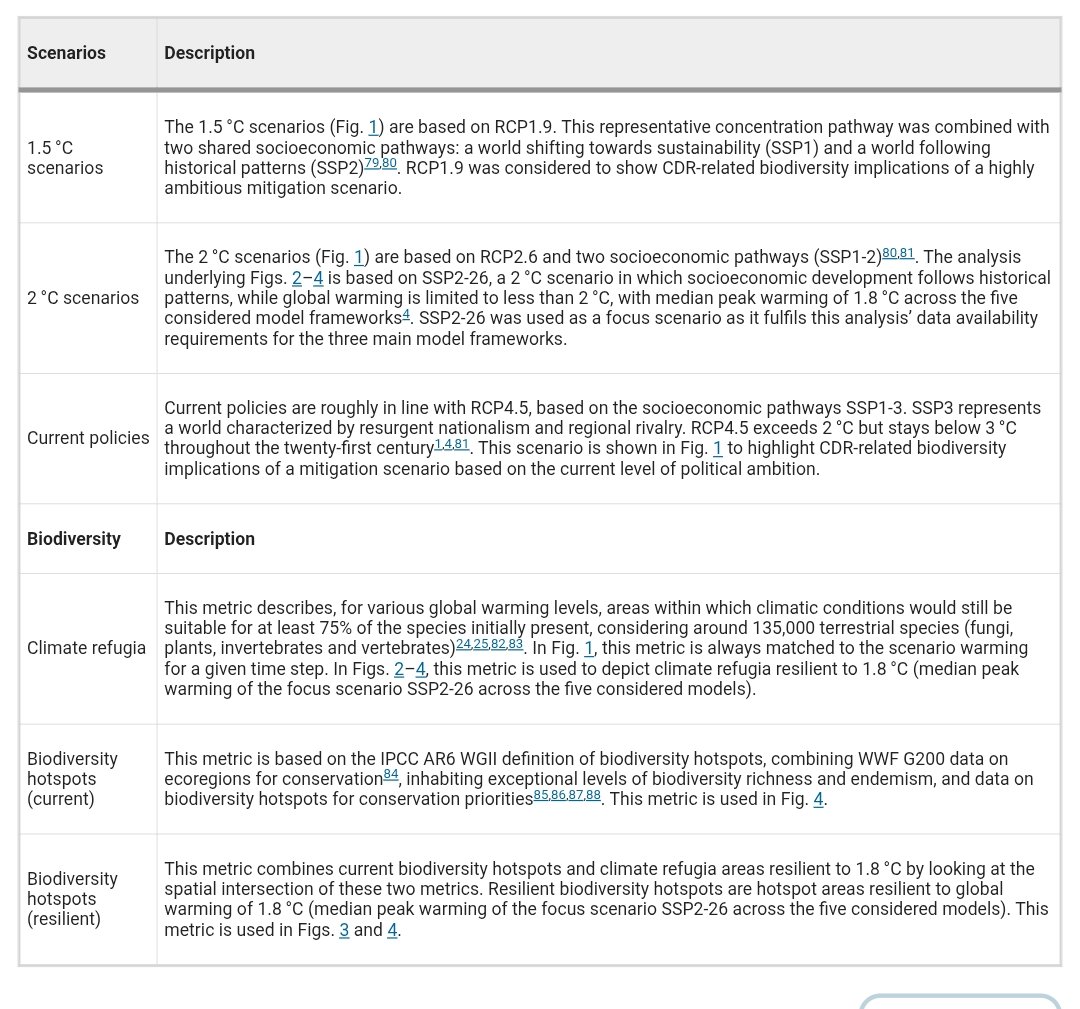
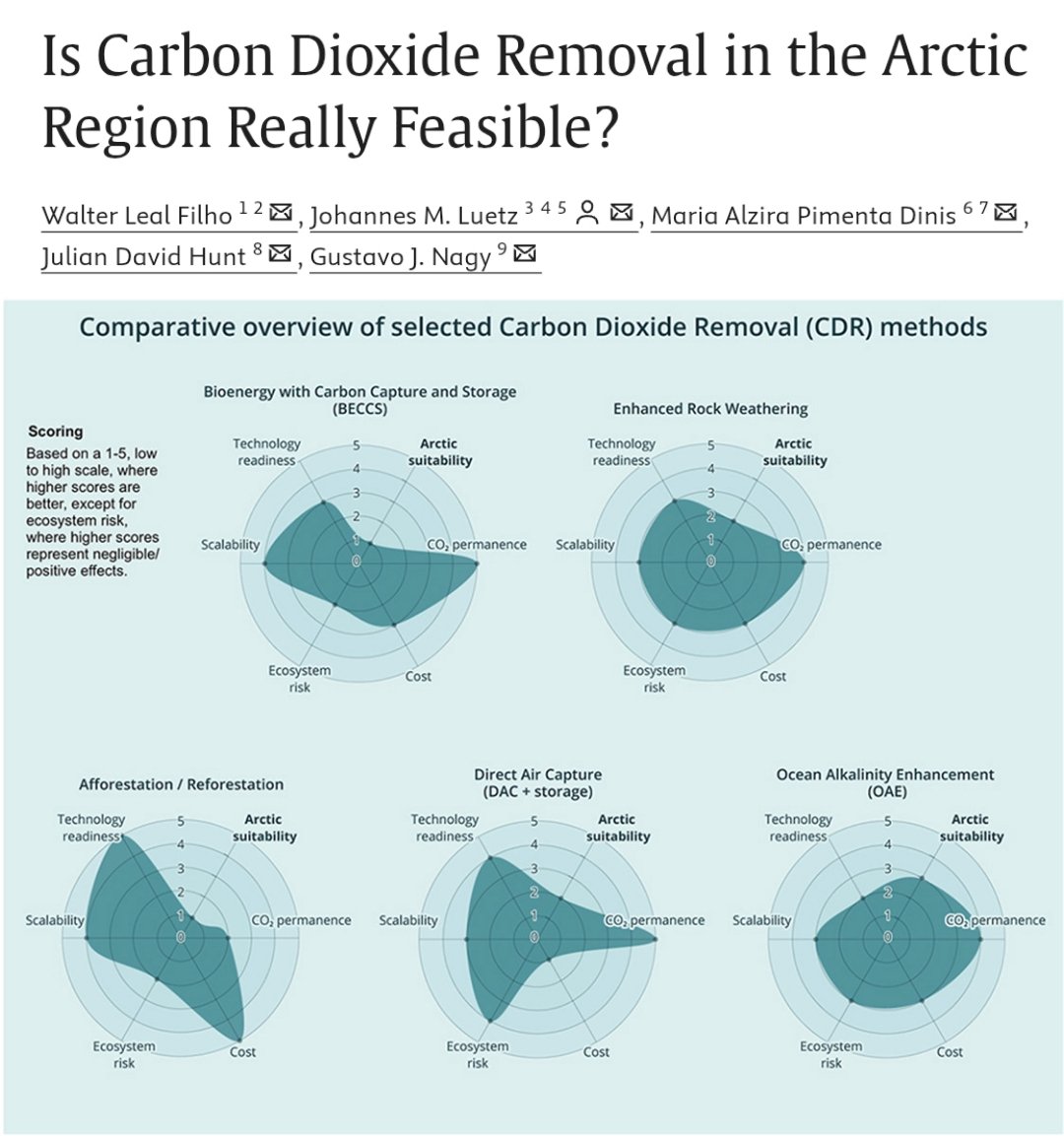
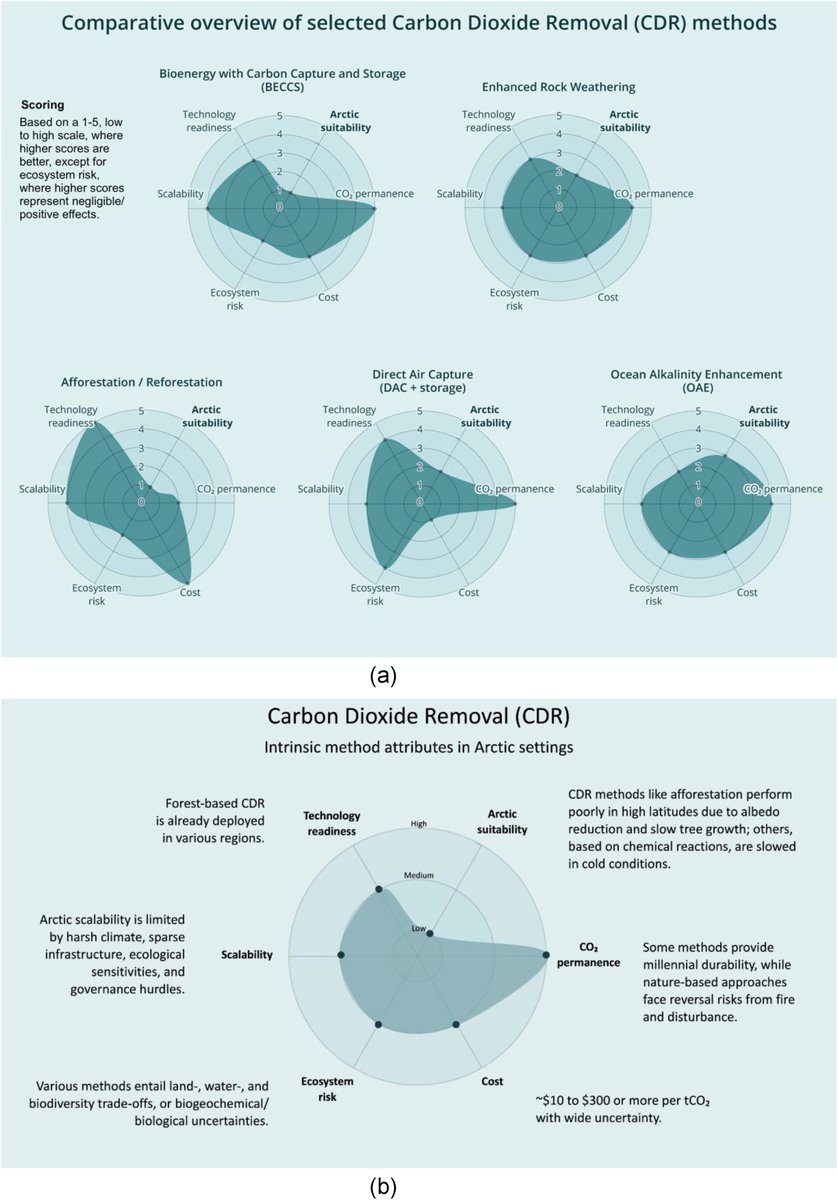
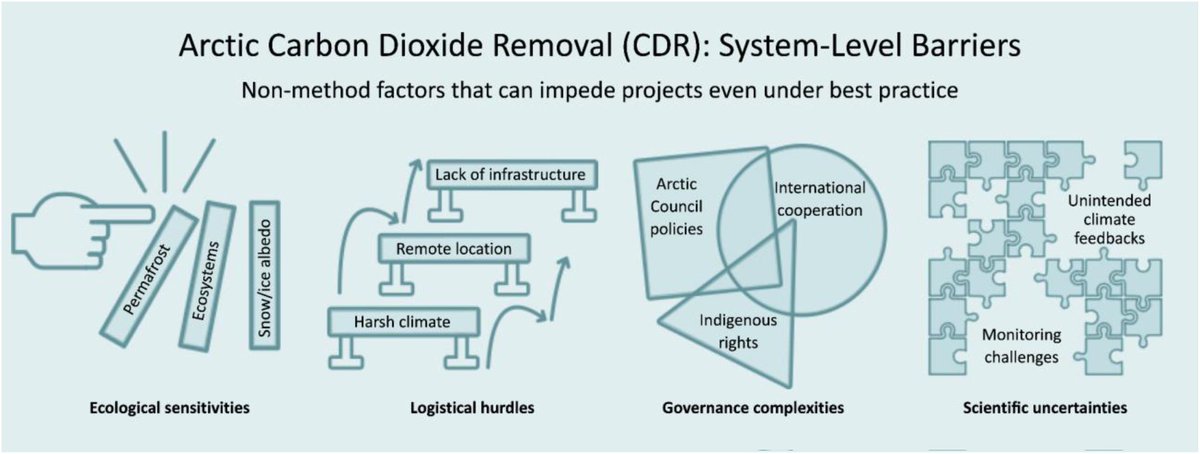
🚨𝐅𝐨𝐫 #𝐂𝐃𝐑 𝐅𝐨𝐥𝐤𝐬!🚨
ICYM any recent developments in the field of #CarbonDioxideRemoval published btw 𝐉𝐚𝐧𝐮𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝟐𝟎𝟐𝟑 & 𝐀𝐩𝐫𝐢𝐥 𝟐𝟎𝟐𝟑, here are links to (in🧵⬇️) all pertinent research papers, news articles, reports, thesis, event recordings, & podcasts ⬇️
ICYM any recent developments in the field of #CarbonDioxideRemoval published btw 𝐉𝐚𝐧𝐮𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝟐𝟎𝟐𝟑 & 𝐀𝐩𝐫𝐢𝐥 𝟐𝟎𝟐𝟑, here are links to (in🧵⬇️) all pertinent research papers, news articles, reports, thesis, event recordings, & podcasts ⬇️

If you want to keep updated with the latest #CarbonDioxideRemoval news, subscribe ➡️rb.gy/0r86d
#DirectAirCapture 🎛️
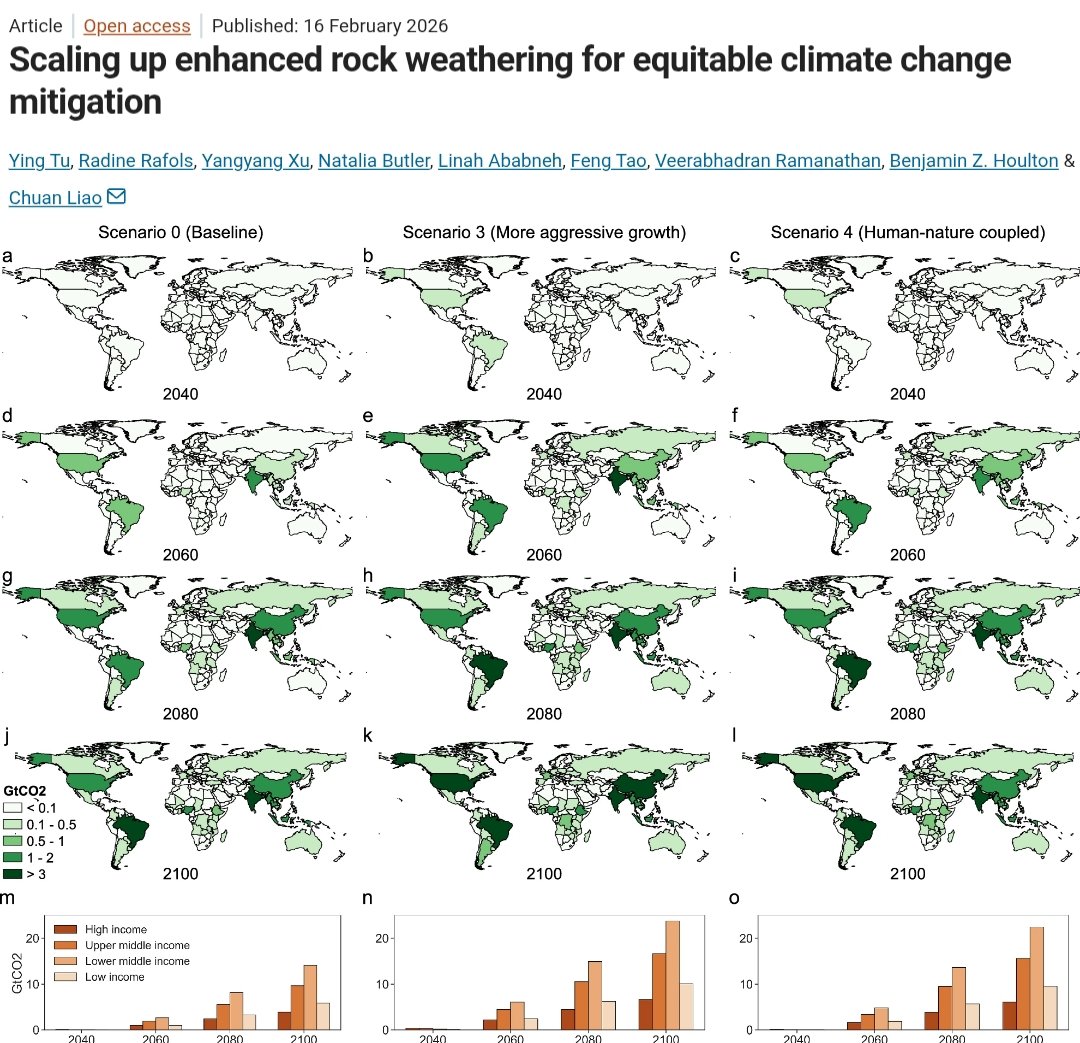
#EnhancedWeathering 🌱🚜
#OceanAlkalinityEnhancement 🌊
#Afforestation 🌳🌲
#OceanIronFertilization 🌊
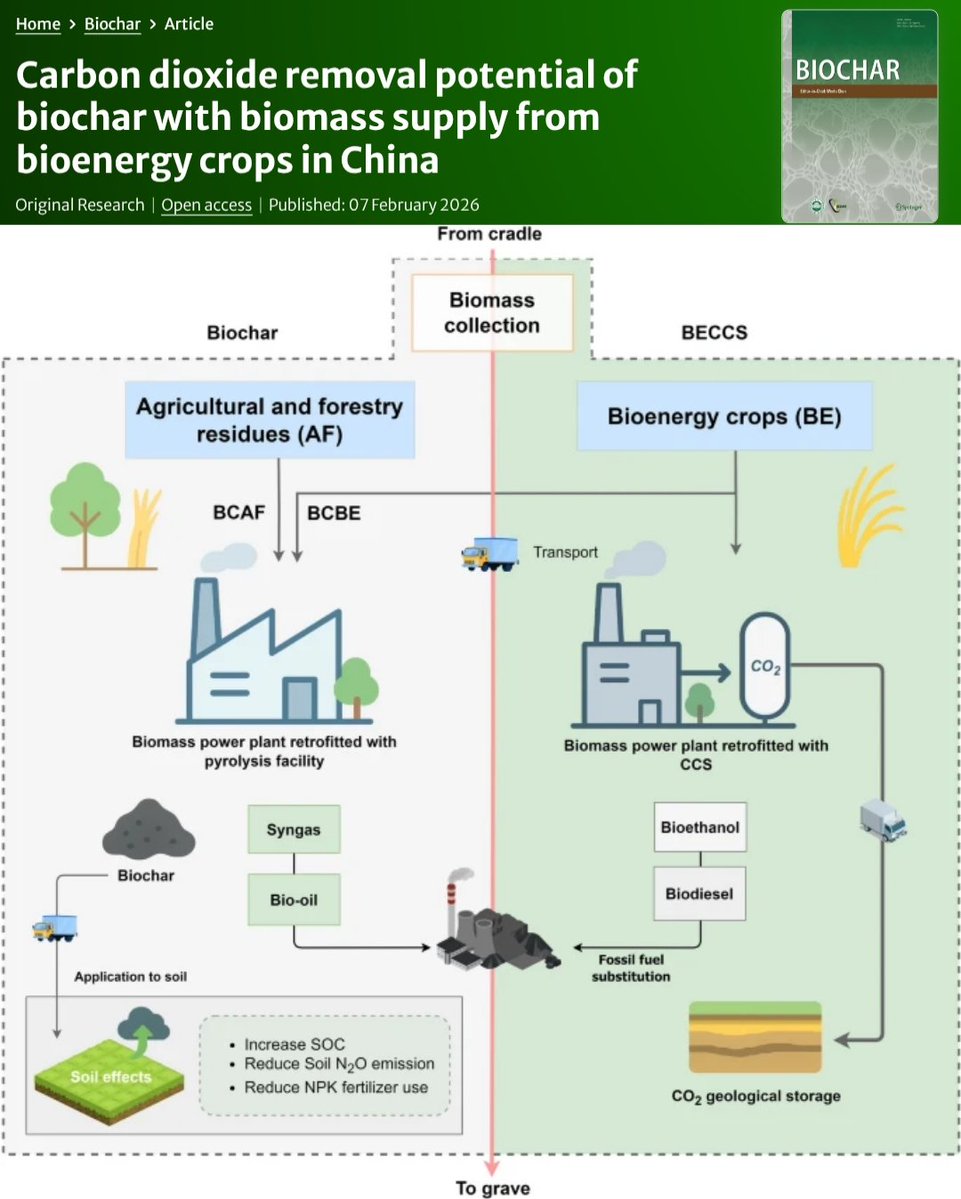
#Biochar 🪨
#BECCS 🌿🌾🥜
6/6



#DirectAirCapture 🎛️
#EnhancedWeathering 🌱🚜
#OceanAlkalinityEnhancement 🌊
#Afforestation 🌳🌲
#OceanIronFertilization 🌊
#Biochar 🪨
#BECCS 🌿🌾🥜
6/6



• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh