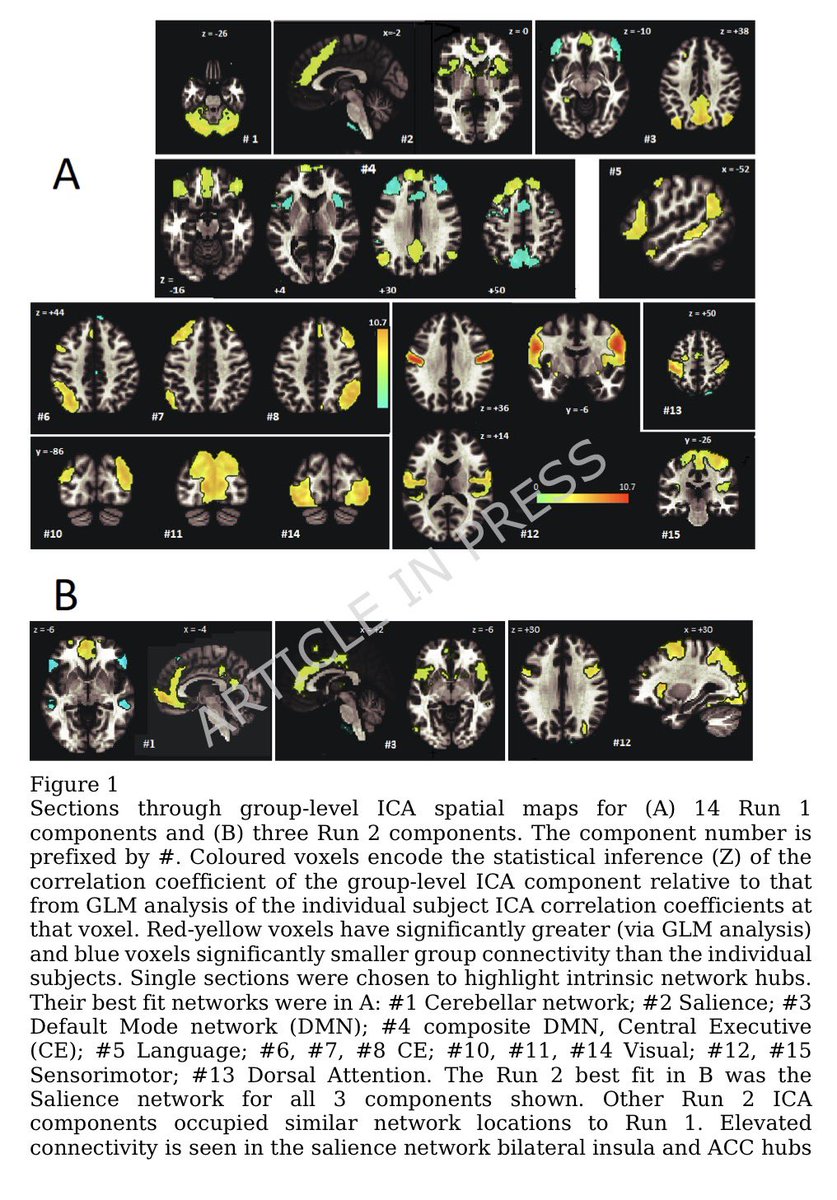
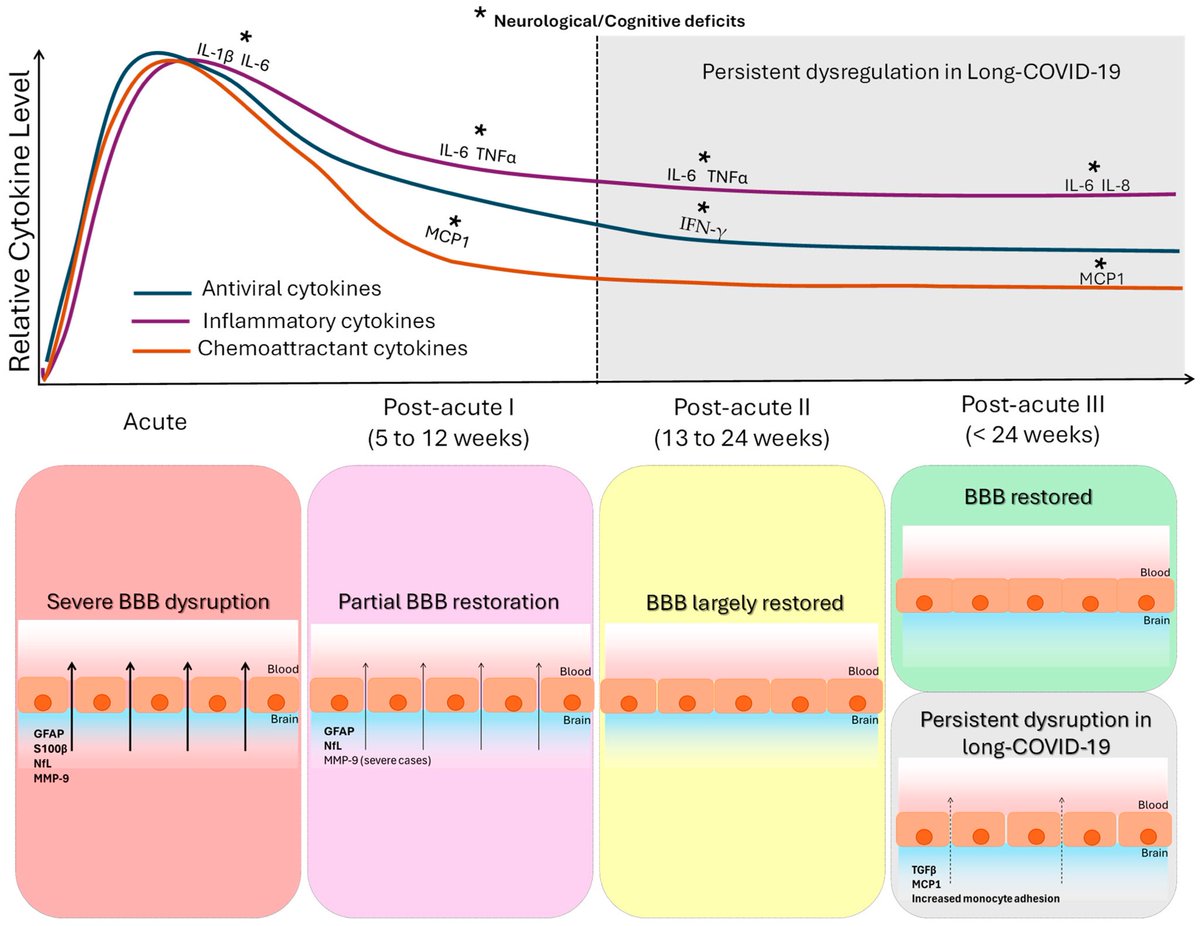
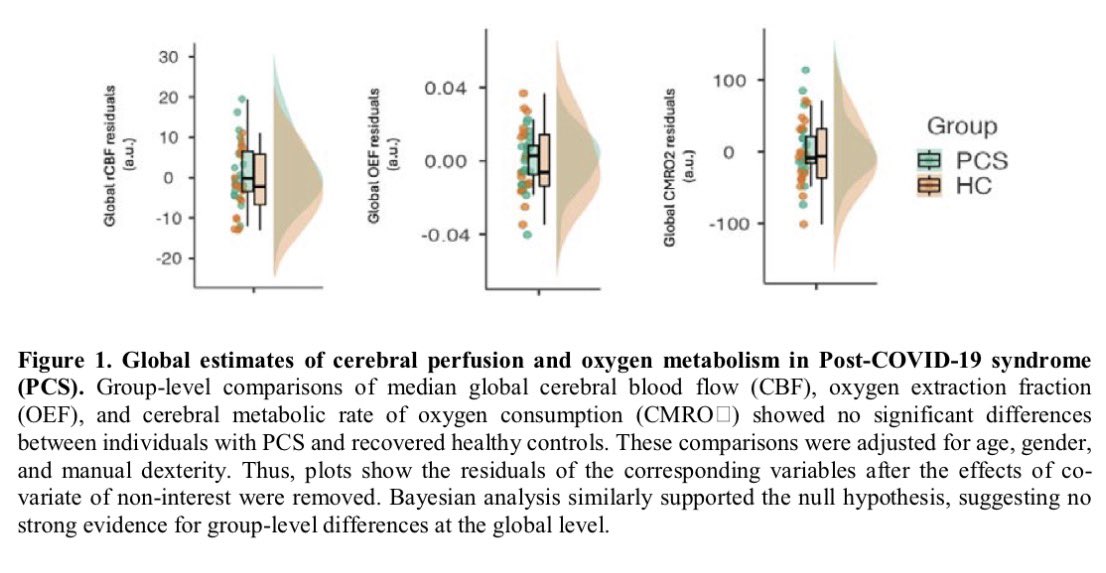
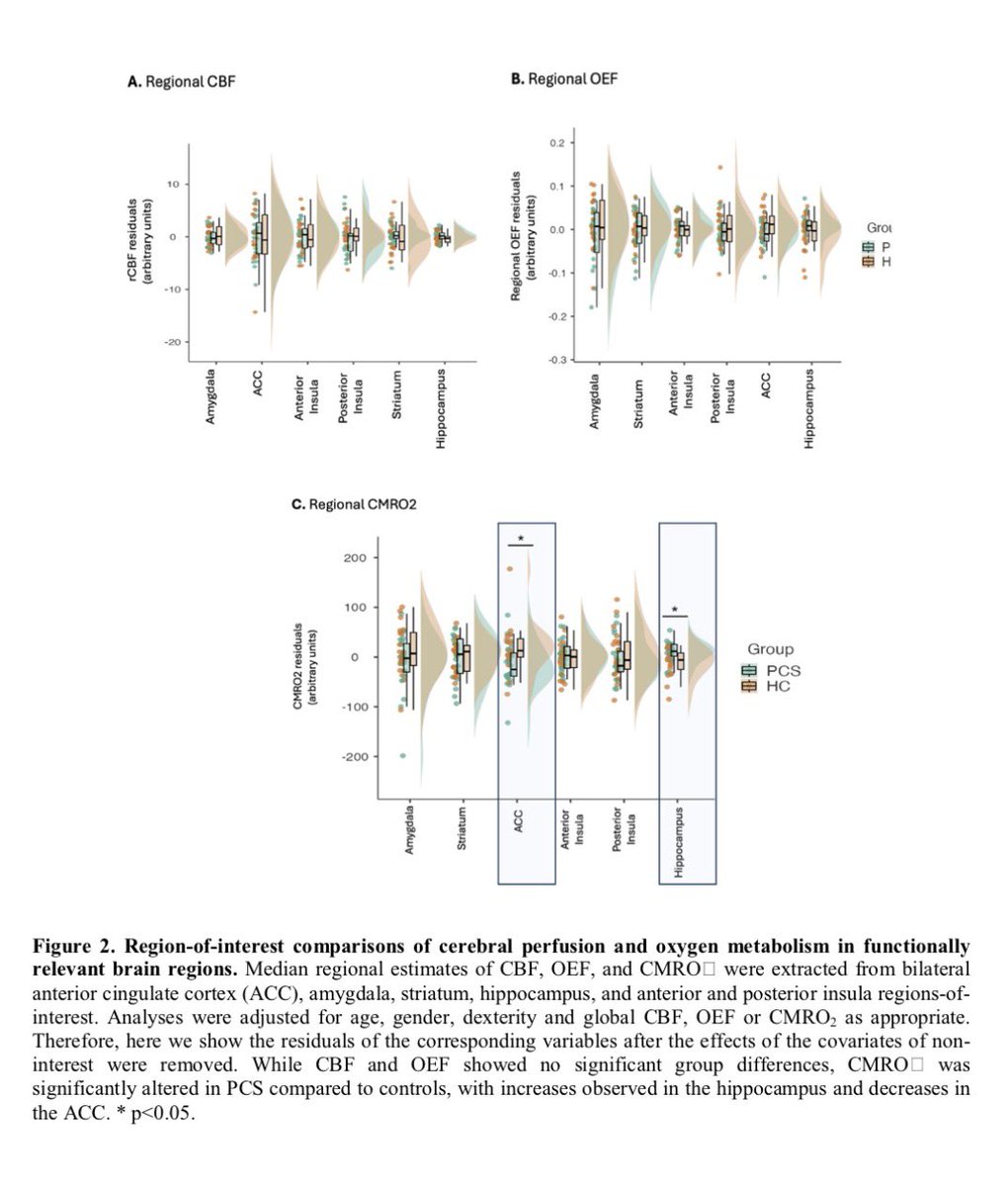
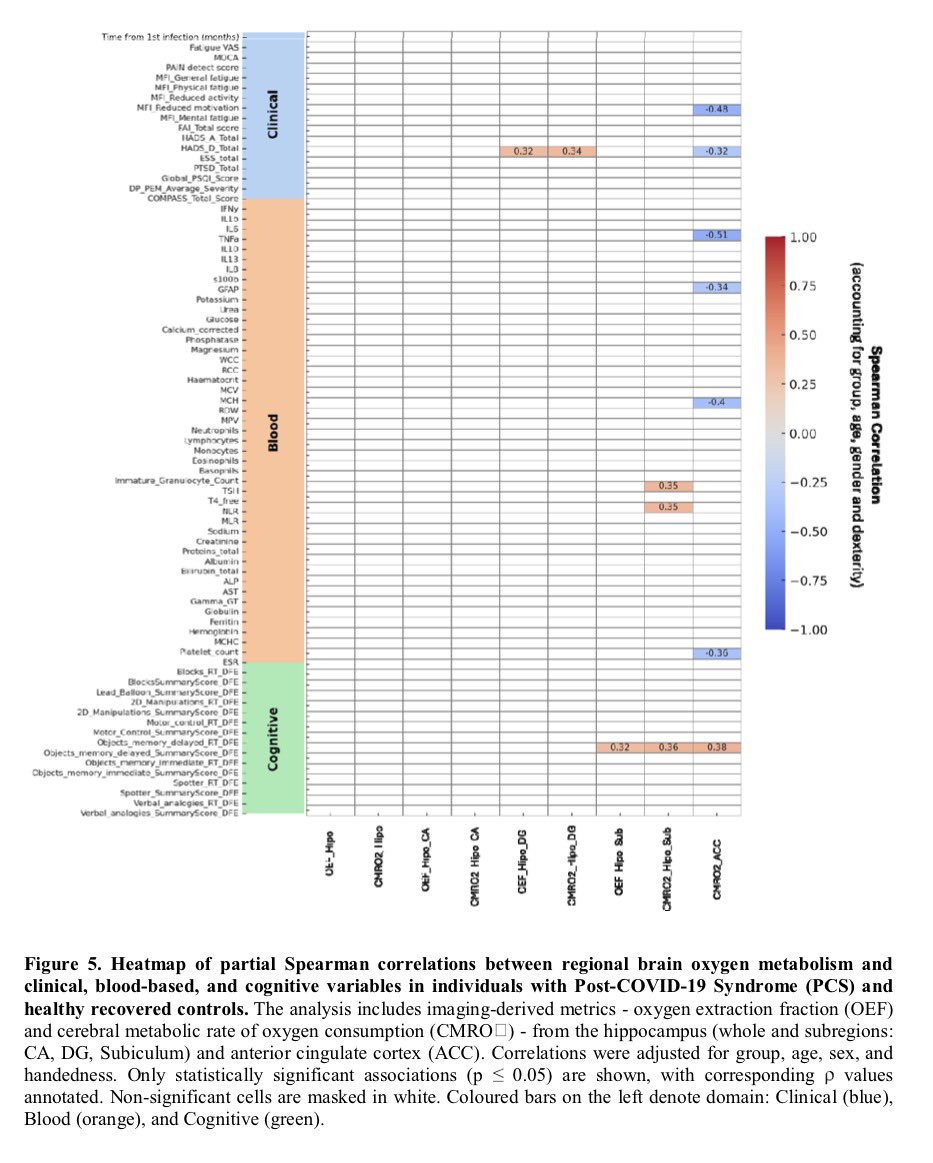
The indian saga of XBB.1.16 #Arcturus
It has been a month when @siamosolocani 1st flagged this variant. Later, I started tracking it. We are still amid an ongoing surge, it’s time to take a stock of the situation: what we do know, what we don’t 1/
It has been a month when @siamosolocani 1st flagged this variant. Later, I started tracking it. We are still amid an ongoing surge, it’s time to take a stock of the situation: what we do know, what we don’t 1/
https://twitter.com/siamosolocani/status/1633128707232616456?s=46&t=Uqf1V489rmyfecmkYvIrXw
What do we know for sure!
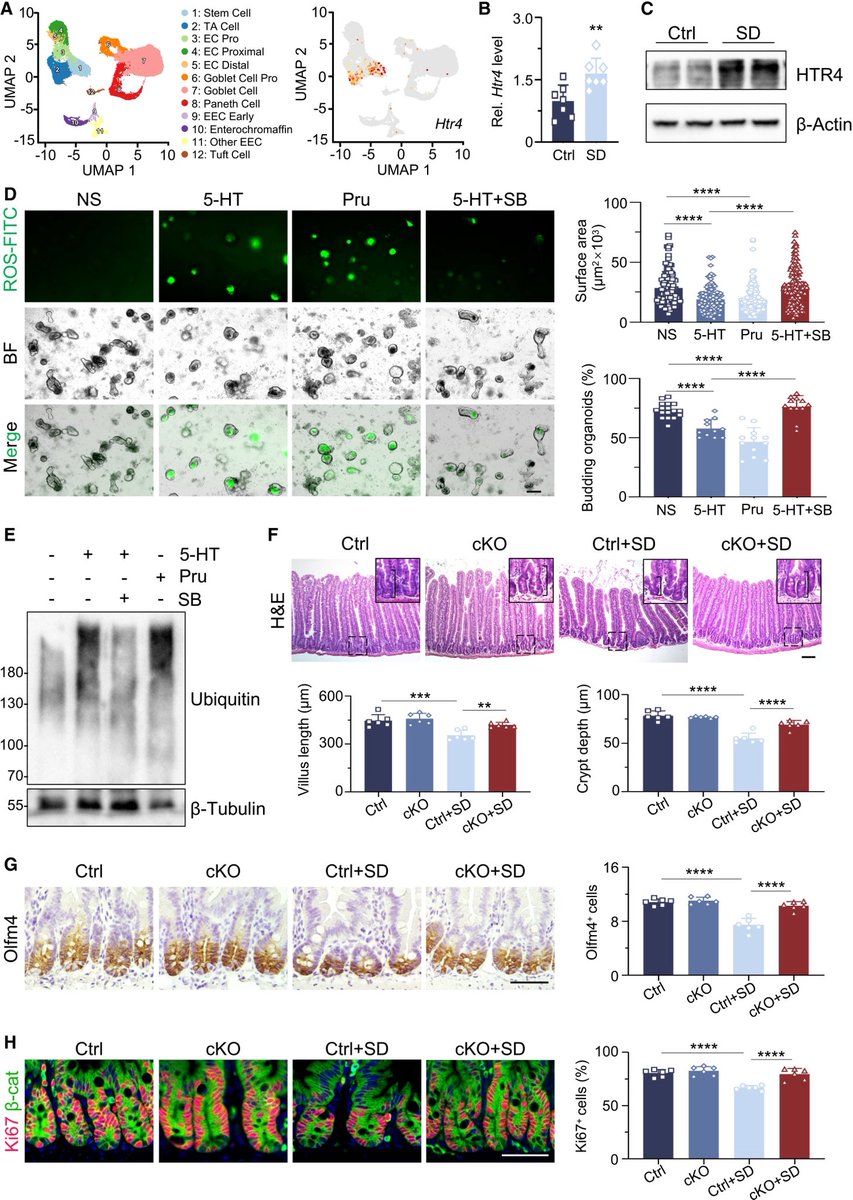
1-XBB.1.16 has succeeded in creating a new, significant surge in India after a gap of >6 months. A feat that even BA.5, BQ.1 & XBB.1.5 failed to achieve!
2/

1-XBB.1.16 has succeeded in creating a new, significant surge in India after a gap of >6 months. A feat that even BA.5, BQ.1 & XBB.1.5 failed to achieve!
2/


2-XBB.1.16 definitely has got a growth advantage & more fitter than other circulating XBBs & has even replaced some other similar sublineages like XBB.1.5 & XBB.1.9 3/
@vinodscaria
@vinodscaria

3-XBB.1.16 is definitely not a more pathogenic variant than other Omicron’s progenies
4-This variant is still evolving, adding few more mutations. But not all new mutations are beneficial to the virus (i.e. E180V). 4/
4-This variant is still evolving, adding few more mutations. But not all new mutations are beneficial to the virus (i.e. E180V). 4/

5-The chances of XBB.1.16 leading a new, significant wave (i.e. the 4th wave) akin to Jan’ 22 BA.2 wave are remote 5/
@JPWeiland
@JPWeiland

6-The new surge in cases is yet to peak in India. According to @JPWeiland India is more than 2 weeks from peak cases. 6/ 

And, now let’s see what we still don’t know:
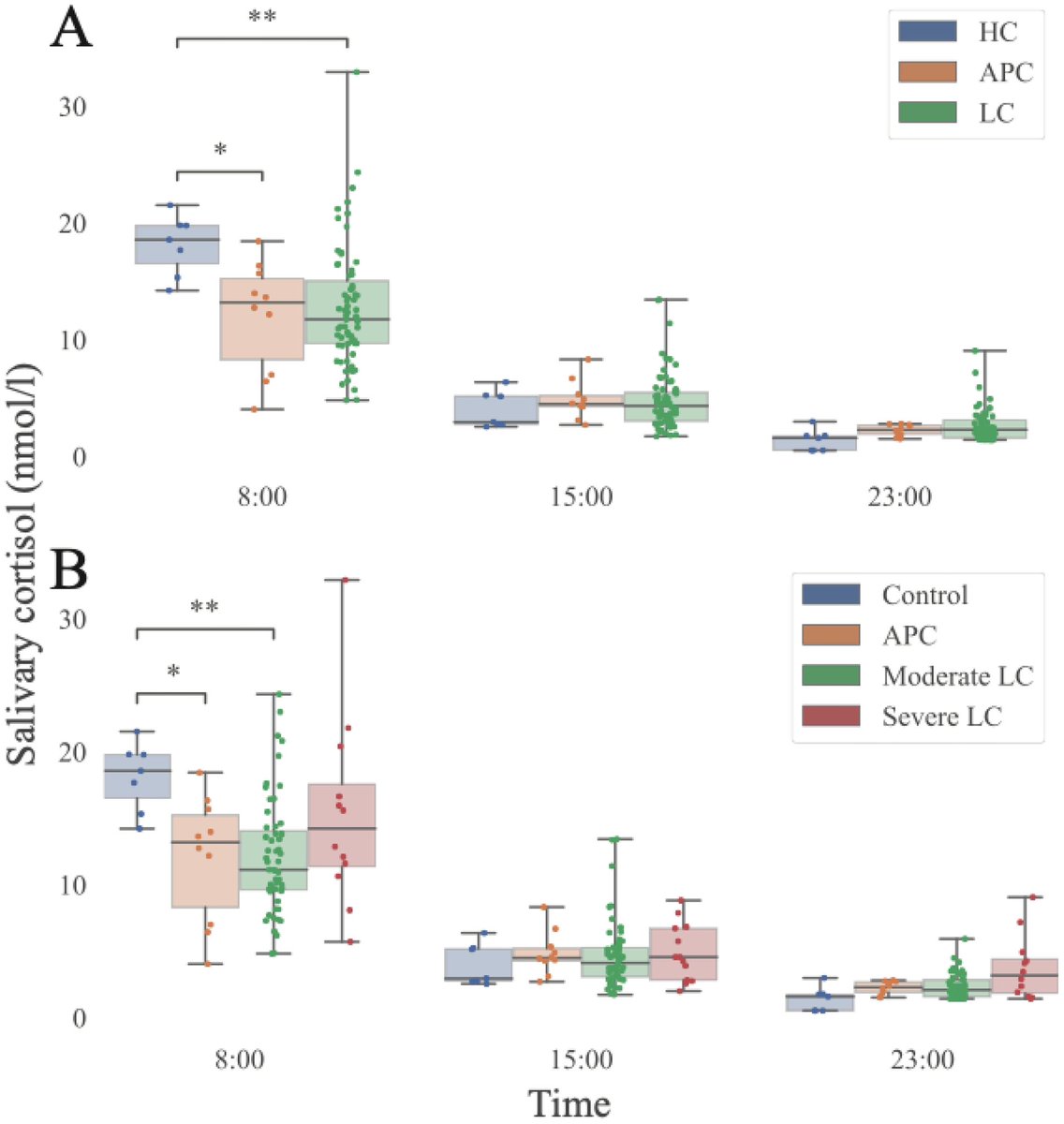
1-How big this new surge would be?
2-What are the key factors responsible for making XBB.1.16 a more fitter variant than its contemporaries? Higher immune evasion?
Higher infectiousness, i.e. higher ACE2 binding? 7/
1-How big this new surge would be?
2-What are the key factors responsible for making XBB.1.16 a more fitter variant than its contemporaries? Higher immune evasion?
Higher infectiousness, i.e. higher ACE2 binding? 7/
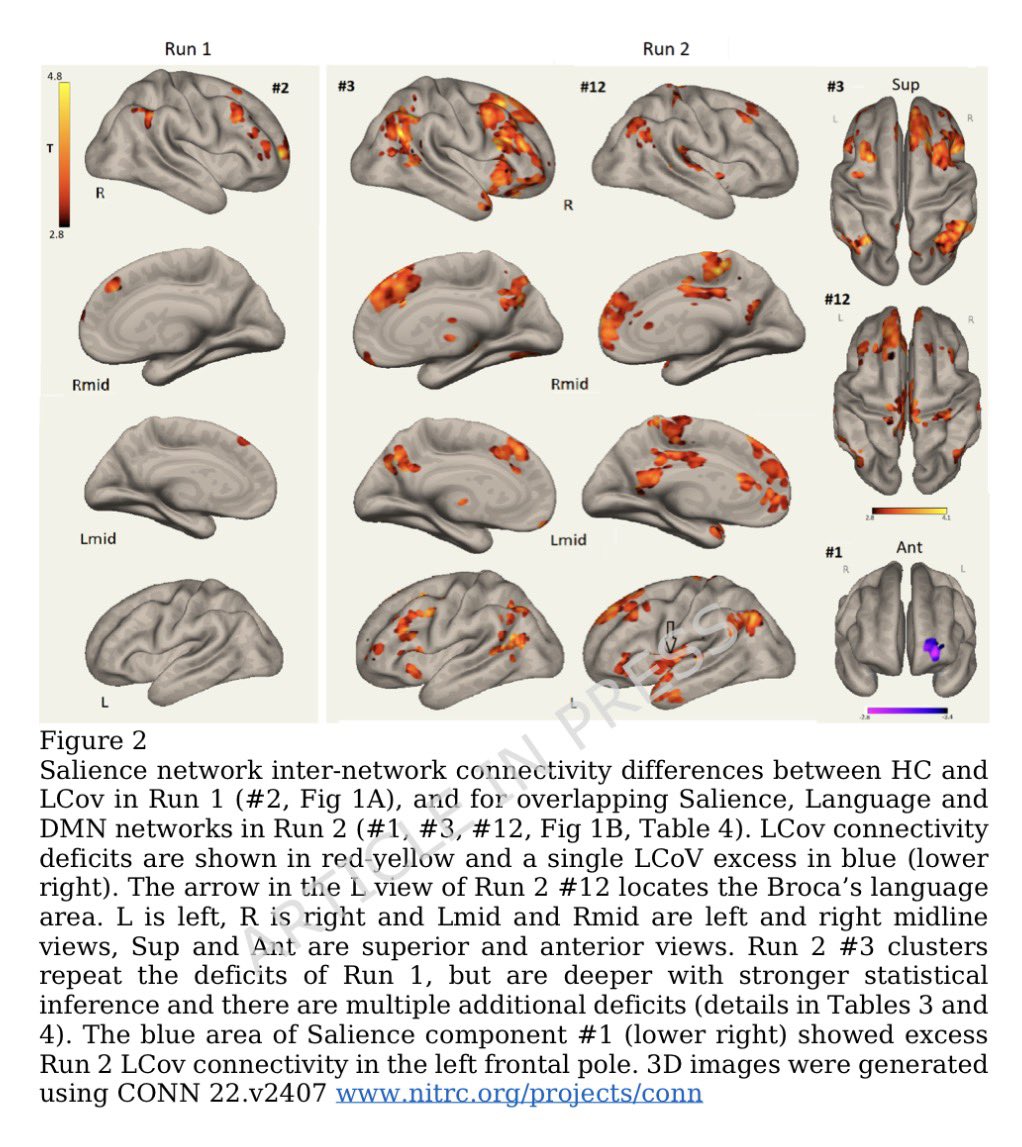
A new study by @SystemsVirology suggests:
-a higher infectiousness (~1.2-fold greater than that of XBB.1.5) 8/

-a higher infectiousness (~1.2-fold greater than that of XBB.1.5) 8/
https://twitter.com/systemsvirology/status/1644186056160583681?s=46&t=Uqf1V489rmyfecmkYvIrXw

However, XBB.1.16 doesn’t have significantly greater immune evasion than XBB.1.5. 9/
@SystemsVirology
@SystemsVirology

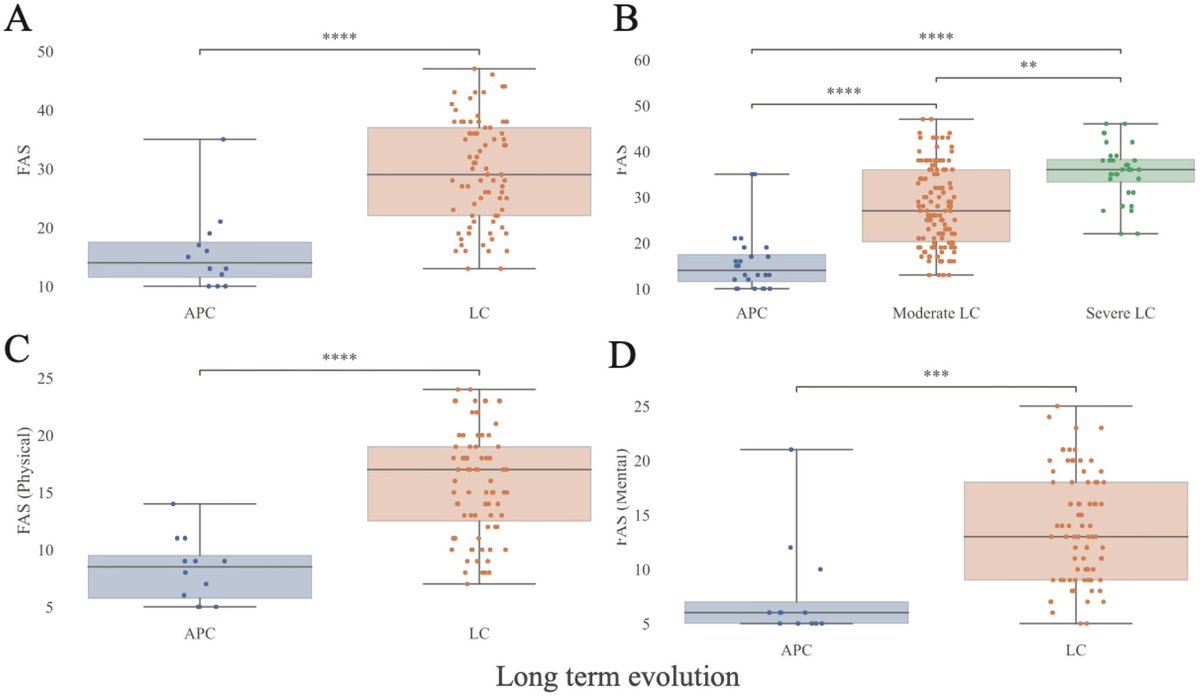
We know XBB.1.5 & XBB.1.16 have almost similar Spike barring a few Spike mutations. However, above study suggests that mutations in the non-Spike region may be responsible for increased viral growth of XBB.1.16 10/ 

The above mentioned study & some early work done by @StuartTruvile in NSW, Australia points that XBB.1.16 is not more immune evasive than XBB.1.5. @StuartTurville calls it “super similar to XBB.1.5 in neut evasion”. 11/ 

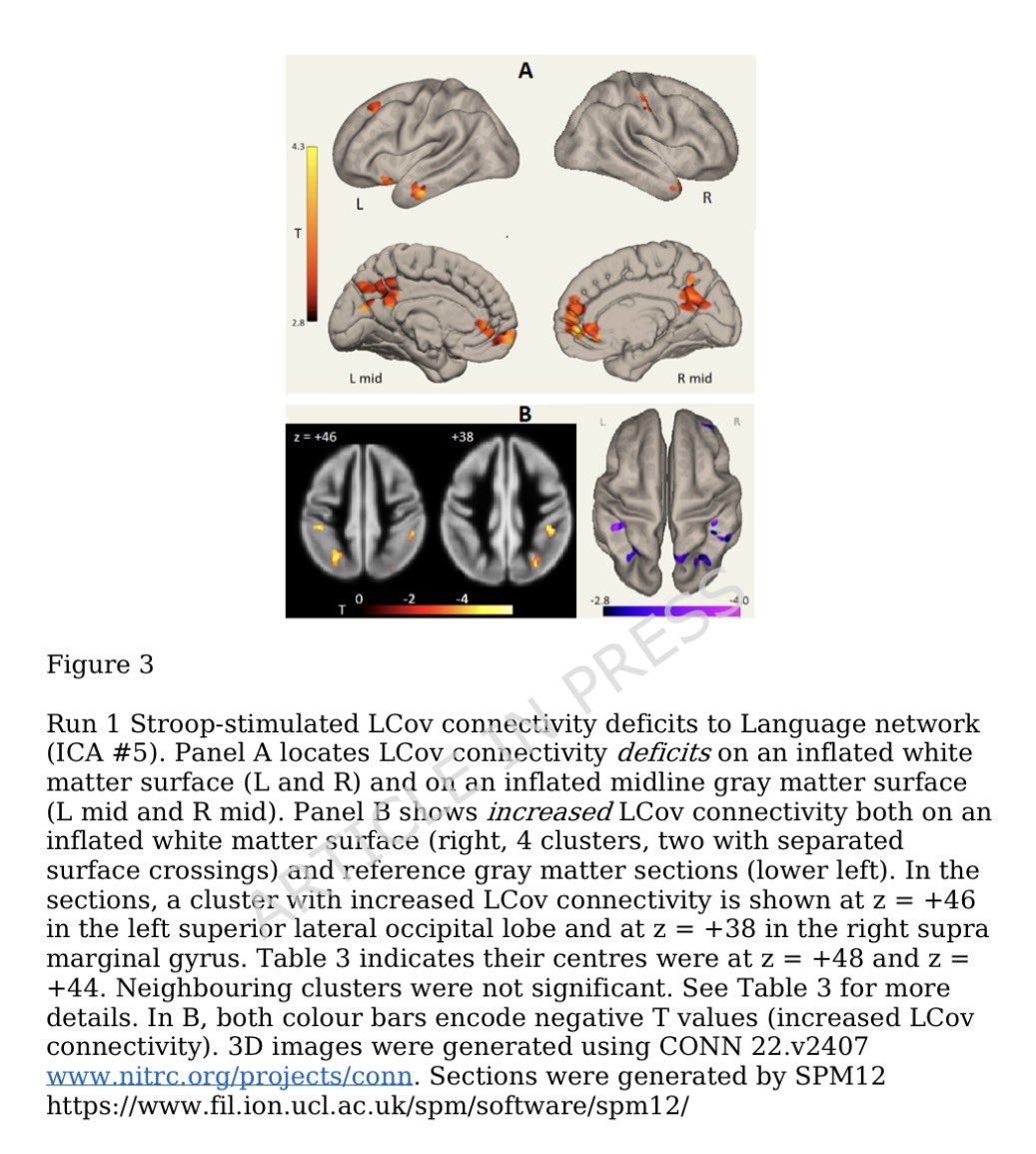
Now, If it's not immune evasion, is the growth advantage is because of stronger ACE2 binding then?
No, in fact, the entry into cells is similar as with Omicrons including XBB.1.5. @StuartTurville has shown this 👇 12/
No, in fact, the entry into cells is similar as with Omicrons including XBB.1.5. @StuartTurville has shown this 👇 12/

Most evolutionary biologists now agree to believe that the increased fitness is mainly due to changes at non-Spike region of this variant.
Acc to @LongDesertTrain ORF1a:L3829F is probably the key mute responsible for its advantage over XBB.1.9 13/
Acc to @LongDesertTrain ORF1a:L3829F is probably the key mute responsible for its advantage over XBB.1.9 13/

As per @SolidEvidence mutation in NSP6 of ORF1ab may be behind this higher fitness 14/ 

Now, most experts believe the extra mutations at ORF9b & ORF1a are responsible to give “teeth” to this variant.
ORF9b is thought to be involved with suppressing interferon response, so they might make the virus slightly fitter by counteracting the innate immune system. 15/
ORF9b is thought to be involved with suppressing interferon response, so they might make the virus slightly fitter by counteracting the innate immune system. 15/
https://twitter.com/PriscillaFalzi1/status/1633201479933648897

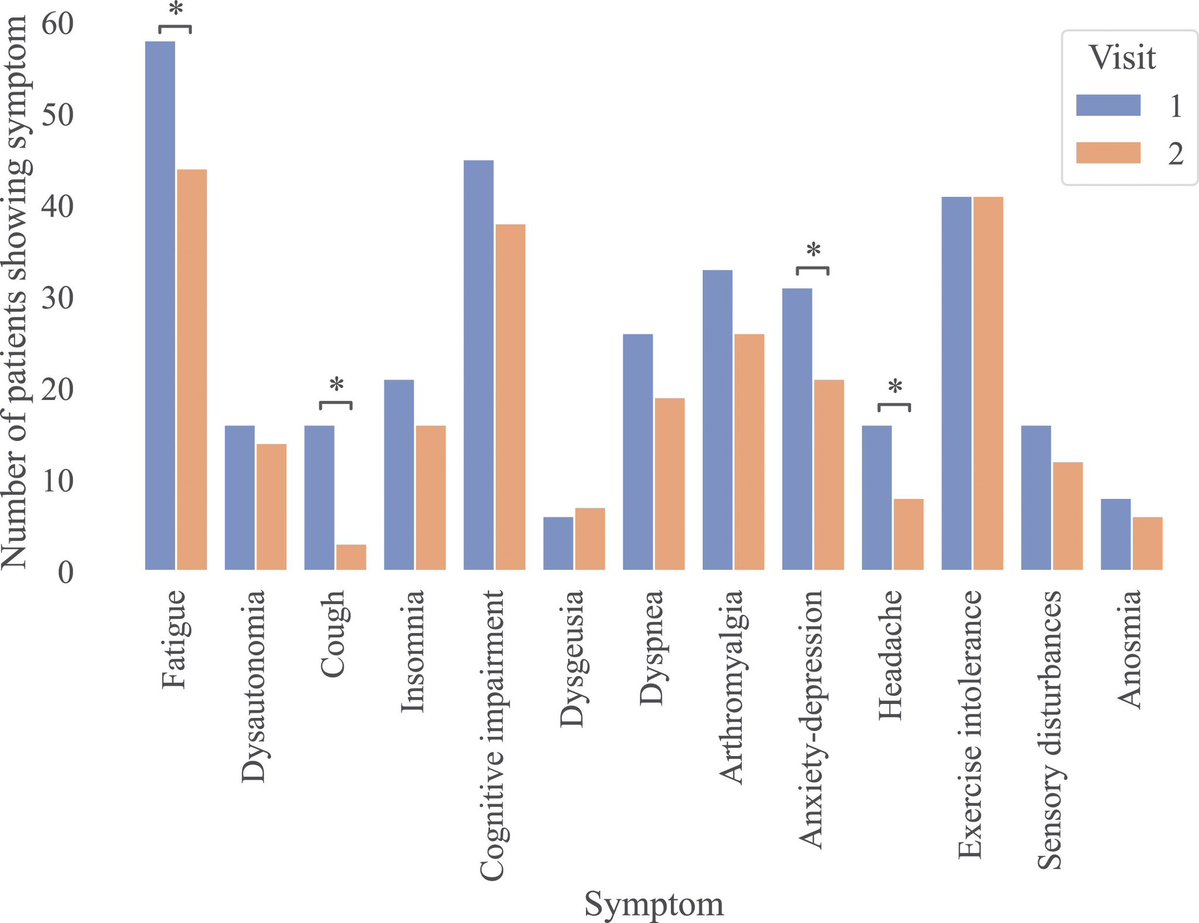
We still don’t know whether XBB.1.16 will become a global thing replacing the existing dominant variant XBB.1.5. However, all the indications point it will. This is the current projection by @JPWeiland for the US (an update on the CDC graph) 16/ 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh