1/Were you today years old when you learned ASL wasn’t just short for American Sign Language?
A #tweetorial about a key perfusion method: arterial spin labeling (ASL) in collaboration w/@RadioGraphics!
Featuring this current issue article: doi.org/10.1148/rg.220…
#RGPHx
A #tweetorial about a key perfusion method: arterial spin labeling (ASL) in collaboration w/@RadioGraphics!
Featuring this current issue article: doi.org/10.1148/rg.220…
#RGPHx

2/In perfusion imaging, we want to know how blood is flowing
Usually, we do that by adding IV contrast to blood—to go along for the ride. We can track contrast by changes in MR signal
So if contrast runs w/blood, we can track blood by extension & know how it’s flowing. #RGPhx
Usually, we do that by adding IV contrast to blood—to go along for the ride. We can track contrast by changes in MR signal
So if contrast runs w/blood, we can track blood by extension & know how it’s flowing. #RGPhx

3/But what if we want to do perfusion imaging & don’t want to use contrast?
For example, in kids, we’d prefer not to give contrast.
Also, if there is an allergy, we REALLY don’t want to give contrast.
There must be another way.
#RGPhx
For example, in kids, we’d prefer not to give contrast.
Also, if there is an allergy, we REALLY don’t want to give contrast.
There must be another way.
#RGPhx

4/If we want to know how fast something is traveling—be it blood or a whale—we need a way to keep track of it. We need to TAG it
For whales, they literally shoot a tag into a whale to keep track of it. They track the tagged whale to see how fast the whole herd is moving
#RGPhx
For whales, they literally shoot a tag into a whale to keep track of it. They track the tagged whale to see how fast the whole herd is moving
#RGPhx

5/Tagging is important, especially if you’re trying to keep track of 1 whale in a sea of whales
Same w/blood. If you’re trying to track how fast blood is flowing, you need to make sure you’re tracking the same blood the whole time—otherwise you get lost in a sea of blood
#RGPhx
Same w/blood. If you’re trying to track how fast blood is flowing, you need to make sure you’re tracking the same blood the whole time—otherwise you get lost in a sea of blood
#RGPhx

6/So since we can’t harpoon blood—how do we tag it?
We can do it w/magnetization. We essentially zap some of the blood w/a radiofrequency pulse.
This changes the magnetic properties of the blood we zap—making them different or TAGGED compared to the rest of the blood
#RGPhx
We can do it w/magnetization. We essentially zap some of the blood w/a radiofrequency pulse.
This changes the magnetic properties of the blood we zap—making them different or TAGGED compared to the rest of the blood
#RGPhx

7/It’s like in “Spiderman.” Being bitten by a radioactive spider transformed Peter Parker into something different than everyone else—Spiderman
The spider “tagged” him
Same w/blood. It’s “bitten” by a radiofrequency pulse & becomes different from the remaining blood
#RGPhx
The spider “tagged” him
Same w/blood. It’s “bitten” by a radiofrequency pulse & becomes different from the remaining blood
#RGPhx

8/Tagged blood is like a dye to track blood flow
It’s like finding river velocity w/dye
Tagging blood is like dropping dye at a start line. You wait a minute & then check how much dye got to the finish
You know distance & time, so that gives you river (blood) velocity. #RGPhx
It’s like finding river velocity w/dye
Tagging blood is like dropping dye at a start line. You wait a minute & then check how much dye got to the finish
You know distance & time, so that gives you river (blood) velocity. #RGPhx

9/This is what we do in ASL
We tag blood at the start line (in the neck), then wait a little bit, & then check how much dyed/tagged blood made it to the finish line (the head)
This gives cerebral blood flow or CBF. CBF is the only perfusion parameter ASL can measure
#RGPhx
We tag blood at the start line (in the neck), then wait a little bit, & then check how much dyed/tagged blood made it to the finish line (the head)
This gives cerebral blood flow or CBF. CBF is the only perfusion parameter ASL can measure
#RGPhx

10/Sadly, ASL has poor signal to noise
Tagging blood in our vessels isn’t like dropping dye into a canal—it’s dropping it in a mountain river
Dye gets diluted by other contributing streams & also washes out into other vessels, so very little actually gets to the brain #RGPhx
Tagging blood in our vessels isn’t like dropping dye into a canal—it’s dropping it in a mountain river
Dye gets diluted by other contributing streams & also washes out into other vessels, so very little actually gets to the brain #RGPhx

11/To increase signal to noise, we subtract out the background
We take a background image w/no tagged blood & subtract it from the image w/tagged blood
This way, background noise is subtracted out & only tagged blood signal remains--like digital subtraction angiography #RGPhx
We take a background image w/no tagged blood & subtract it from the image w/tagged blood
This way, background noise is subtracted out & only tagged blood signal remains--like digital subtraction angiography #RGPhx

12/Tagging blood is like dyeing water. How do we pour in the dye?
We can be like a little kid & pour all our dye into the river at once
Or we can be like an adult & patiently distribute it over time—like pouring small glasses of koolaid to serve all the kids at a party. #RGPhx
We can be like a little kid & pour all our dye into the river at once
Or we can be like an adult & patiently distribute it over time—like pouring small glasses of koolaid to serve all the kids at a party. #RGPhx

13/Going from the neck to the head is like running a marathon for blood
Pouring all the dye in at once is like all-out sprinting the start of a marathon—you’ll get drained
Tagging blood all at once is called continuous ASL. It runs out of steam & has poor signal to noise #RGPhx
Pouring all the dye in at once is like all-out sprinting the start of a marathon—you’ll get drained
Tagging blood all at once is called continuous ASL. It runs out of steam & has poor signal to noise #RGPhx

14/Instead of all-out sprinting, you could save your energy. Run a little, rest a little, run a little
This surely gives more endurance—you won’t exhaust yourself, but you won’t be fast
This is pulsed ASL—tagging in short bursts. Good signal to noise, but not efficient #RGPhx
This surely gives more endurance—you won’t exhaust yourself, but you won’t be fast
This is pulsed ASL—tagging in short bursts. Good signal to noise, but not efficient #RGPhx

15/Let’s combine the two approaches.
All out sprint for a bit, but also take a short rest before all out sprinting again. This way, you have speed & endurance.
This is pseudocontinous ASL—tag for long periods but take a break in between. It’s best for SNR & efficiency #RGPhx
All out sprint for a bit, but also take a short rest before all out sprinting again. This way, you have speed & endurance.
This is pseudocontinous ASL—tag for long periods but take a break in between. It’s best for SNR & efficiency #RGPhx

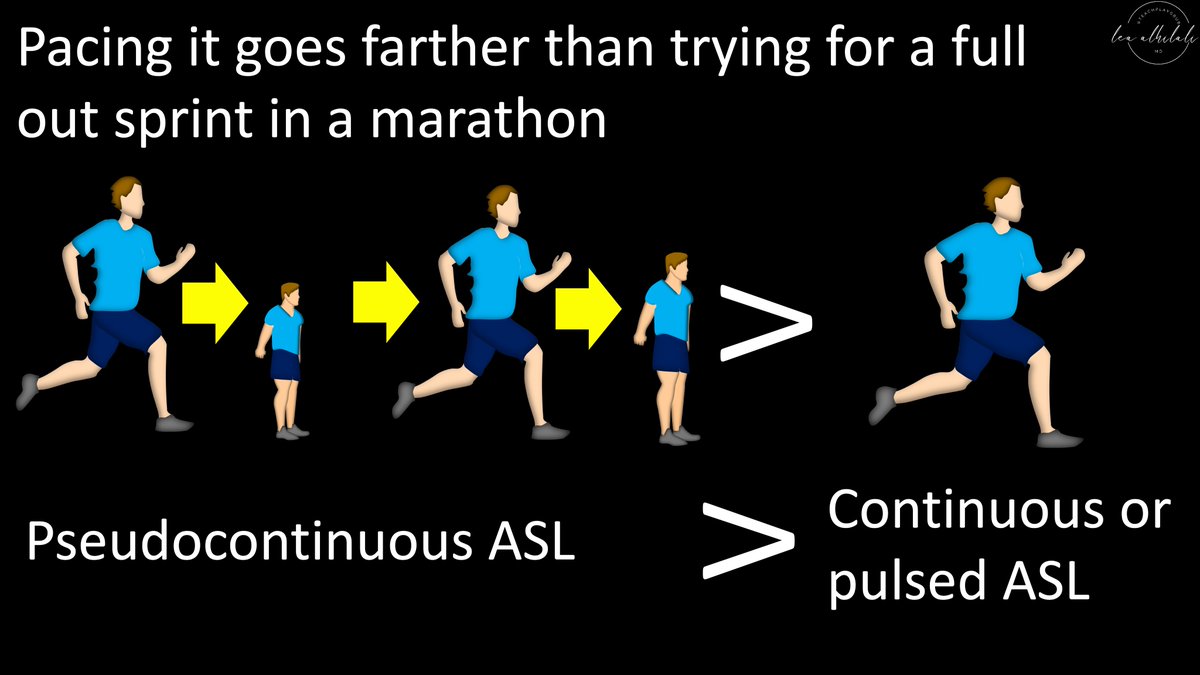
16/Best way to run a marathon is to go hard as long as you can, but also have short rests so you don’t exhaust yourself (pseudocontinuous running).
Same w/ASL. Best way to tag blood is to tag for a long period of time & take small breaks. This is pseudocontinous ASL. #RGPhx
Same w/ASL. Best way to tag blood is to tag for a long period of time & take small breaks. This is pseudocontinous ASL. #RGPhx
17/So remember—you don’t need contrast for perfusion! ASL can transform blood into a superhero that doesn’t need contrast!
Be sure to check out the excellent review by Iutaka et. al. on ASL, featured in the current issue of @RadioGraphics: doi.org/10.1148/rg.220…
#RGPhx
Be sure to check out the excellent review by Iutaka et. al. on ASL, featured in the current issue of @RadioGraphics: doi.org/10.1148/rg.220…
#RGPhx

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















