🧵 1/16
Russian forces are revamping their assault tactics after experiencing failures with their current structure. The Battalion Tactical Groups (BTGs) are getting replaced with a new unit called the "Assault Unit" or "Assault Detachment", which I will discuss in this thread.
Russian forces are revamping their assault tactics after experiencing failures with their current structure. The Battalion Tactical Groups (BTGs) are getting replaced with a new unit called the "Assault Unit" or "Assault Detachment", which I will discuss in this thread.

2/16
Based on a captured russian manual, the Assault Unit (or Detachment) is a battalion-sized force designed to perform assaults in fortified tree lines and urban environments. It is essentially a reinforced battalion with a specific focus on assault operations.
Based on a captured russian manual, the Assault Unit (or Detachment) is a battalion-sized force designed to perform assaults in fortified tree lines and urban environments. It is essentially a reinforced battalion with a specific focus on assault operations.

3/16 The Assault Detachment is customizable to mission requirements and consists of 2-3 assault companies, a command unit, an artillery support unit, and other groups: recon, tank, EW, AD, fire support, UAV, Medevac, flamethrowing, assault engineering, reserve, equipment recovery 

4/16
Assault unit armament:
- Three T-72 tanks
- Two Zu-23, and 3 MANDAPS
- 12 man-portable flamethrowers
- Six SPGs (2S9),
- Six Towed artillery guns (D30)
- Two AGS-17
- Two Kord HMGs,
- Two ATGMs
- Two sniper pairs.
- BREM-L
Assault unit armament:
- Three T-72 tanks
- Two Zu-23, and 3 MANDAPS
- 12 man-portable flamethrowers
- Six SPGs (2S9),
- Six Towed artillery guns (D30)
- Two AGS-17
- Two Kord HMGs,
- Two ATGMs
- Two sniper pairs.
- BREM-L

5/16
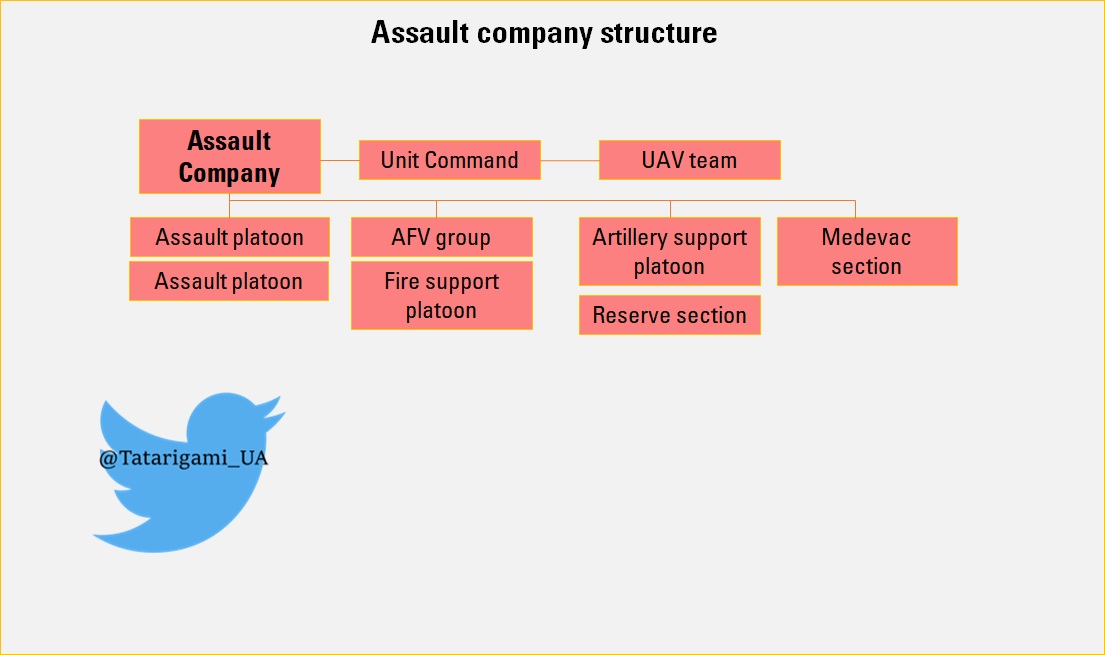
The main unit of the assault detachment is an assault company consisting of a command unit, a UAV team, assault platoons, an artillery support platoon, a tank group, a reserve section, artillery support platoons, medevac section.
The main unit of the assault detachment is an assault company consisting of a command unit, a UAV team, assault platoons, an artillery support platoon, a tank group, a reserve section, artillery support platoons, medevac section.
6/16
Assault company armament:
- Four BMP or BMD-2
- One T-72
- Two AGS-17,
- Two Kord HMG
- Two ATGM
- Two sniper pairs
- Two mortars - either 82 or 120 mm mortar
- One D30 or 2S9
Assault company armament:
- Four BMP or BMD-2
- One T-72
- Two AGS-17,
- Two Kord HMG
- Two ATGM
- Two sniper pairs
- Two mortars - either 82 or 120 mm mortar
- One D30 or 2S9

7/16
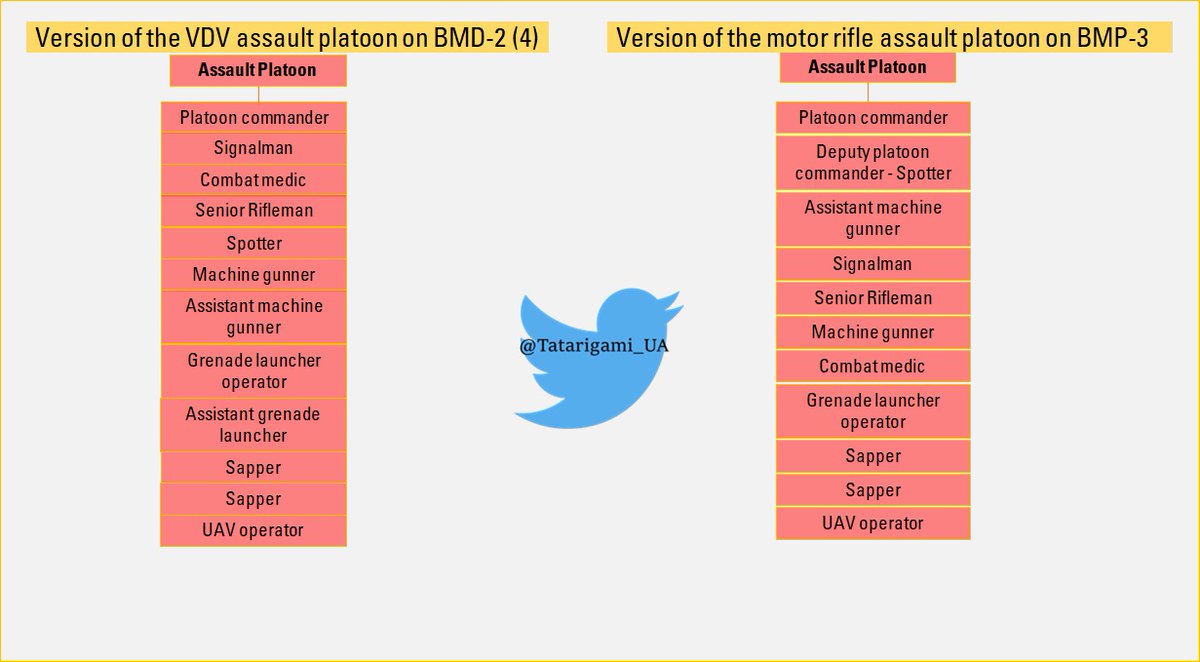
The primary component of the combat formation is the assault platoon, which may consist of an advance party, safeguard, command group, and fire support platoon strengthened by additional firepower: AGS, mortar, D-30 gun, armored group, and evacuation squad.
The primary component of the combat formation is the assault platoon, which may consist of an advance party, safeguard, command group, and fire support platoon strengthened by additional firepower: AGS, mortar, D-30 gun, armored group, and evacuation squad.
8/16
An assault platoon comprises 12-15 members, divided into tactical groups of 3 people, and equipped based on mission requirements. A reserve section can supplement the platoon with additional firepower - machine gunner, assistant machine gunner, riflemen.
An assault platoon comprises 12-15 members, divided into tactical groups of 3 people, and equipped based on mission requirements. A reserve section can supplement the platoon with additional firepower - machine gunner, assistant machine gunner, riflemen.

9/16
Main assault provisions:
• The pause between the assault and artillery fire on fortified positions should be no longer than one minute
• Using UAVs for reconnaissance is advised, but it is not recommended to use them for battle monitoring to avoid the loss of the UAV.
Main assault provisions:
• The pause between the assault and artillery fire on fortified positions should be no longer than one minute
• Using UAVs for reconnaissance is advised, but it is not recommended to use them for battle monitoring to avoid the loss of the UAV.
10/16
• Occupying abandoned trenches is prohibited because they may have been booby-trapped or could have been prepared as targets for artillery strikes.
• Assaulters cannot evacuate the wounded themselves; they must relay the wounded's coordinates to the evacuation team.
• Occupying abandoned trenches is prohibited because they may have been booby-trapped or could have been prepared as targets for artillery strikes.
• Assaulters cannot evacuate the wounded themselves; they must relay the wounded's coordinates to the evacuation team.

11/16
• The platoon commander controls mortar fire.
• The platoon/company commander decides on artillery targets, but only the unit commander can provide the air support.
• A recommended firing method for the AGS-17 is indirect fire, with a preferred firing range of 600-1700 m
• The platoon commander controls mortar fire.
• The platoon/company commander decides on artillery targets, but only the unit commander can provide the air support.
• A recommended firing method for the AGS-17 is indirect fire, with a preferred firing range of 600-1700 m
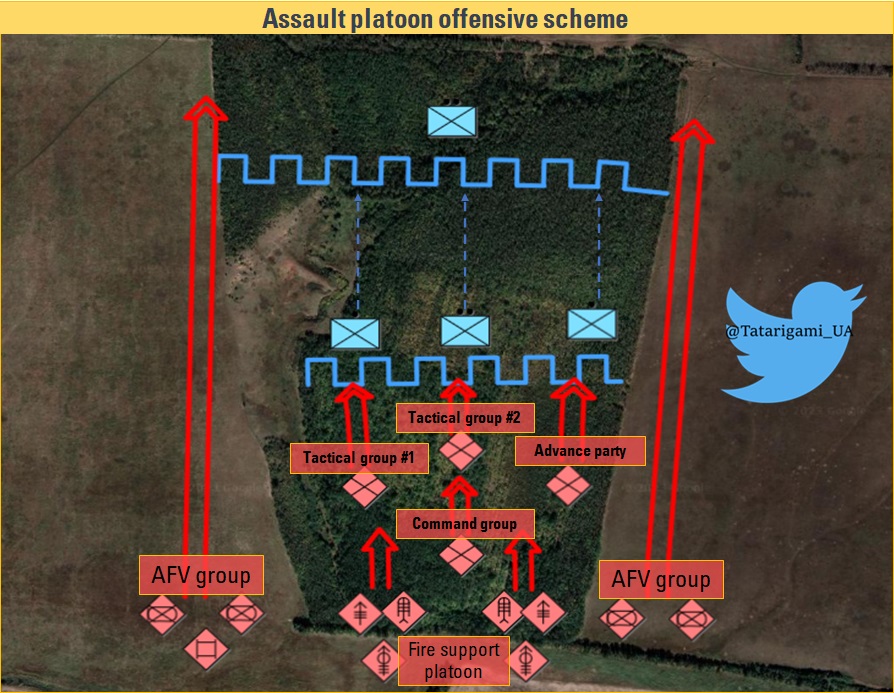
12/16
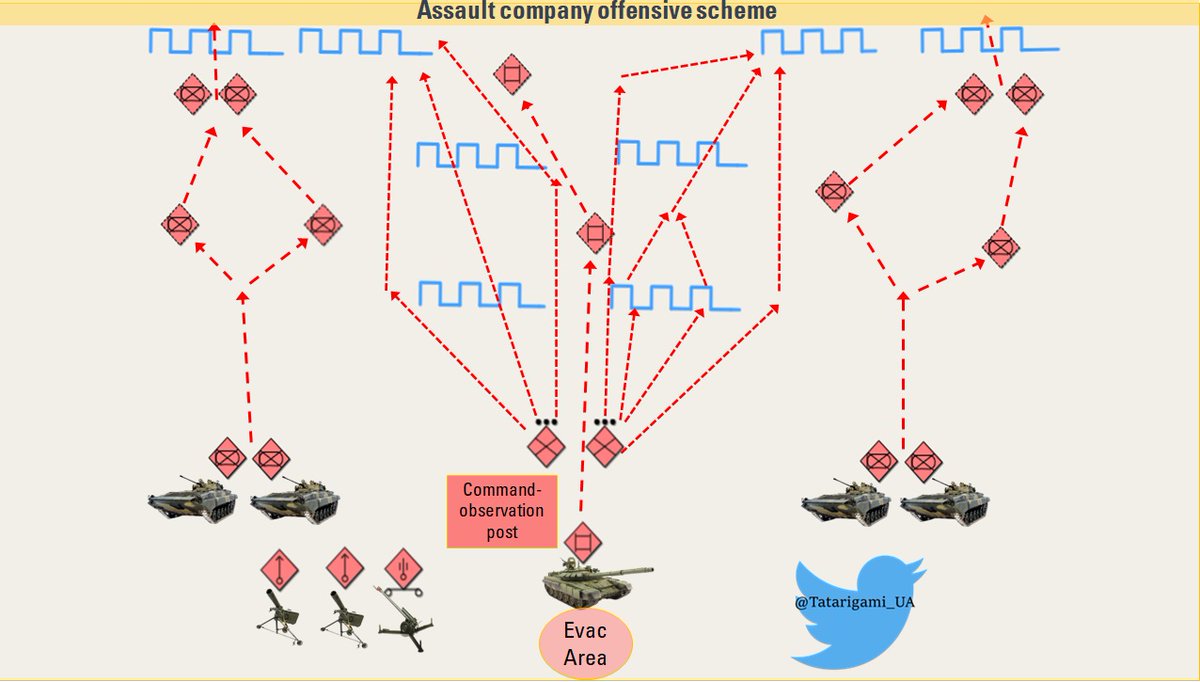
During the assault, the armored group can act as a whole or be divided between platoons. The artillery support platoon's mortars are distributed between assault platoons, while the artillery gun reports directly to the commander.
During the assault, the armored group can act as a whole or be divided between platoons. The artillery support platoon's mortars are distributed between assault platoons, while the artillery gun reports directly to the commander.
13/16
• During the treeline assault, the platoon should move in a diamond formation
• During an assault, it is prohibited for an assault company or platoon to move through open spaces and they should instead move solely within the treeline.
• During the treeline assault, the platoon should move in a diamond formation
• During an assault, it is prohibited for an assault company or platoon to move through open spaces and they should instead move solely within the treeline.
14/16
The russians are transitioning from larger structures, such as BTGs, to smaller, more agile assault units. However, they still rely heavily on artillery support. It is uncertain if they have enough scarce weapons like 2S9, mortars, AGS, and ammo to equip all units.
The russians are transitioning from larger structures, such as BTGs, to smaller, more agile assault units. However, they still rely heavily on artillery support. It is uncertain if they have enough scarce weapons like 2S9, mortars, AGS, and ammo to equip all units.
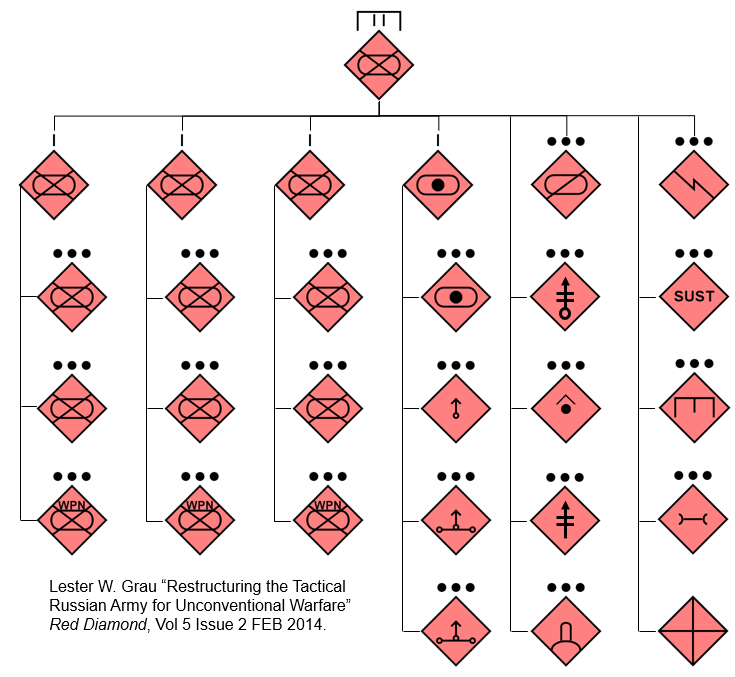
15/16
This decision seems to be influenced by Wagner's advances in the Bakhmut area and the decreased availability of vehicles and weaponry since February 2022. Unlike BTG, assault detachments doesn’t seem to have a logistics or MLRS units in their structure.
This decision seems to be influenced by Wagner's advances in the Bakhmut area and the decreased availability of vehicles and weaponry since February 2022. Unlike BTG, assault detachments doesn’t seem to have a logistics or MLRS units in their structure.
16/16
In the upcoming part, which I will be publishing next week, I plan to expand on this topic further and discuss urban tactics and recommendations. I invite you to follow me to stay updated, as social media algorithms may not prioritize war-related content.
In the upcoming part, which I will be publishing next week, I plan to expand on this topic further and discuss urban tactics and recommendations. I invite you to follow me to stay updated, as social media algorithms may not prioritize war-related content.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh