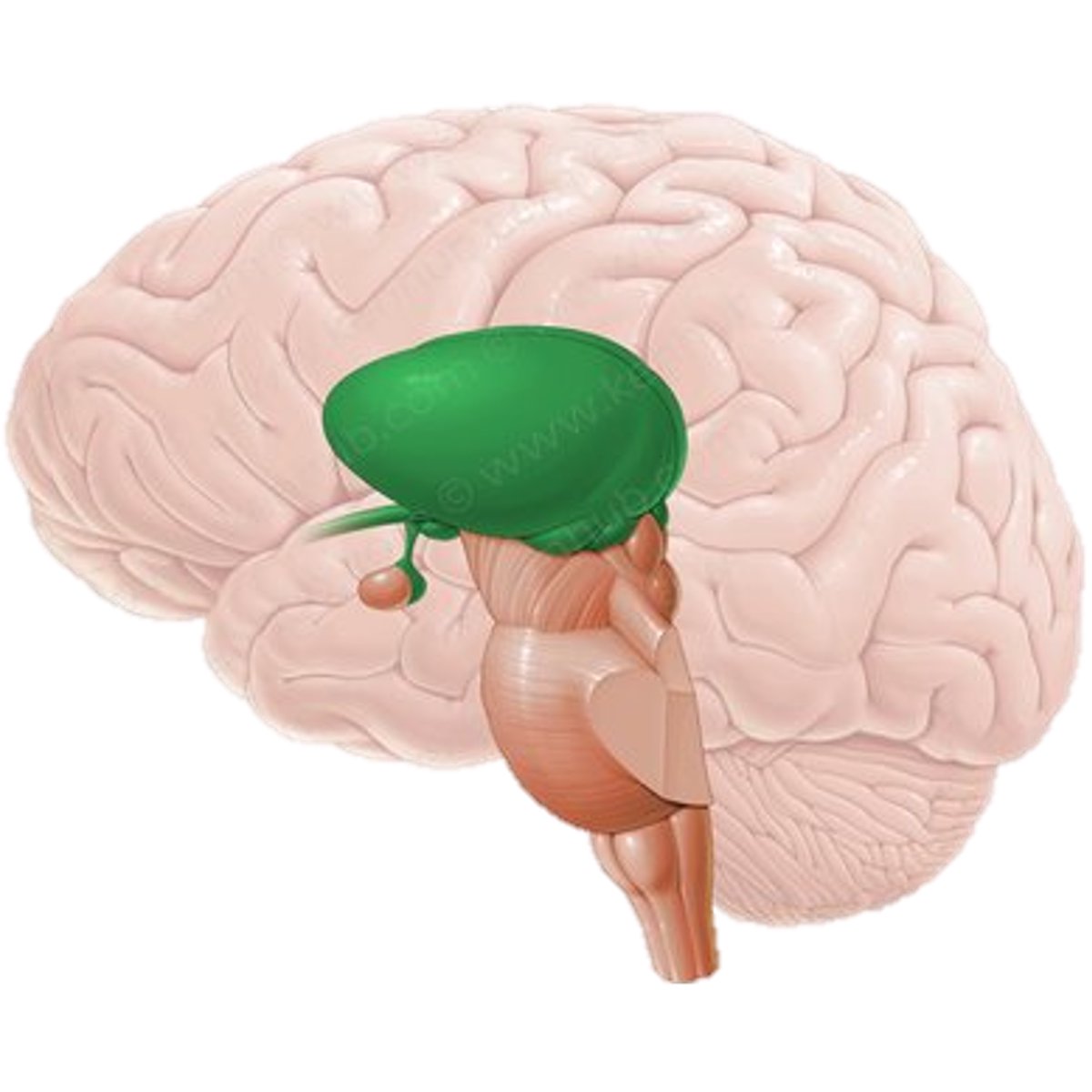
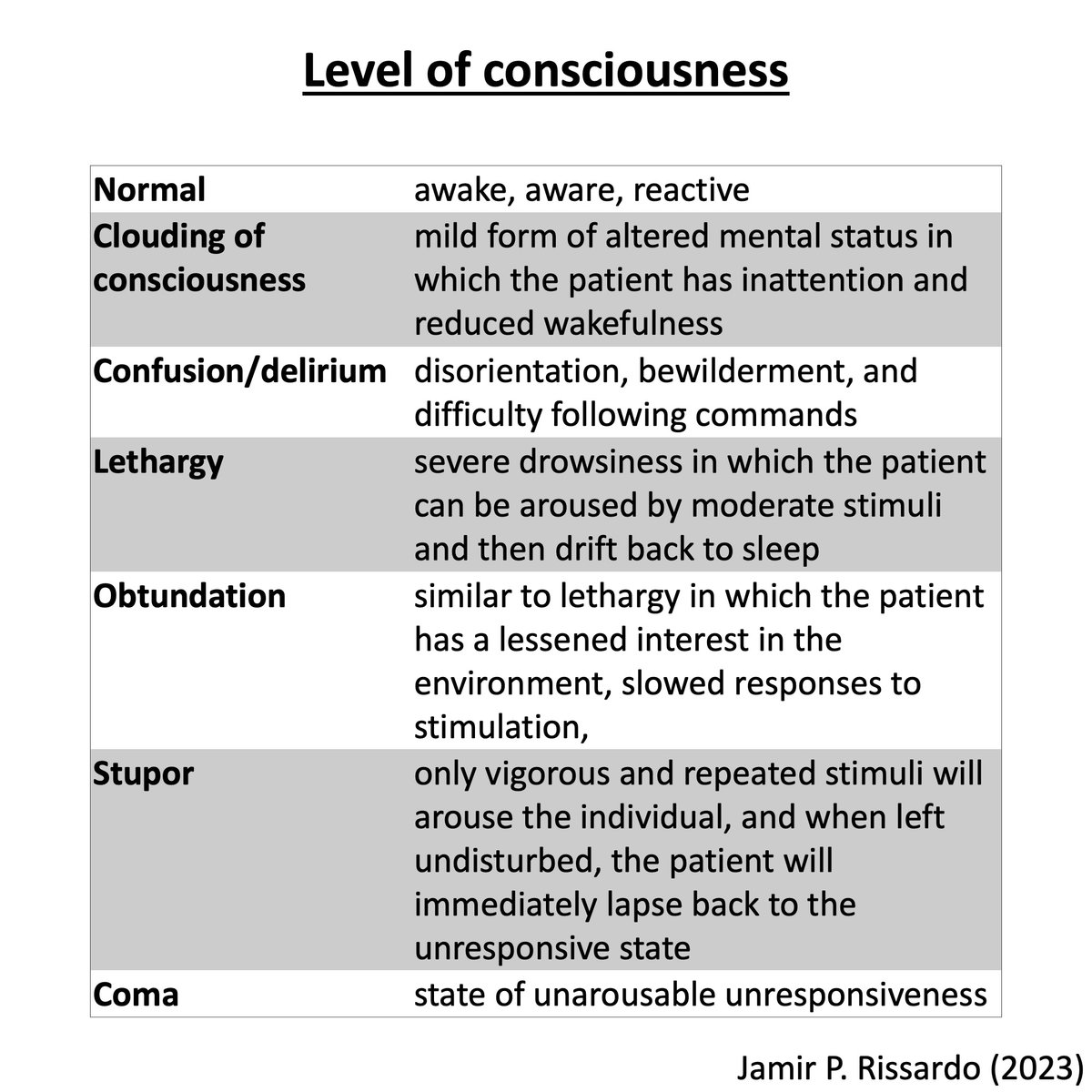
Diencephalon location
- around the 3rd ventricle
The cavity of the diencephalon is ----- the 3rd ventricle
All of the structures of the diencephalon are around the 3rd ventricle, so the cavity of the diencephalon is the 3rd ventricle.
2/
- around the 3rd ventricle
The cavity of the diencephalon is ----- the 3rd ventricle
All of the structures of the diencephalon are around the 3rd ventricle, so the cavity of the diencephalon is the 3rd ventricle.
2/
Components (ETHOS)
Epithalamus (habenular & pineal)
- sleep-wake cycle
Thalamus
- relay center for sensory information
Hypothalamus (mammillary body & tuber cinereum)
- autonomic function & endocrine system
Optic nerve
Subthalamus
- inhibition of involuntary movements
4/
Epithalamus (habenular & pineal)
- sleep-wake cycle
Thalamus
- relay center for sensory information
Hypothalamus (mammillary body & tuber cinereum)
- autonomic function & endocrine system
Optic nerve
Subthalamus
- inhibition of involuntary movements
4/

Epithalamus
“melatonin control”
5/
“melatonin control”
5/
Function
- connects limbic system to other parts of the brain
- controls the circadian rhythm
6/
- connects limbic system to other parts of the brain
- controls the circadian rhythm
6/
Thalamus
“the major component of diencephalon”
10/
“the major component of diencephalon”
10/
Structure
Thalami nuclei are divided by “Y” shaped white matter (internal medullary lamina)
- anterior, medial, and lateral nuclear groups
Pulvinar: Post end of Pos Pole of thalamus
11/
Thalami nuclei are divided by “Y” shaped white matter (internal medullary lamina)
- anterior, medial, and lateral nuclear groups
Pulvinar: Post end of Pos Pole of thalamus
11/
Function
Major sensory relay center
12/
Major sensory relay center
12/
🅐 Anterior Nucleus
Alertness, Attention, Affect, Acute memory
*these are the main functions of limbic system – Papez circuit
Afferent: mammillary body
Efferent: cingulate gyrus
14/
Alertness, Attention, Affect, Acute memory
*these are the main functions of limbic system – Papez circuit
Afferent: mammillary body
Efferent: cingulate gyrus
14/
🅑Ventral anterior nucleus
Basal ganglia
Afferent: globus pallidus and substantia nigra
Efferent: Broadmann area 6 (prefrontal and premotor cortex)
15/
Basal ganglia
Afferent: globus pallidus and substantia nigra
Efferent: Broadmann area 6 (prefrontal and premotor cortex)
15/
🅒 Ventral lateral nucleus
Co-ordination & Cerebellum
Afferent: cerebellum (dentate nucleus) & basal ganglia
Efferent: Broadmann area 4 (primary motor cortex)
16/
Co-ordination & Cerebellum
Afferent: cerebellum (dentate nucleus) & basal ganglia
Efferent: Broadmann area 4 (primary motor cortex)
16/
🅓 Ventral posterior nucleus
Dermatome (sensory)
Afferent:
- Ventro-post-med (VPM):
> Medial: Mask (face & taste)
- Ventro-post-lat(VPL):
> VPL: Vibration, Pain, Pressure, Proprioception, Light touch and temperature
Efferent:
- Brodmann Area 3, 1, 2 (sensory cortex)
17/
Dermatome (sensory)
Afferent:
- Ventro-post-med (VPM):
> Medial: Mask (face & taste)
- Ventro-post-lat(VPL):
> VPL: Vibration, Pain, Pressure, Proprioception, Light touch and temperature
Efferent:
- Brodmann Area 3, 1, 2 (sensory cortex)
17/
🅔 Geniculate bodies
Eye and Ear
Lateral geniculate body: Light (eyes)
Afferent: optic tract
Efferent: calcarine sulcus (area 17)
Medial geniculate body: Music (ear)
Afferent: superior olive & inferior colliculus
Efferent: primary auditory cortex (area 41 & 42)
18/
Eye and Ear
Lateral geniculate body: Light (eyes)
Afferent: optic tract
Efferent: calcarine sulcus (area 17)
Medial geniculate body: Music (ear)
Afferent: superior olive & inferior colliculus
Efferent: primary auditory cortex (area 41 & 42)
18/
🅕 Medial dorsal nucleus
Feelings (limbic system)
Afferent: amygdala & olfactory cortex
Efferent: prefrontal cortex & limbic system
19/
Feelings (limbic system)
Afferent: amygdala & olfactory cortex
Efferent: prefrontal cortex & limbic system
19/
🅖 Pulvinar
Gloat (“fix” – control of eye movements)
Afferent: pretectal nucleus & superior colliculus
Efferent: association cortex
20/
Gloat (“fix” – control of eye movements)
Afferent: pretectal nucleus & superior colliculus
Efferent: association cortex
20/
🅗 Reticular nucleus
Halt thalamus
Afferent: cortex and interthalamic nuclei
* interthalamic connections largely inhibiton
Efferent: thalamic nuclei
21/
Halt thalamus
Afferent: cortex and interthalamic nuclei
* interthalamic connections largely inhibiton
Efferent: thalamic nuclei
21/
🅘 Intralaminar nucleus
Intent and arousal in Intralaminar nucleus
*alertness
Afferent: cortex, brainstem, and spinal cord
Efferent: cortex & basal ganglia
22/
Intent and arousal in Intralaminar nucleus
*alertness
Afferent: cortex, brainstem, and spinal cord
Efferent: cortex & basal ganglia
22/
Caudate nucleus
“It is a rat”
Head, body, and tail (amygdaloid body)
Cheese – lentiform nucleus
Salad – internal capsule
Egg – thalamus
25/
“It is a rat”
Head, body, and tail (amygdaloid body)
Cheese – lentiform nucleus
Salad – internal capsule
Egg – thalamus
25/

Function
“HEAL”
Homeostasis of
Endocrine + ANS + Limbic systems
27/
“HEAL”
Homeostasis of
Endocrine + ANS + Limbic systems
27/
Anatomy
- part of the diencephalon
- beneath the thalamus ("hypo"thalamus)
- posteriorly and dorsally to the optic chiasm
28/
- part of the diencephalon
- beneath the thalamus ("hypo"thalamus)
- posteriorly and dorsally to the optic chiasm
28/
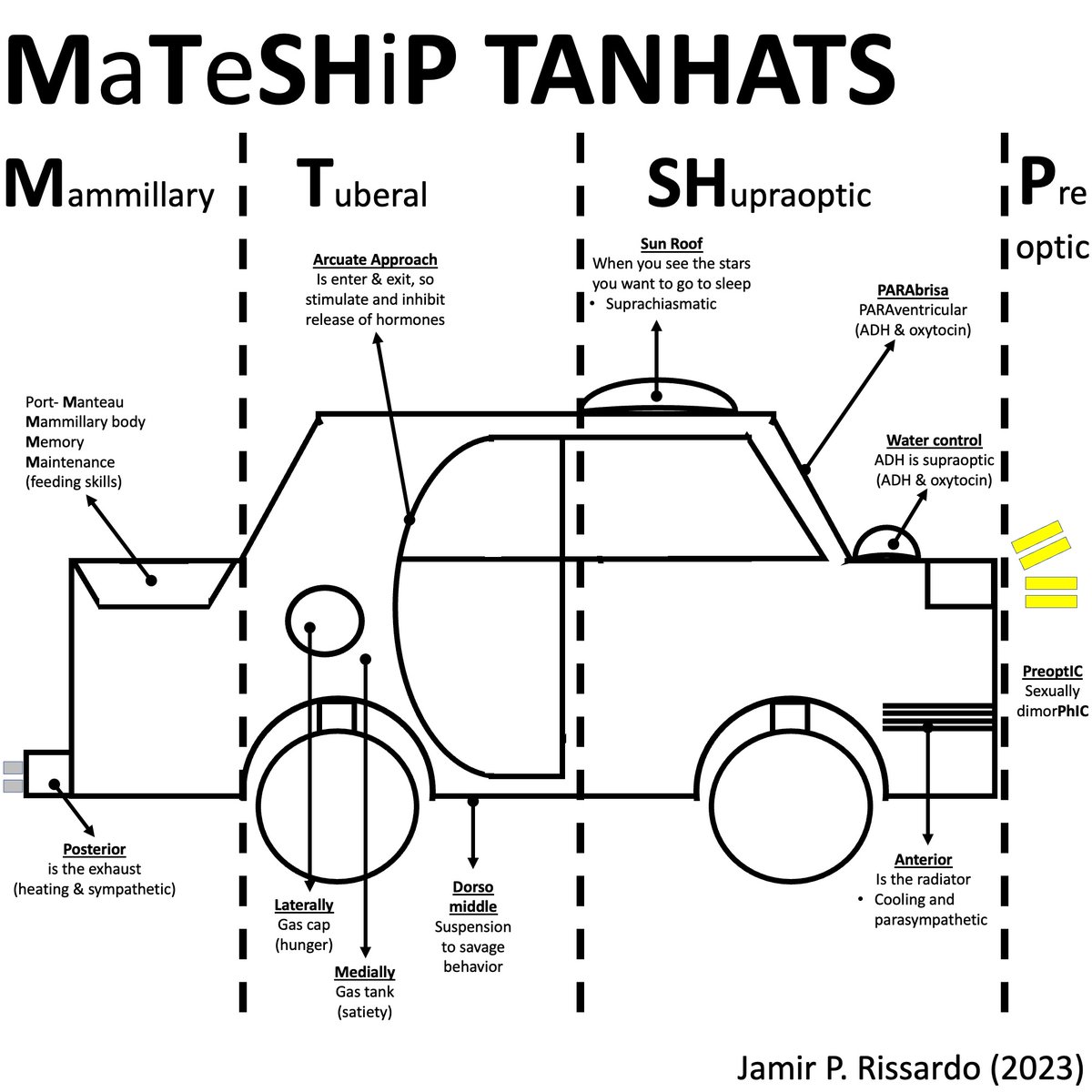
Mnemonic
“maintains homeostasis by regulating TANHATS”
Thirst and water balance
Adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary)
Neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary)
Hunger
Autonomic nervous system
Temperature
Sexual urges
31/
“maintains homeostasis by regulating TANHATS”
Thirst and water balance
Adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary)
Neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary)
Hunger
Autonomic nervous system
Temperature
Sexual urges
31/
Subthalamus
33/
33/
Function
“part of the indirect pathway of the basal ganglia”
34/
“part of the indirect pathway of the basal ganglia”
34/
Components
Nuclear FIFA
Nuclear: subthalamic nucleus
Fasciculus: subthalamic fasciculus
Incerta: zona incerta
Forel: fields of Forel
Ansa: ansa lenticularis
35/
Nuclear FIFA
Nuclear: subthalamic nucleus
Fasciculus: subthalamic fasciculus
Incerta: zona incerta
Forel: fields of Forel
Ansa: ansa lenticularis
35/

NeuroTeach - Content
The blog contains all the threads and videos.
neuronland.blogspot.com/2022/11/neurot…
Have a great day!
The blog contains all the threads and videos.
neuronland.blogspot.com/2022/11/neurot…
Have a great day!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh