
Pediatrician, ‘rational’ vaccine thinker, Editor Covid Vaccines, TB on Vaccines & many others, Past-Convener IAP COI, Member-WHO-VSN https://t.co/eOvazlWmWg
36 subscribers
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


 This discovery may explain why some people with chronic constipation do not respond to usual treatments.
This discovery may explain why some people with chronic constipation do not respond to usual treatments.
 Key findings in 228 adults:
Key findings in 228 adults: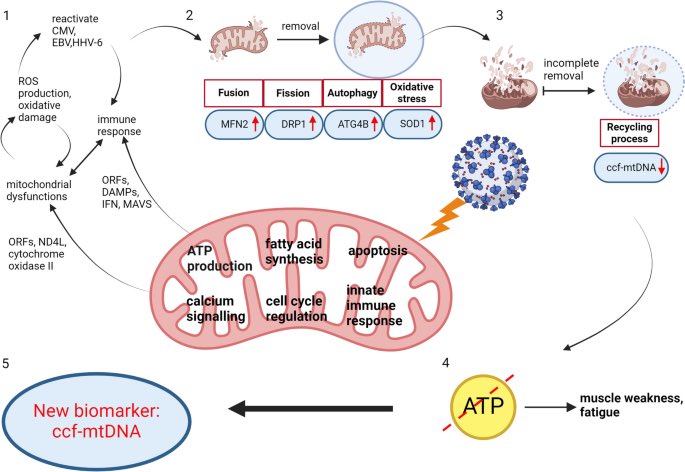
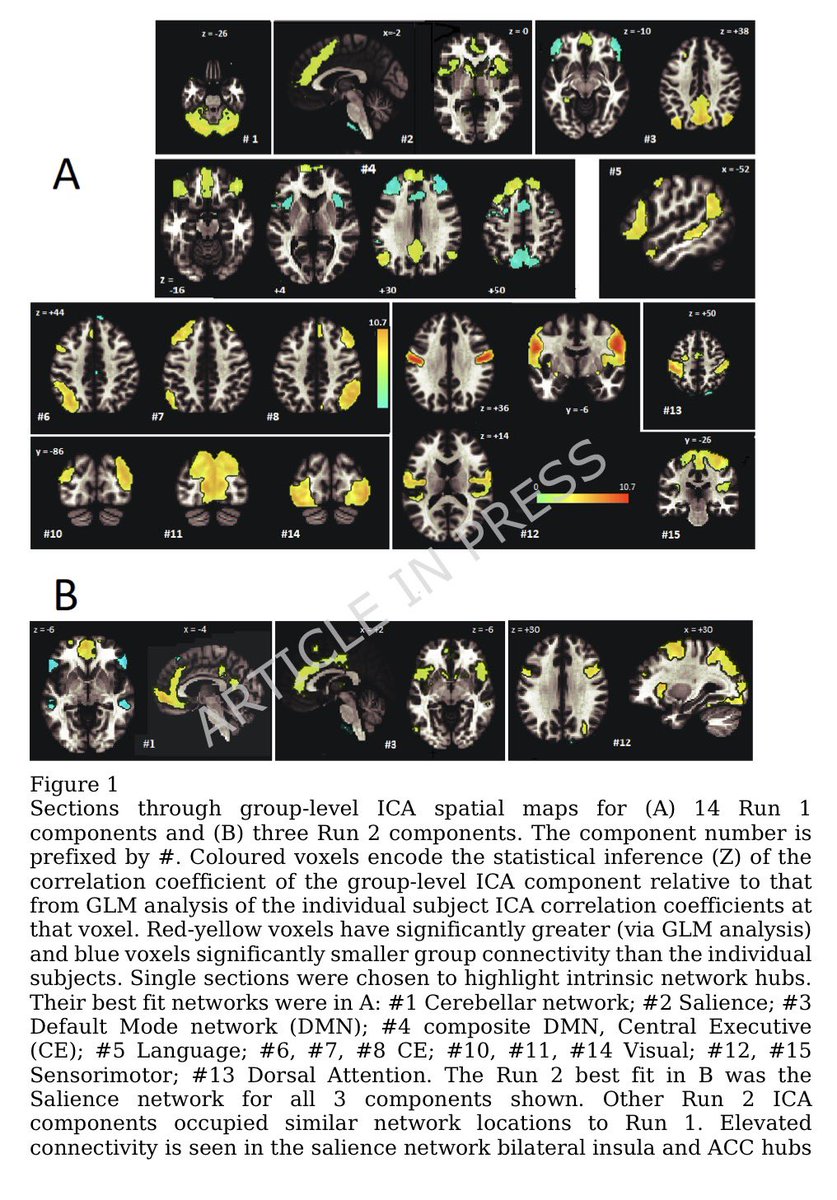
 Researchers found altered connectivity in key brain networks:
Researchers found altered connectivity in key brain networks: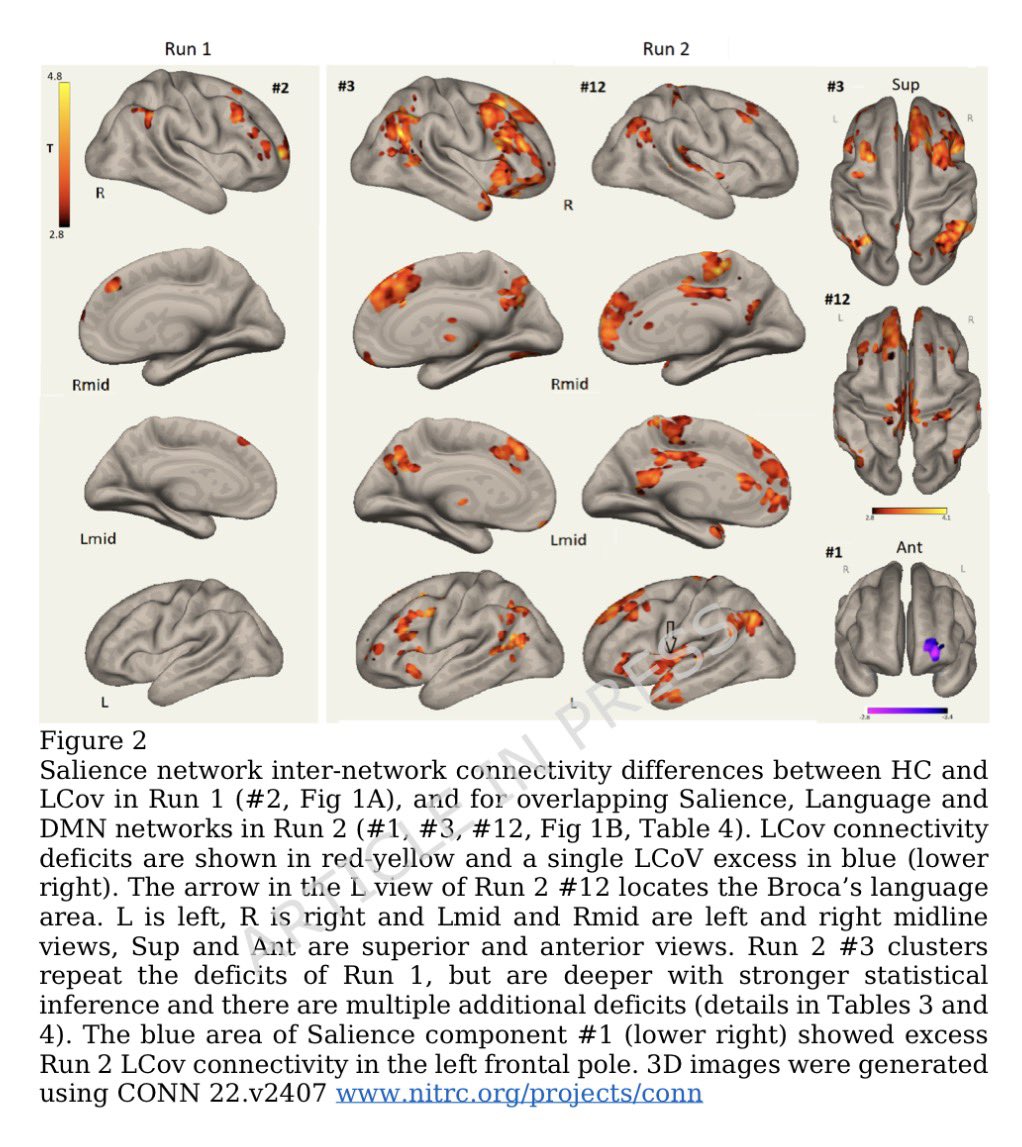
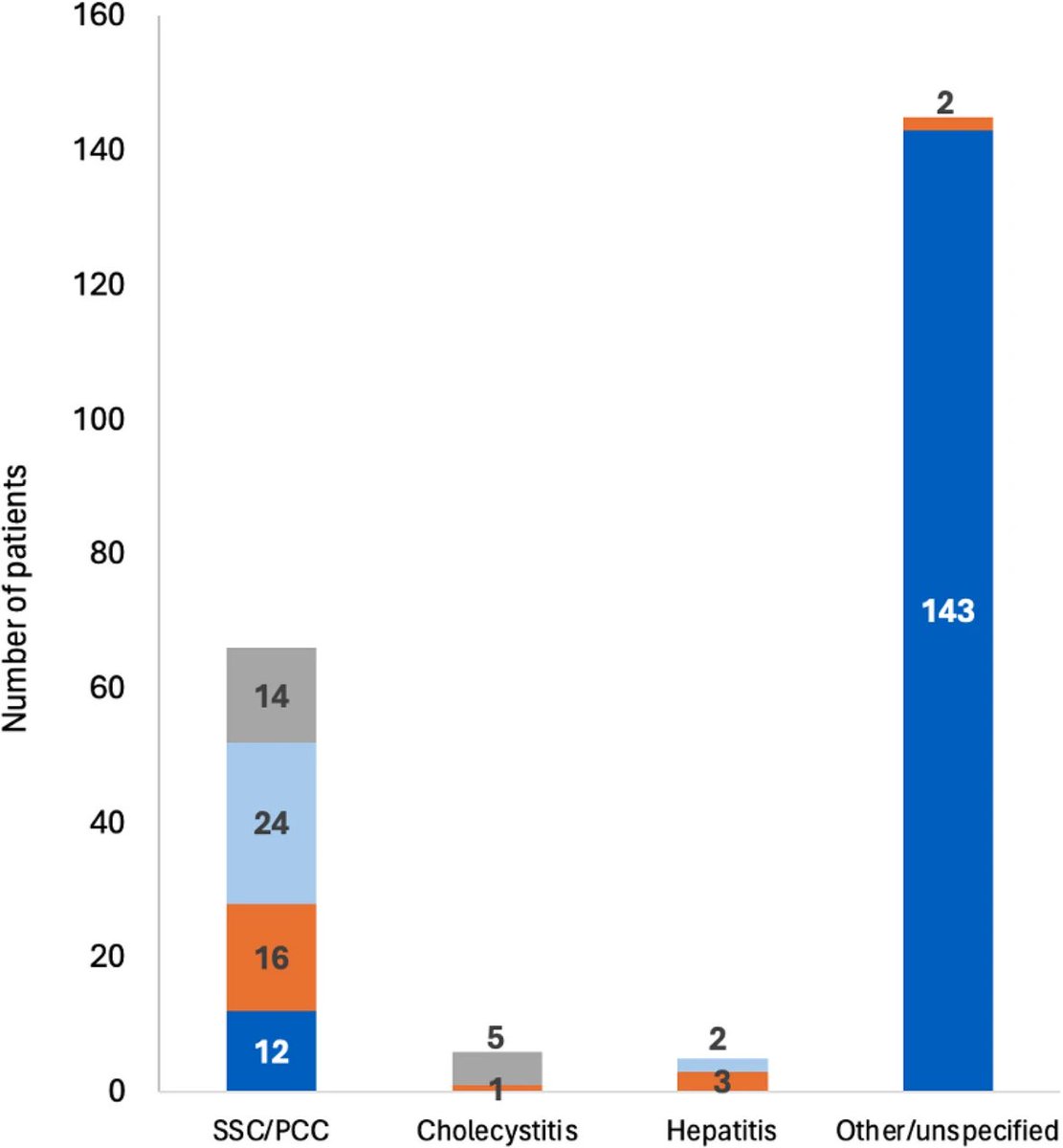
 The most common serious complication was post-COVID bile-duct disease (cholangitis or cholangiopathy).
The most common serious complication was post-COVID bile-duct disease (cholangitis or cholangiopathy).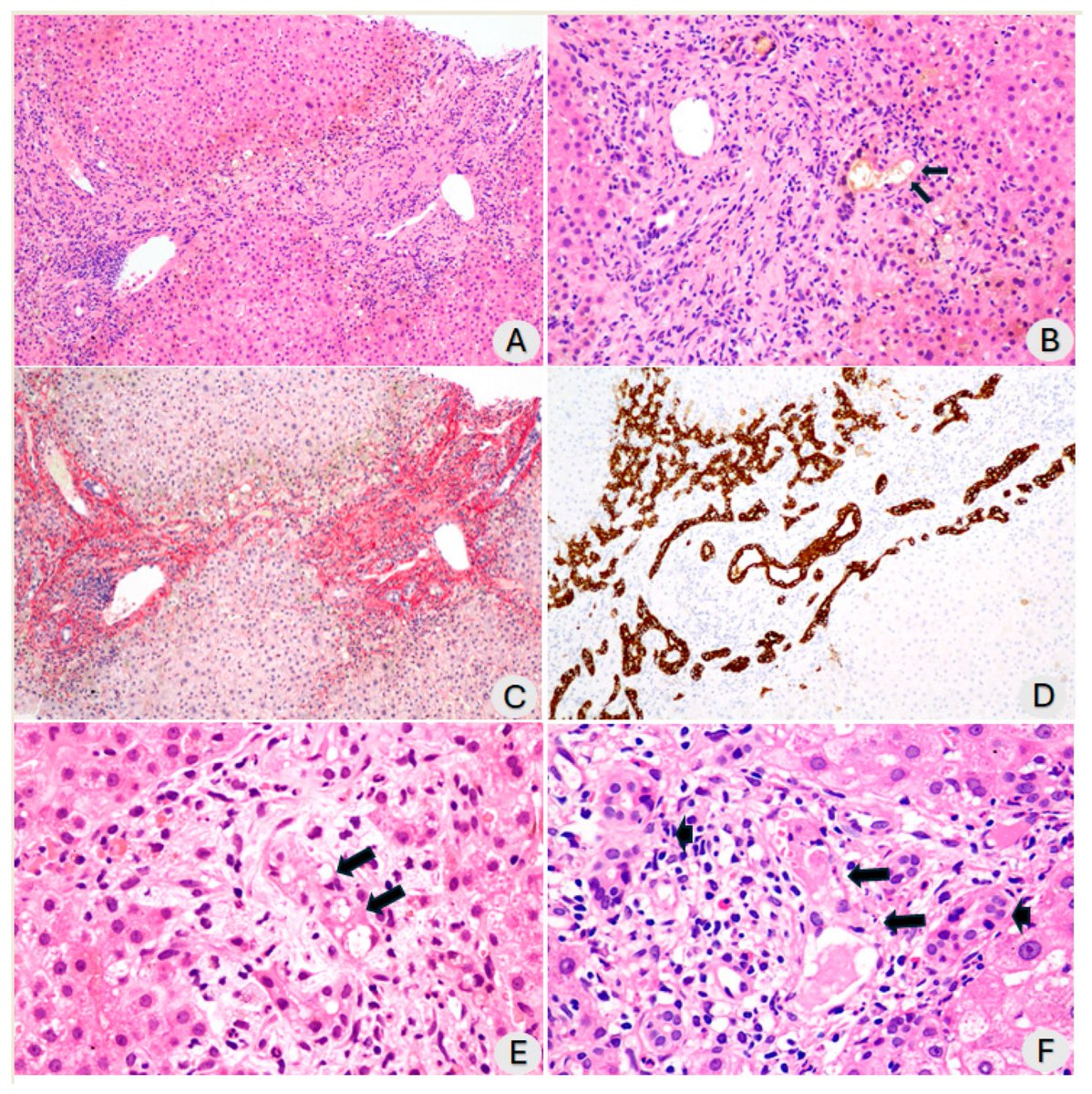
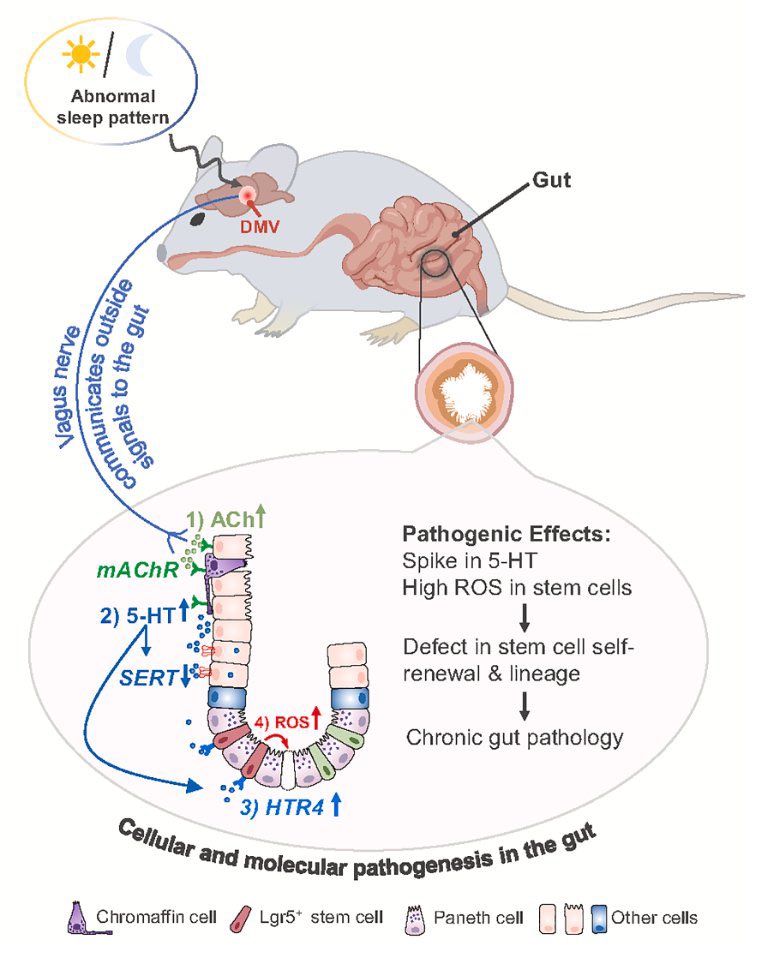
 Key cellular changes after sleep deprivation:
Key cellular changes after sleep deprivation: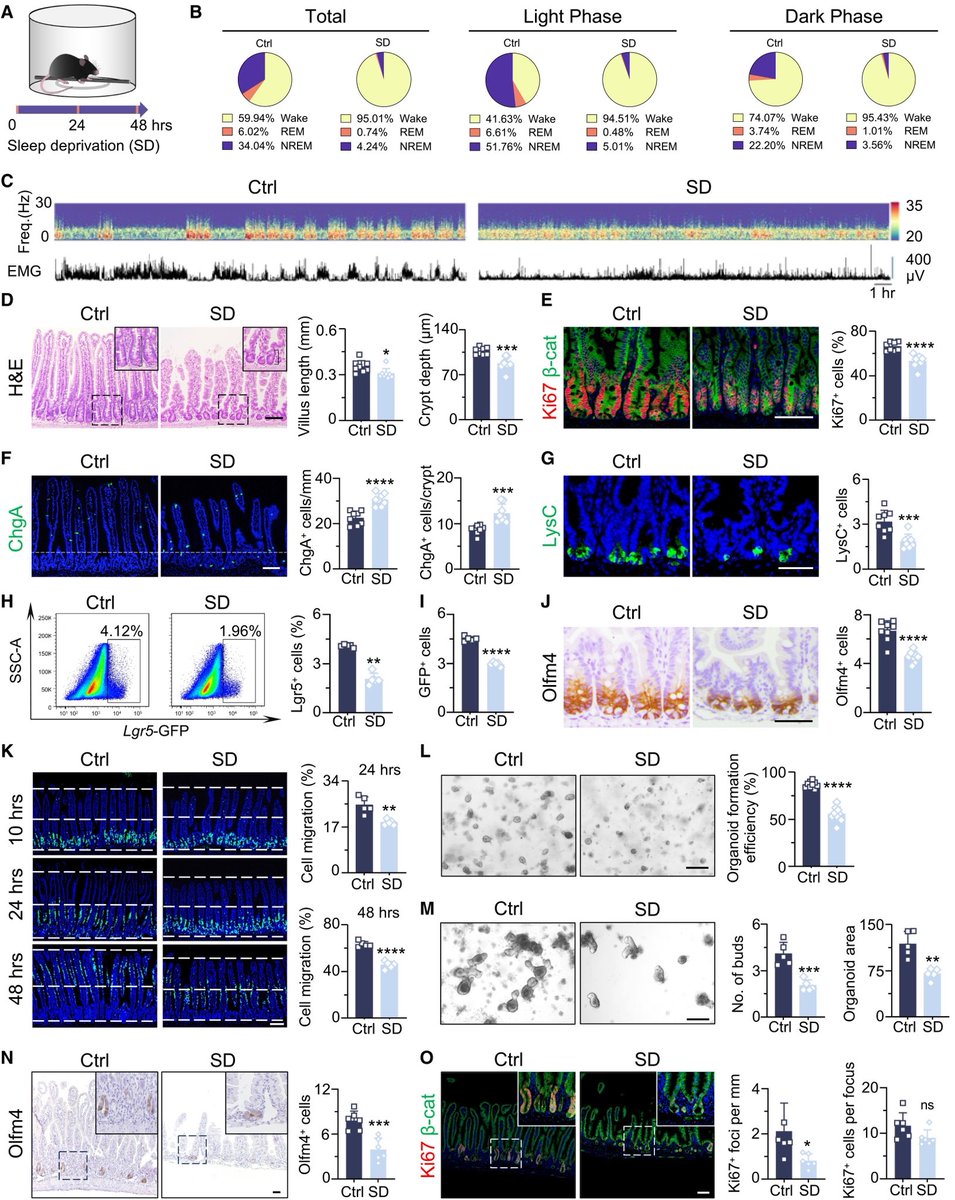
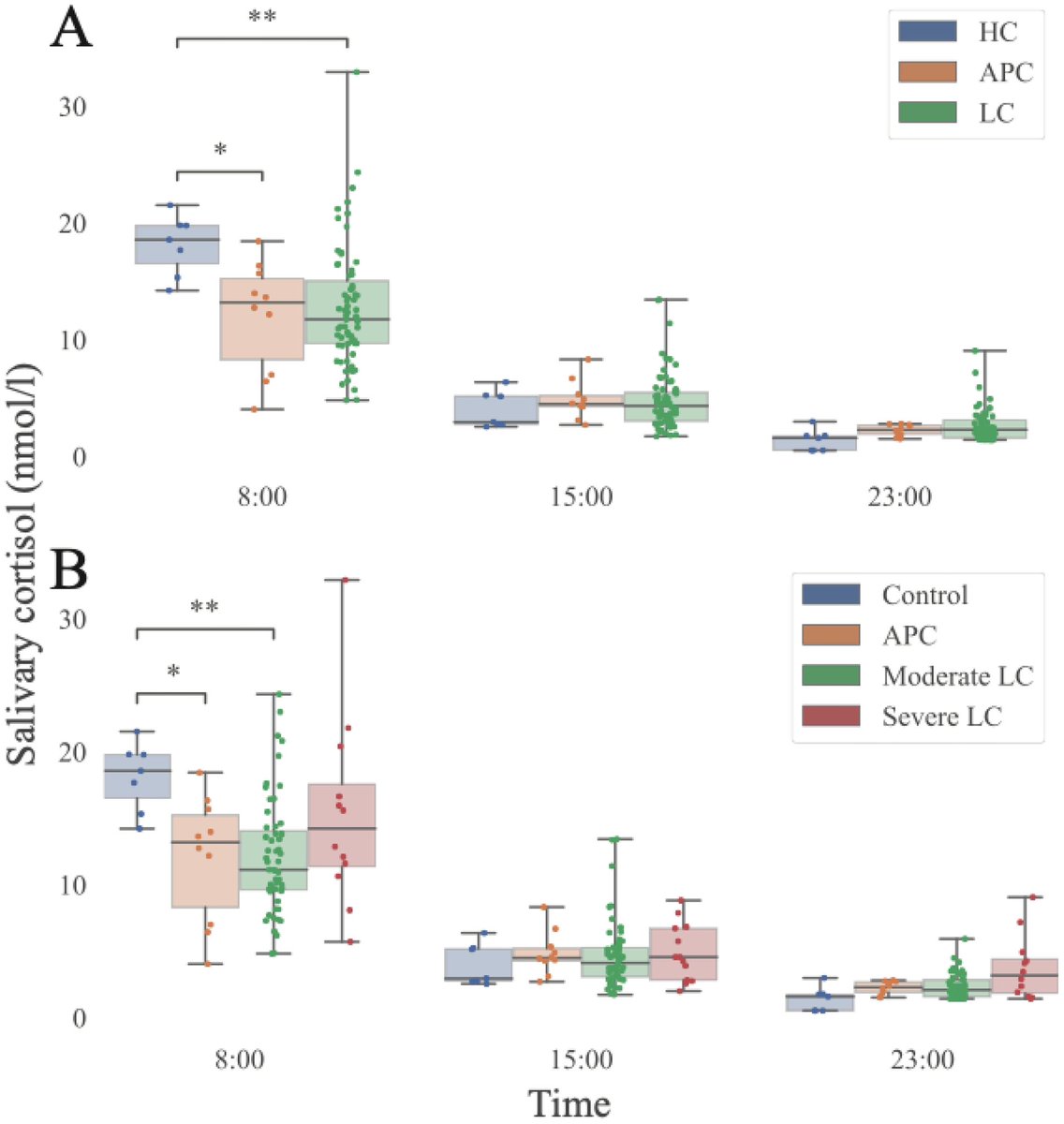
 Prospective study of post-COVID patients:
Prospective study of post-COVID patients: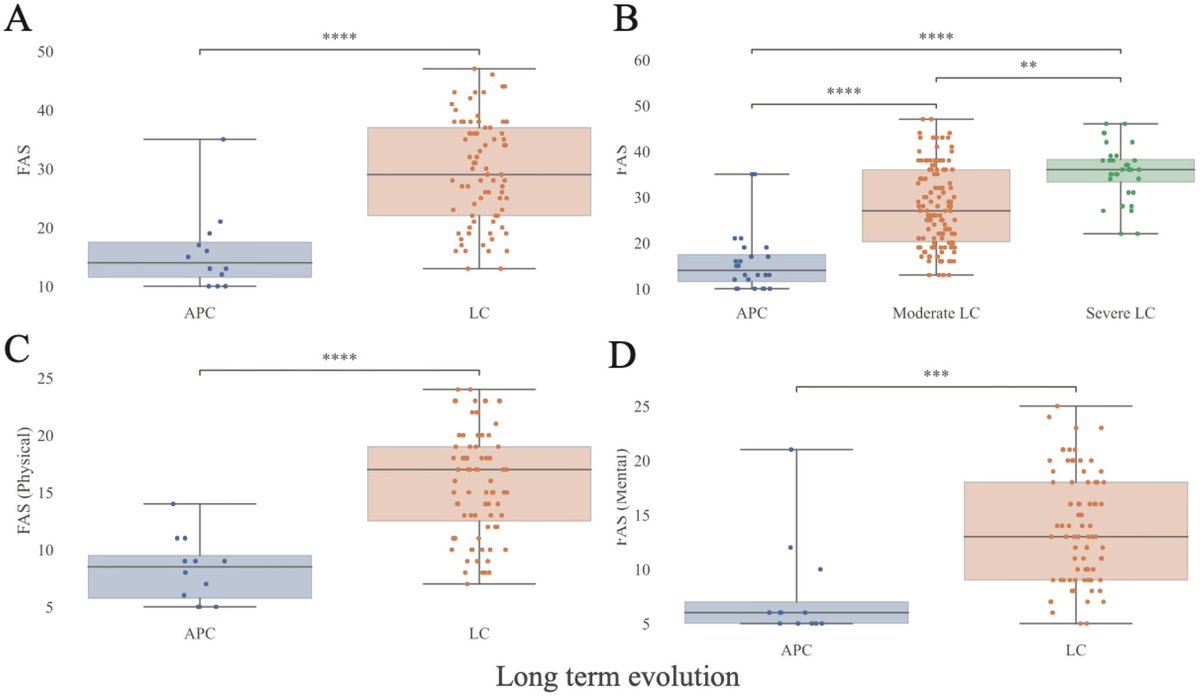
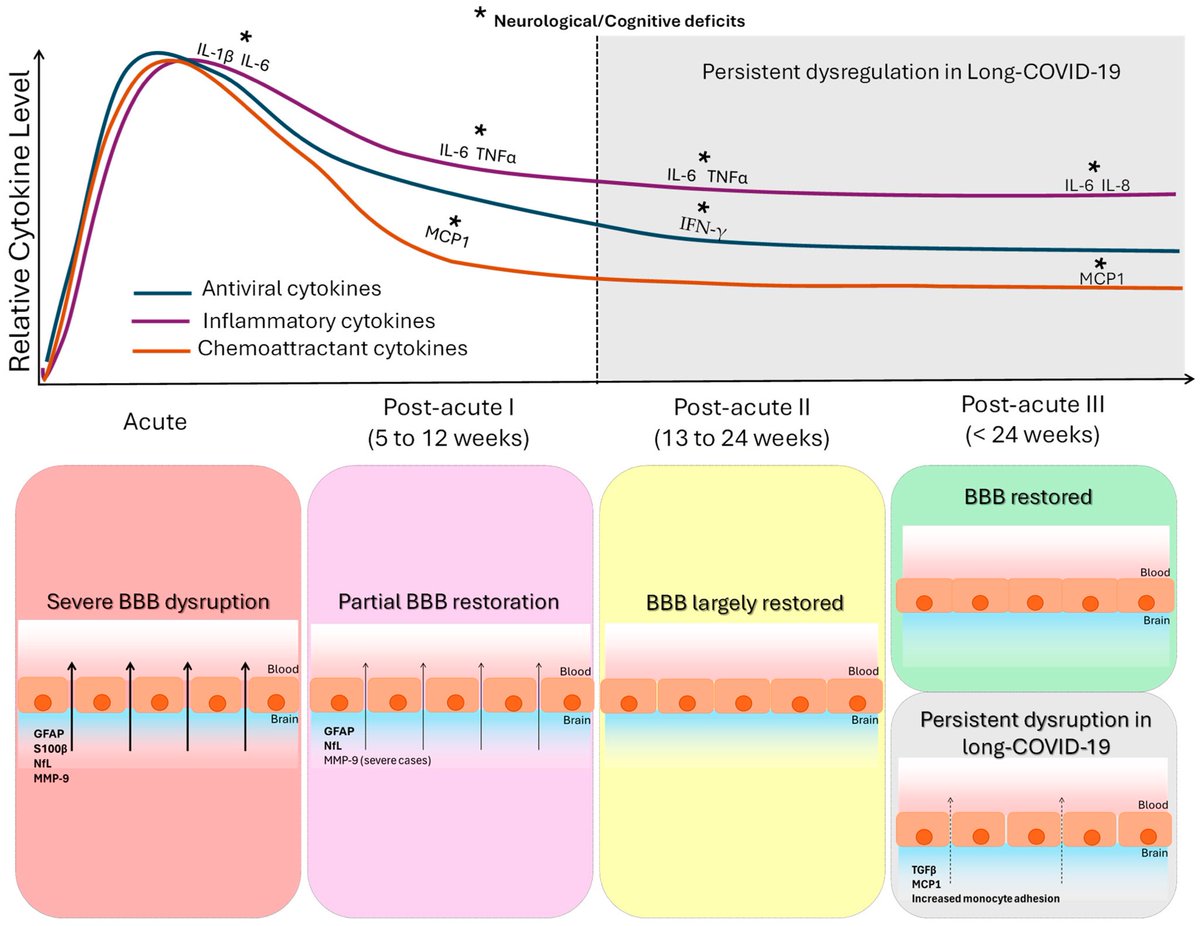
 Cytokine signature of cognitive impairment in #LongCOVID:
Cytokine signature of cognitive impairment in #LongCOVID: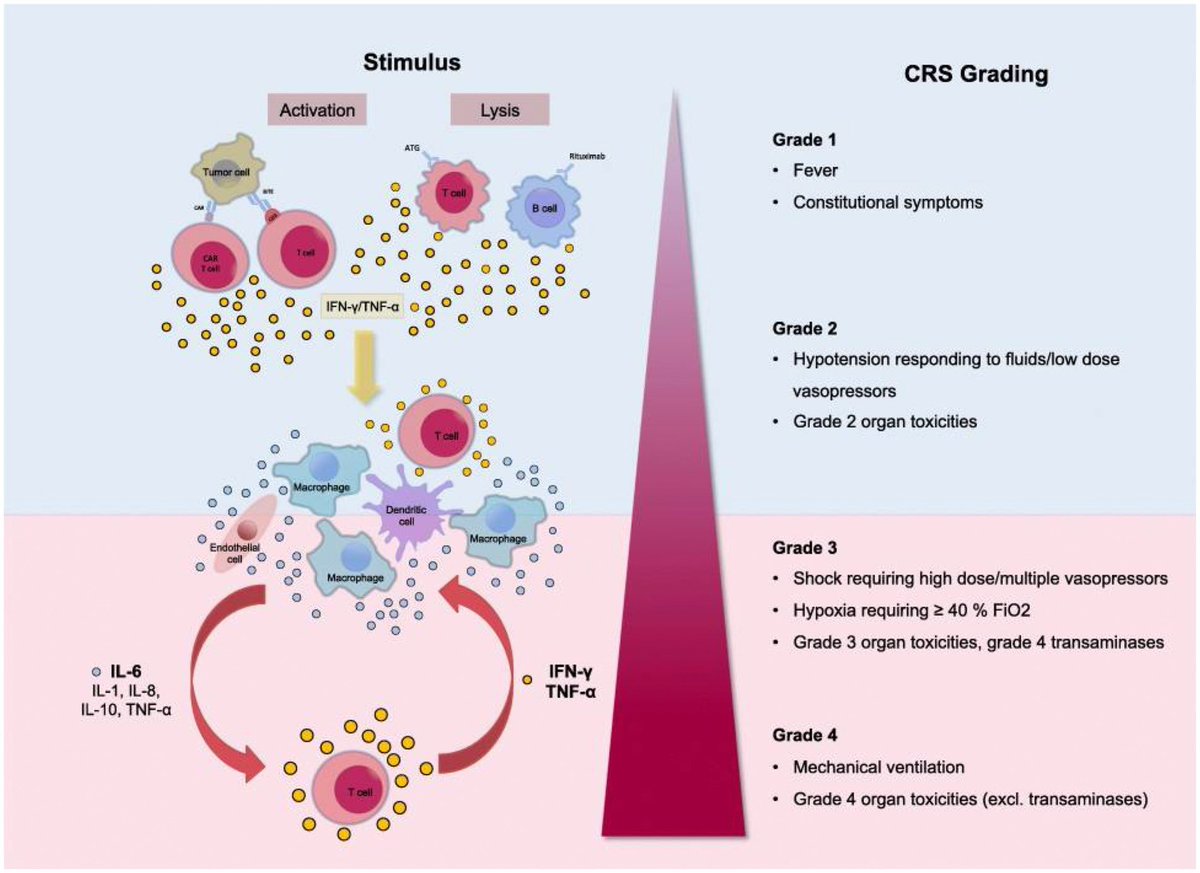
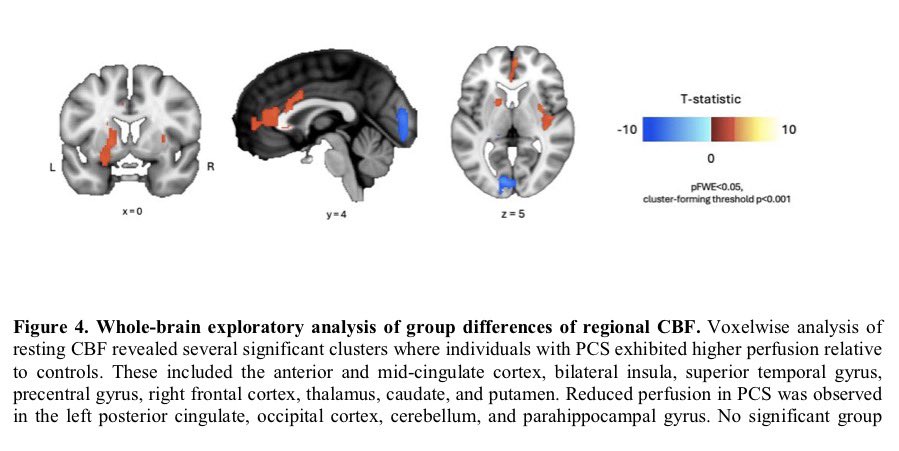
 Why this matters:
Why this matters: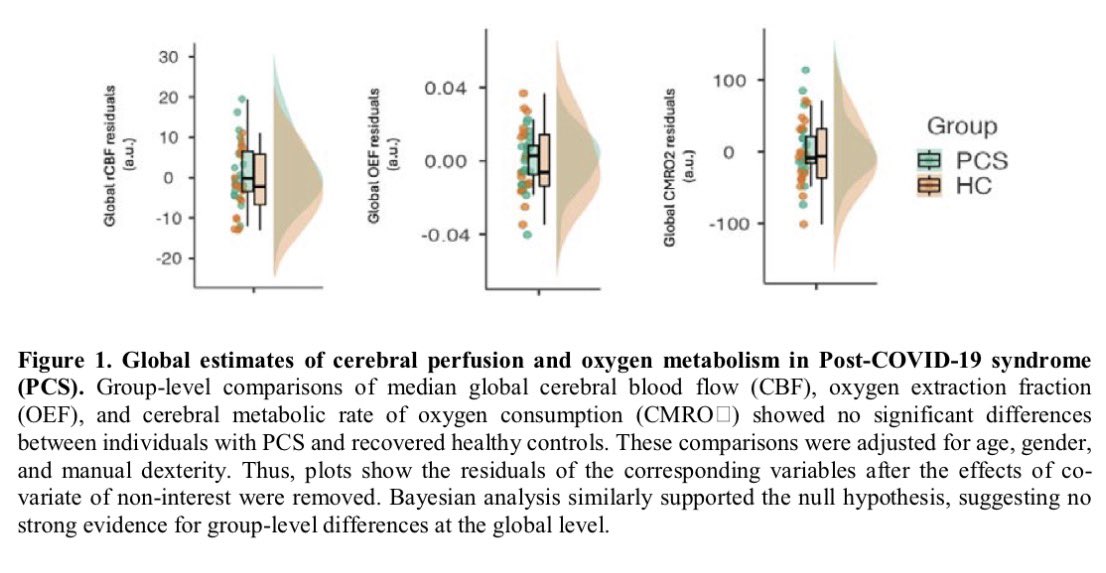
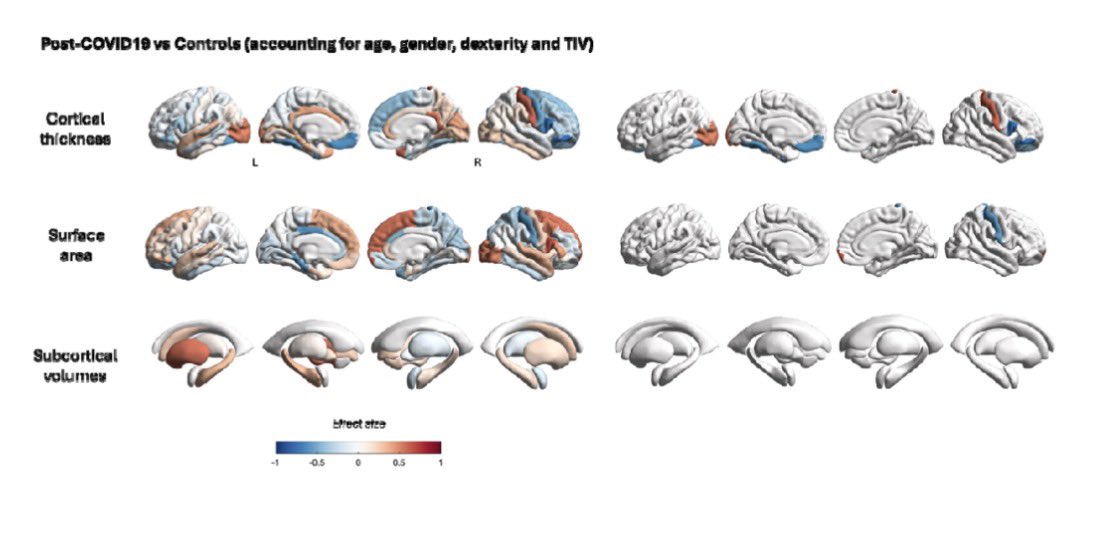

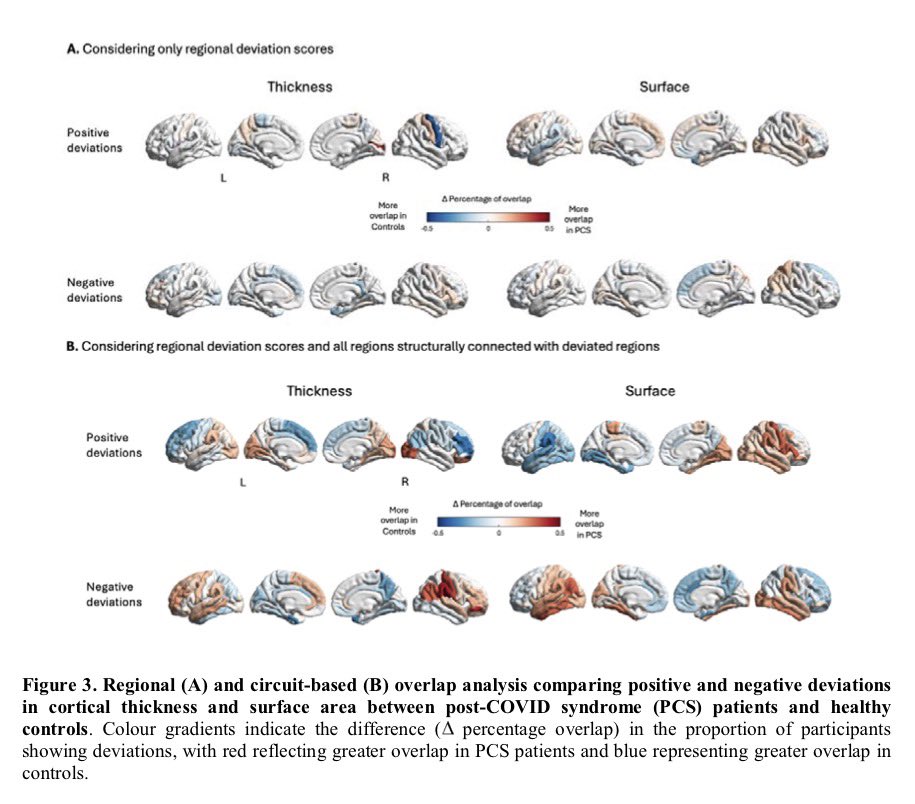 Importantly, the brain regions affected overlap with areas that naturally express TMPRSS2, a protein that helps SARS-CoV-2 enter cells — suggesting certain brain circuits may be more vulnerable to the virus. 2/
Importantly, the brain regions affected overlap with areas that naturally express TMPRSS2, a protein that helps SARS-CoV-2 enter cells — suggesting certain brain circuits may be more vulnerable to the virus. 2/ 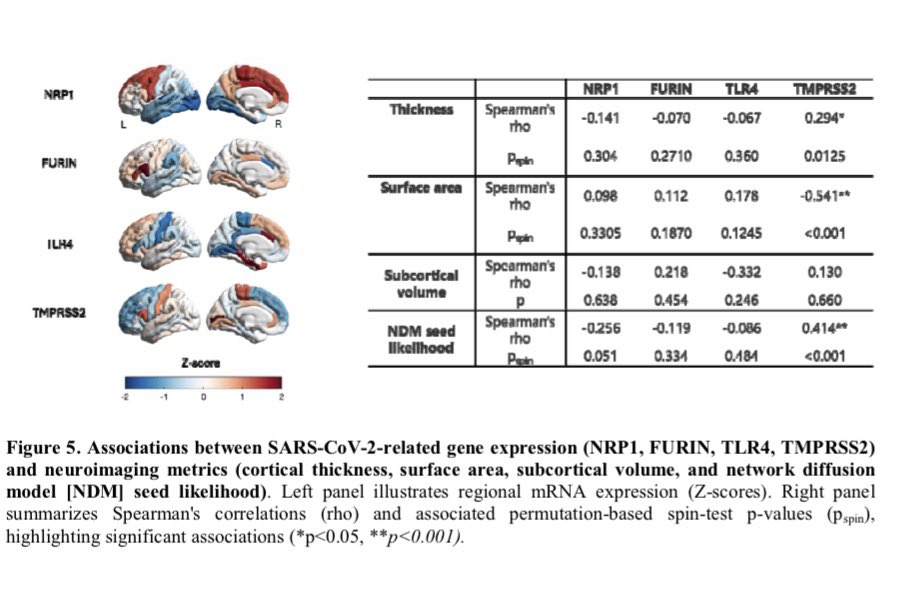
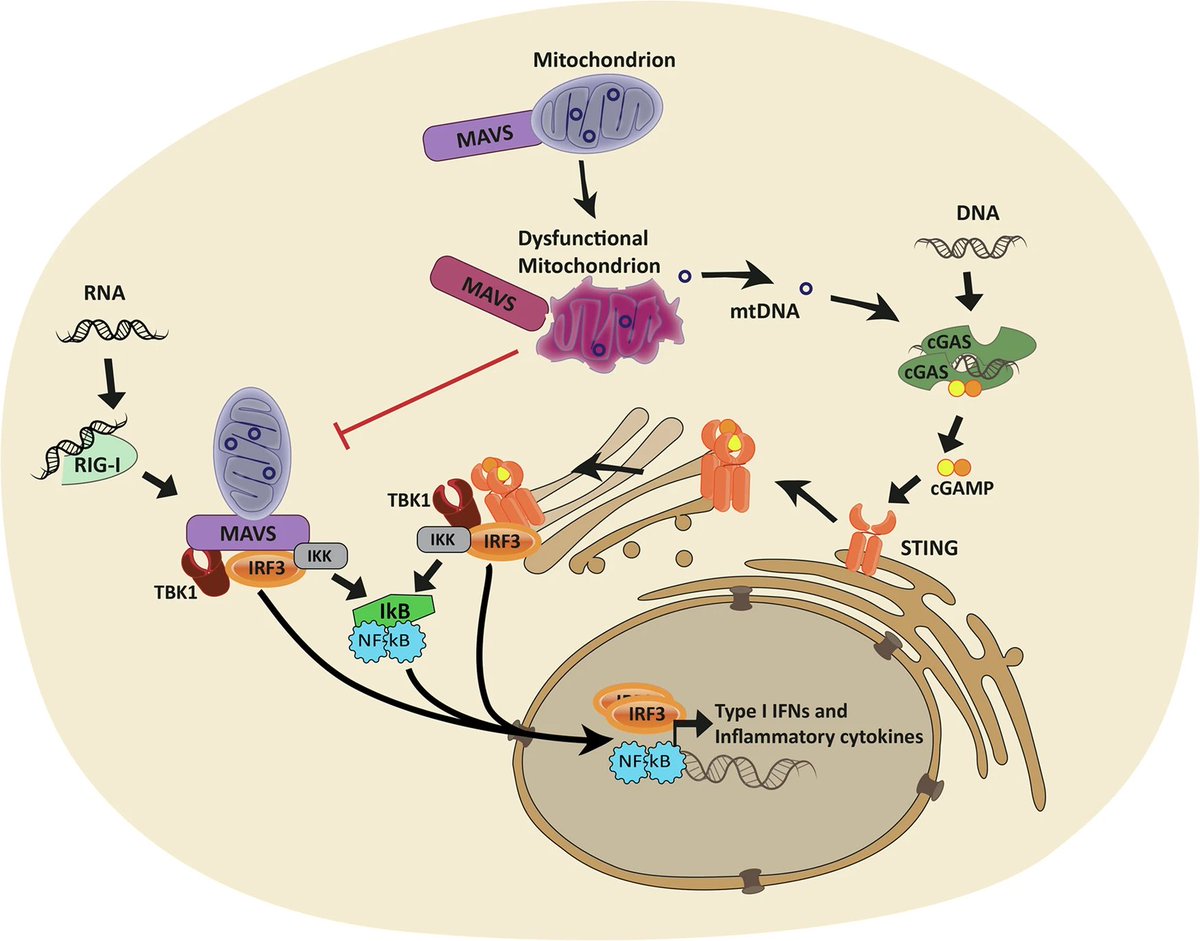
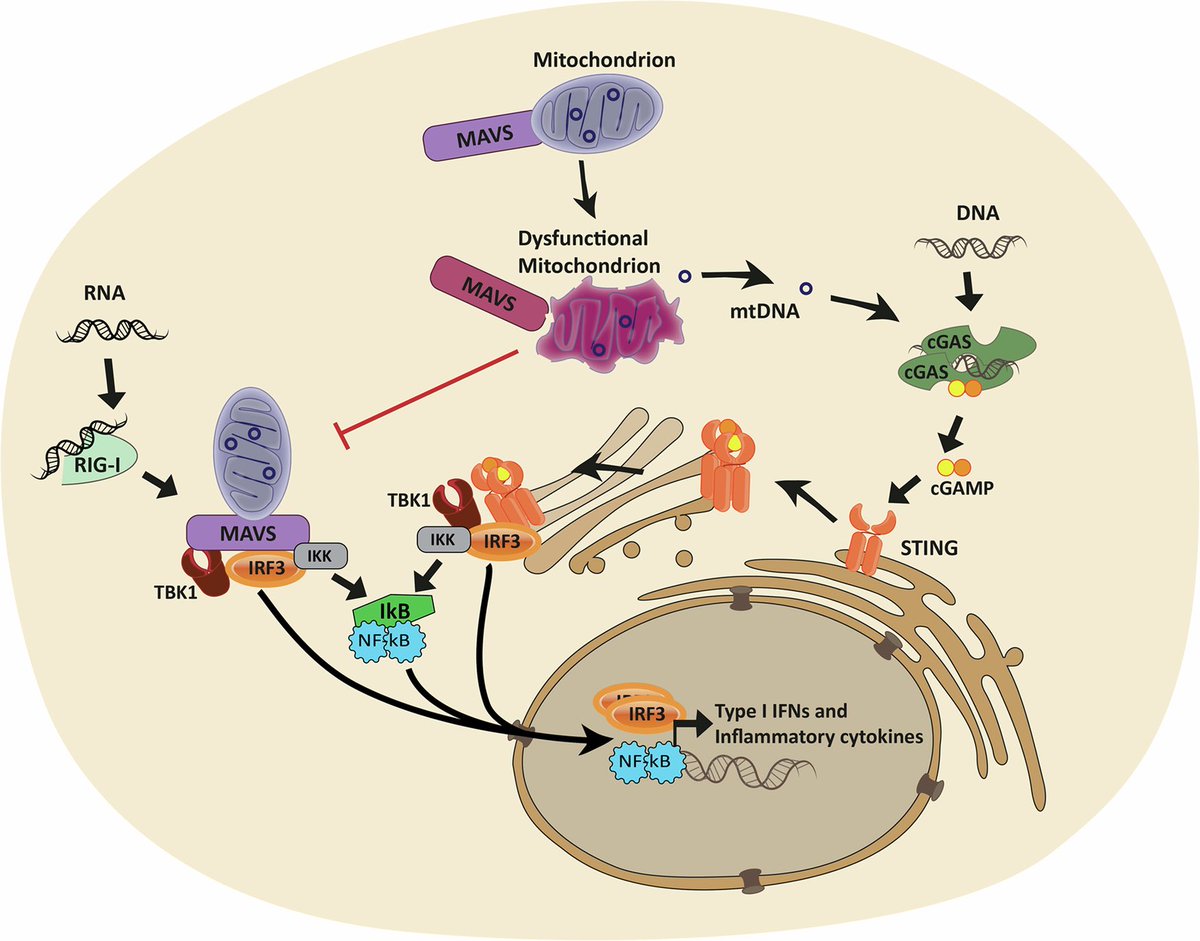
 By comparing people who died from severe COVID-19, those who recovered, and healthy individuals, researchers found lasting changes in how mitochondrial genes are regulated. These changes were most prominent in genes involved in energy production and metabolism. 2/
By comparing people who died from severe COVID-19, those who recovered, and healthy individuals, researchers found lasting changes in how mitochondrial genes are regulated. These changes were most prominent in genes involved in energy production and metabolism. 2/ 
 All patients carried MTHFR polymorphisms (C677T or A1298C)—recently linked to hEDS/HSD.
All patients carried MTHFR polymorphisms (C677T or A1298C)—recently linked to hEDS/HSD.
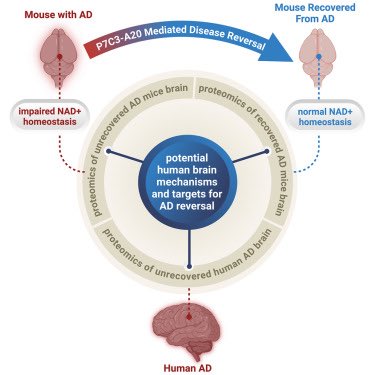
 The team showed that NAD⁺ deficiency is a central driver of AD pathology—leading to blood-brain barrier breakdown, neuroinflammation, oxidative damage, and impaired neurogenesis. 2/
The team showed that NAD⁺ deficiency is a central driver of AD pathology—leading to blood-brain barrier breakdown, neuroinflammation, oxidative damage, and impaired neurogenesis. 2/ 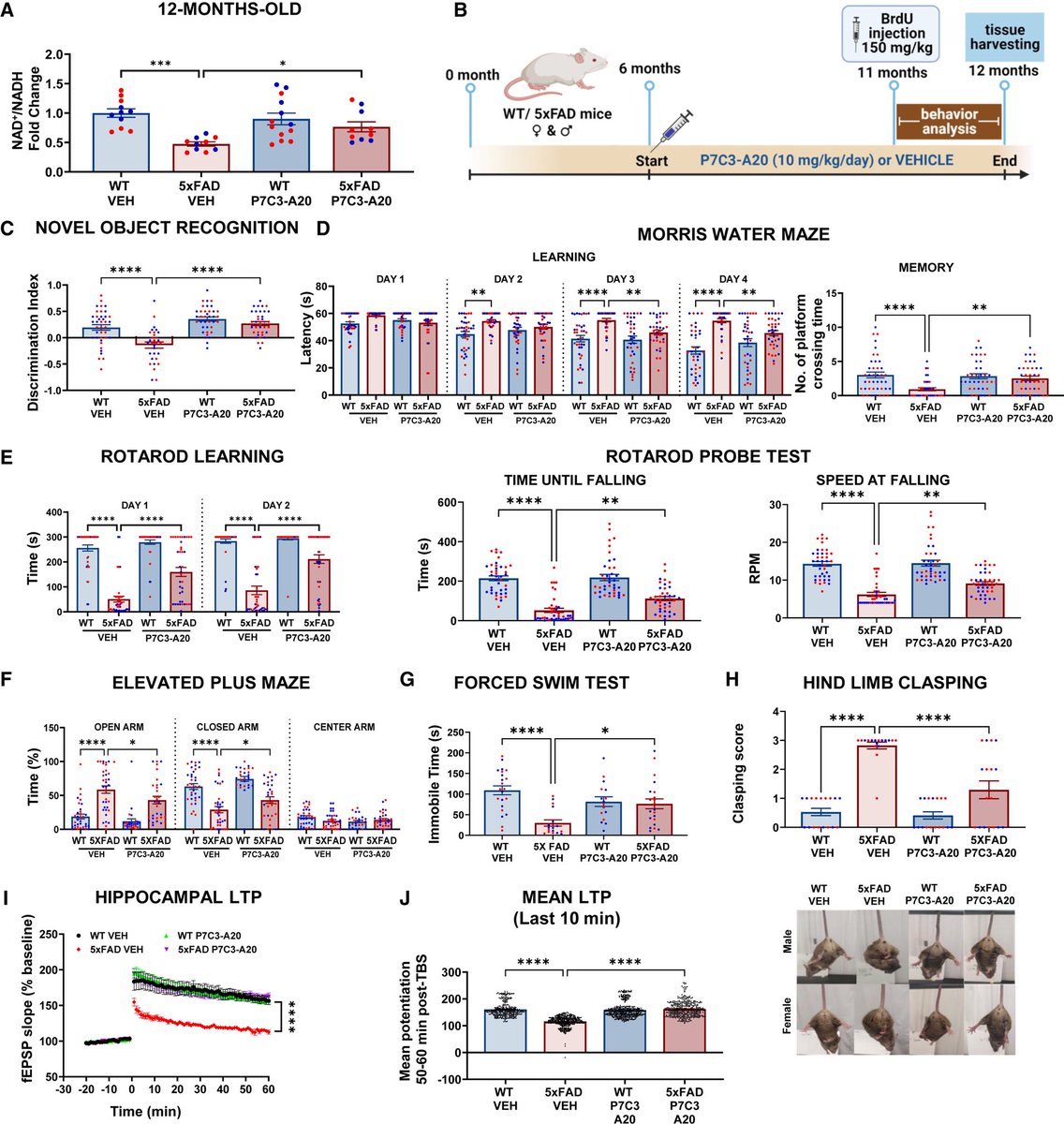
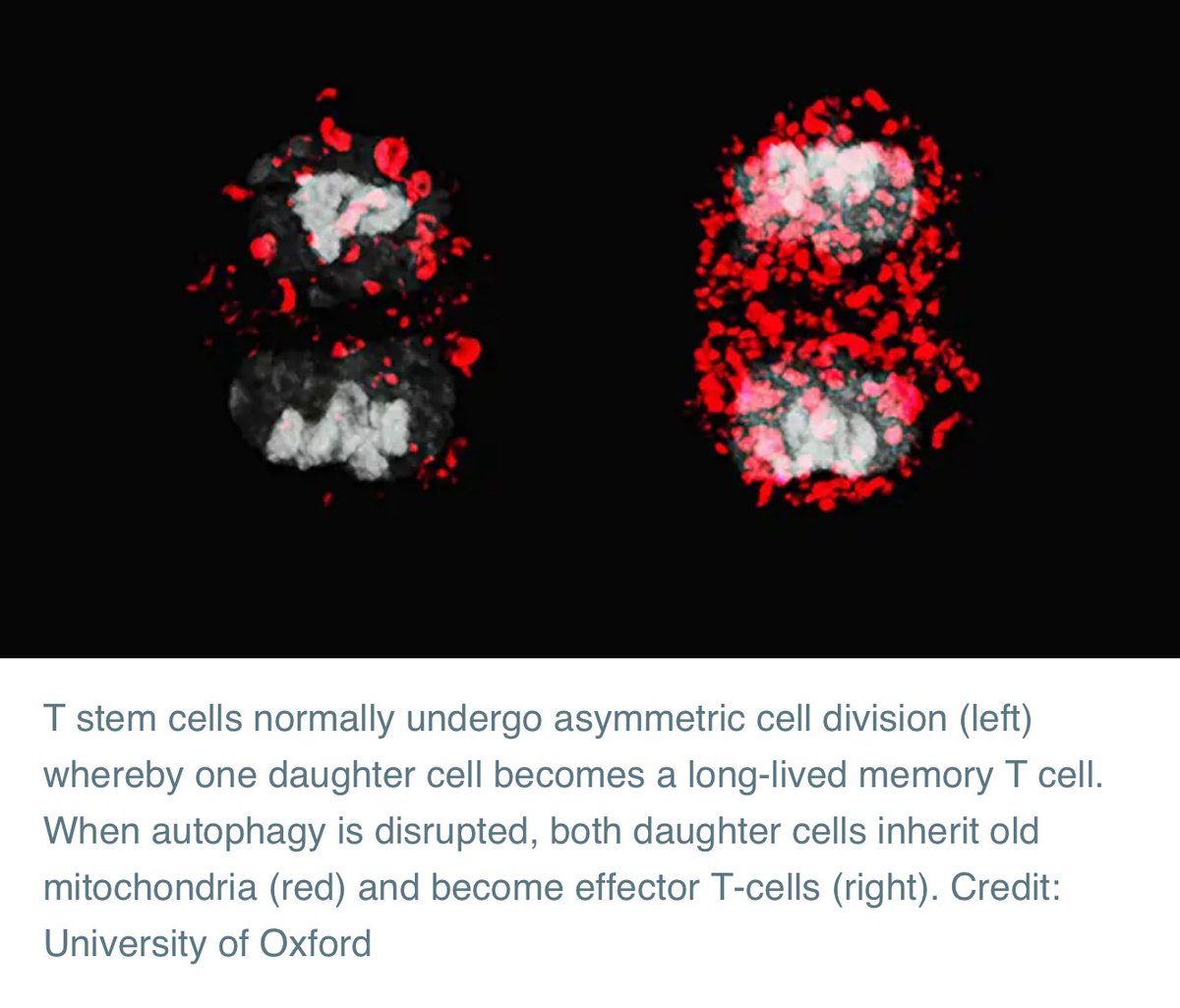
 When a T-cell divides, it can make two daughter cells with different future roles: one becomes a long-lived ‘memory T cell’ that helps protect against future infections, and the other becomes a short-lived ‘effector T cell’ that fights the immediate infection.
When a T-cell divides, it can make two daughter cells with different future roles: one becomes a long-lived ‘memory T cell’ that helps protect against future infections, and the other becomes a short-lived ‘effector T cell’ that fights the immediate infection. 

 This metabolic switch:
This metabolic switch: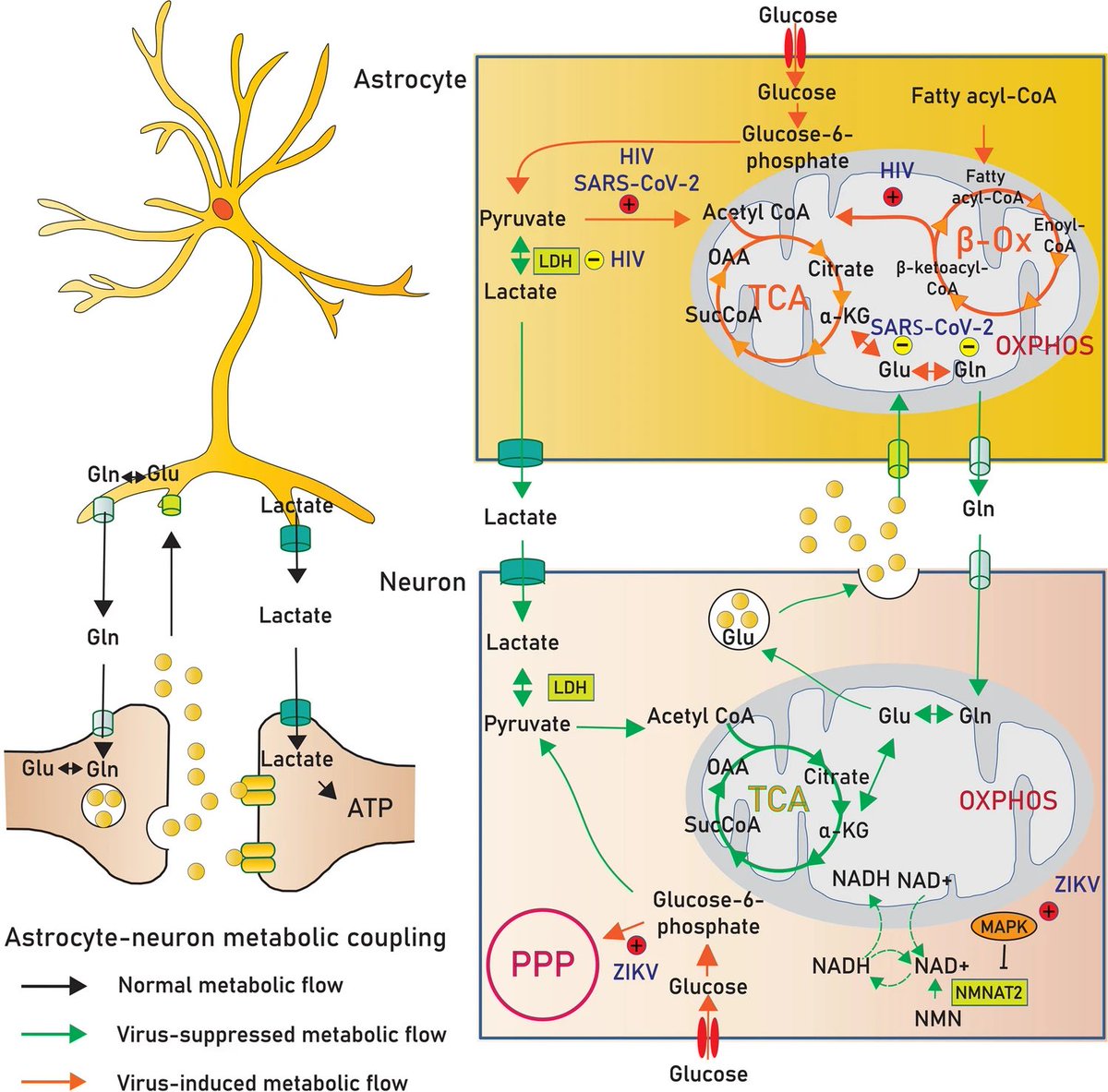
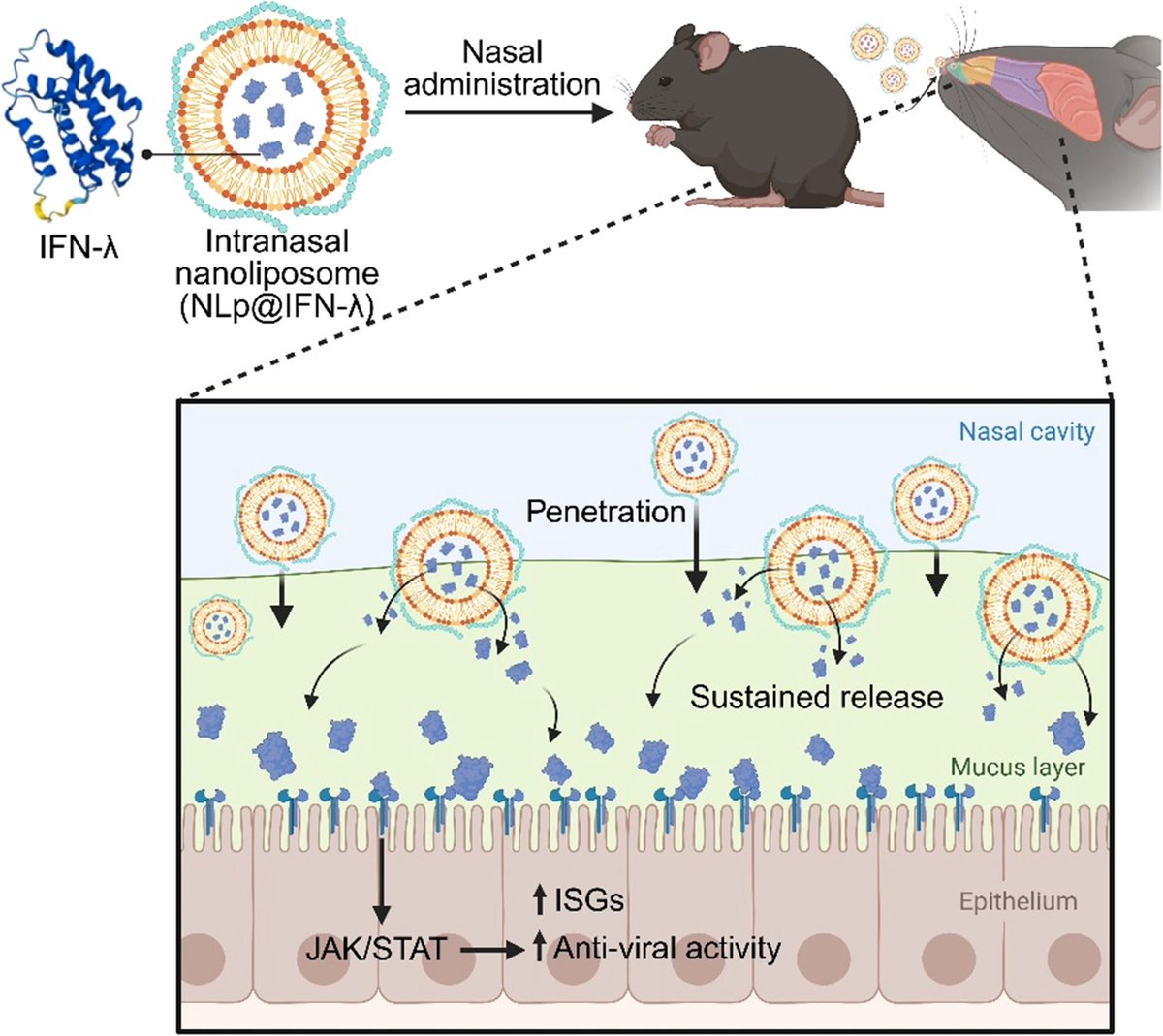
 The platform is based on interferon-lambda, a natural antiviral protein, redesigned using AI protein engineering to overcome major limitations: poor heat stability and rapid clearance from nasal mucosa.
The platform is based on interferon-lambda, a natural antiviral protein, redesigned using AI protein engineering to overcome major limitations: poor heat stability and rapid clearance from nasal mucosa.

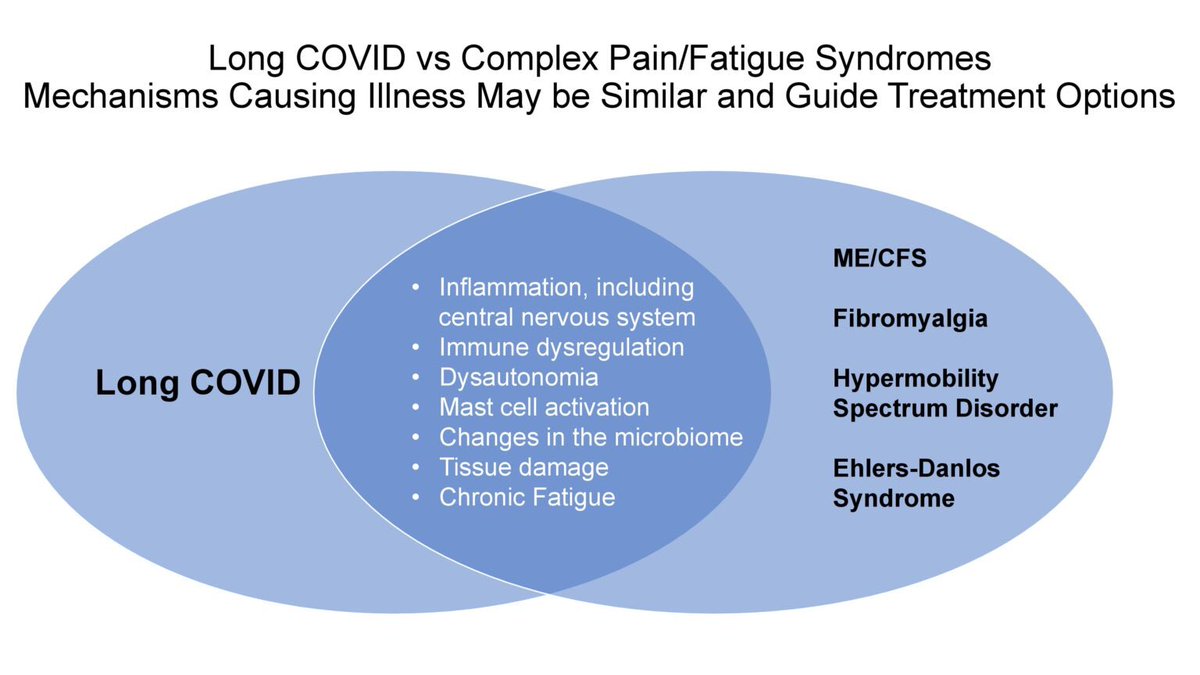
 Key findings point to chronic inflammation, altered cytokine responses, and immune imbalance, which may explain prolonged symptoms such as fatigue, pain, and neurocognitive complaints.
Key findings point to chronic inflammation, altered cytokine responses, and immune imbalance, which may explain prolonged symptoms such as fatigue, pain, and neurocognitive complaints.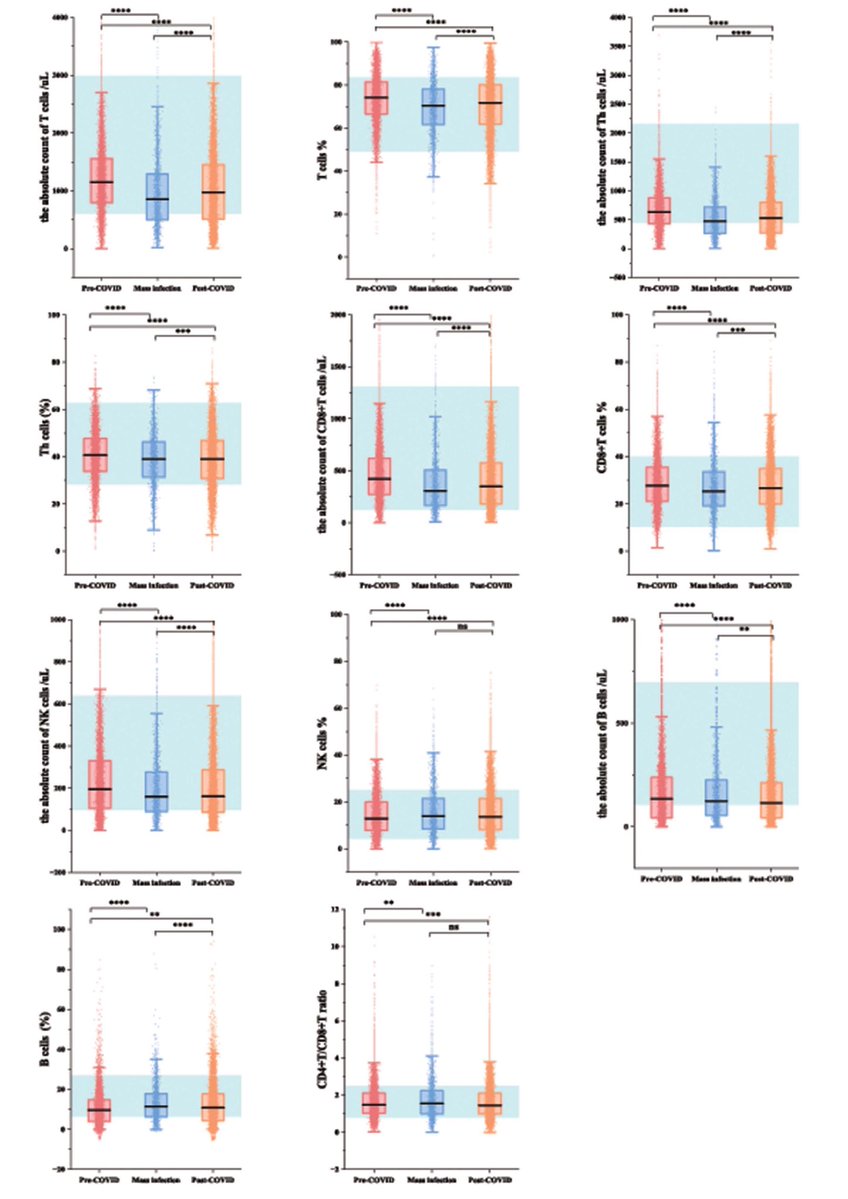

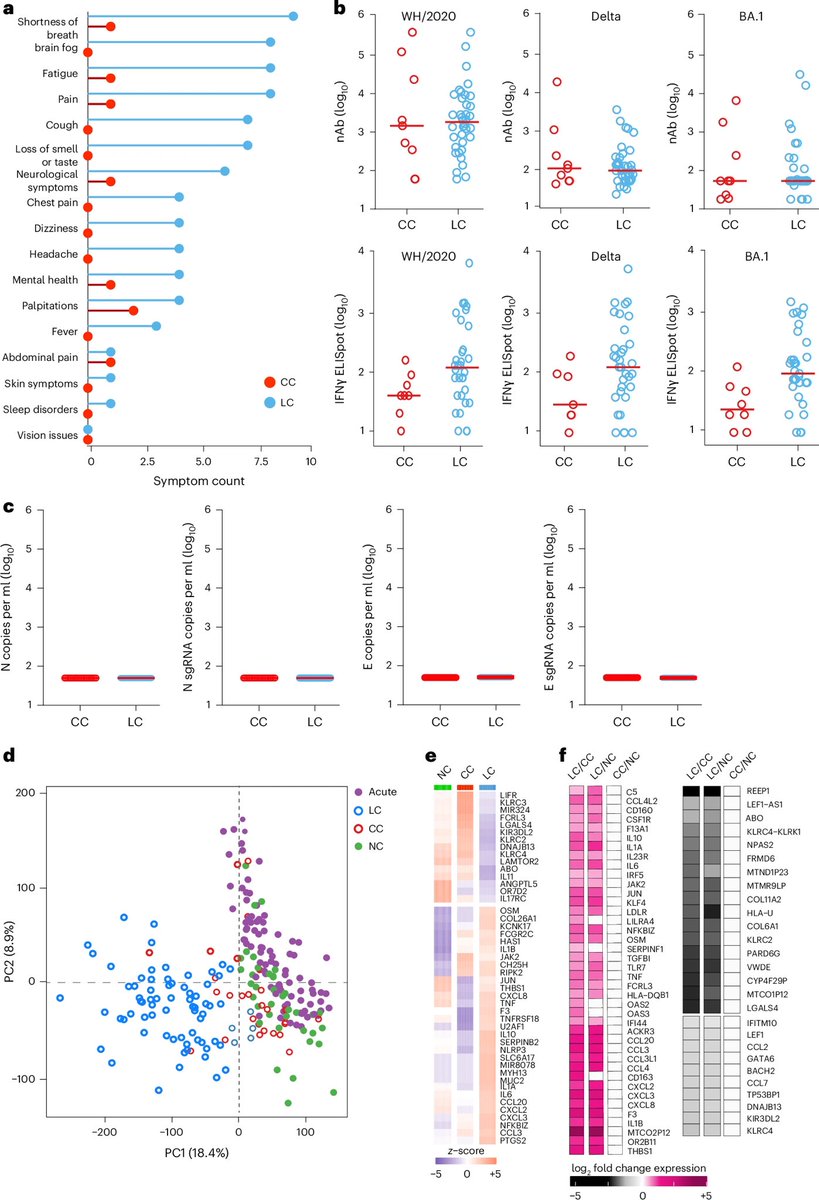
 These immune differences help explain lingering symptoms — such as fatigue, brain fog and breathlessness — and point to specific inflammatory pathways that could be targeted for treatment. This work opens new avenues for better therapies for millions living with longCOVID. 2/
These immune differences help explain lingering symptoms — such as fatigue, brain fog and breathlessness — and point to specific inflammatory pathways that could be targeted for treatment. This work opens new avenues for better therapies for millions living with longCOVID. 2/ 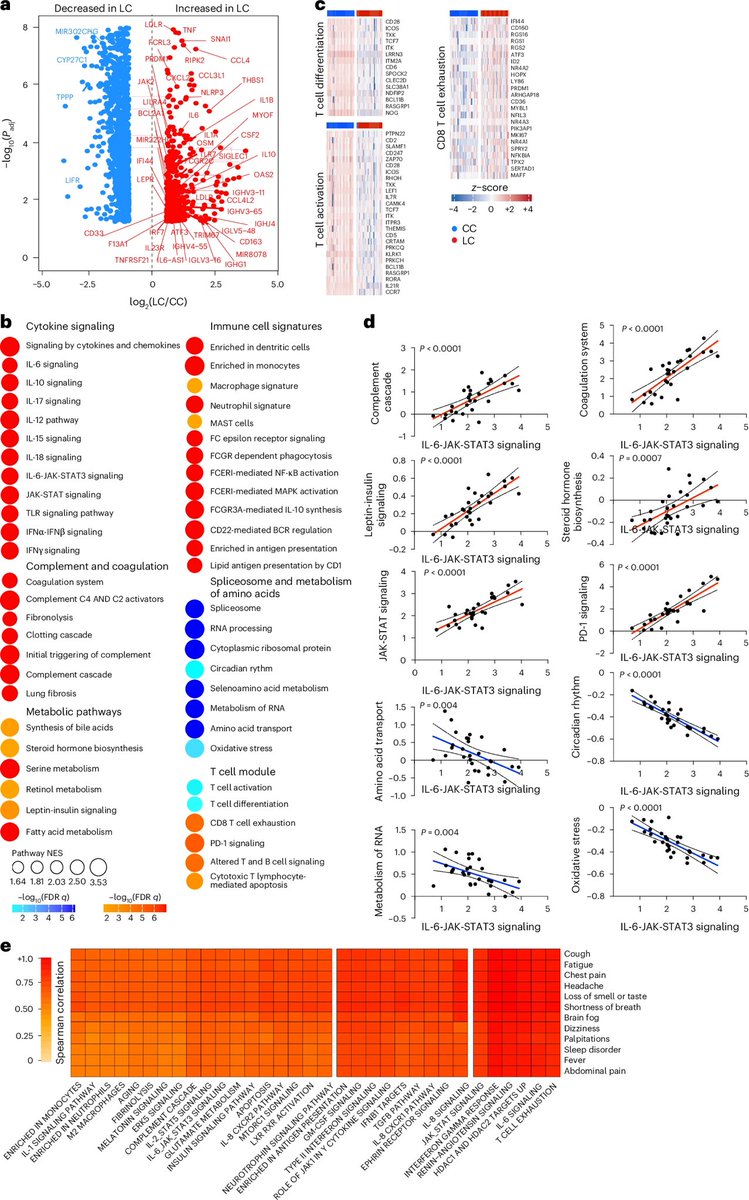

 Researchers tested immune cells from healthy individuals and COVID-19 survivors, both with and without latent TB infection (LTBI).
Researchers tested immune cells from healthy individuals and COVID-19 survivors, both with and without latent TB infection (LTBI).
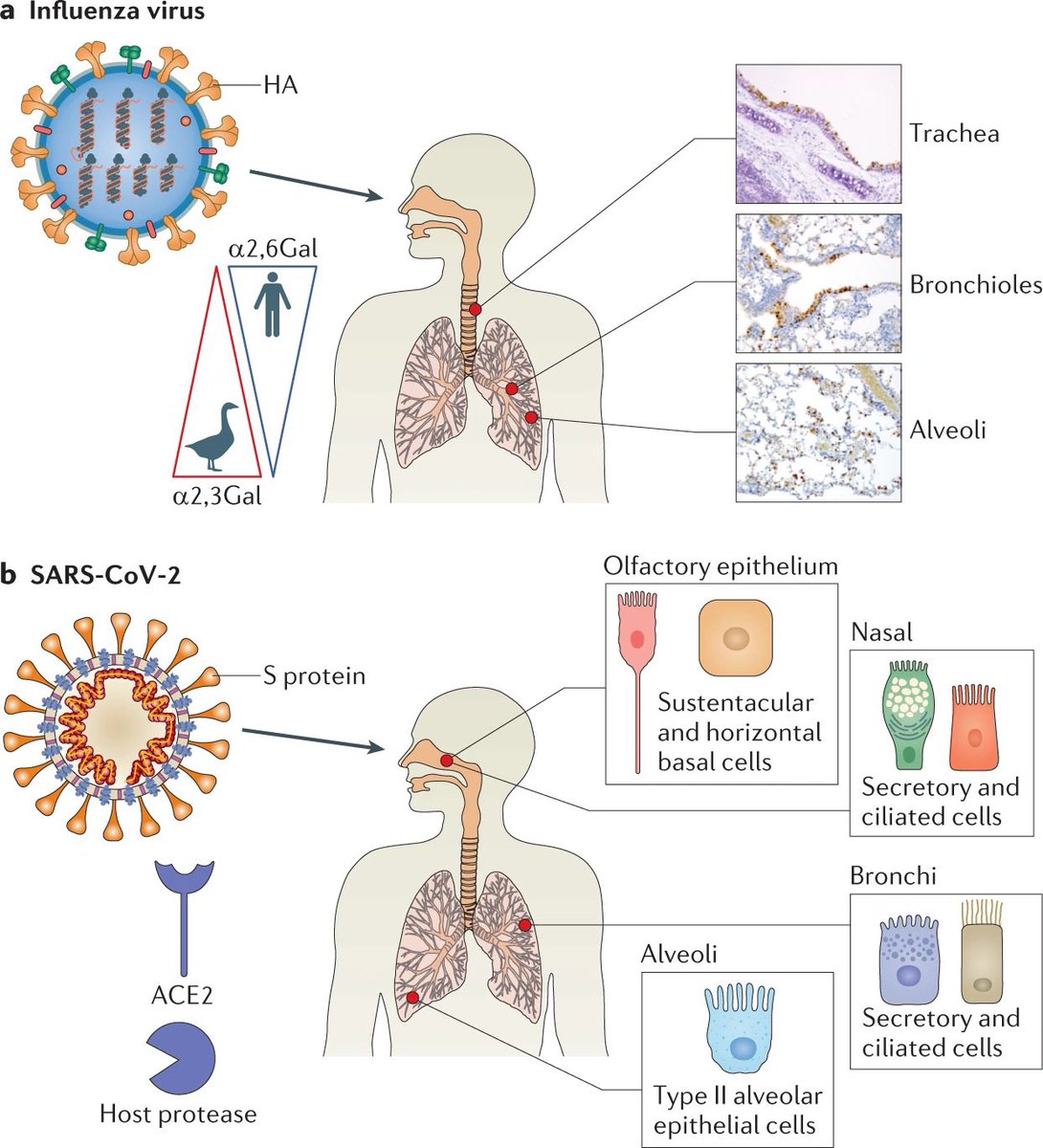
 Post-COVID patients showed increased CXCR3 and CCR6 expression across multiple lymphocyte populations.
Post-COVID patients showed increased CXCR3 and CCR6 expression across multiple lymphocyte populations.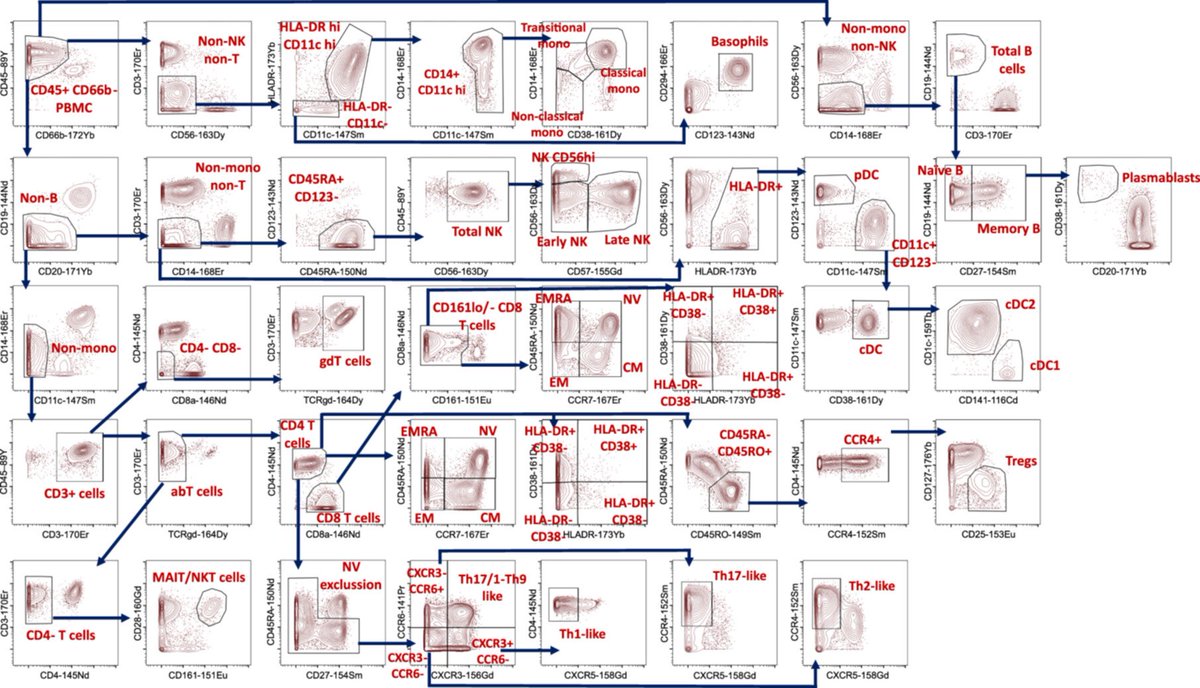
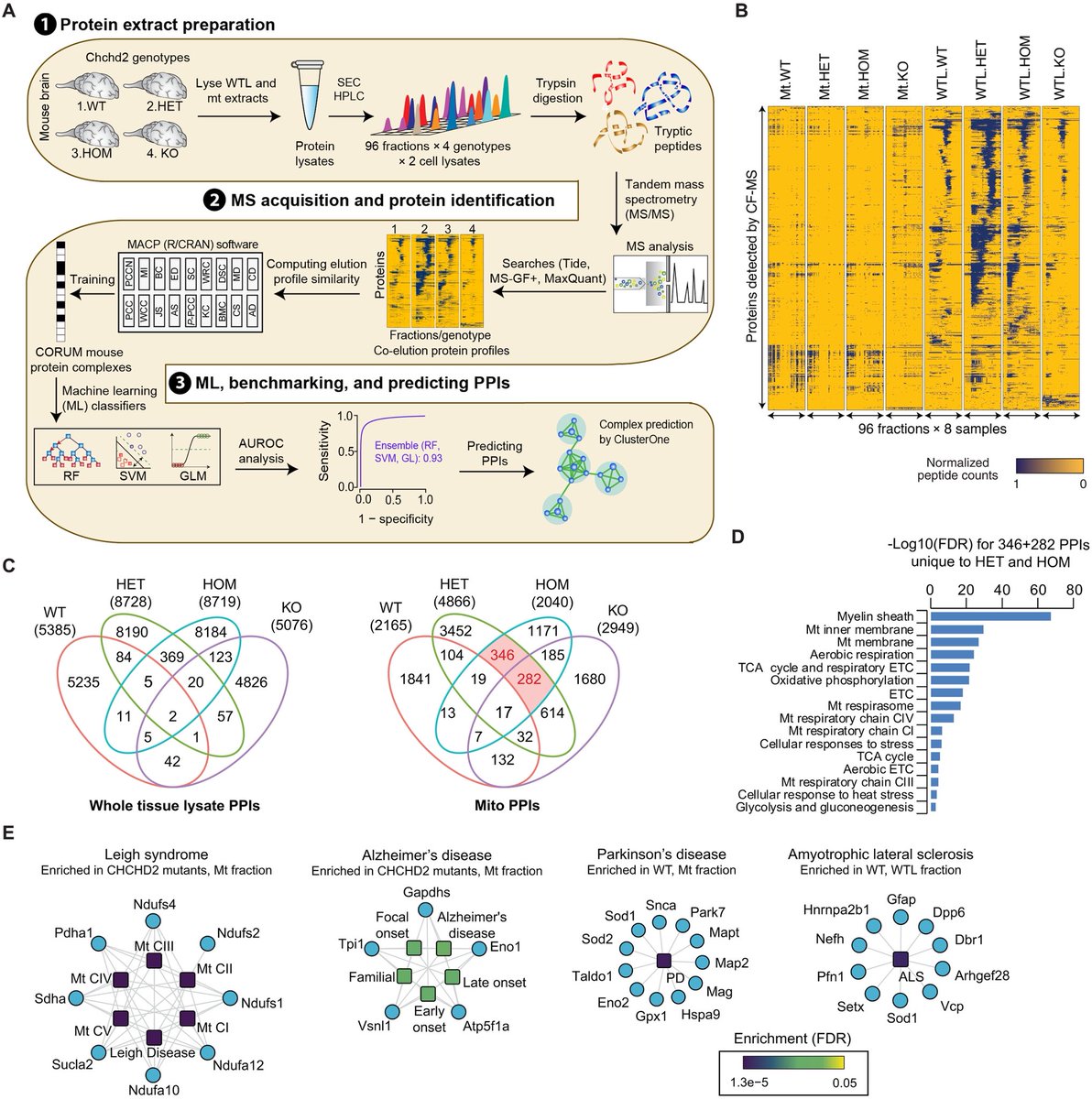
 Key Findings
Key Findings

 Researchers studied 78 people with LongCOVID (mostly mild initial cases) and compared them to 62 who recovered fully.
Researchers studied 78 people with LongCOVID (mostly mild initial cases) and compared them to 62 who recovered fully.