Statins are nuking your mitochondria.
This 🧵explores how statins impact our metabolic pathways and how this relates to the side-effects people experience.
#Statins #Mitochondria
This 🧵explores how statins impact our metabolic pathways and how this relates to the side-effects people experience.
#Statins #Mitochondria

Statins act by reversibly and competitively inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, a key enzyme in the mevalonate pathway of which cholesterol is a final product.
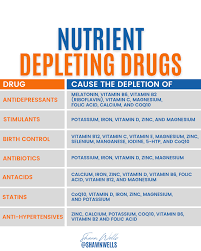
Cholesterol acts as an intermediate for steroid hormones, bile acids and vitamin D, CoQ10 and is crucial to the integrity of all cell membranes.
This partly explains the plethora of statin-associated symptoms (SAS) that manifest in up to 30% of patients.
This partly explains the plethora of statin-associated symptoms (SAS) that manifest in up to 30% of patients.
Statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS) manifest in the form of muscle weakness, muscle fatigue, pain, tendon pain, cramping and rhabdomyolysis.
The reliance of skeletal muscle on energy consumption places mitochondrial dysfunction at the epicentre of SAMS pathogenesis.
This is evidenced by the high blood Lactate/Pyruvate ratio and impaired metabolic recovery observed in statin users.
This is evidenced by the high blood Lactate/Pyruvate ratio and impaired metabolic recovery observed in statin users.
Statins can cause metabolic dysfunction via both direct and indirect mechanisms.
In this thread we will be covering 4 major processes.
In this thread we will be covering 4 major processes.
1. Statins cause CoQ10 depletion.
CoQ10 has high antioxidant activity and regenerates other antioxidants such as vitamin C & vitamin E.
A deficiency in CoQ10 is associated with heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, muscular and neurological disorders.
CoQ10 has high antioxidant activity and regenerates other antioxidants such as vitamin C & vitamin E.
A deficiency in CoQ10 is associated with heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, muscular and neurological disorders.

The majority of CoQ10 circulates bound to ApoB containing lipoproteins.
The inhibition of the mevalonate pathway by statins causes secondary CoQ10 depletion by 16-54%.
The inhibition of the mevalonate pathway by statins causes secondary CoQ10 depletion by 16-54%.
This results in:
- Mitochondrial dysfunction through the inhibition of ETC complexes
- Disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential
- Decrease of mtDNA
- Impairment of oxidative phosphorylation
- Release of Cytochrome C.
- Mitochondrial dysfunction through the inhibition of ETC complexes
- Disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential
- Decrease of mtDNA
- Impairment of oxidative phosphorylation
- Release of Cytochrome C.
A trial found that those experiencing significant reduction in muscle CoQ10 had a simultaneous decrease in respiratory chain enzyme and citrate synthase activity.
Because citrate synthase is an enzyme located in the mitochondrial matrix and involved in the first step of the citric acid cycle, its activity is proportional to mitochondrial function.
Statin induced mitochondrial dysfunction can be averted by supplementation with ubiquinol (activated CoQ10) or antioxidants such as quercetin.
Lipophilic statins such as simvastatin result in a significant decrease in mtDNA.
Interestingly, vitamin D supplementation prevents the depletion of mtDNA.
Maybe this is because vitamin D upregulates the biosynthesis of CoQ10, and also has antioxidant properties.
Interestingly, vitamin D supplementation prevents the depletion of mtDNA.
Maybe this is because vitamin D upregulates the biosynthesis of CoQ10, and also has antioxidant properties.
Vitamin D has been shown to modulate the expression of genes involved in antioxidant defence, including superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx).
Due to their high reliance on mitochondrial energy production, muscle cells produce more ROS from mitochondria than other cell types.
In cells such as cardiac myofibers that have a robust antioxidant system including SOD, catalase, and GPx, ROS accumulation caused by statins is limited.
However, in cells more vulnerable to oxidative stress such as fast twitch muscle fibres due to their preference for anaerobic respiration, ROS accumulation due to statins may cause significant damage.
This might explain the targeted nature of SAS to proximal muscle groups.
This might explain the targeted nature of SAS to proximal muscle groups.
The electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes located in the inner mitochondrial membrane that play a critical role in oxidative phosphorylation, the process by which cells generate ATP.
Stains directly inhibit ETC complexes which has been proposed as potential mechanism for SAMS.
TLDR:
Statins nuke your mitochondria in a variety of ways:
1) CoQ10 depletion
2) Mitochondrial loss
3) Oxidative Stress
4) ETC complex impairment
Resulting metabolic dysfunction likely plays a role in the side effects that manifest in statin usage.
Statins nuke your mitochondria in a variety of ways:
1) CoQ10 depletion
2) Mitochondrial loss
3) Oxidative Stress
4) ETC complex impairment
Resulting metabolic dysfunction likely plays a role in the side effects that manifest in statin usage.
Shoutout to @holmanm for being the statin GOAT and inspiring this deep-dive.
Check her out if you want to learn more about #statins.
Check her out if you want to learn more about #statins.
If you enjoyed this content and want to learn more about #metabolism:
1. Follow me for more content about mitochondria.
2. Like and Retweet this thread
1. Follow me for more content about mitochondria.
2. Like and Retweet this thread
https://twitter.com/sam_soete/status/1657013095510966272?s=20
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh