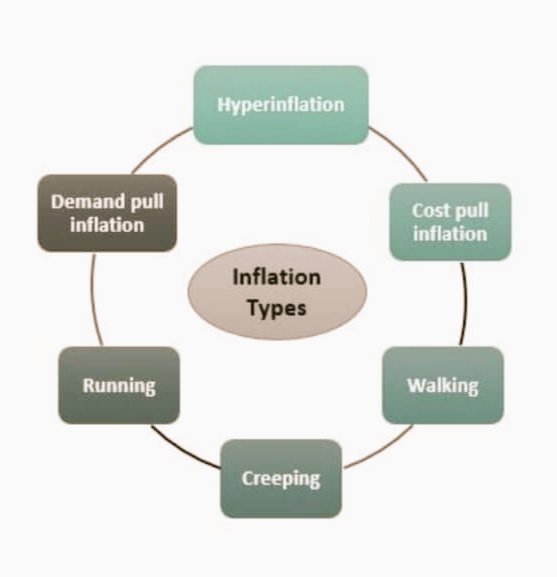
Inflation Types
#1 – Demand Pull Inflation
#2 – Creeping Inflation
#3 – Cost-Pull Inflation
#4 – Walking Inflation
#5 – Galloping Inflation
#6 – Hyperinflation
#1 – Demand Pull Inflation
#2 – Creeping Inflation
#3 – Cost-Pull Inflation
#4 – Walking Inflation
#5 – Galloping Inflation
#6 – Hyperinflation
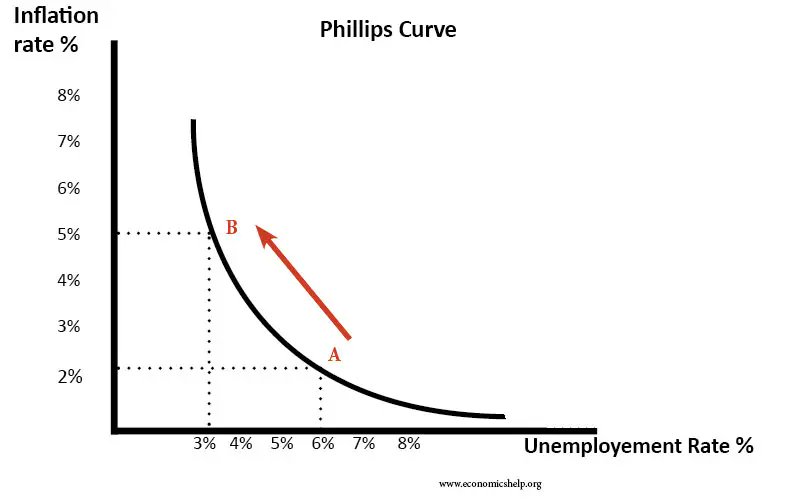
#1 Demand pull infation-If aggregate demand (AD) rises faster than productive capacity,then firms will respond by putting up prices,creating inflation.
See below 👇
A rise in demand causes a fall Unemployment (from 6% to 3%) but an increase in inflation from inflation of 2% to 5%
See below 👇
A rise in demand causes a fall Unemployment (from 6% to 3%) but an increase in inflation from inflation of 2% to 5%
#2 –Creeping Inflation a condition where the inflation in a country increases slowly but continuously over a period of time and the effect of inflation is noticed after a long period of time.
Ex-if the inflation is at the rate of 3% it will take 33 years for the prices to double.
Ex-if the inflation is at the rate of 3% it will take 33 years for the prices to double.
#3 – Cost-Pull Inflation
This situation appears when the cost of production forces firms to increase their prices. For example, the factors of production like labor, raw material, and technology are getting expensive.
This situation appears when the cost of production forces firms to increase their prices. For example, the factors of production like labor, raw material, and technology are getting expensive.
4-Walking Inflation is faster than creeping inflation,but not as fast as galloping or hyperinflation. It is harmful to the economy because it heats up economic growth too quickly.People start to buy more than they need in order to avoid tomorrow's much higher prices.
#5-Galloping Inflation
When inflation rises to 10% or more, it can be very damaging to the economy. Money loses value so quickly that business and employee income can't keep up with costs and prices.The economy becomes unstable, and government leaders lose credibility.
When inflation rises to 10% or more, it can be very damaging to the economy. Money loses value so quickly that business and employee income can't keep up with costs and prices.The economy becomes unstable, and government leaders lose credibility.
#6 Hyperinflation- occurs when prices skyrocket by more than 50% per month. It is very rare.most examples of hyperinflation occur when governments print money to pay for wars. One of the most extreme examples is Hungary, where in 1945, prices doubled every 15 hours.
#UPSC2023
#UPSC2023
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh
 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter