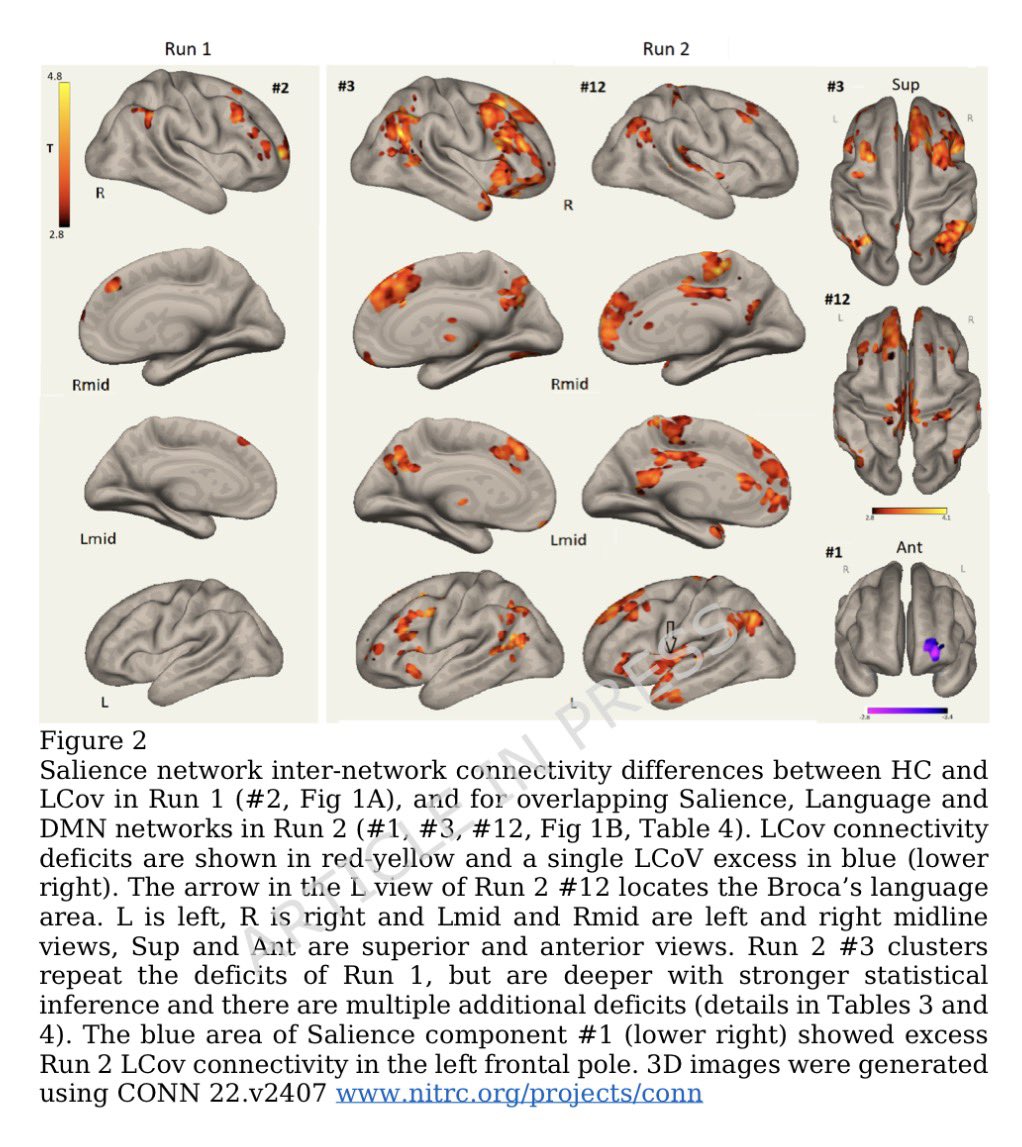
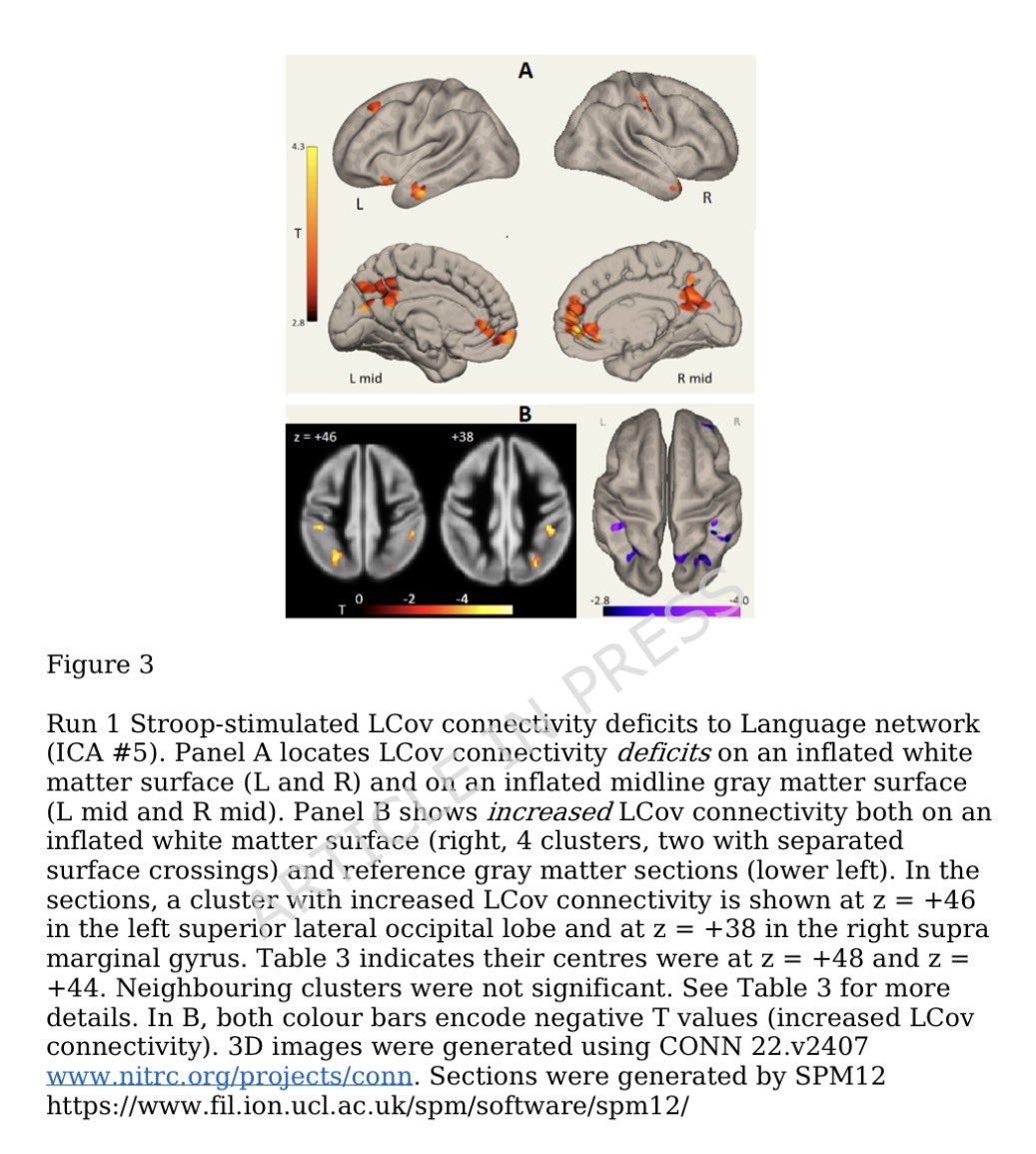
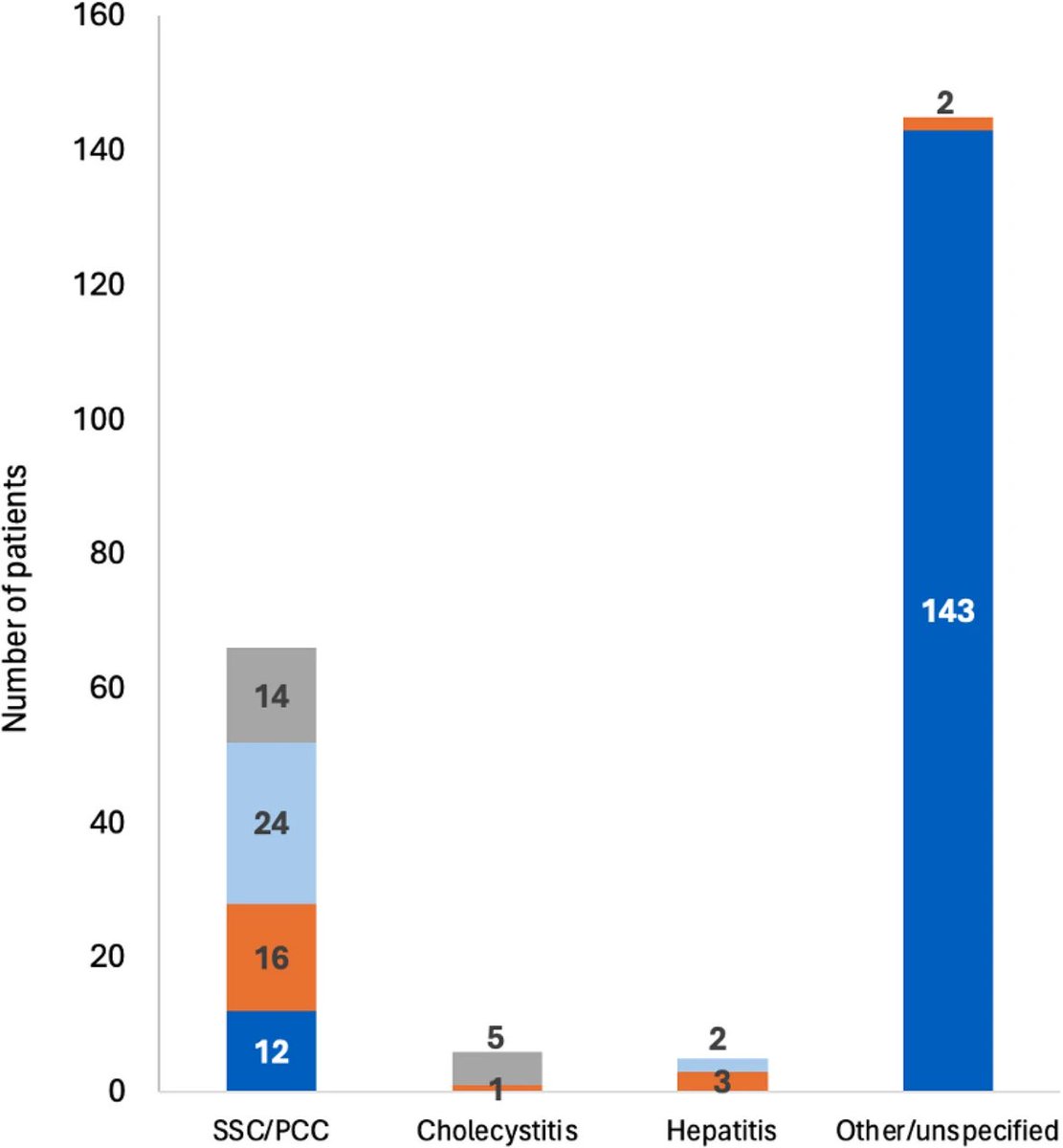
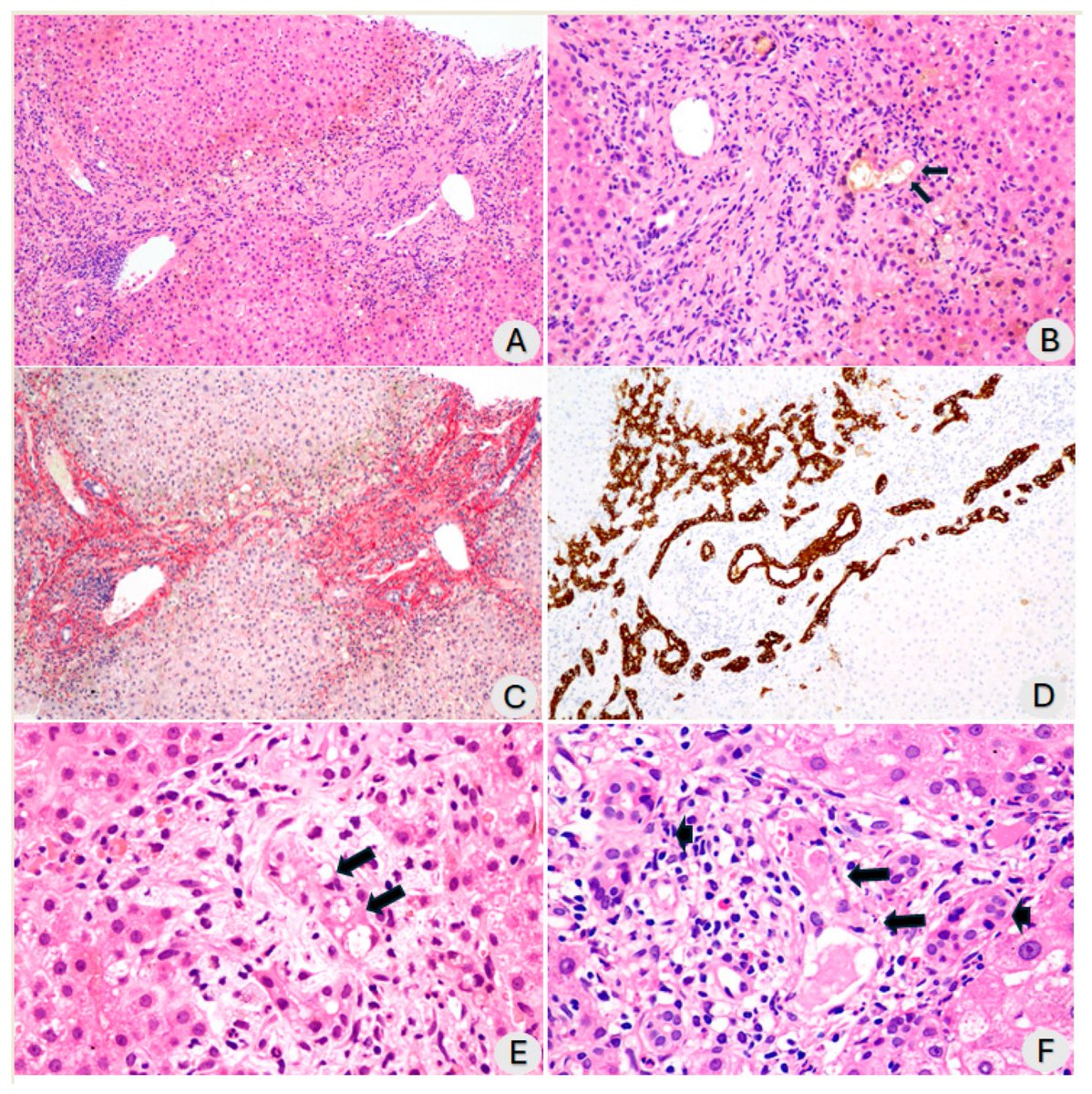
Some more info on XBB.2.3. Aka #Acrux
➡️ XBB.2.3 has 4 defining mutations:
-Spike mutations: S:D253G & S:P521S
-ORF mutations: ORF1a:G2091S & ORF7a:A13V
-Beyond XBB.2, #Acrux XBB.2.3 has the Spike P521S & S486P mutations 1/
H/T: @T_Brautigan
➡️ XBB.2.3 has 4 defining mutations:
-Spike mutations: S:D253G & S:P521S
-ORF mutations: ORF1a:G2091S & ORF7a:A13V
-Beyond XBB.2, #Acrux XBB.2.3 has the Spike P521S & S486P mutations 1/
H/T: @T_Brautigan
➡️ Acrux XBB.2.3 was first spotted in India (Karnataka) & then in the USA—origin is somewhat unclear.
Here is the animated map by @Mike_Honey_ showing the spread of the XBB.2.3.* "Acrux" variant around the world. 2/
Here is the animated map by @Mike_Honey_ showing the spread of the XBB.2.3.* "Acrux" variant around the world. 2/
➡️ Singapore (26%) and India (22%) are still the hotspots.
Spain (11%) and Australia (8%) are also showing recent growth.
Spotted in many other countries including Japan, South Korea, China, the UK & the US. 3/
Spain (11%) and Australia (8%) are also showing recent growth.
Spotted in many other countries including Japan, South Korea, China, the UK & the US. 3/

Though it is present in China & Japan, but still trying to find its way through some other dominant XBBs like XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.1.9 etc 4/ 

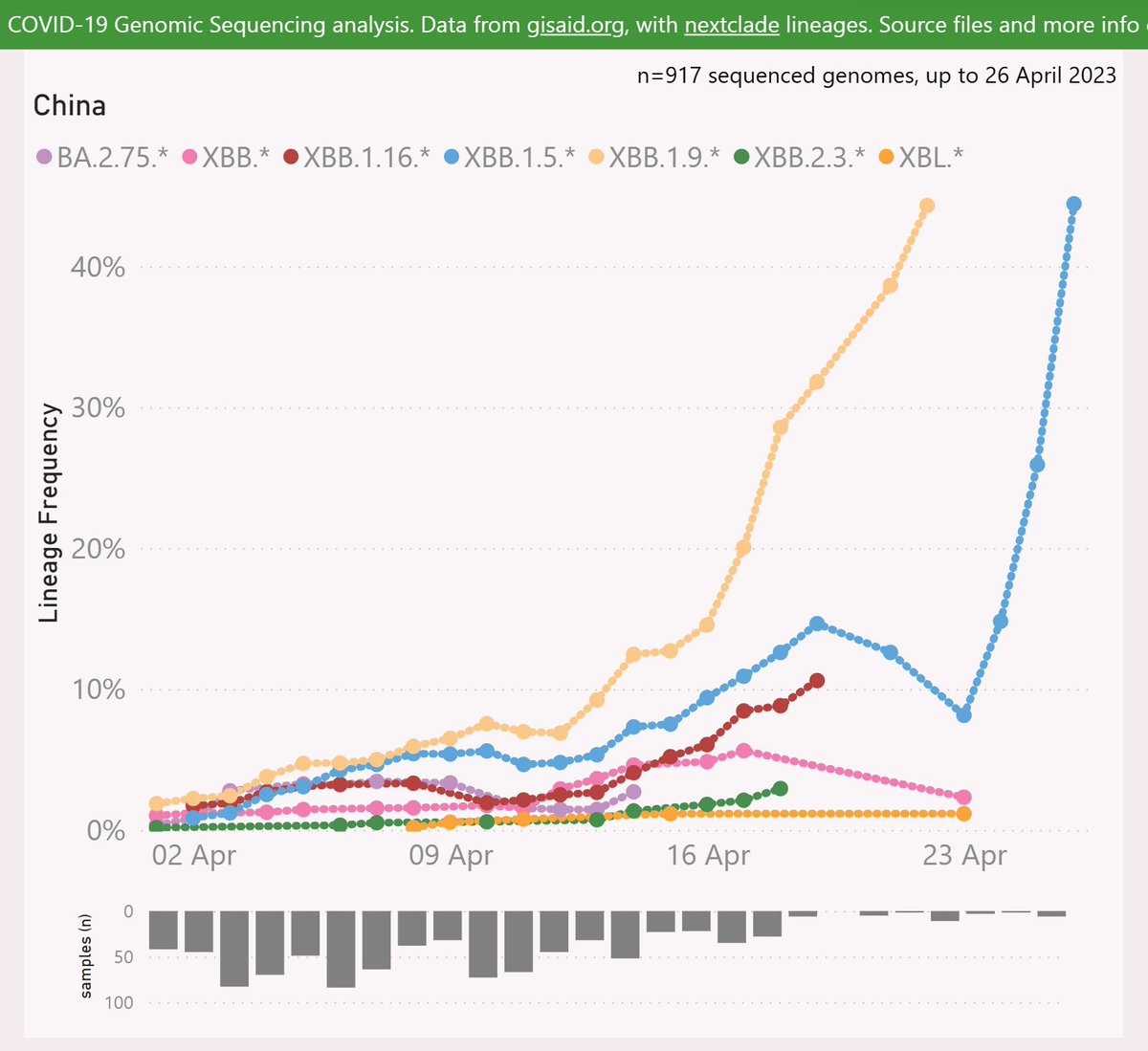

➡️ #Acrux is evolving fast in to many offsprings, and one of its descendants, XBB.2.3.2 is considered to be the fastest.
According to @LongDesertTrain, XBB.2.3.2 also has an interesting mute ORF1a:R2159W (NSP3_R1341W) that has shown up in several fast-growing lineages 5/
According to @LongDesertTrain, XBB.2.3.2 also has an interesting mute ORF1a:R2159W (NSP3_R1341W) that has shown up in several fast-growing lineages 5/
➡️ In India, the share of #Acrux XBB.2.3 is increasing, but still it is not able to outcompete currently dominant #Arcturus. However, its offspring XBB.2.3.2 may have some edge over it 6/
H/T: @siamosolocani
H/T: @siamosolocani

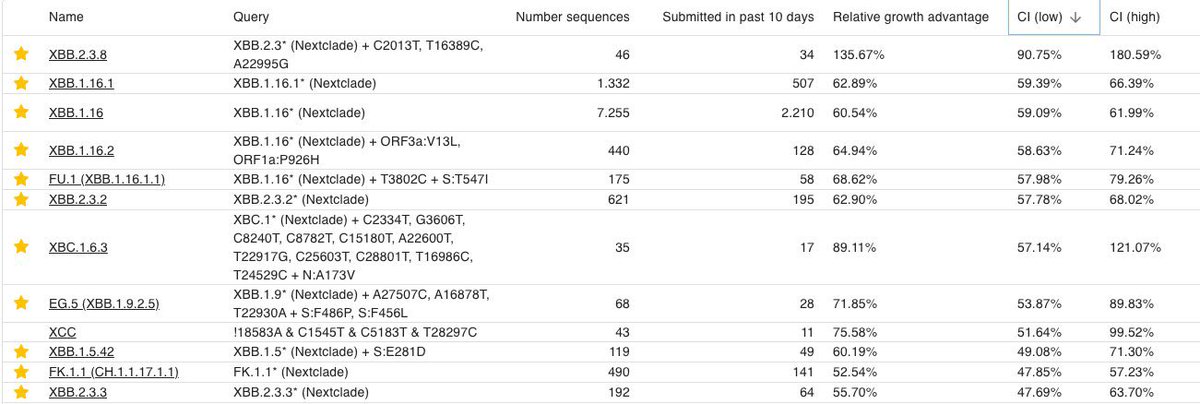
➡️ Another offspring of the XBBB.2.3 aka #Acrux, XBB.2.3.8 +478R is worth monitoring.
Here is the latest table of currently dominant, some key subvariants by @siamosolocani 7/
Here is the latest table of currently dominant, some key subvariants by @siamosolocani 7/
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh