1/Your baby’s all grown up! Cerebellum may mean “little cerebrum” but its jobs are anything but little
Do you know cerebellar anatomy beyond vermis & hemispheres?
Here’s a #tweetorial about the functional #anatomy of the cerebellum!
#medtwitter #neurotwitter #neurorad #meded
Do you know cerebellar anatomy beyond vermis & hemispheres?
Here’s a #tweetorial about the functional #anatomy of the cerebellum!
#medtwitter #neurotwitter #neurorad #meded
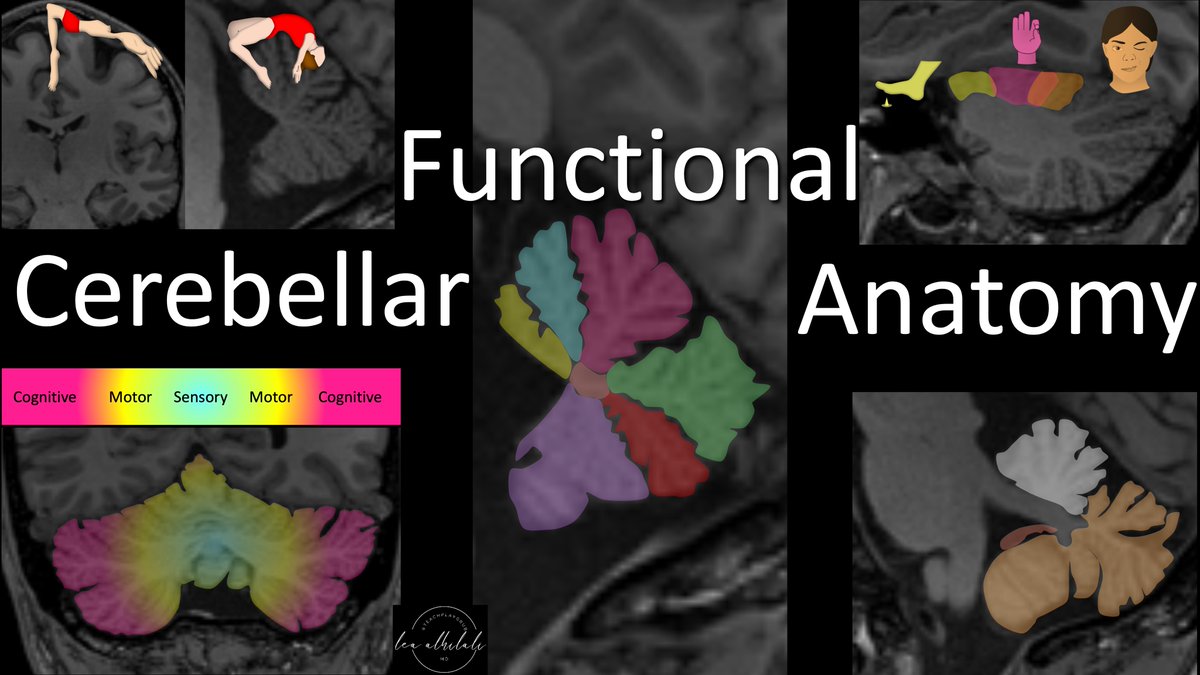
2/Cerebellum means “little cerebrum” or “little brain” bc it looks like a mini brain--a mini me to the cerebrum one might say.
However, it does not play a mini role. In fact, despite being significantly smaller than the cerebrum, it contains as many neurons as the cerebrum
However, it does not play a mini role. In fact, despite being significantly smaller than the cerebrum, it contains as many neurons as the cerebrum

3/When most people think of cerebellar function, they think of balance. And the first thing that comes to mind with cerebellar dysfunction is imbalance & dizziness.
However, the cerebellum is involved in much more, including cognitive functions
However, the cerebellum is involved in much more, including cognitive functions

4/The cerebellum is divided into anterior & posterior lobes by the primary fissure. Then, along its undersurface is the flocculonodular lobe.
I think this anatomy looks like a dog with his tongue sticking out—the tongue being the flocculonodular lobe
I think this anatomy looks like a dog with his tongue sticking out—the tongue being the flocculonodular lobe

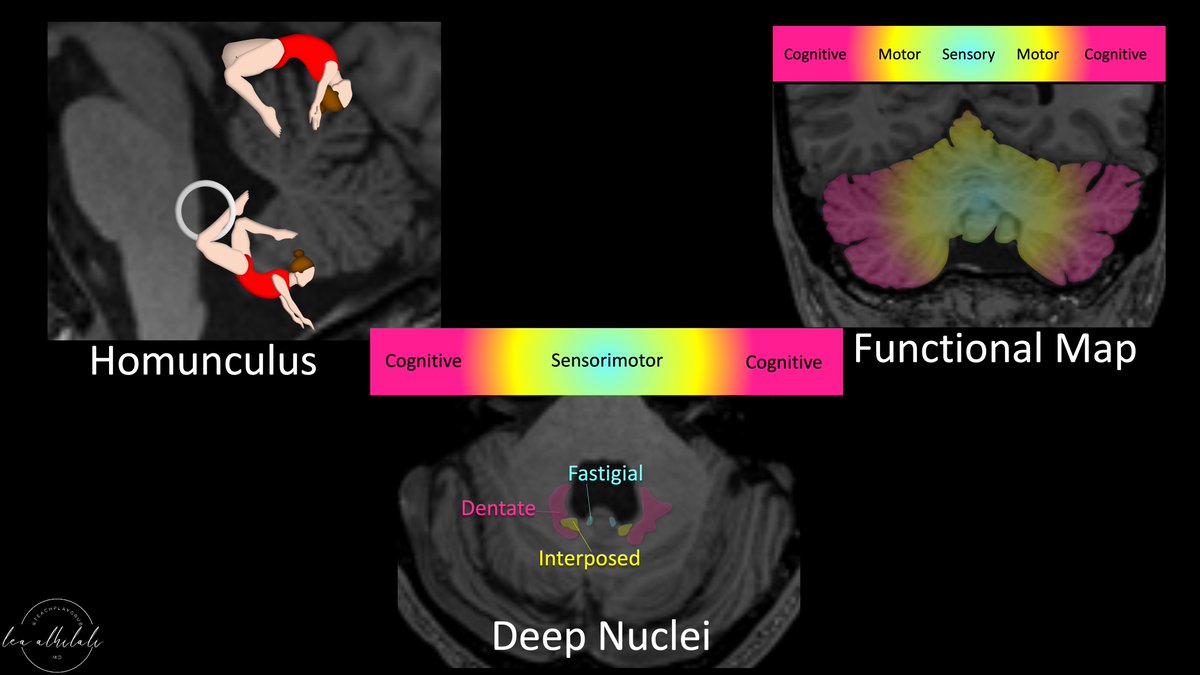
5/Cerebellum has a homunculus. In fact, it has 2!
It has a primary homunculus in along the top of the anterior lobe & a secondary homunculus along the bottom of the posterior lobe—like a reflection of the primary homunculus along the bottom of the cerebellum
It has a primary homunculus in along the top of the anterior lobe & a secondary homunculus along the bottom of the posterior lobe—like a reflection of the primary homunculus along the bottom of the cerebellum

6/Cerebellar homunculus looks like 2 gymnasts spread over the top and bottom of the cerebellum.
You have to picture their arms going out laterally, because the homunculus of the cerebellum also spreads out from midline.
You have to picture their arms going out laterally, because the homunculus of the cerebellum also spreads out from midline.

7/How to remember which way the gymnasts are facing?
Well, just like the homunculus in the cerebrum, the feet/legs hang over the edge.
So the feet of the cerebellar homunculus are dangling over the edge towards the fourth ventricle
Well, just like the homunculus in the cerebrum, the feet/legs hang over the edge.
So the feet of the cerebellar homunculus are dangling over the edge towards the fourth ventricle

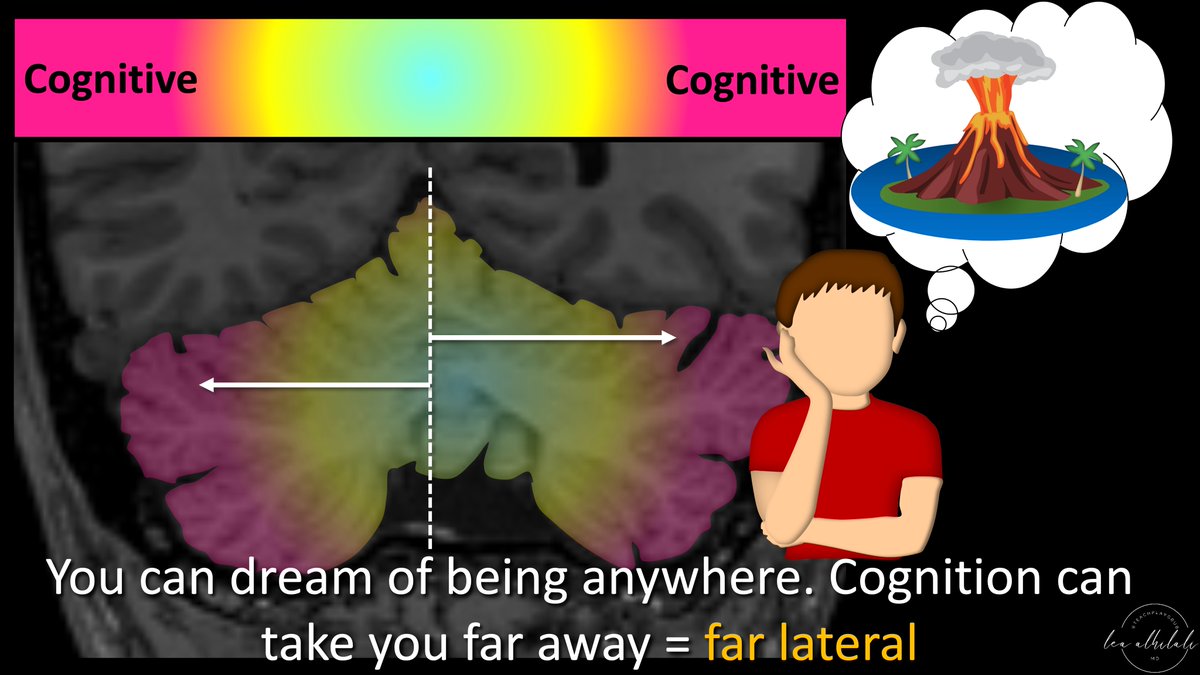
8/Cerebellum is involved in a variety of functions. The functional regions are organized in a gradient.
Most medial regions are for sensory, slightly more lateral for motor, & finally most lateral is for cognitive functions. Bet you didn’t know your little brain was thinking!
Most medial regions are for sensory, slightly more lateral for motor, & finally most lateral is for cognitive functions. Bet you didn’t know your little brain was thinking!

9/This distribution actually reflects the evolution of the cerebellum.
As species evolved & the frontal cortex/cognitive functions became more pronounced, the lateral hemispheres of the cerebellum enlarged too—helping to serve these new cognitive functions
As species evolved & the frontal cortex/cognitive functions became more pronounced, the lateral hemispheres of the cerebellum enlarged too—helping to serve these new cognitive functions

10/You can remember this distribution by thinking of the midline as home.
For sensory, you can only sense things close by (touch close by things, see things only in your line of sight).
Thus, sensory doesn’t take you far from home—you have to stay close (medial)
For sensory, you can only sense things close by (touch close by things, see things only in your line of sight).
Thus, sensory doesn’t take you far from home—you have to stay close (medial)

11/With motor functions (ie, walking, running), you can get a little bit away from home. You can run away—but you don’t get too far. There is only so far you can run!
So motor functions are slightly removed from midline
So motor functions are slightly removed from midline

12/Finally is cognitive. With your mind, you can transport yourself anywhere—you can dream of places very far away from home.
So cognitive functions are the farthest removed from home—they are the most lateral
So cognitive functions are the farthest removed from home—they are the most lateral
13/This gradient of sensorimotor function being more medial & cognitive functions being more lateral persists for the deep cerebellar nuclei.
There are three main deep nuclei: dentate, interposed (a combination of 2 small nuclei), & fastigial
There are three main deep nuclei: dentate, interposed (a combination of 2 small nuclei), & fastigial

14/Fastigial is the most medial. You can remember it’s mainly sensory bc fastigial sounds like fastidious, which means sensitive or picky.
Sensitive/sensory means most medial. Big role of fastigial is the sensory input from the vestibular system
Sensitive/sensory means most medial. Big role of fastigial is the sensory input from the vestibular system

15/Interposed is in between.
When you interpose yourself, you kind of insert yourself or intervene in an argument. You are interposed between the two sides.
That is exactly what the interposed nuclei are for—coordinating opposing muscles on the two sides of a motion
When you interpose yourself, you kind of insert yourself or intervene in an argument. You are interposed between the two sides.
That is exactly what the interposed nuclei are for—coordinating opposing muscles on the two sides of a motion

16/Last is the dentate nucleus. Dentate sounds like teeth & the dentate looks like teeth as well, with an irregular, almost jagged edge.
Your teeth are in your head, so the dentate is very involved in cognitive function (head = cognitive)
Your teeth are in your head, so the dentate is very involved in cognitive function (head = cognitive)

17/So now you know the functional anatomy of the cerebellum—the homunculus, the functional topology, and organization of the nuclei.
So when it comes to the “little brain,” your knowledge will be anything but little!
So when it comes to the “little brain,” your knowledge will be anything but little!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















