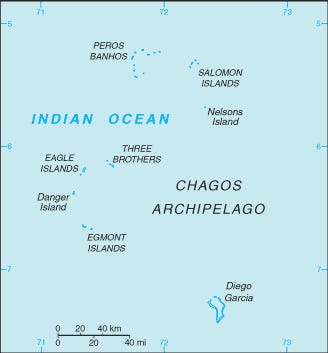
8 Disputed Island of the World.
#upsc
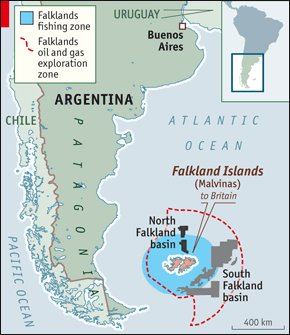
1-Falkland Islands Claims by United Kingdom and Argentina.
Location- south-west Atlantic Ocean
#upsc
1-Falkland Islands Claims by United Kingdom and Argentina.
Location- south-west Atlantic Ocean
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh