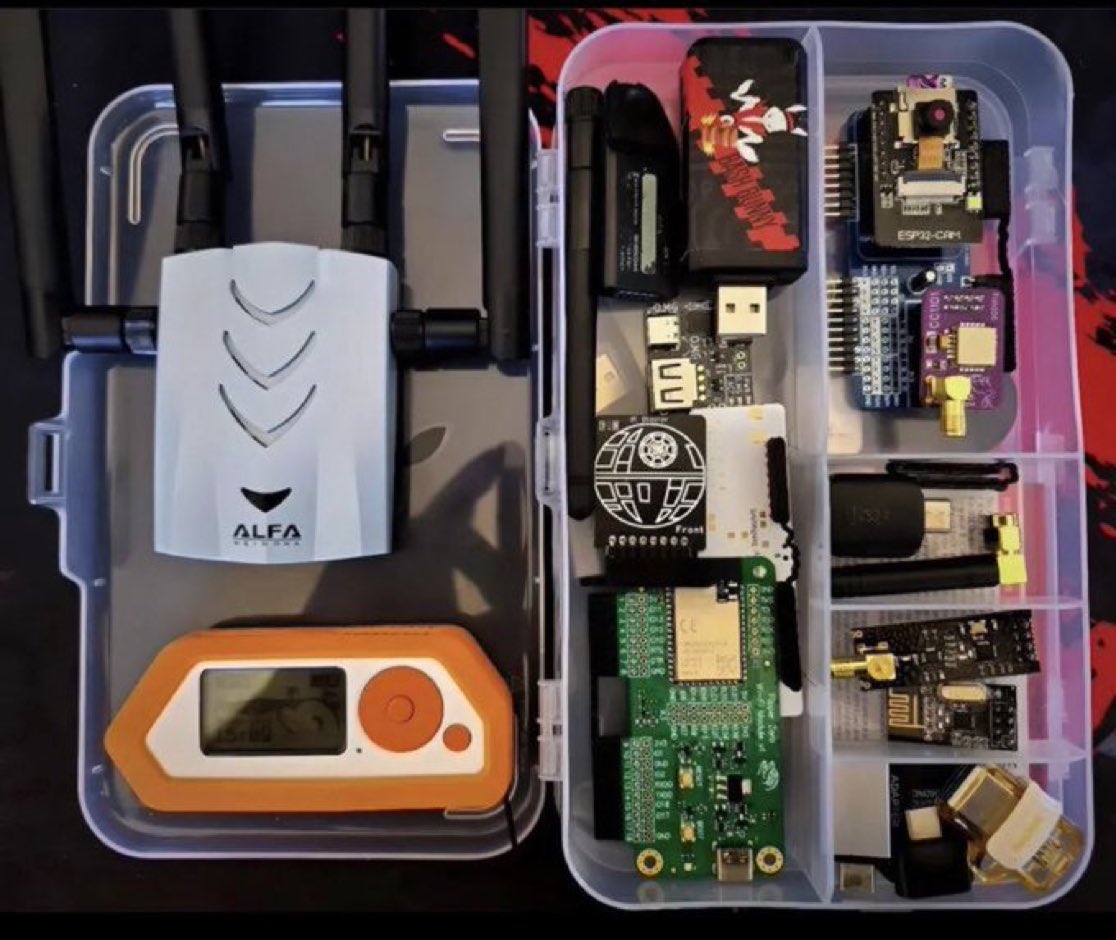
Top 9 Hacker Gadgets
1. Raspberry Pi:
This is a low cost credit card sized desktop computer that runs Linux and it also provides a set of GPIO (general purpose input/output) pins. It enables people to explore computing and learn Programming.
1. Raspberry Pi:
This is a low cost credit card sized desktop computer that runs Linux and it also provides a set of GPIO (general purpose input/output) pins. It enables people to explore computing and learn Programming.

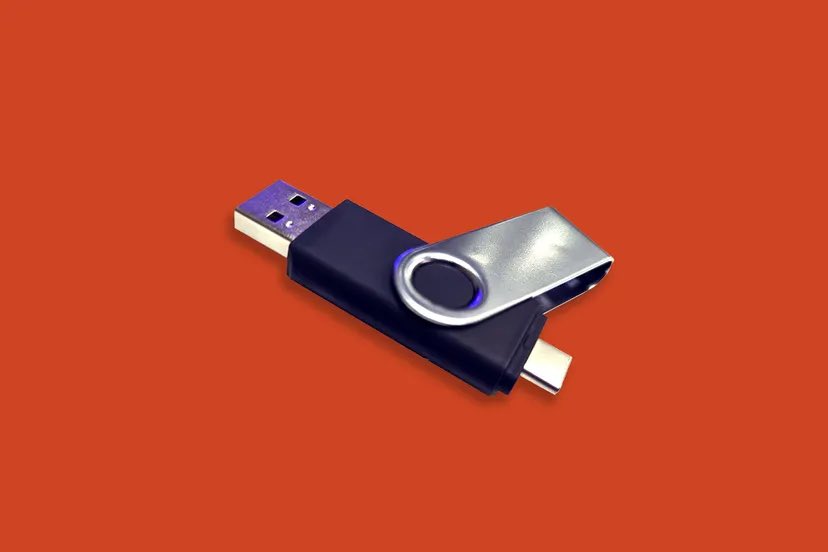
2. Rubber Ducky USB
The Rubber ducky looks similar to a USB Pen drive, it can be used for variety of attacks, hack a system, inject a keystroke into a system, inject payloads and also steal information and sensitive data.
The Rubber ducky looks similar to a USB Pen drive, it can be used for variety of attacks, hack a system, inject a keystroke into a system, inject payloads and also steal information and sensitive data.

3. LAN Turtle
The LAN Turtle by Hak5 is a covert Systems Administration and Penetration Testing tool providing stealth remote access, network intelligence gathering, and man-in-the-middle surveillance capabilities through a simple graphic shell.
The LAN Turtle by Hak5 is a covert Systems Administration and Penetration Testing tool providing stealth remote access, network intelligence gathering, and man-in-the-middle surveillance capabilities through a simple graphic shell.

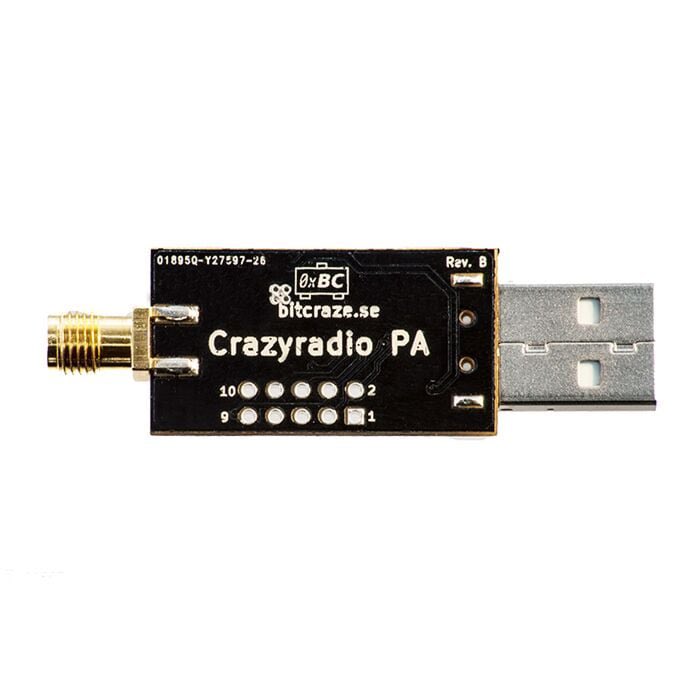
4. Crazy Radio
This is a long range open USB radio dongle Radio power amplifier giving 20dBm output power · 1km range LOS with Crazyflie 2.0. It is also a great building block for systems that require longer range than WiFi
This is a long range open USB radio dongle Radio power amplifier giving 20dBm output power · 1km range LOS with Crazyflie 2.0. It is also a great building block for systems that require longer range than WiFi

5. Cactus WHID (Keylogger)
This is a Keylogger it allows Keystrokes to be sent through WiFi to a target Machine.
The target recognises the Ducky as both a standard HID keyboard and a serial port, allows interactive commands and scripts to be executed on the target remotely.
This is a Keylogger it allows Keystrokes to be sent through WiFi to a target Machine.
The target recognises the Ducky as both a standard HID keyboard and a serial port, allows interactive commands and scripts to be executed on the target remotely.

6. Dstike Wi-Fi Duether
Dstike can kick devices off a network irrespective of whether you are connected to it or not, it scans for nearby networks and selects individuals or networks it wants to kick out then kick it out
Dstike can kick devices off a network irrespective of whether you are connected to it or not, it scans for nearby networks and selects individuals or networks it wants to kick out then kick it out
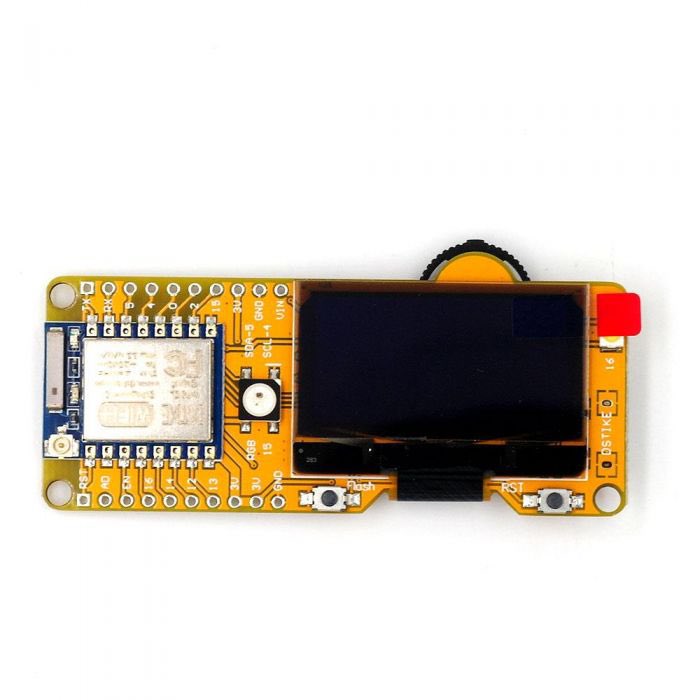
7. Magspoof
Magspoof allows its user to store different kind of credit cards and magstripes in one device. The device that can spoof/emulate any magnetic stripe or credit card
Magspoof allows its user to store different kind of credit cards and magstripes in one device. The device that can spoof/emulate any magnetic stripe or credit card

8. Ubertooth One
Ubertooth One is a small, open-source USB device with an antenna powered by an ARM Cortex-M3 chip and a CC2400 wireless transceiver. You can sniff and monitor Bluetooth signals from nearby devices
Ubertooth One is a small, open-source USB device with an antenna powered by an ARM Cortex-M3 chip and a CC2400 wireless transceiver. You can sniff and monitor Bluetooth signals from nearby devices

9. Wi-Fi Pineapple
Wi-Fi Pineapple is a wireless auditing platform from Hak5 that allows network security administrators to conduct penetration tests.
#cybersecurity #Hacked #Hacker
Wi-Fi Pineapple is a wireless auditing platform from Hak5 that allows network security administrators to conduct penetration tests.
#cybersecurity #Hacked #Hacker

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh