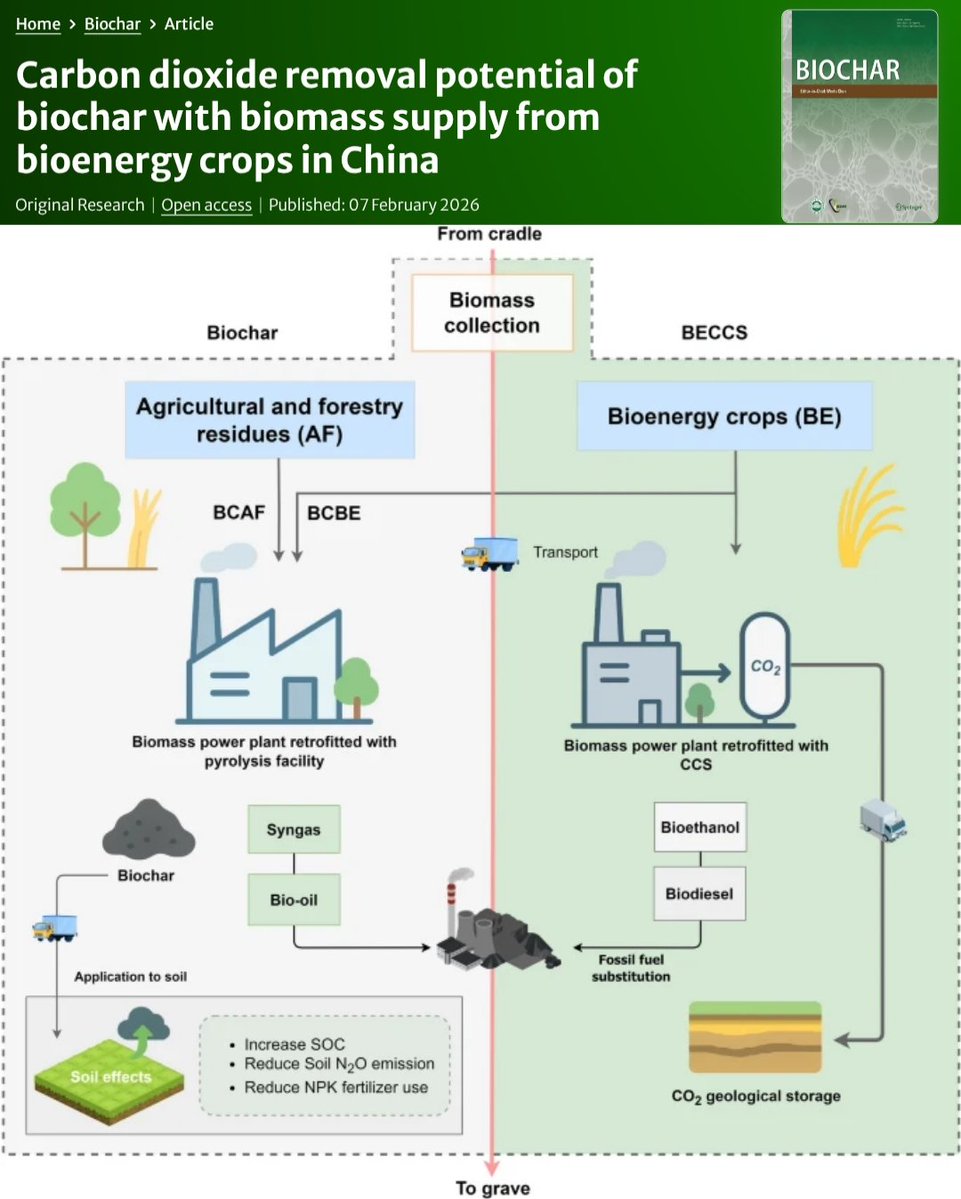
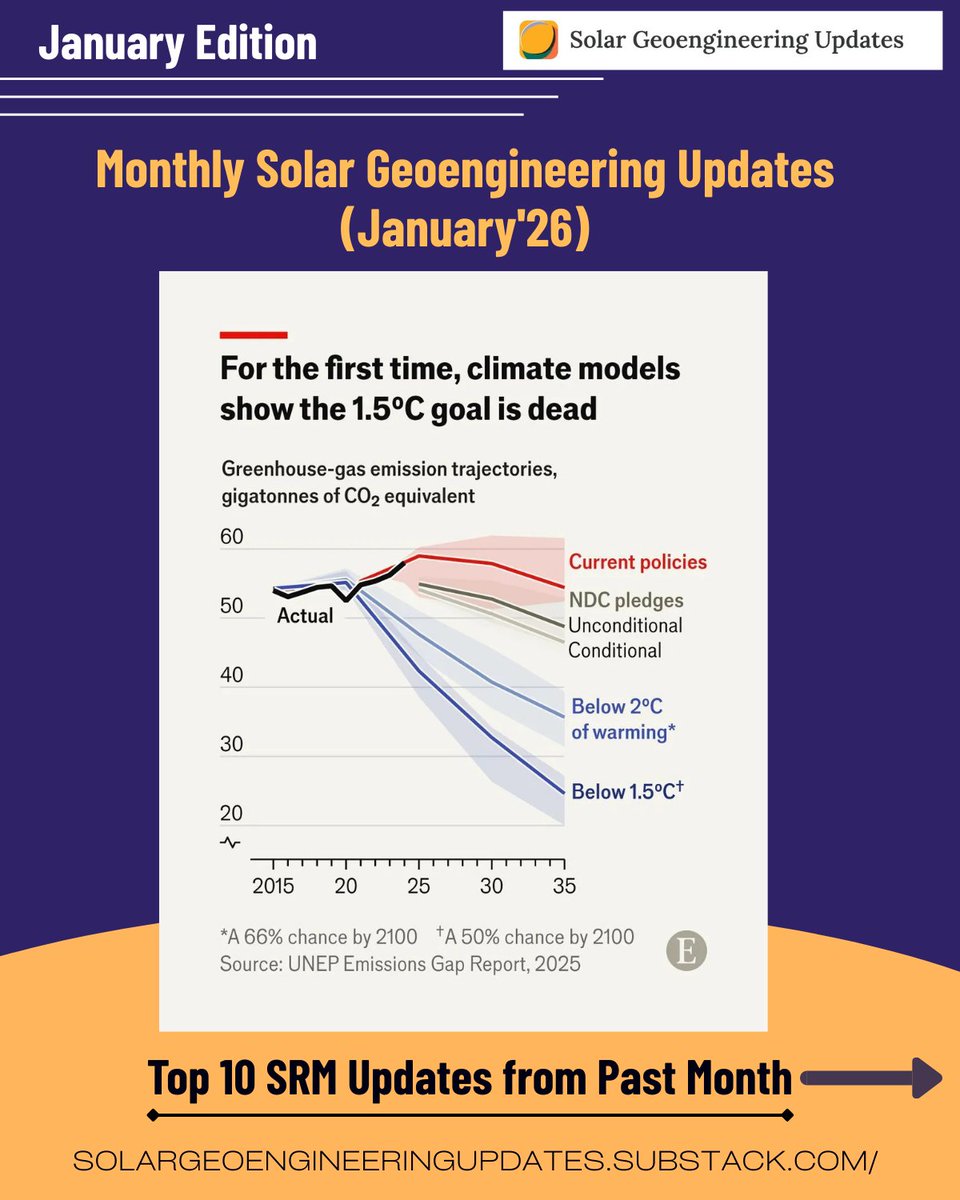
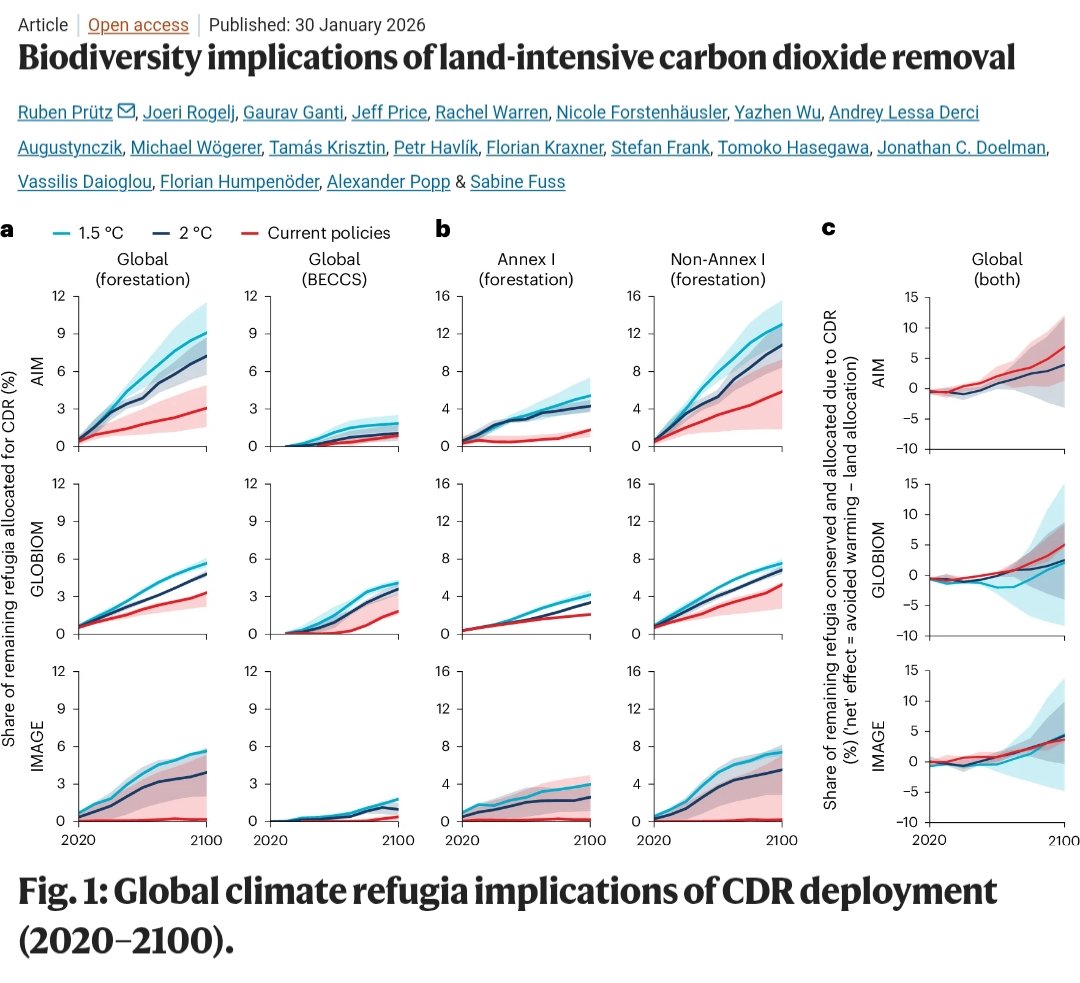
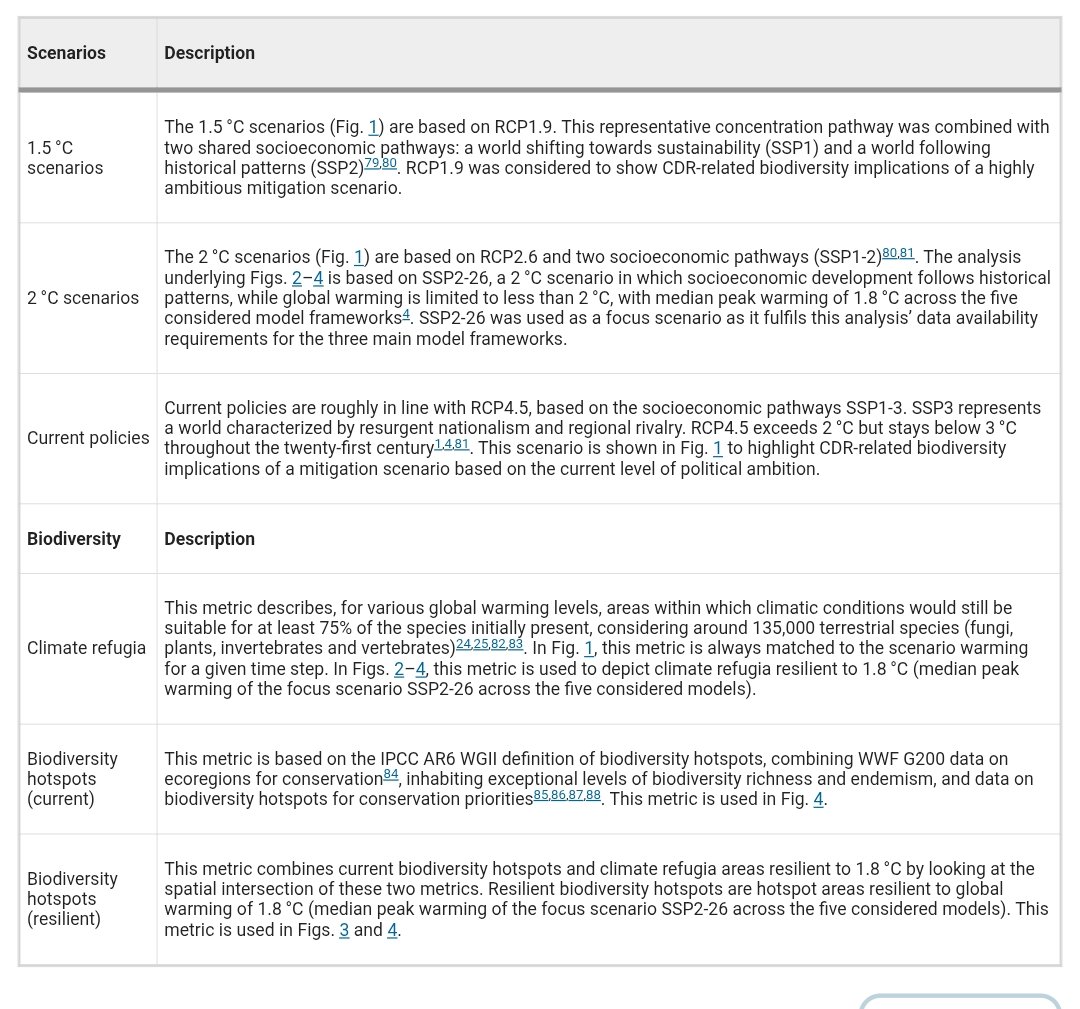
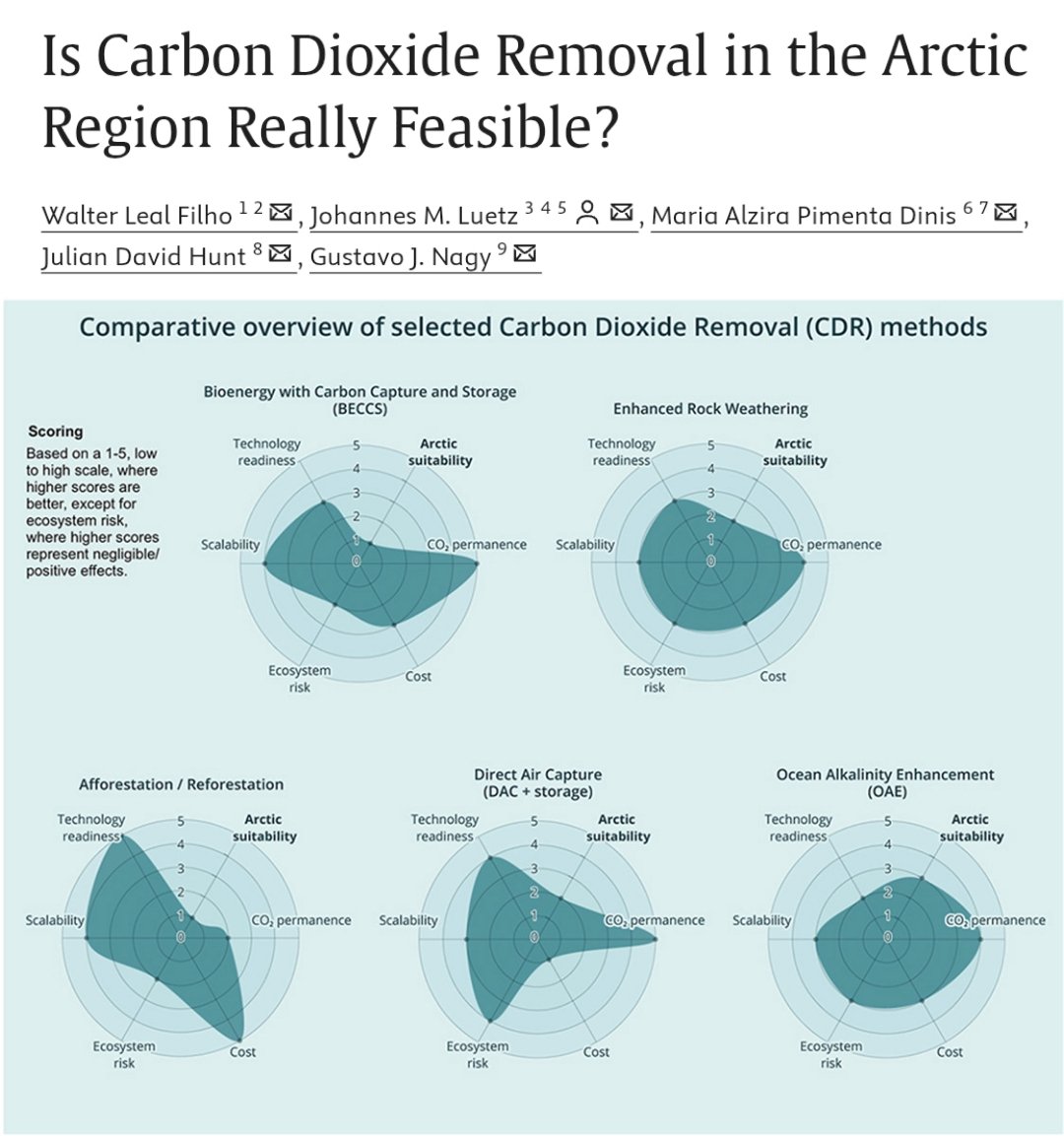
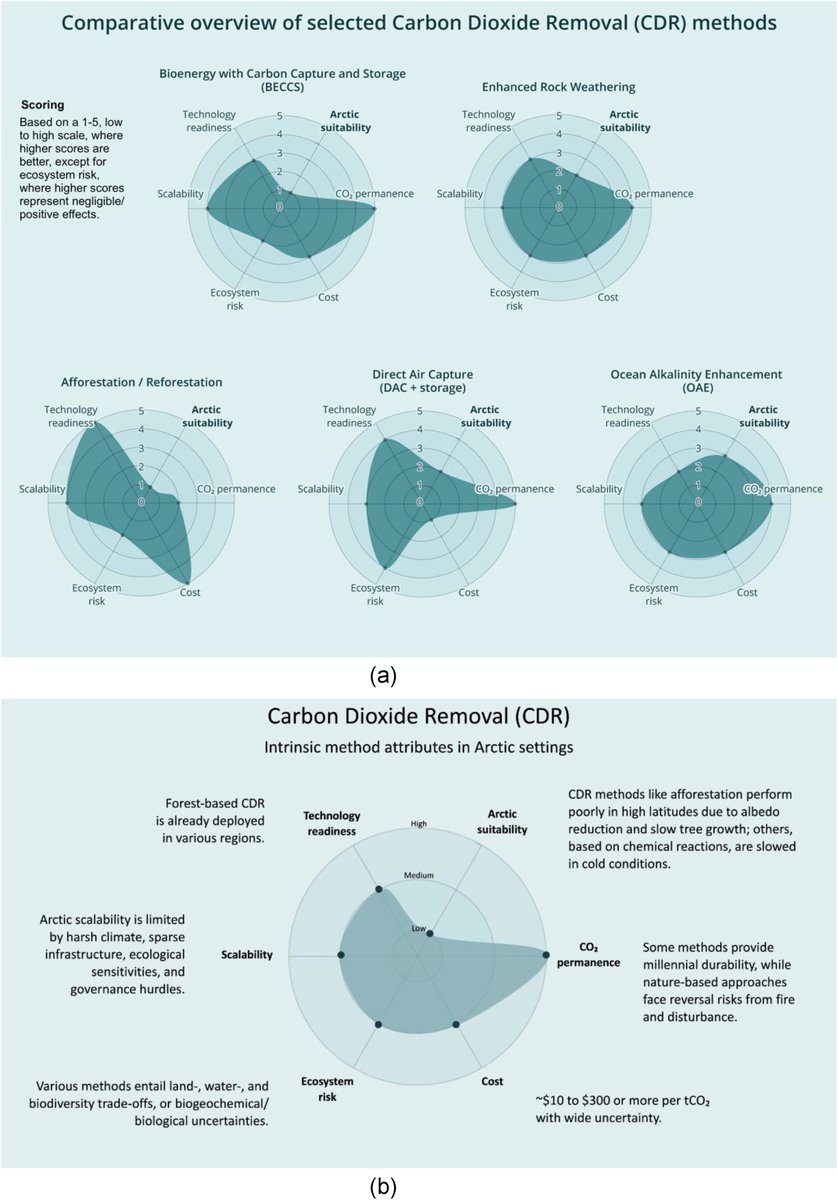
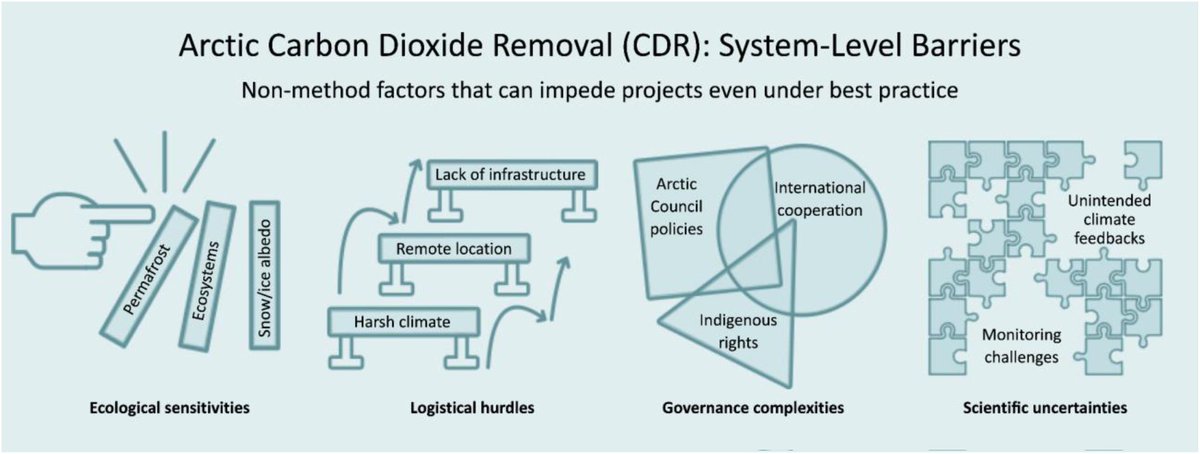
🚨NEW REVIEW PAPER🚨
"This review provides an extensive evaluation of recent advances in multiscale models used for the theoretical physical descriptions of #DirectAirCapture."
🧵
1/8
"This review provides an extensive evaluation of recent advances in multiscale models used for the theoretical physical descriptions of #DirectAirCapture."
🧵
1/8

"Reviewed (CO2 mass) transfer works span from the ab initio density functional theory calculation relationships to mesoscale Monte Carlo, molecular dynamics simulations & micro-kinetics, adsorption/desorption, & most commonly-investigated specific macroscale concept."
#DAC
2/8
#DAC
2/8

The modelled #DAC processes properties reported in the literature have been compared by the authors of this review paper, which allowed them "to identify the most effective sorbents."
3/8



3/8




This paper found that "Amine functionalized metal-organic frameworks exhibit low energy requirements, the lowest reported was 1000 kWh tCO2−1, while the lowest published cost was 60 $ tCO2−1."
#DAC
4/8
#DAC
4/8

Researchers also figured out that "the market demand for CO2 is expected to exponentially rise up to 6.1 Gt in 2050, while the cost of implementing #DAC technologies is predicted to be reduced under 125 $ tCO2−1 in the year 2030."
5/8
5/8

This paper concluded that, "further #DAC modelling research activities in CO2 (sorption) bed form phenomena could not only break the barriers of current renewable tech., but also couple the CO2 reactions with the sequestration, reactors, or with electrolysis for e-fuels."
6/8
6/8

Read the open-access review paper based on multiscale modelling of Direct Air Capture ⬇️
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
#DirectAirCapture
#DAC
#MultiscaleModellingSimulations
7/8
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
#DirectAirCapture
#DAC
#MultiscaleModellingSimulations
7/8

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh