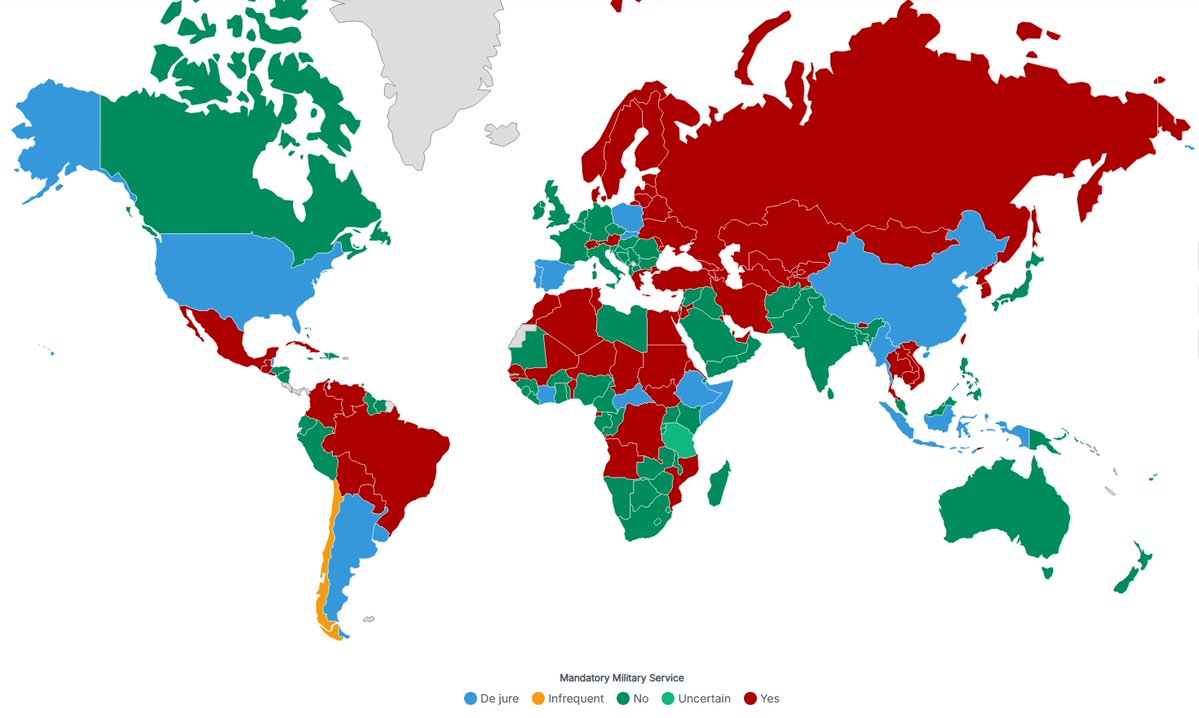
In today's #vatniksoup, I'll talk about a phenomenon called information laundering. It refers to an activity where false or deceitful information is legimitised through a network of intermediaries, such as fake news blogs and/or social media networks.
1/20
1/20

When for example the Kremlin wants to spread a narrative, they spread it through various channels to legitimatize it. As basically no one trusts the Russian TASS anymore, Russian propagandists must get creative and use various backchannels to legimitise the information...
2/20
2/20

...in order to inject into the mainstream. To do this, they'll have to "pass the information" around some other news outlets, preferably that the people (at least some) trusts. The groundwork for these outlets has been created a long time ago - for example a well-known...
3/20

3/20


...conspiracy theory website, Veteran's Today, was established already back in 2003, and the pro-Kremlin financial blog and "news aggregator" Zero Hedge was launched in 2009. Some of these may have even started as a legitimate info sources, but at some point they...
4/20

4/20

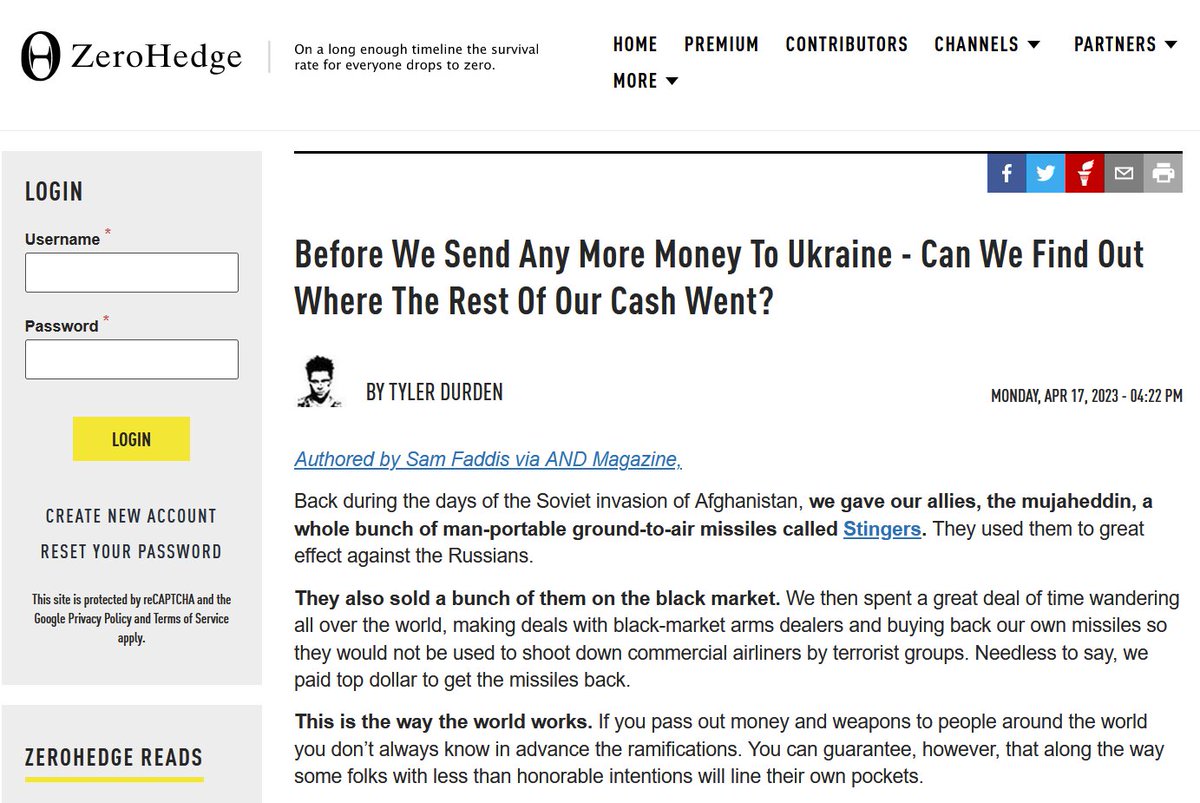
...turned into information laundering platforms. Also, many of the Facebook groups that were later exposed to be troll farms were established already around 2013.
technologyreview.com/2021/09/16/103…
5/20
technologyreview.com/2021/09/16/103…
5/20
Like money launderers who use shell companies, info launderers rely on certain social media accounts or fake news blogs that can then mask the original source and its intent.
6/20
6/20

Social media can also help with the legitimisation process, as people often perceive stories that are liked and shared as something important. In addition, a study has shown that fake news tends to spread much, much faster than factual news.
7/20
7/20
Troll farms can also be used to spread these messages even faster,and since Elon's takeover, these farms have regained their power to spread disinfo on Twitter.Both Russia & the CCP also use diplomat and embassy accounts actively to spread disinformation and false narratives.8/20 




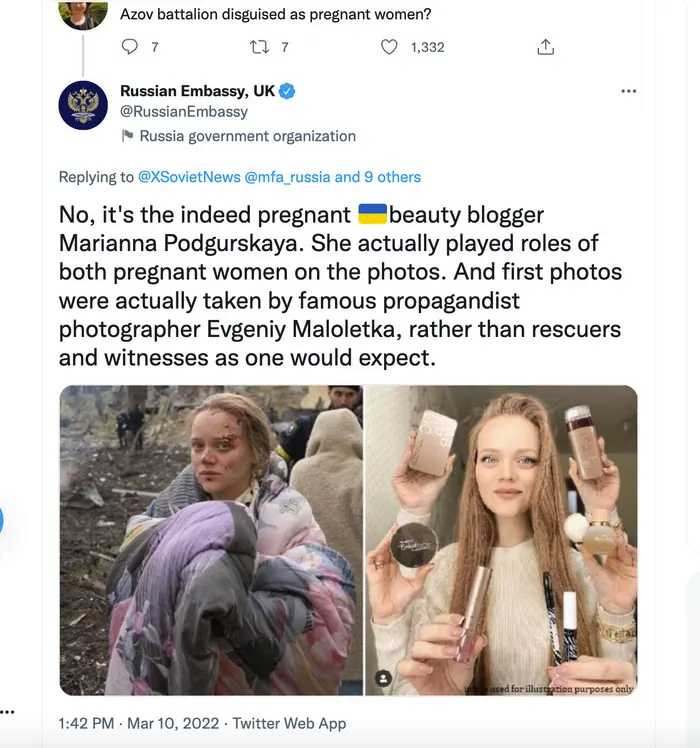
Social media platforms can also be the original source which is then spread throughout the fake news blogs. For example photoshopped images (Ukrainians with Nazi flags, doctored documents, etc.) or old videos with wrong context often start spreading on social media, ...
9/20

9/20
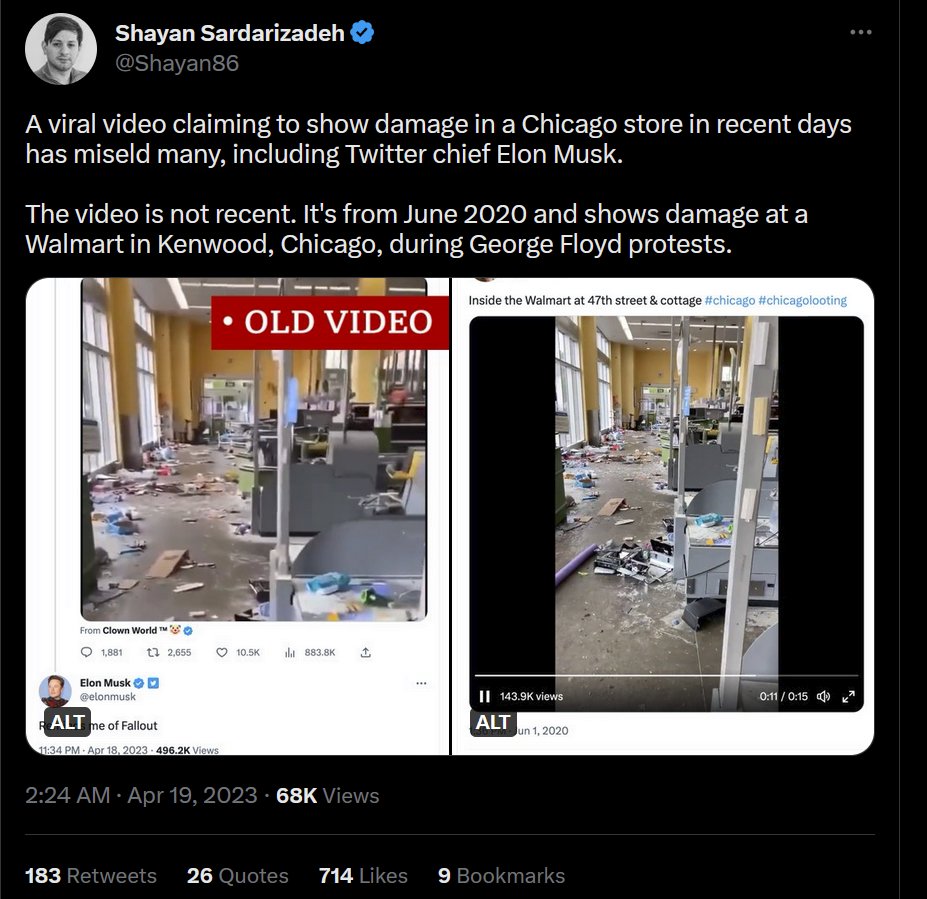

...after which the fake news blogs publish articles on them, hoping for the mainstream to take the bait.
The goal with all this is to "layer" the disinformation so, that it spreads from its point of origin to more credible sources.
10/20
The goal with all this is to "layer" the disinformation so, that it spreads from its point of origin to more credible sources.
10/20

This credibility can then be increased with reposts, likes and shares on social media. For example, the hacked Podesta e-mails in 2016 were spread through various middle-men, including WikiLeaks. These seemingly authentic platforms provided credibility and the ...
11/20
11/20

...hack-and-leak operation wasn't immediately identified as a Russian intelligence operation. The illusion of legitimacy of fake news blogs and/or individual "journalists" can also be increased by awards and nominations. One example of this is the "Serena Shim Award for...
12/20
12/20
...Uncompromised Integrity in Journalism", that's been awarded to totalitarian regime bootlickers like Max Blumenthal, Aaron Maté and Jackson "Z" Hinkle.
Both Russia and China also like to use Western public figures to propagate their agenda and strengthen it in their own..13/20
Both Russia and China also like to use Western public figures to propagate their agenda and strengthen it in their own..13/20

...news outlets. Outlets like TASS and Global Times often interview MEP's like Clare Daly, Mick Wallace or Maximillian Krah to promote their ideology, for example in case of genocide denial in Xinjiang or in Ukraine.
14/20

14/20


One example of relatively successful information laundering was the "secret bioweapons labs in Ukraine" hoax. The bioweapons lab theory (re-)surfaced on the same day when Russia started its invasion in Ukraine, and it was initially suggested by QAnon podcast host Jacob...
15/20
15/20

..."RedPill78" Creech from the US. He claimed that the Russians only bombed the locations of these bioweapons labs, and that this was the reason for the invasion. Three days later the story was tweeted out by the Russian Embassy in Bosnia and Herzegovina and from there...
16/20
16/20

...it quickly spread to fake news blogs and eventually to the mainstream media. It was even discussed on Tucker Carlson on many occasions and Russia's UN Ambassador Vassily Nebenzia repeated the allegations.
17/20
17/20

But information laundering isn't limited just to news blogs - it is often used in academia, too. The information laundered through these "scientific journals" is often outright propaganda camouflaged as research. Especially Alexander Dugin has been active in establishing...
18/20
18/20
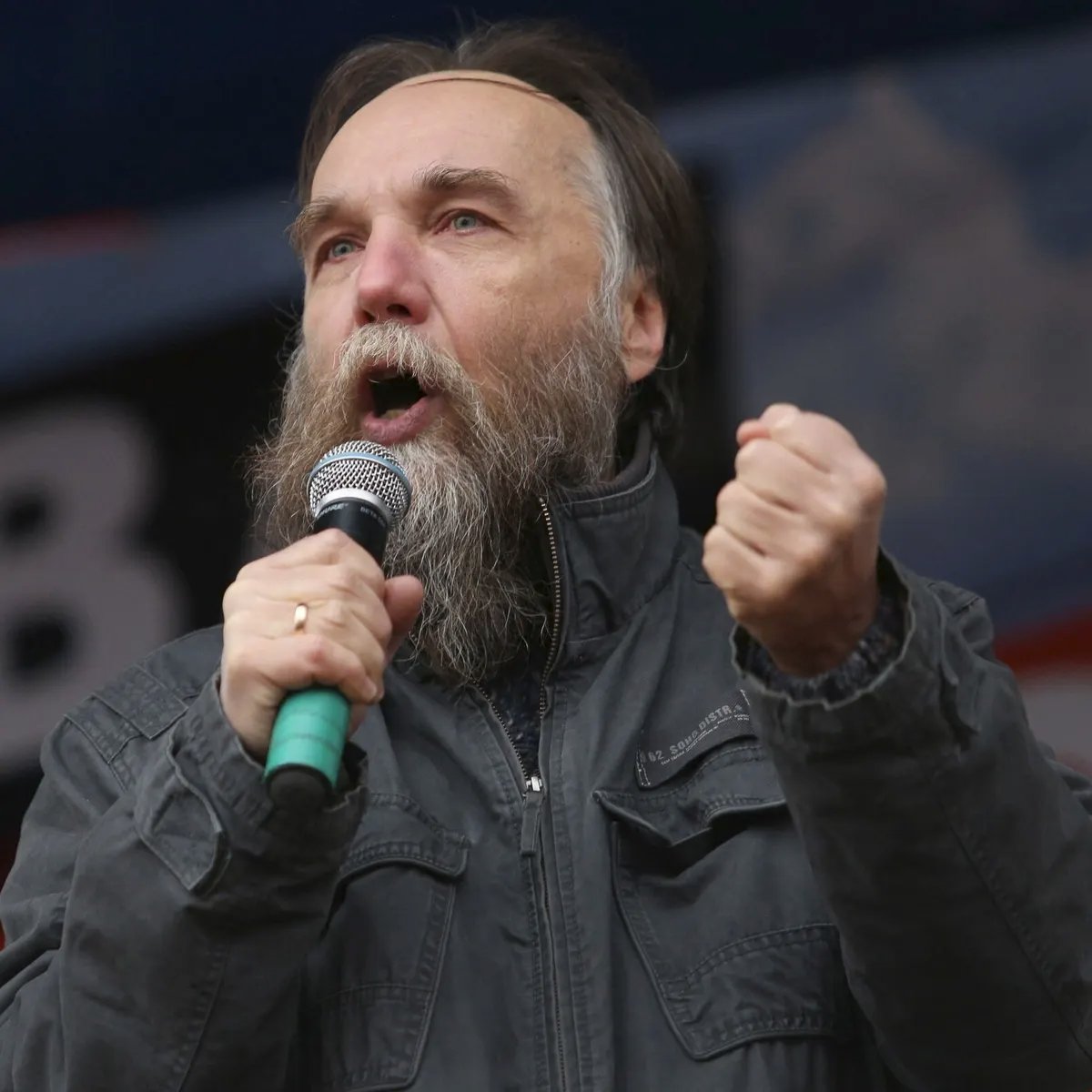

...credibility for pro-Kremlin narratives in academia. Once published, these propaganda pieces can be used to counter publications of Western academia (which to be fair, can also be straight up propaganda).
19/20
19/20
To conclude: information laundering is relatively effective method of injecting disinformation and propaganda into the mainstream, and it's yet another form of hybrid warfare in which Russia and China have been forerunners for a good decade.
BTW, do follow @Shayan86!
20/20
BTW, do follow @Shayan86!
20/20

Source: stratcomcoe.org/publications/i…
Support my work: buymeacoffee.com/PKallioniemi
Past soups: vatniksoup.com
Related soups:
Russian narratives:
Troll farms:
Russiagate:
Manipulation:
Support my work: buymeacoffee.com/PKallioniemi
Past soups: vatniksoup.com
Related soups:
Russian narratives:
https://twitter.com/P_Kallioniemi/status/1634168118992949251
Troll farms:
https://twitter.com/P_Kallioniemi/status/1601115023589658624
Russiagate:
https://twitter.com/P_Kallioniemi/status/1617852982095405056
Manipulation:
https://twitter.com/P_Kallioniemi/status/1605106747575771138
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh