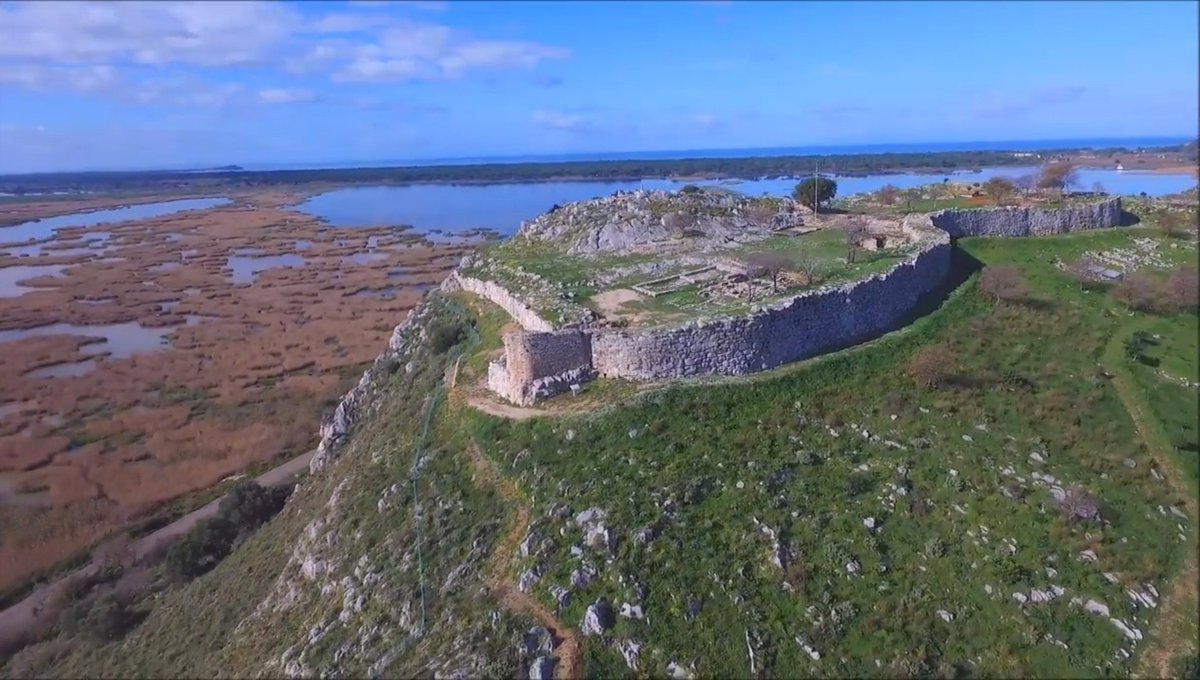
1/ 1200/1190 BC - Aegean: the palatial centers of the mainland disappear one after the other in the rush of the cataclysmic events of the LBA Collapse, taking with them forever the splendor and glamor of a refined Mycenaean elite, which shone for at least two centuries. 

2/ Some important cultural skills of the palatial period were also lost with them, such as writing, monumental architecture and palatial bureaucracy. The most former palatial centers are abandoned for centuries after the destructions or Post-Palatial activity is limited. 

3/ However, there is one palatial site in mainland Greece that shows a rapid reconstruction and significant recovery after its destruction at the very beginning of the 12th century BC, becoming the most important economic center of the Post-Palatial Period. 

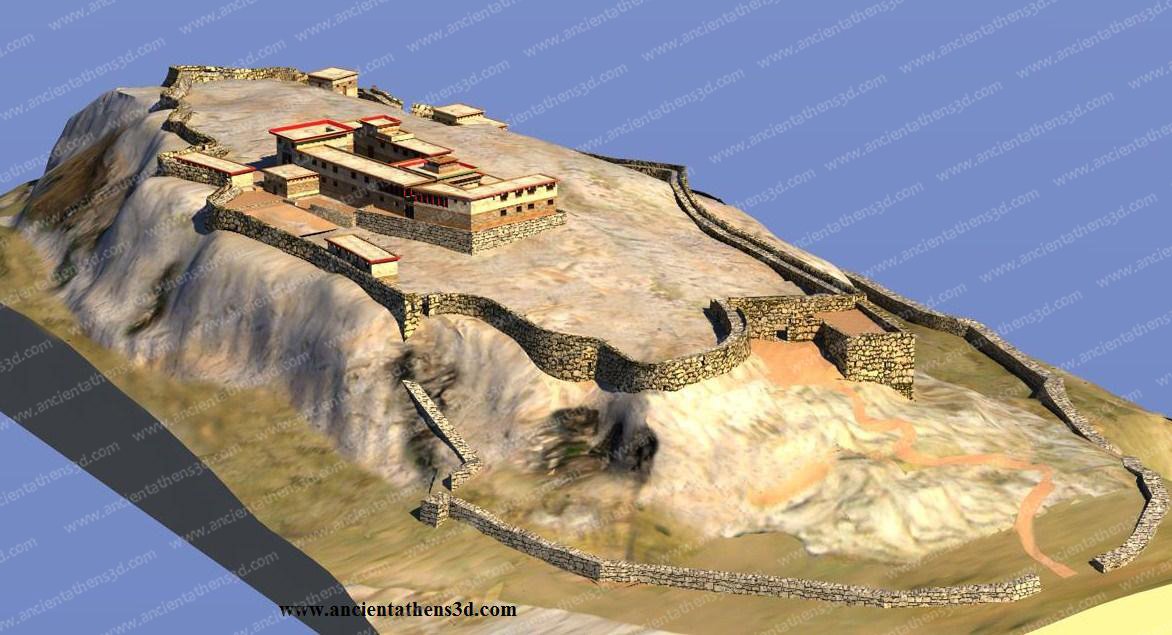
4/ Throughout the palatial period, Tiryns was the central commercial port of Argolis, which was under the control of the ruling elite of Mycenae. Thus the city of Tiryns, as well as the nearby Midea, were under the shadow of the Atreids and their bureaucracy. 

5/ Although it can be assumed that the Mycenaean elite of Tiryns had become autonomous from Mycenae during LH IIIB2 enjoying great wealth from foreign trade, the final disengagement came after the LBA Collapse destructions across the Argolic plain. 
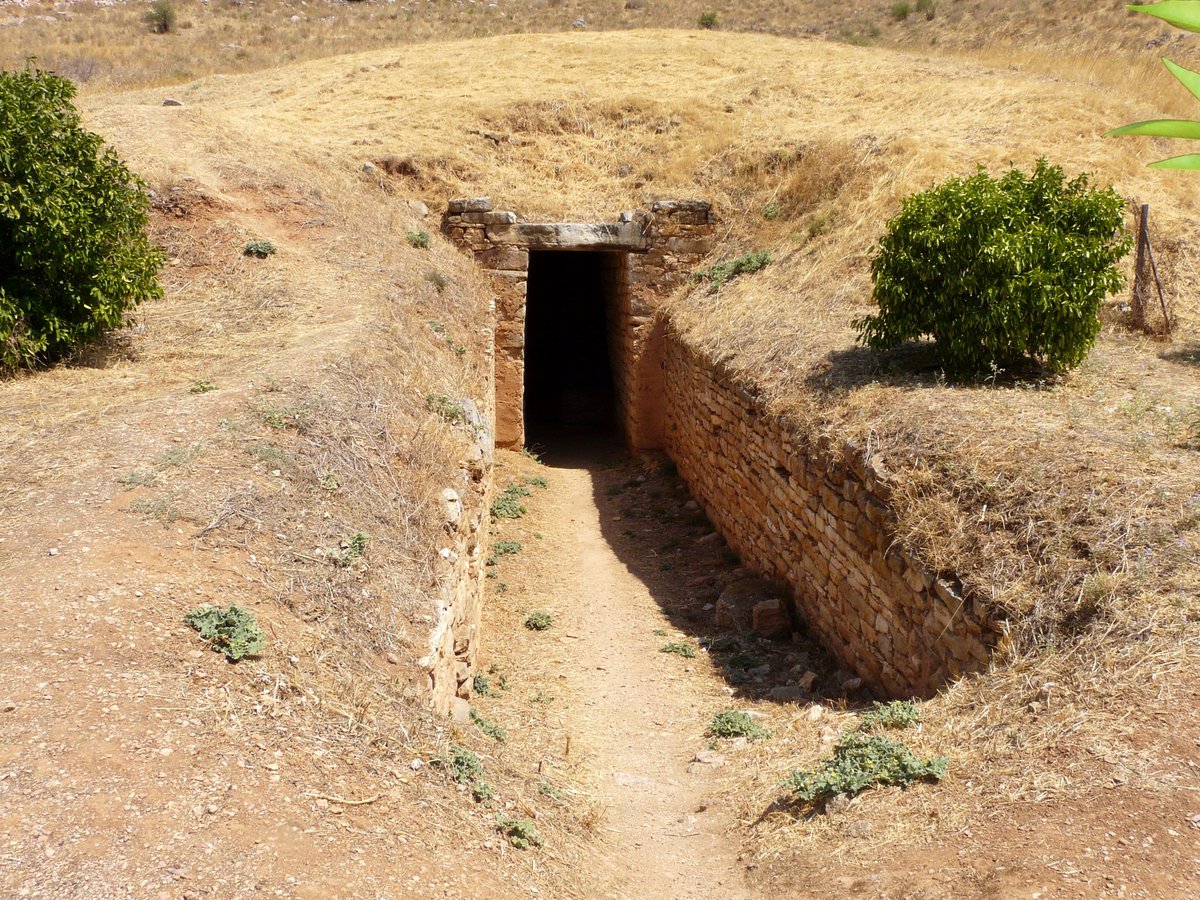



6/ During that dark period, the invaders attack the central palatial complex of the Upper Citadel and cause widespread destructions. The members of the Mycenaean elite seem not to have expected such a development and lived carefree in their false bliss. 

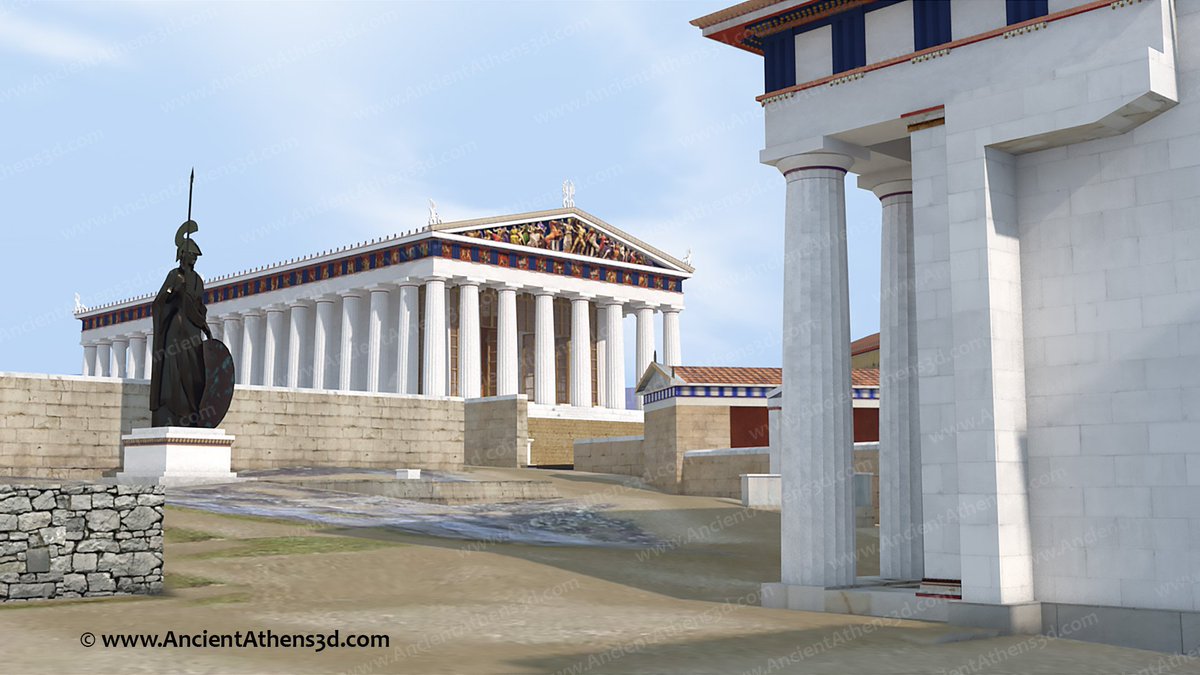
7/ Maybe did the attack have social characteristics? The only thing that is certain is that after a few years, ambitious members of the local community built on the ruins of the eastern part of the palace, a new long, narrow, megaron-shaped building that included the throne room. 

8/ Thus a distinct building is created in piles of rubble, used by the new ruling class of the city probably as a gathering place. The new elite attempts to appropriate the central symbols of palatial power to serve their own political aspirations. 

9/ The non-reconstruction of the walls of the Upper Citadel and the transformation of the palace altar into a platform reveals the desire of the new lords of the city to project various rituals and practices in order to establish their ambitions and claims within the community. 

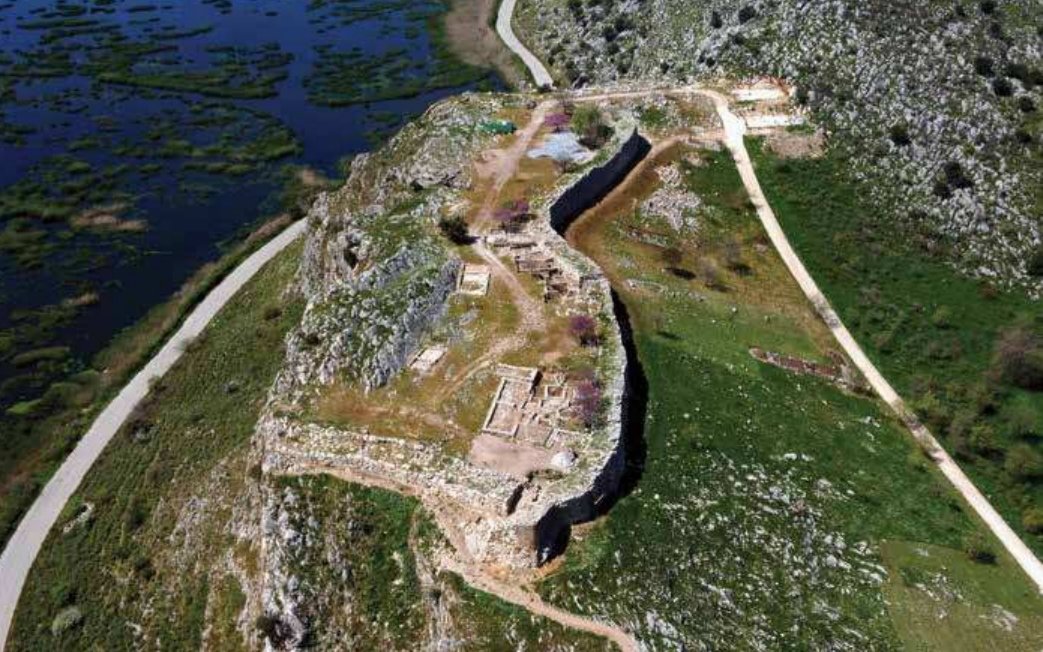
10/ Recent archaeological surveys have demonstrated a particularly interesting element, which suggests a close connection between the Palatial and Post-Palatial Periods. In the final phase before the destruction, ➡️ 

➡️ the palatial elite of Tiryns embarked on an ambitious construction project: the diverting of local river, which often caused severe floodings, by building a dam and opening a new artificial riverbed to flow away from the affected Lower Town. 
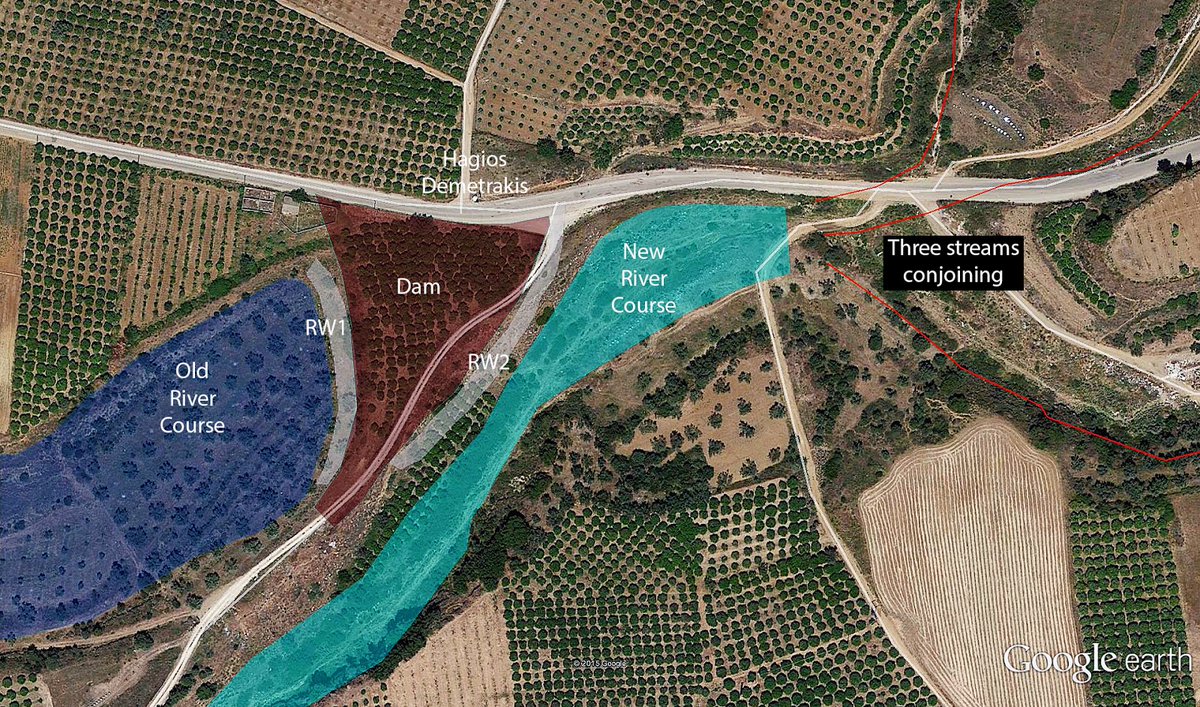
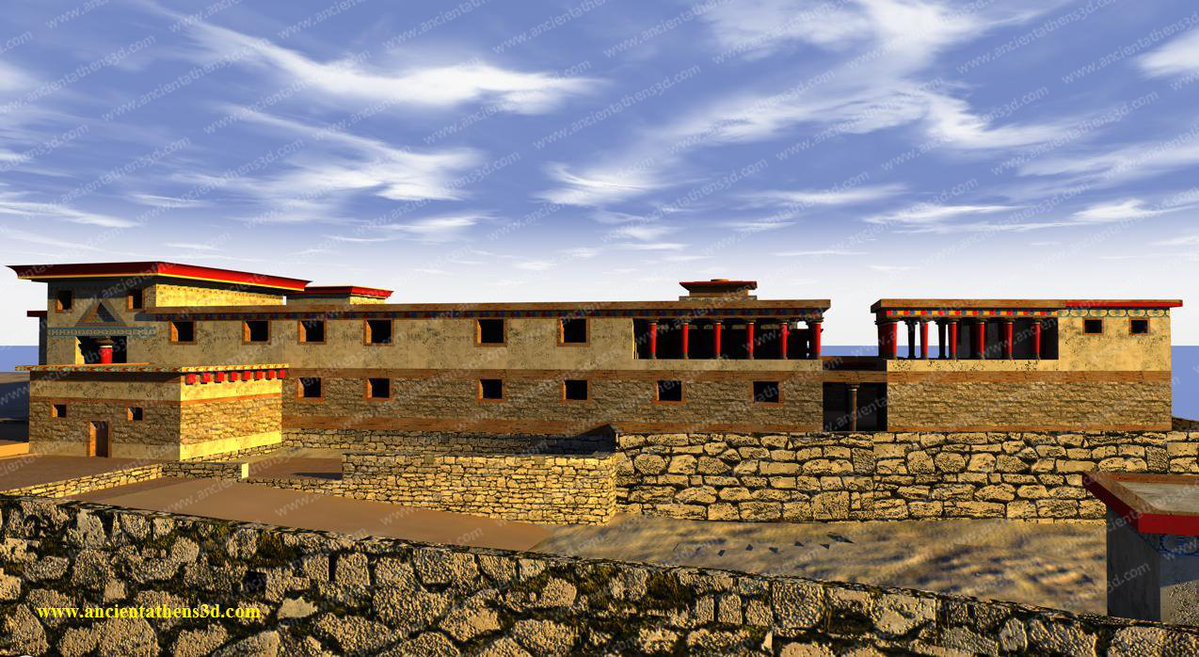
11/ With the construction of this land improvement project, the palatial elite of Tiryns sought to utilize the area north of the Citadel that was adjacent to the original course of the river, installing groups of palatial artists, who processed valuable types of wood and ivory. 

12/ However, the large area occupied by the Post-Palatial Lower Town (over 250 acres) led the new lords to complete the reconstruction program of the area north of the Citadel, which offered them a virgin land without previous building remains. 

13/ The building activity covered a period between 1200-1120 BC and was the only major construction project carried out during the Post-Palatial Period, intended to cover the housing needs of newly arrived populations, coming from either nearby or distant areas. 

14/ Post-Palatial Tiryns was part of an extensive long-distance network despite the turmoil prevailing in the Eastern Mediterranean, being an important cross-cultural trading port of the time, where native and foreign cultural elements came into contact. 

15/ The findings have demonstrated a strong Italic presence in LH IIIC Tiryns with the presence of Handmade Burnished Ware vessels associated with parallels from central and southern Italy, while a first-appearing type of situla refers to NE Italy. 

16/ The trade brought wealth to the city and several members of its new elite were still able to acquire luxury items, as demonstrated by the discovery of the famous Treasure of Tiryns (gold jewellery, bronze vessels, iron dagger). ➡️ 

➡️ The ceremonial gatherings and public symposiums offered to the members of new elites the opportunity to display their wealth through which they consolidated their new leadership identity to the rest of the community. 

17/ The heyday of LHIIIC Tiryns was a short-lived episode of three generations with the northern part of the Lower Town showing signs of abandonment as early as 1130BC and the Lower Citadel along with the rest of the Lower Town to remain relatively densely populated until 1050BC. 

18/However, Post-Palatial Tiryns is a unique event for the Aegean because it expanded and flourished when destruction and disturbance led the other palatial centers to shrink and be abandoned,testifying to the connecting link between the palatial past and the new era which arose. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh