THE MOST COMMON PROBLEM WITH MEN'S PANTS
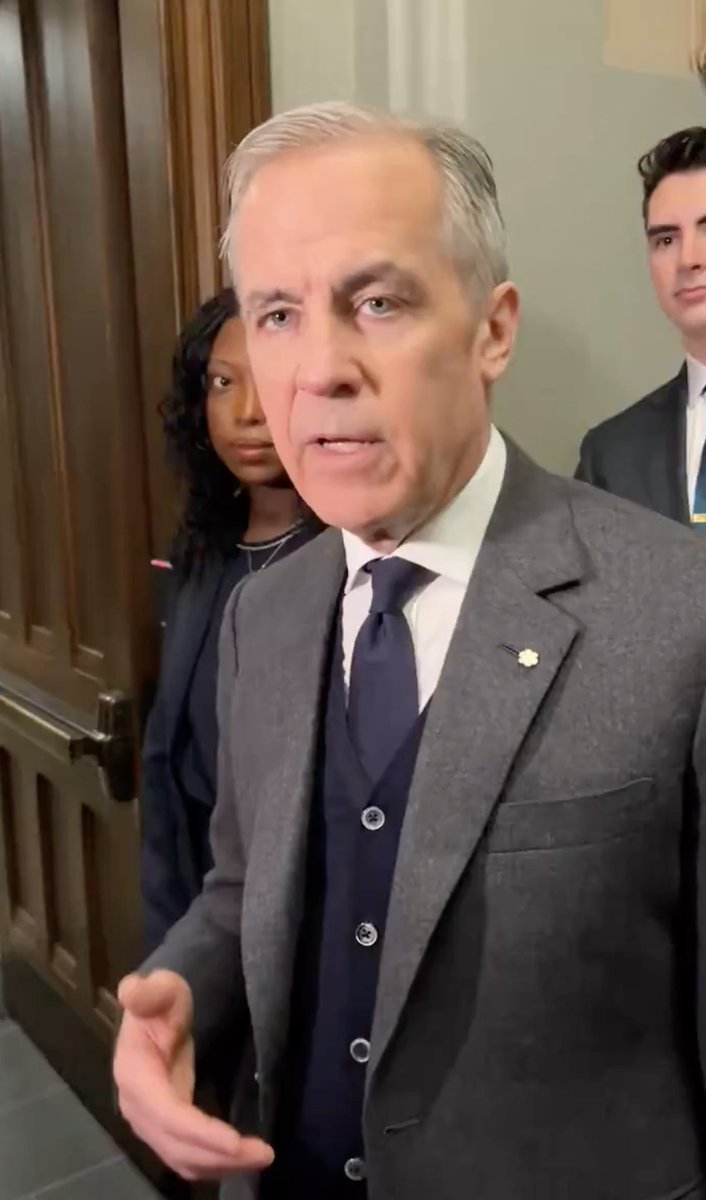
DeSantis' outfit here illustrates one of the most common problems with pants—and the one that requires a bit of know-how to fix. So let's talk about it. 🧵
DeSantis' outfit here illustrates one of the most common problems with pants—and the one that requires a bit of know-how to fix. So let's talk about it. 🧵
https://twitter.com/BryanDGriffin/status/1651939867545440256
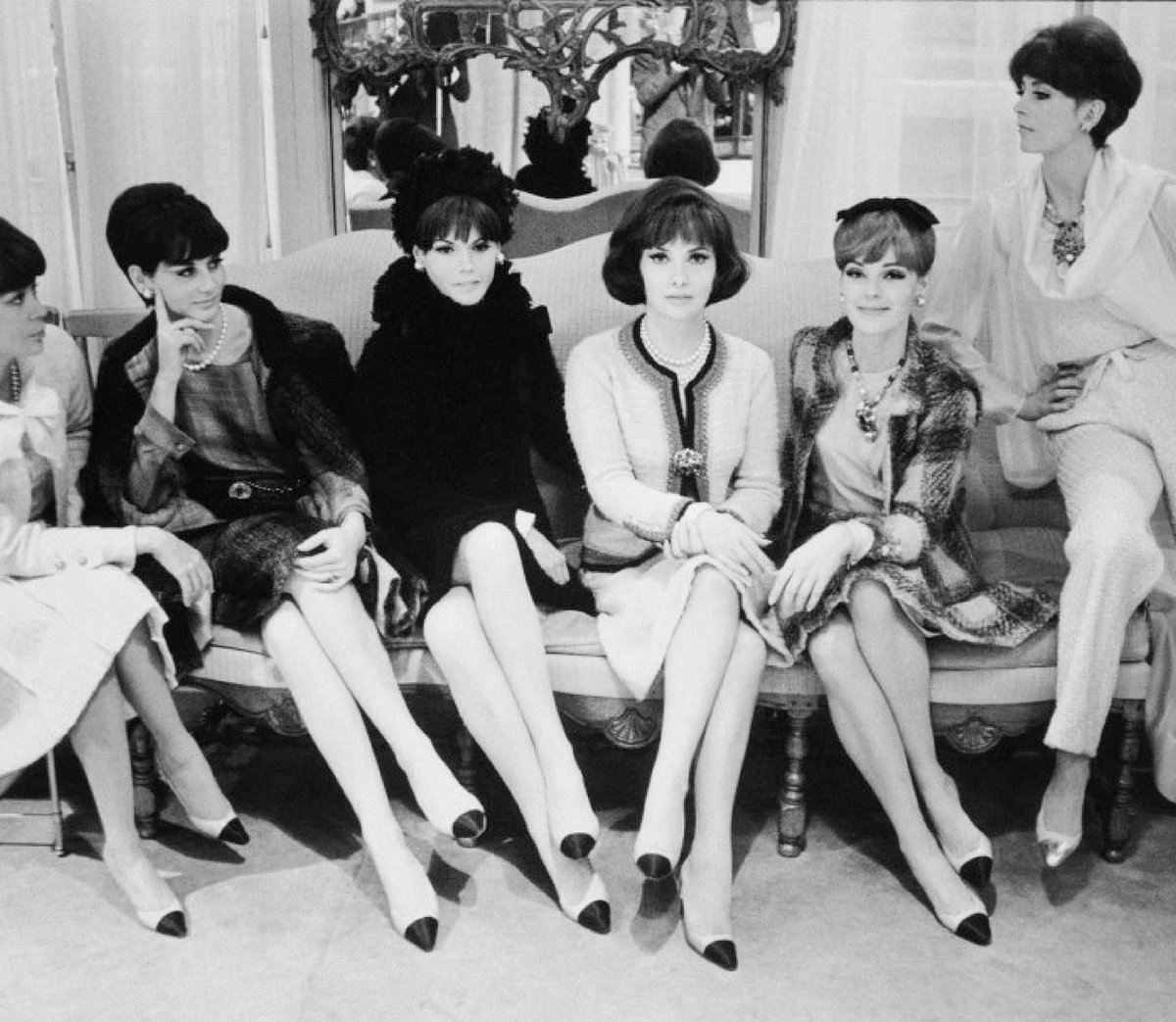
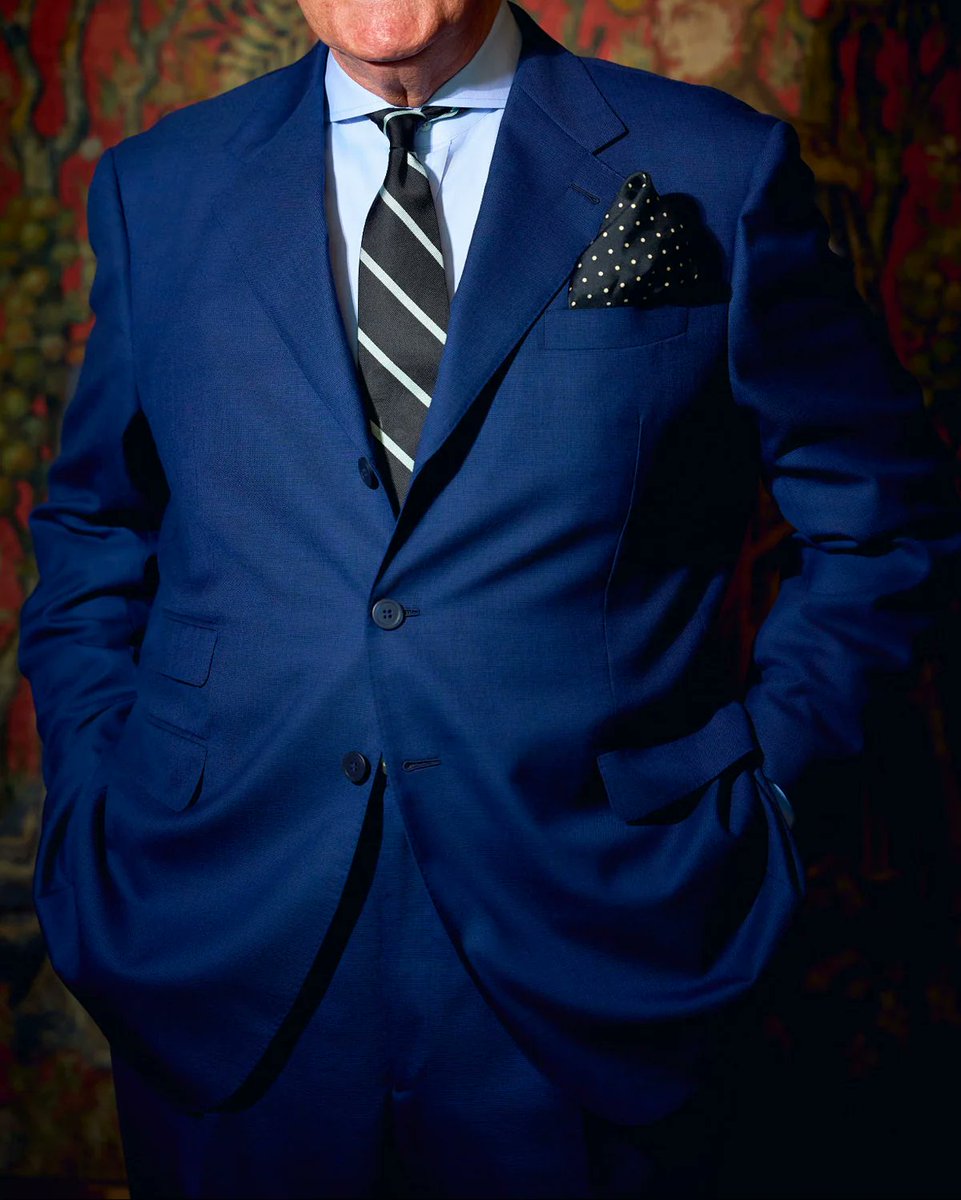
Compare these two people's trousers. Badenoch's trousers fall cleanly, such that there are relatively straight lines going from her trouser band to her hem. DeSantis' trousers, on the other hand, have messy folds all over. What gives? 





When most people buy pants, they look at themselves first in the mirror (well, hopefully, at least). When doing so, they are often standing in front of a single-frame mirror, like so: 

What they should do is find a three-way mirror, hopefully also with the assistance of a good and honest tailor, fitter, or sales associate (although these are rare nowadays). Three-way mirrors give you a better look at how your outfit looks from various angles. 

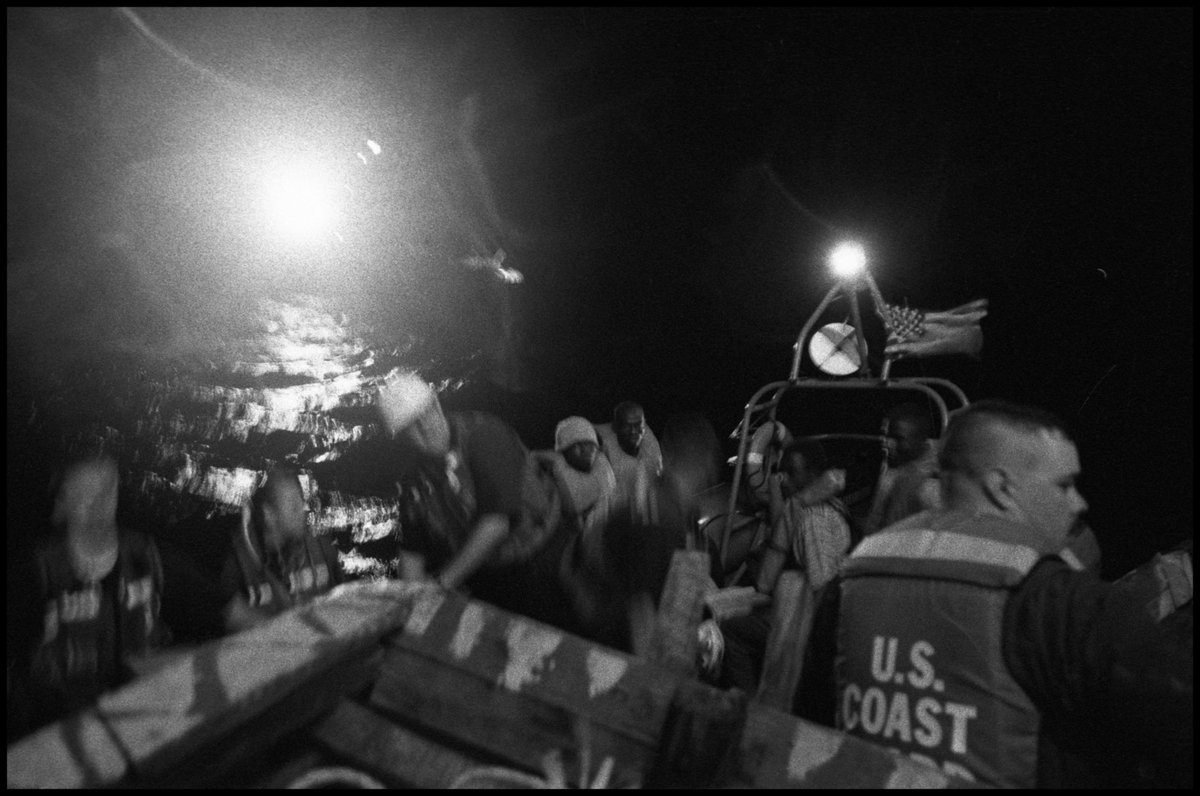
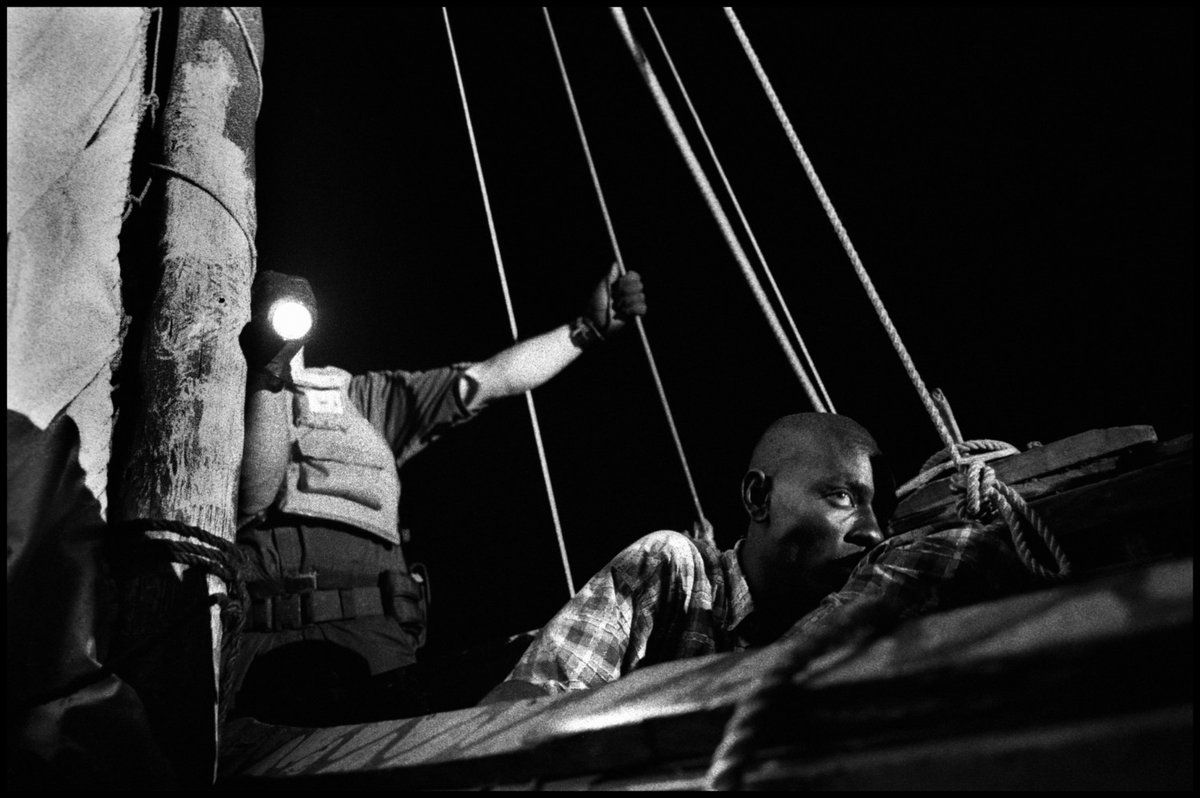
When you look at yourself in a single-frame mirror, you are only getting a view of yourself from the front (pic 1). But many problems have to do with the back, causing the drag lines and folds you see in pics 2 and 3 here: 





Why do these folds occur? It's because clothing manufacturers commonly build their trousers with an overly long back rise. That's the measurement from the center back down to the crotch. They do this so the pants feel comfy to a wider range of body types (no wedgies) 

The problem is that most people don't need all this material. Additionally, they stand with what a friend once described as an "auditioning porn star" posture. That means they naturally stand with their hips forward and knees locked. Go ahead—stand up and see if you do this.
I once heard a bespoke tailor suggest this is increasingly common in modern society because people have desk jobs, so their legs are weak. He said his clients who do manual labor have the opposite posture: knees slightly bent and hips back.
When you have a long back rise and stand with your hips back, knees locked, all of that excess material ends up collapsing under your seat and rippling down the back of your legs. That's what you see with DeSantis here. 



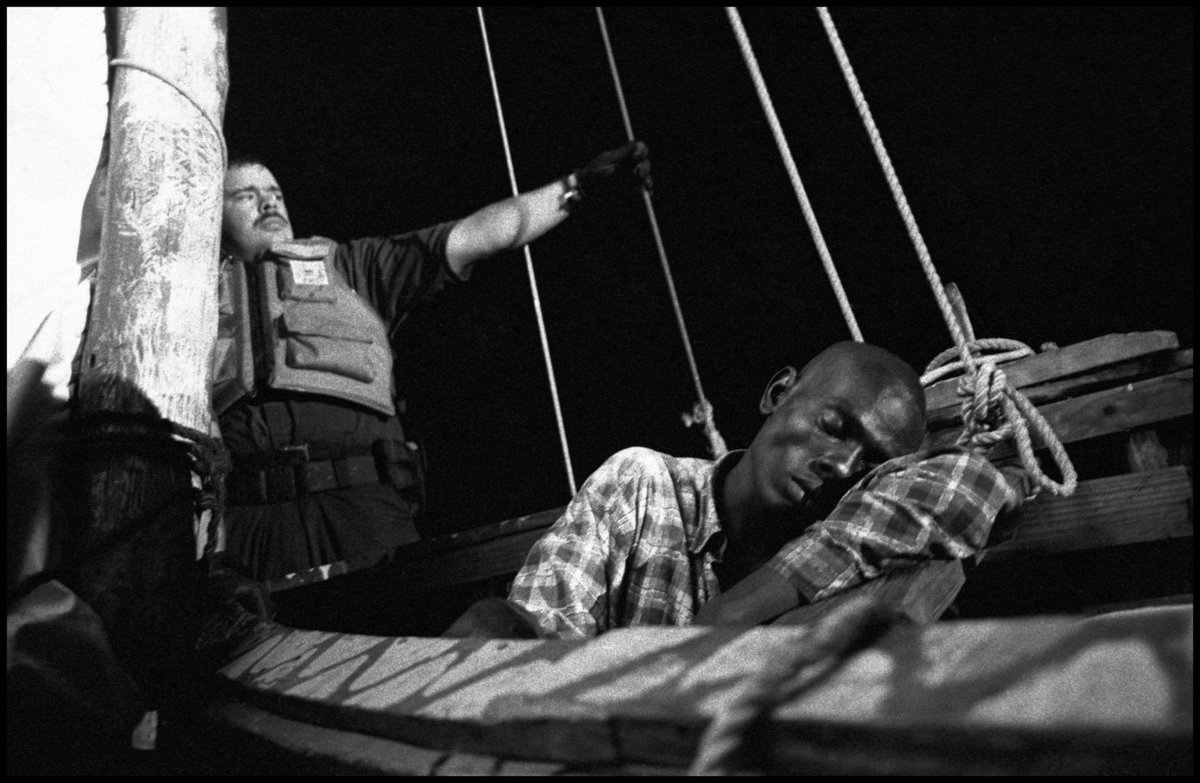
How to fix this? The best course is to have trousers made for you by a skilled bespoke tailor. See how these trousers fall cleanly.
Unfortunately, bespoke trousers are dearly expensive, commonly around $1k to $1.5k in the US. (Don't scream at me; I didn't set the price)


Unfortunately, bespoke trousers are dearly expensive, commonly around $1k to $1.5k in the US. (Don't scream at me; I didn't set the price)



The more affordable option is to know how to buy better pants. Tips:
1. If you're between sizes, err on the side of bigger. It's easier to take things in than let things out.
2. Know what can be adjusted. Assuming there's enough material, you can let out the waist by 2 inches
1. If you're between sizes, err on the side of bigger. It's easier to take things in than let things out.
2. Know what can be adjusted. Assuming there's enough material, you can let out the waist by 2 inches
It's also relatively easy to taper the legs from the knee down.
3. The most critical part is to look at how the trousers fit around the seat, thighs, and rise. These can be expensive to adjust.
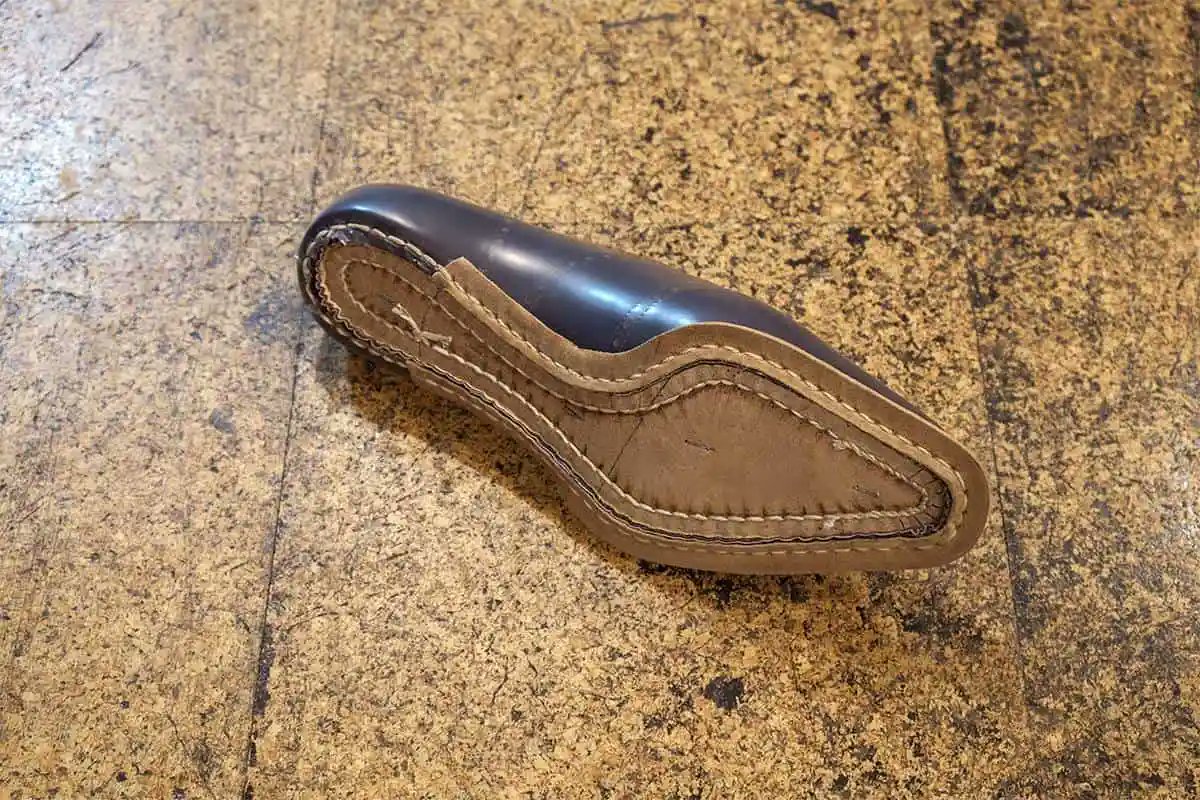
For an overly long back rise, look if there's a lot of inlay along the crotch seam
3. The most critical part is to look at how the trousers fit around the seat, thighs, and rise. These can be expensive to adjust.
For an overly long back rise, look if there's a lot of inlay along the crotch seam

To fix an overly long back rise, a tailor has to pin the back of the pants up, shortening the rise (see below). However, to make sure you don't get a wedgie, they have to let out the crotch seam. This requires enough inlay along the crotch seam inside the pants. 

Cheap pants, such as those from The Gap, won't have a lot of inlay because the manufacturer needed to scrimp on material costs. However, high-end trousers, such as those from Rota, will because there's enough margin.
See the before and after of this alteration. Magic!

See the before and after of this alteration. Magic!


If you're in the Bay Area, the best spot for custom trousers is Tailor's Keep in San Francisco. They make fully handmade pants on-premise for $1.5k. I know, the price is crazy, but they're a diamond in the rough. My pants from them are better than what I've gotten on Savile Row. 



They also have a made-to-measure program for $650. These have as much handwork as bespoke (buttonholes, pick stitch, internal waistband), but are not made in-house. Lots of room for adjustment: rise, thigh, waist, and seat, along with posture and body type (full seat, flat seat) 



Ultimately, you have to find your own fit challenges and figure out solutions. But when buying tailored trousers (and these concepts only apply to tailored trousers, not jeans), check to see if everything falls cleanly. Aim for the fit on the left, not the right. 



This tweet should say, "when you stand with your hips forward and knees locked," not "hips back." The problem of an overly long back rise is made worse when you stand like an "auditioning porn star," as my friend put it.
https://twitter.com/dieworkwear/status/1652104061641170944
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh