wilhelmina, who succeeded William to the Dutch throne. 

Following the German invasion of the Netherlands in 1940, Wilhelmina fled to Britain and took charge of the Dutch government-in-exile.
Queen Wilhelmina of the Netherlands, Hudson Motor Car Company of Detroit, MI’s main stockholder.
The name "Hudson" came from Joseph L. Hudson,
Queen Wilhelmina of the Netherlands, Hudson Motor Car Company of Detroit, MI’s main stockholder.
The name "Hudson" came from Joseph L. Hudson,

a Detroit department store entrepreneur and founder of Hudson's department store, who provided the necessary capital and gave permission for the company to be named after him.
One of the lead "car men" and an organizer of the company was Roy D. Chapin Sr., a young executive
One of the lead "car men" and an organizer of the company was Roy D. Chapin Sr., a young executive
who had worked with Ransom E. Olds.
During his tenure as Secretary of Commerce, Chapin was unsuccessful in persuading Henry Ford to provide financial help to avoid the collapse of the Union Guardian Trust Company of Detroit. Ford's refusal to aid the bank in averting a
During his tenure as Secretary of Commerce, Chapin was unsuccessful in persuading Henry Ford to provide financial help to avoid the collapse of the Union Guardian Trust Company of Detroit. Ford's refusal to aid the bank in averting a
financial failure led to the Michigan Bank Holiday, an event that began a series of state bank holidays and ultimately to the passage of Roosevelt administration's Emergency Banking Act of 1933.
The name Roosevelt is an American toponymic surname derived from the Dutch surname Van Rose(n)velt, meaning "from rose field" or "of a rose field."
In 1410, William III, Duke of Bavaria, Count of Holland and of Zeeland granted amt fiefdoms north of Tholen to six lords.
One of
In 1410, William III, Duke of Bavaria, Count of Holland and of Zeeland granted amt fiefdoms north of Tholen to six lords.
One of
the first amt lords was Marijnus van Rosevelt, whose lordship dates back to 1697. Johan Willem van Rosevelt, LL.M, was also an amt lord from 1731 until 1790.
Claes Maartenszen van Rosenvelt, the immigrant ancestor of the Roosevelt family, arrived in Nieuw Amsterdam (present day
Claes Maartenszen van Rosenvelt, the immigrant ancestor of the Roosevelt family, arrived in Nieuw Amsterdam (present day
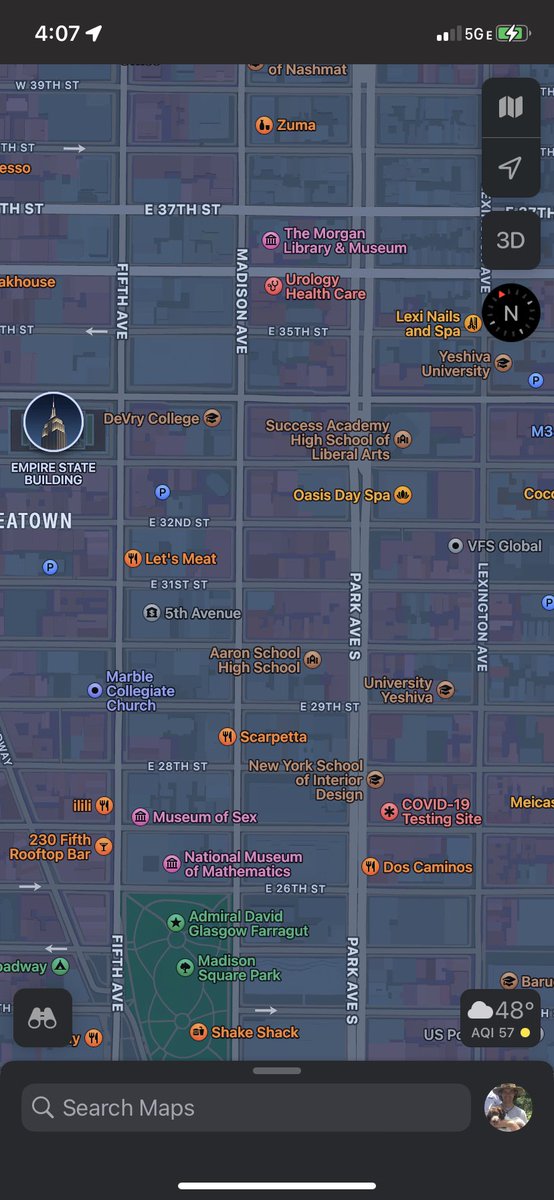
New York City) some time between 1638 and 1649. Around the year 1652, he bought a farm from Lambert van Valckenburgh comprising twenty-four morgens (48 acres) in what is now Midtown Manhattan, including the present site of the Empire State Building.
The property included
The property included
roughly what is now the area between Lexington Avenue and Fifth Avenue bounded by 29th St. and 35th St. 
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




