1/ The discovery of untouched Mesolithic layers in the cave of Cyclops at Youra and a coastal Mesolithic open-air settlement in Maroulas at Kythnos have come to add to the Mesolithic finds from the great cave site at Franchthi, ➡️ 

➡️ offering valuable information for the understanding of the survival strategies of the pre-Neolithic groups of Aegean. 

2/ These demonstrate the existence of a common cultural context, which implies extremely similar stone industry with influences from the Upper Palaeolithic tradition of SE Europe, but having a clear Mesolithic typology. However, some exogenous features are also observed. 

3/ At the same time, the pre-domestication of wild animals and plants cross-reference to a preparatory phase of the Neolithic corresponding to similar periods in Anatolia and the Middle East, with which important contacts had developed through an extensive network of sea routes. 

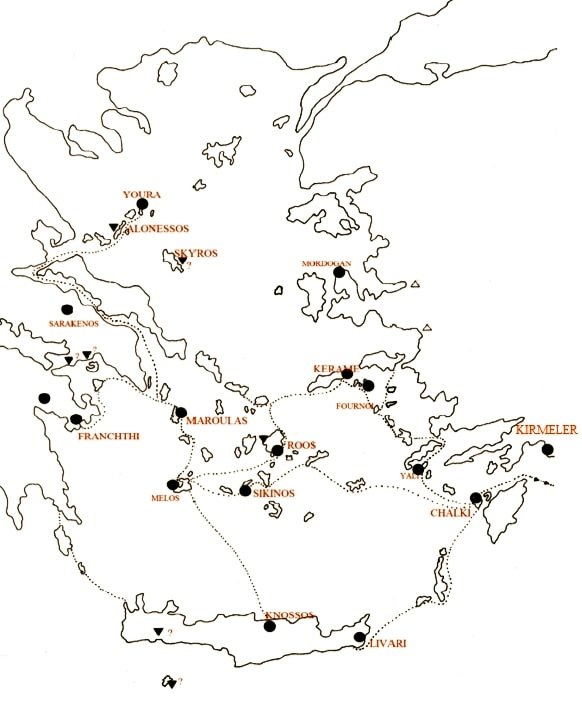
4/Recent field surveys have been directed towards the search for these sea routes by finding the dispersion of the Mesolithic groups within the Archipelago with the results being extremely impressive and clearly demonstrating the great mobility and high seamanship of these groups 

5/ The finding of the site of Kerame at Ikaria by a joint Greek-Polish archaeological expedition in the period 2007-8 is an important discovery in the area of Aegean prehistory, being the first Mesolithic site in the Eastern Aegean region and indeed close to the Asia Minor coast. 

6/ The site of Kerame is located on the SE coast of Ikaria on a high coastal cliff with an altitude of 20 meters, which carries intense alluvial shale - sandstone deposits. The highly eroded surface of the site scattered the majority of the artefacts and, ➡️ 

➡️ in conjunction with the subsequent intensive cultivation of the site, did not yield the presence of bone remains, but isolated shells, suggesting the existence of a dry and slightly moist environment with open lightly shaded habitats. 

7/ No traces of hearths were found at the site, although there are indications of stone structures. The recovered chipped stone assemblage is quite rich and homogeneous, both in its technology and typology. ➡️ 

➡️ Chert of unknown origin was used as raw material, as well as obsidian from Melos, but also from the island of Yiali in the Dodecanese, while some tools were made from local quartz and quartzite, rhyolite and hematite. 

8/The structure of the stone industry of Kerame is similar to that of the Mesolithic ensembles of Maroulas, going back to a typology and technology of the Early Mesolithic. It mainly includes retouched flakes and notched tools, ➡️ 

➡️ two characteristic features of the Aegean Mesolithic, with a portion of these appearing to have been produced after in situ processing. At the same time, various types of microlithics, perforators and end-scrapers were recovered, while the blades are limited. 

9/ The disturbances suffered by the stratigraphy of the site with the destruction of obvious structures and organic remains makes its absolute dating difficult with the only possibility of its interpretation being determined by the scattered stone artefacts ➡️ 

➡️ in various parts of the surface, possibly identifying the existence of several distinct camps, bearing identical stone industry, demonstrating similar activities and individuals with a common cultural tradition. 

11/ Recent dating of two obsidian samples by the method of secondary ion mass spectrometry yielded a date of great discrepancy, but within the context of the Mesolithic Period. The similarities with the stone industry of Maroulas attest to a dating in the Early Mesolithic. 

12/ Also the Mesolithic groups at Kerame seem to have followed the same Ikarian resource exploitation strategies as the corresponding groups at Maroulas: an extensive central camp and various peripheral ephemeral small camps in various parts of the island. 
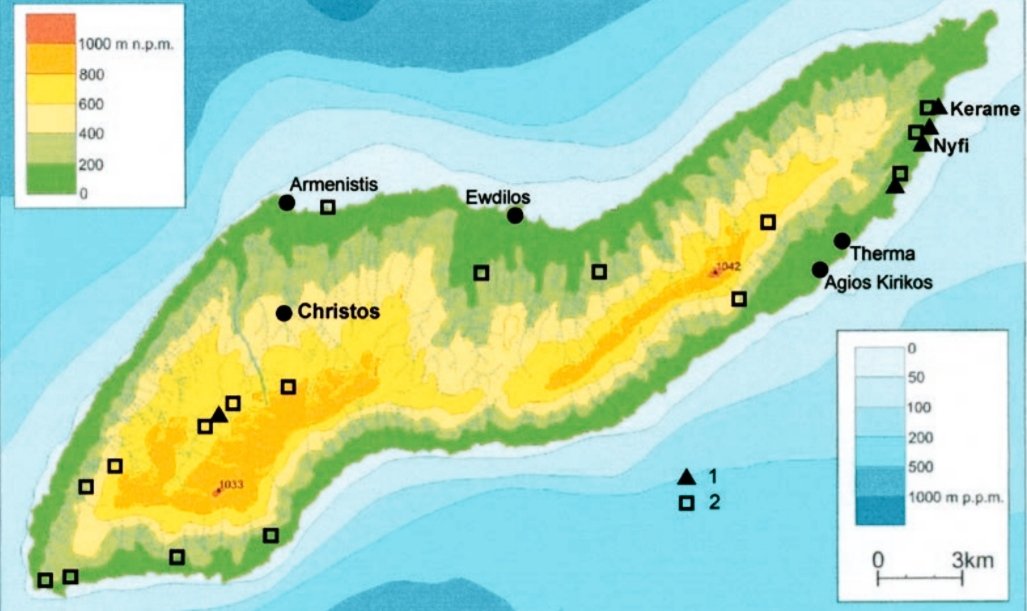
13/ The Mesolithic open-air settlement of Kerame seems to have been very large in area, with the stone artefacts scattered over an area of eight hectares, covering the western part of it ➡️ 

➡️ and suggesting a more permanent settlement, rather than a small short-lived camp, being much larger in size from the corresponding settlement of Maroulas in Kythnos. 

14/ The rocky peninsula of Kerame with its steep shores jutting out into the sea is believed to have been much more extensive in area during this period, covered by huge rocks, which collapsed due to natural erosion and seismic excitation. ➡️ 

➡️ Slabs placed horizontally on the ground may be the remains of structures made of perishable materials, such as wood and organic materials, without leaving traces. 

15/ All evidence suggests that the settlement of Kerame must have had an important role in the Aegean network of contacts and exchanges of the Mesolithic, having close cultural affinities with Kythnos ➡️ 
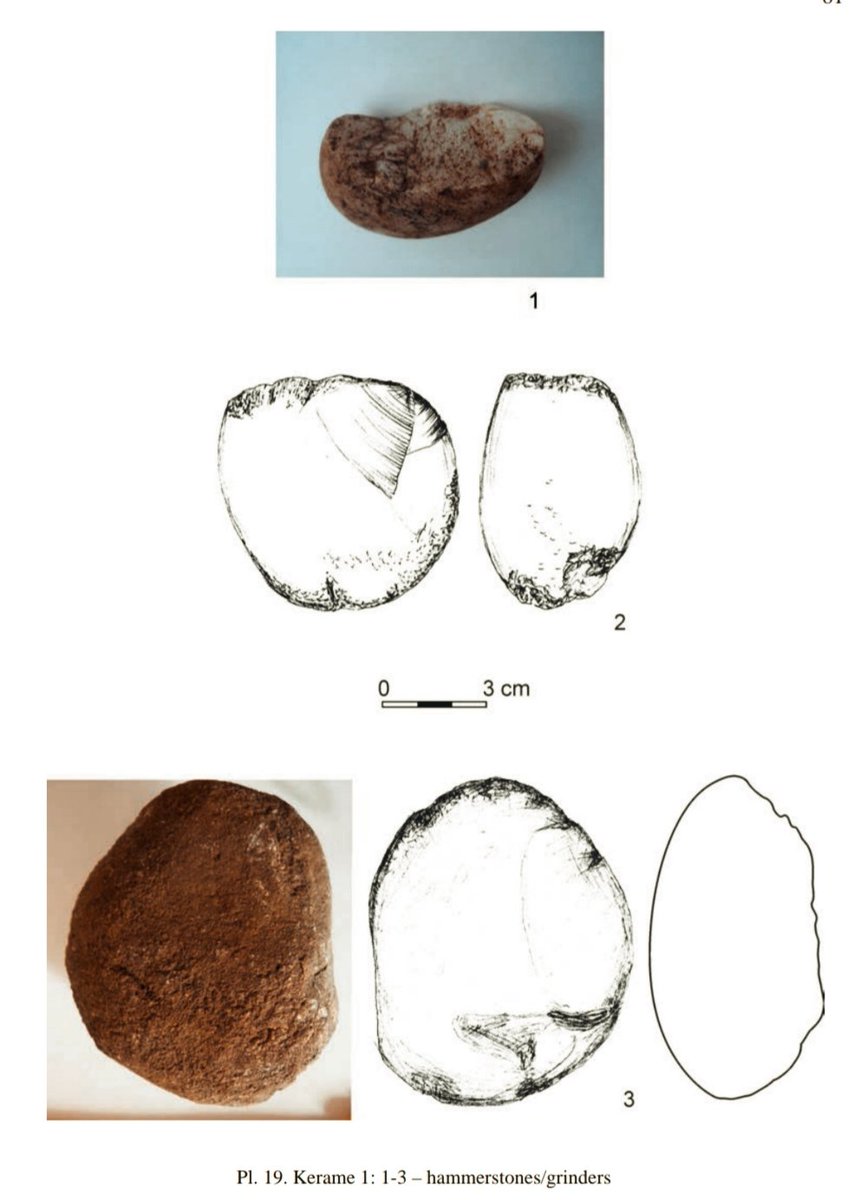

➡️ and indicating the existence of southern sea routes, which led to the Dodecanese and the coasts of Asia Minor and perhaps even further to Cyprus and Syro-Palestine. 
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh