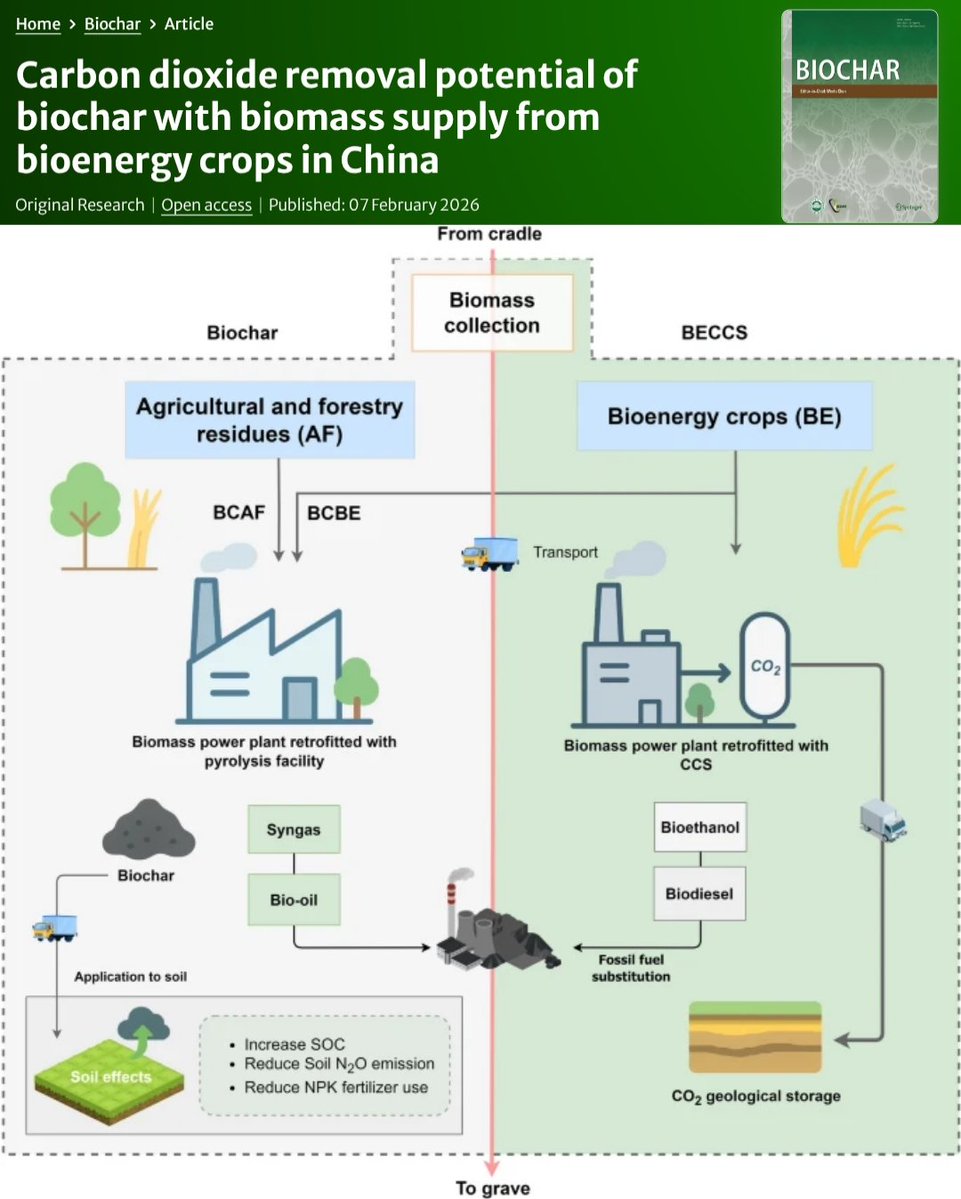
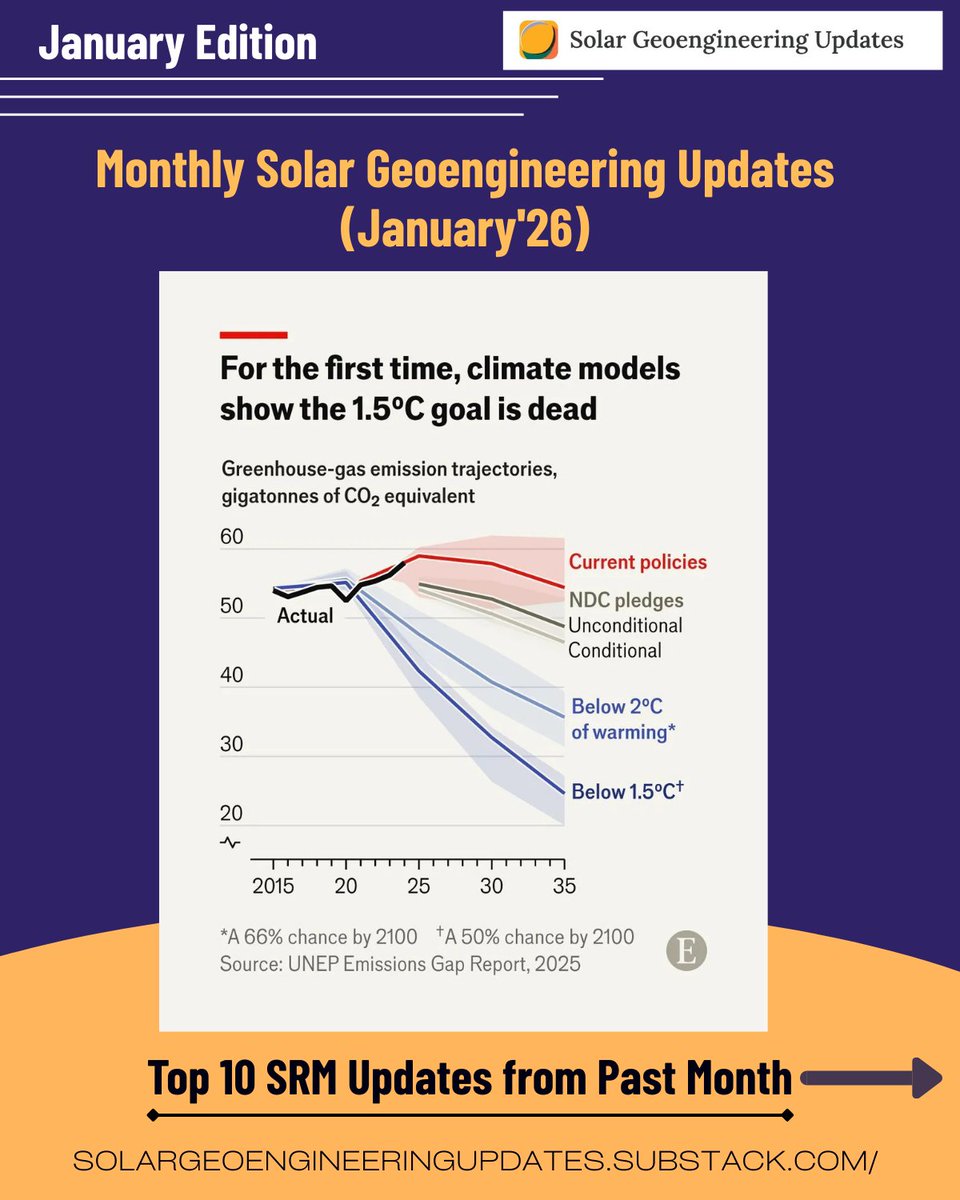
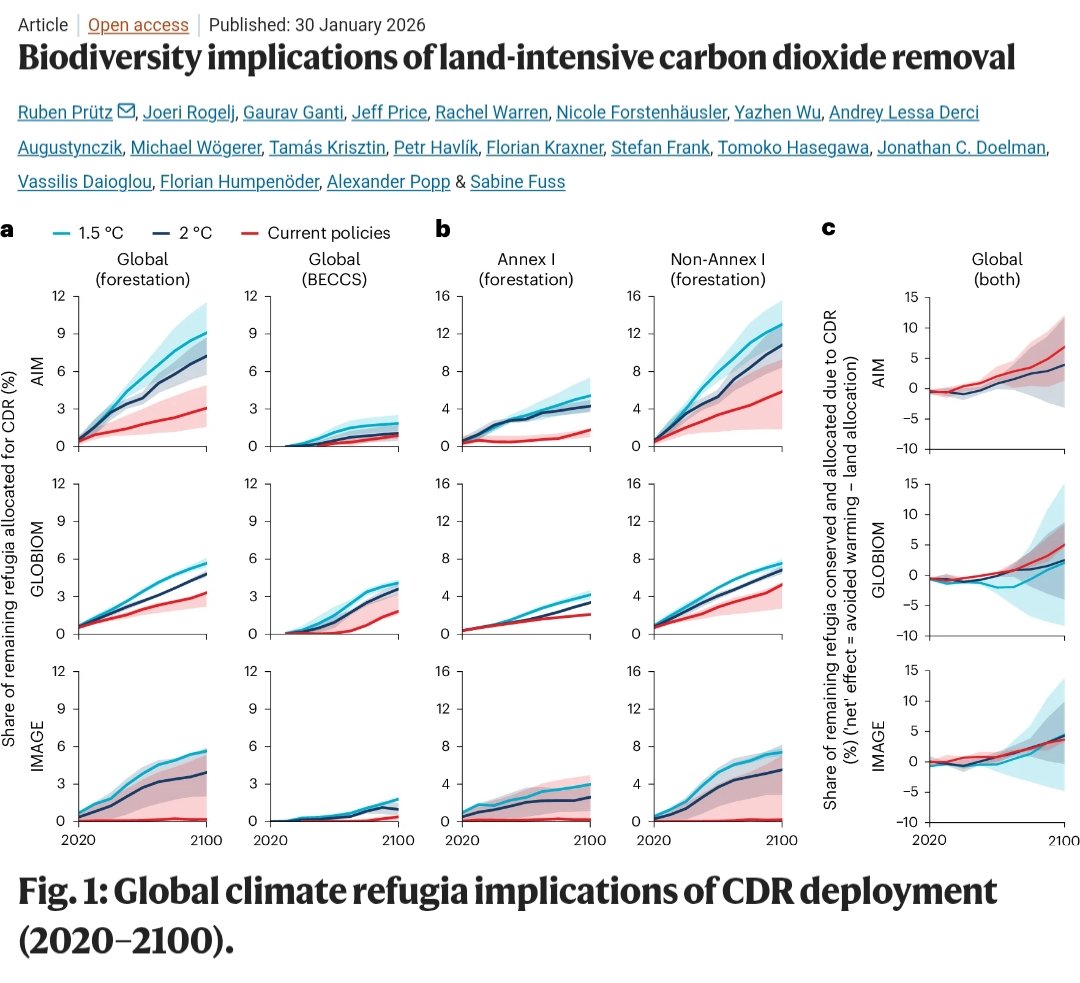
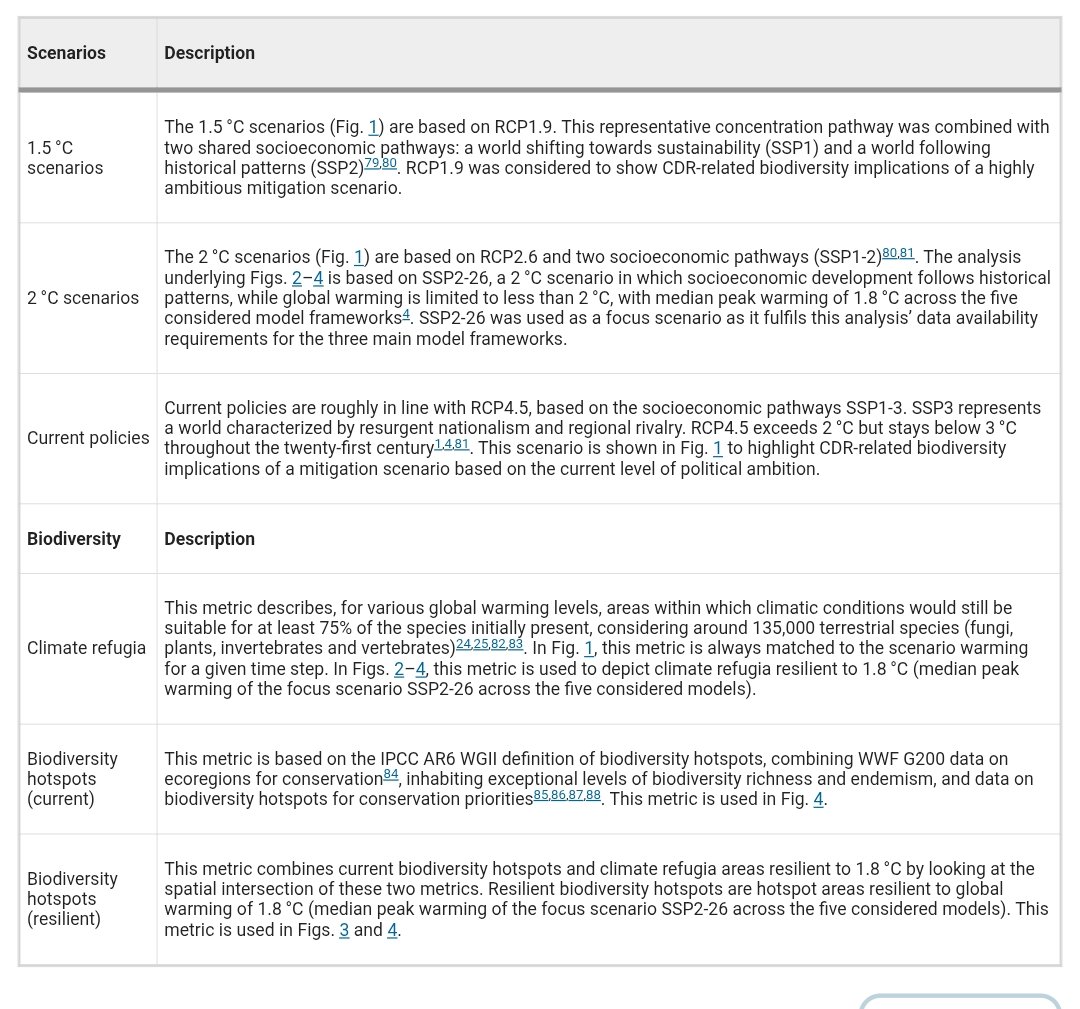
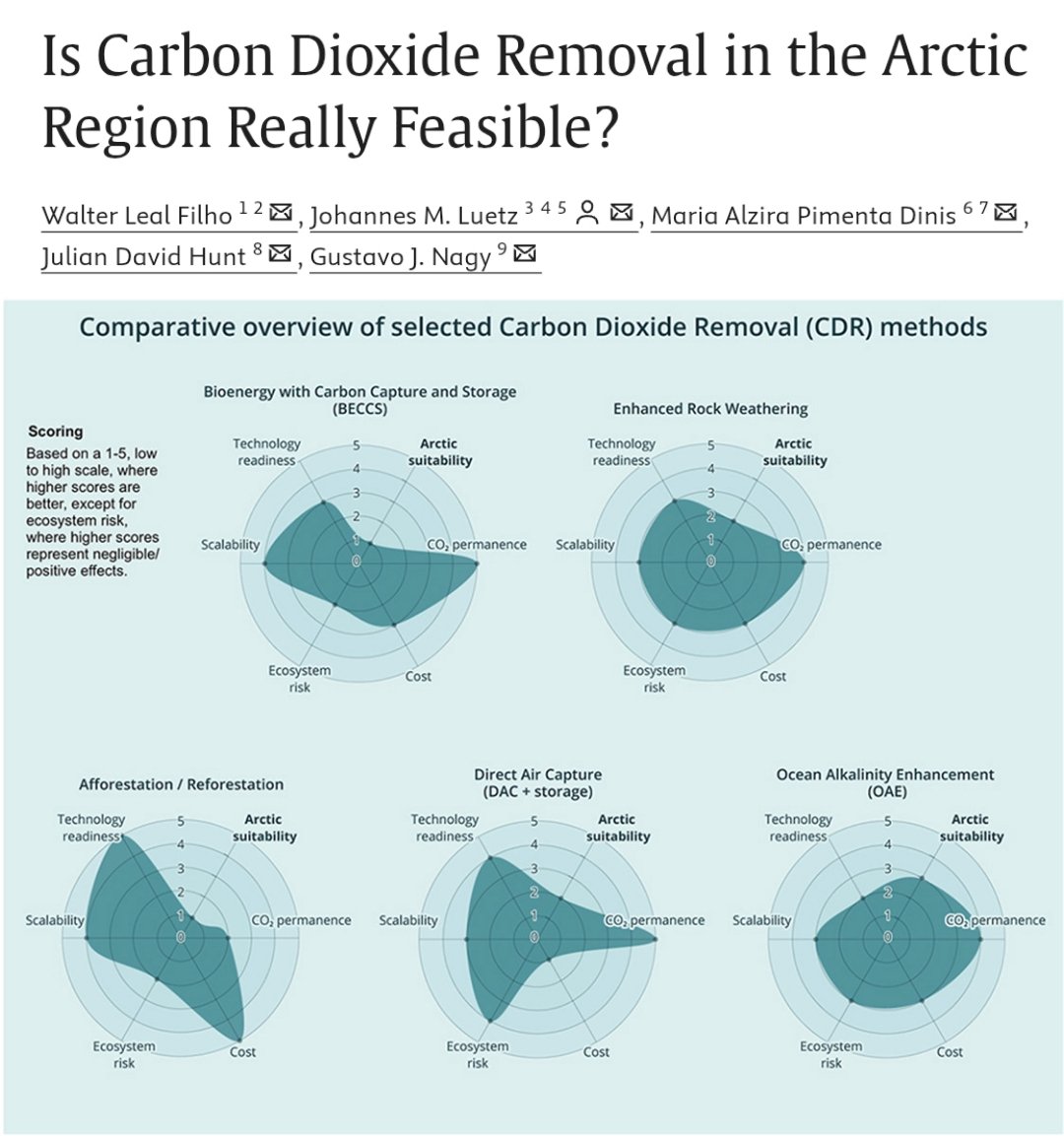
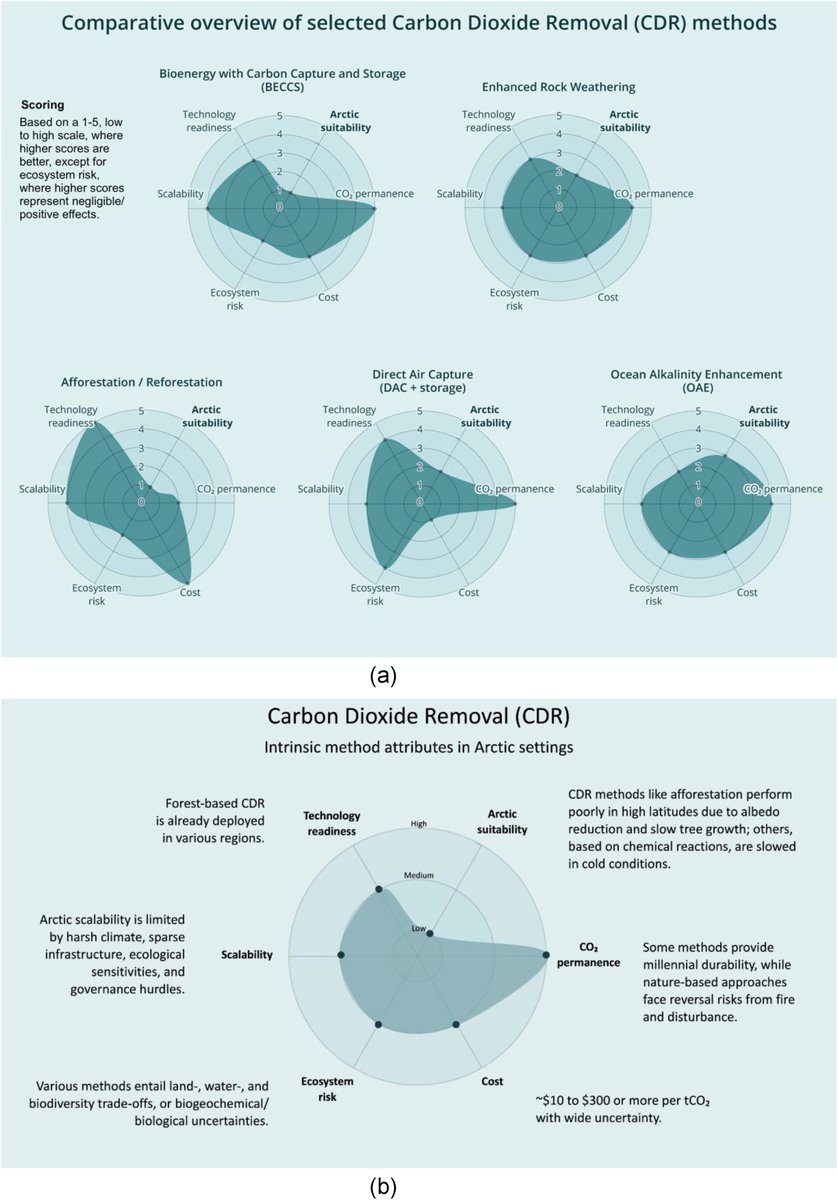
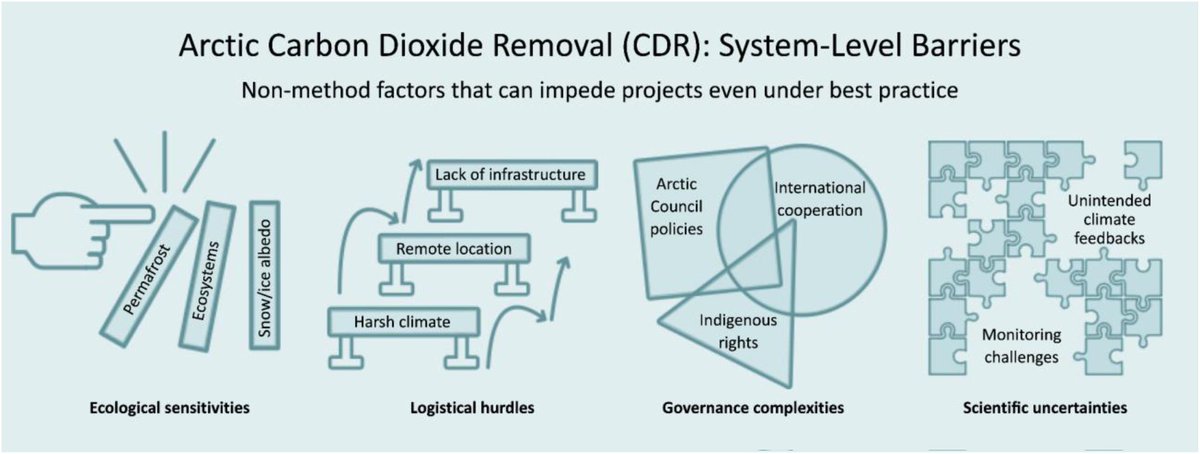
🚨𝐍𝐄𝐖 𝐒𝐓𝐔𝐃𝐘🚨
"Stratospheric Aerosol Geoengineering (SAG) is a proposed #SolarGeoengineering approach to offset #ClimateChange impacts, but may have -ve effects on hydrology."
In this regard new study is published in "𝐶𝑙𝑖𝑚𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝐷𝑦𝑛𝑎𝑚𝑖𝑐𝑠."
Details ⬇️
🧵1/9
"Stratospheric Aerosol Geoengineering (SAG) is a proposed #SolarGeoengineering approach to offset #ClimateChange impacts, but may have -ve effects on hydrology."
In this regard new study is published in "𝐶𝑙𝑖𝑚𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝐷𝑦𝑛𝑎𝑚𝑖𝑐𝑠."
Details ⬇️
🧵1/9
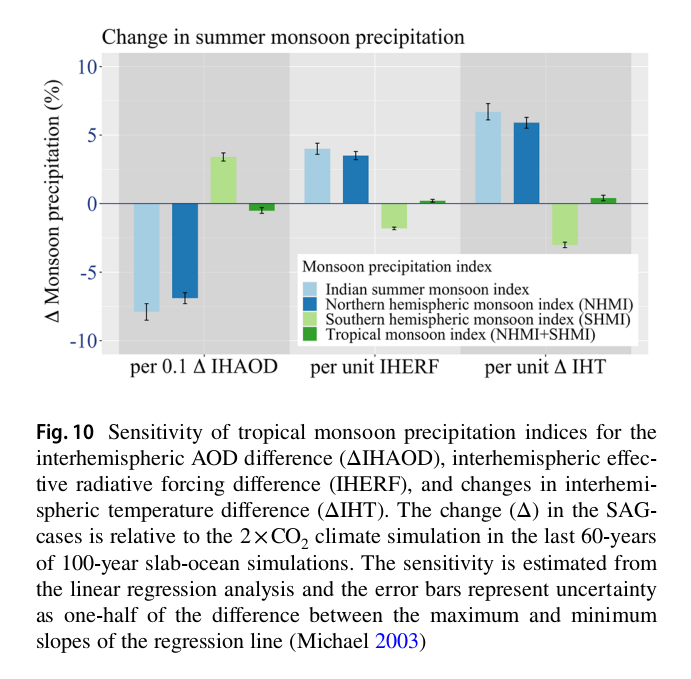
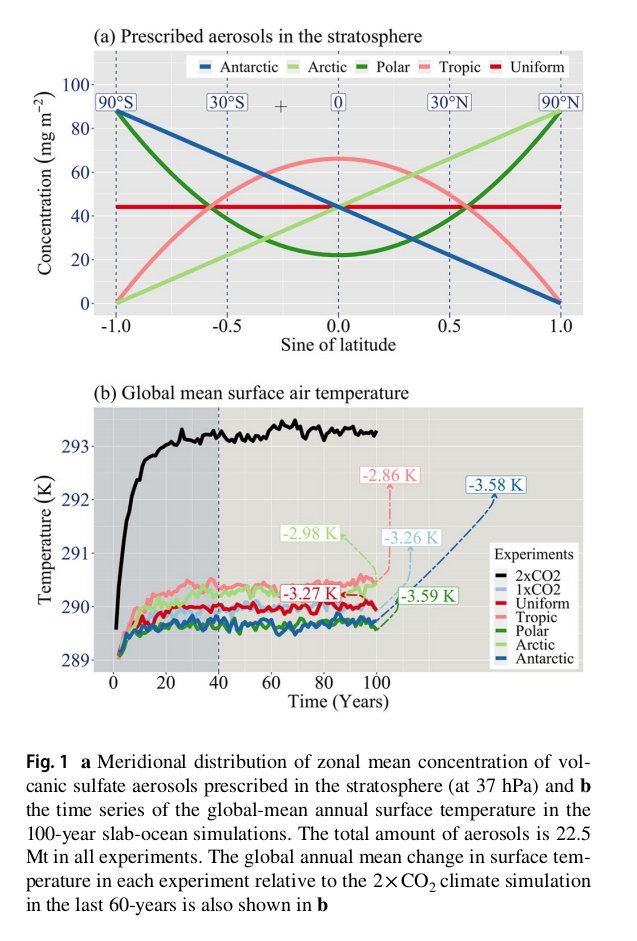
"Using a climate model, researchers quantify the sensitivity of the tropical monsoon precipitation to the meridional distribution of volcanic #SulfateAerosols prescribed in the #stratosphere in terms of the changes in aerosol optical depth (AOD)."
2/9
2/9
"In the experiments, large changes in summer monsoon 🌧️ in the tropical monsoon areas are simulated, mainly over the Indian region, in alliance with meridional shifts in the location of the intertropical convergence zone caused by changes in interhemispheric AOD differences."
3/9
3/9

Based on the simulations of this study, authors "estimate a sensitivity of −1.8°±0.0° meridional shift in global mean ITCZ & a 6.9±0.4% reduction in NH monsoon index (NHMI; summer monsoon precipitation over NH monsoon regions) /0.1 interhemispheric AOD difference (NH-SH)."
4/9
4/9

This study also "quantify the sensitivity in terms of interhemispheric (IH) differences in effective #RadiativeForcing & IH temperature differences: 3.5±0.3% change in NHMI per unit (Wm⁻²) IH radiative forcing difference & 5.9±0.4% change/unit (°C) IH temp. difference."
5/9

5/9


"Similar sensitivity estimates are also made by the researchers of this study for the Indian monsoon precipitation."
6/9

6/9


"The establishment of the relationship btw interhemispheric AOD (or radiative forcing) differences and ITCZ shift as discussed in this paper will further facilitate and simplify understanding of the effects of #StratosphericAerosolGeoengineering on tropical monsoon rainfall."
7/9
7/9

Read the study entitled, "Quantification of tropical monsoon precipitation changes in terms of interhemispheric differences in stratospheric sulfate aerosol optical depth" here ⬇️
researchgate.net/publication/37…
#StratosphericAerosolGeoengineering
#SolarGeoengineering
8/9
researchgate.net/publication/37…
#StratosphericAerosolGeoengineering
#SolarGeoengineering
8/9
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh