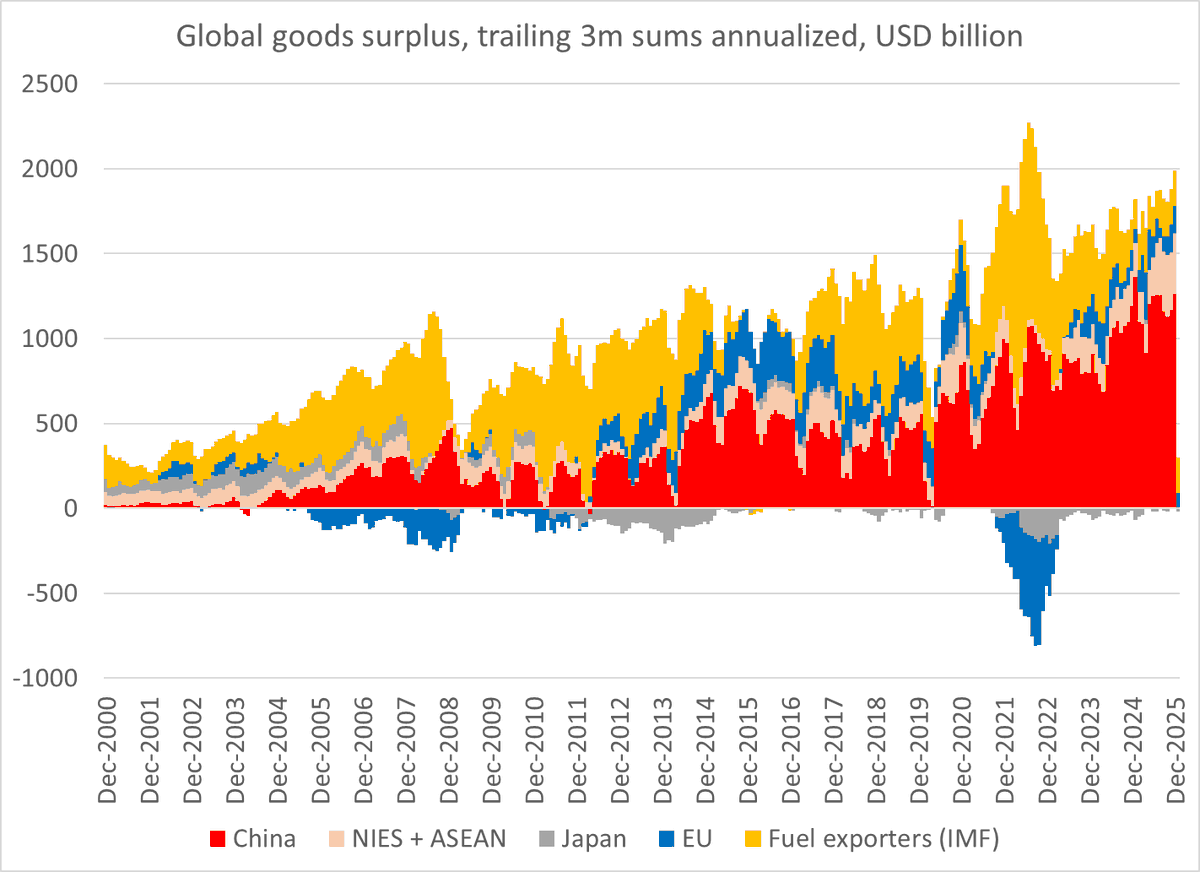
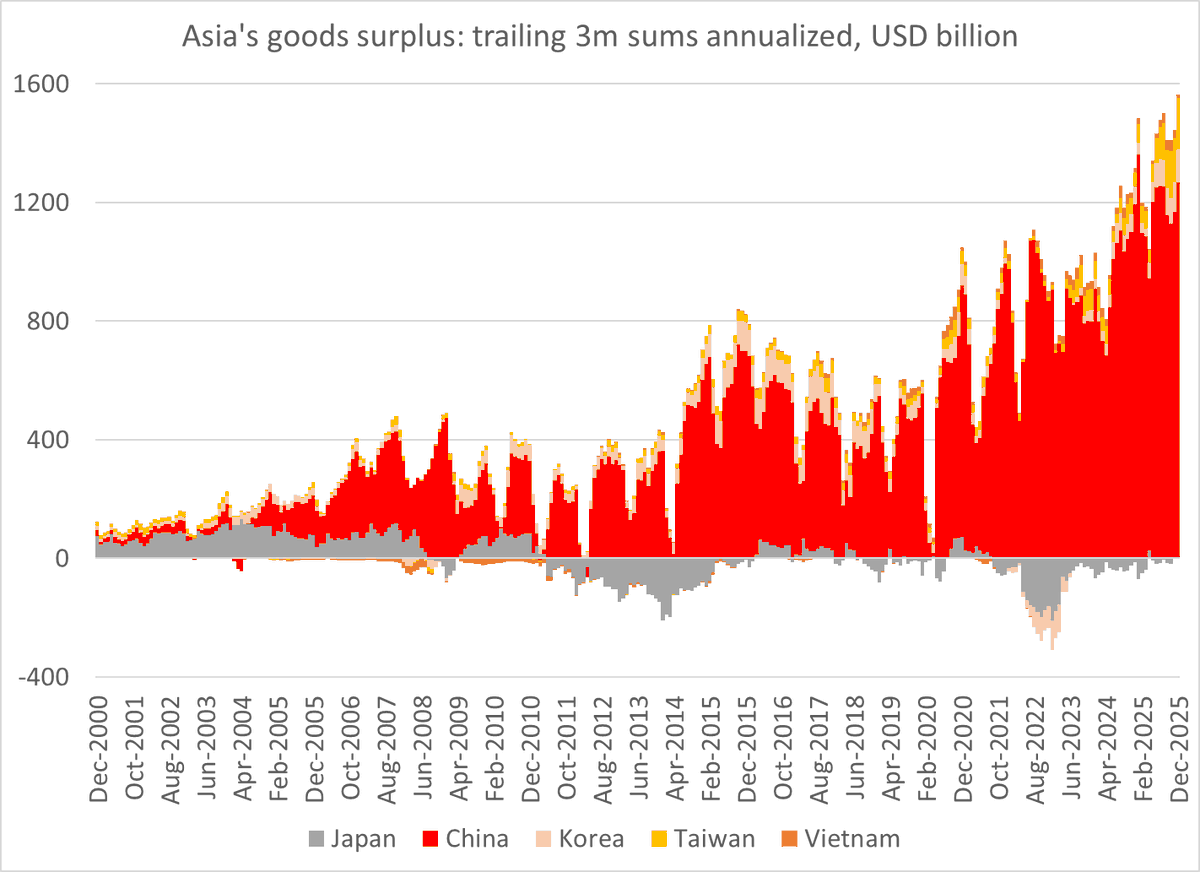
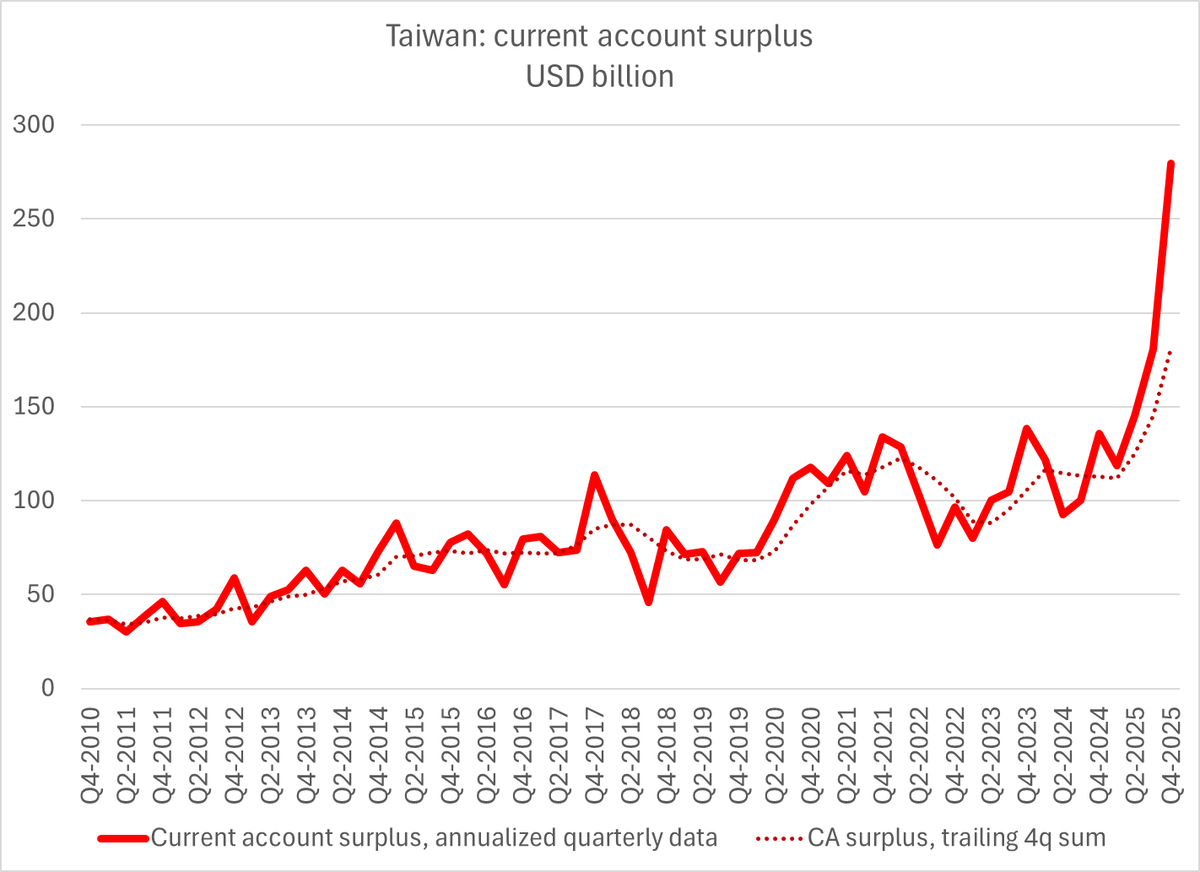
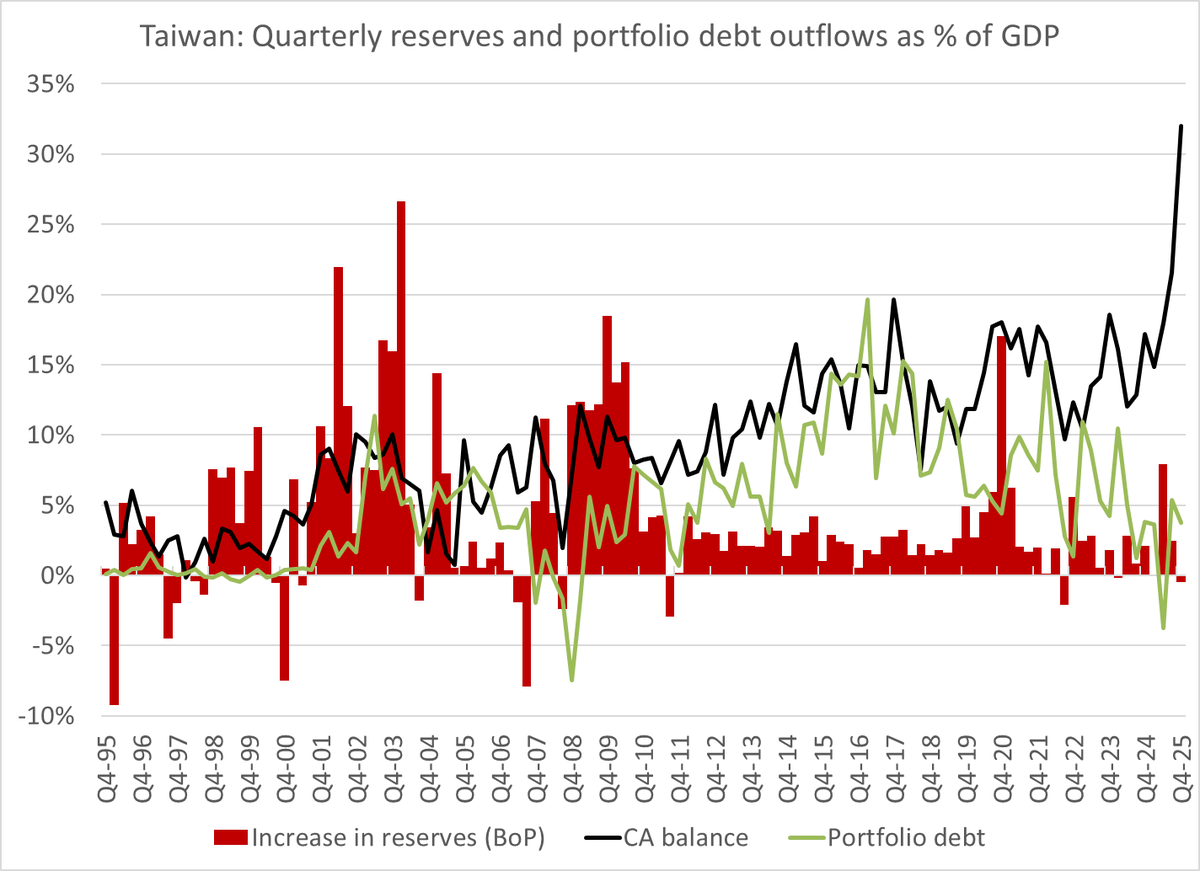
It is a bit hard to believe that any story involving China has been underreported, given China's large role in the global public debate.
But China's transformation into a major auto exporter has been wildly underreported.
(see the hockey stick in exports of finished cars)
1/
But China's transformation into a major auto exporter has been wildly underreported.
(see the hockey stick in exports of finished cars)
1/

China has gone from a large net importer of finished (mostly from the EU, the Japanese firms never thought they could sell in China w/o producing in China) to a net exporter remarkably quickly ...
(China has been a net exporter of auto parts for some time)
2/
(China has been a net exporter of auto parts for some time)
2/

The US has long been a net importer of autos (mostly from Japan and Korea, but to a degree from Europe too).
And the EU has long been a net exporter of autos.
China has suddenly become a major global competitor
3/
And the EU has long been a net exporter of autos.
China has suddenly become a major global competitor
3/

I suspect that you need a Ph.D in political science -- or perhaps psychology and trade law :) -- to understand why the Commission's main response to a surge in Chinese competition (primarily in EVs) has been to threaten to challenge the US in the WTO ...
4/
4/

I do understand that the IRA discriminates against European EV exports to the US (there aren't very many yet & the EU EV market is also undersupplied & will absorb any lost sales)
But the big swing in global demand for EU autos right now is coming from China, not the US.
5/5
But the big swing in global demand for EU autos right now is coming from China, not the US.
5/5

this thread was inspired both by this Bloomberg story, and the EU's current freakout over the IRA (& its long silence over China's obviously discriminatory policies in the EV sector, which have had a much bigger impact on EU auto exports and employment)
bloomberg.com/news/articles/…
bloomberg.com/news/articles/…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh