KILLING ME SOFTLY ! 😰
Constant REINFECTION and exposure to newer variants SHORTEN LIFESPAN of a majority of the exposed population, by inducing major changes in their lymphocytes, what is called LYMPHOCYTOPENIA !
Constant REINFECTION and exposure to newer variants SHORTEN LIFESPAN of a majority of the exposed population, by inducing major changes in their lymphocytes, what is called LYMPHOCYTOPENIA !

2) Lymphopenia (also called lymphocytopenia) is a disorder in which your blood doesn't have enough white blood cells called lymphocytes, which play a protective role in your immune system. 

3) Reference : nature.com/articles/s4139…
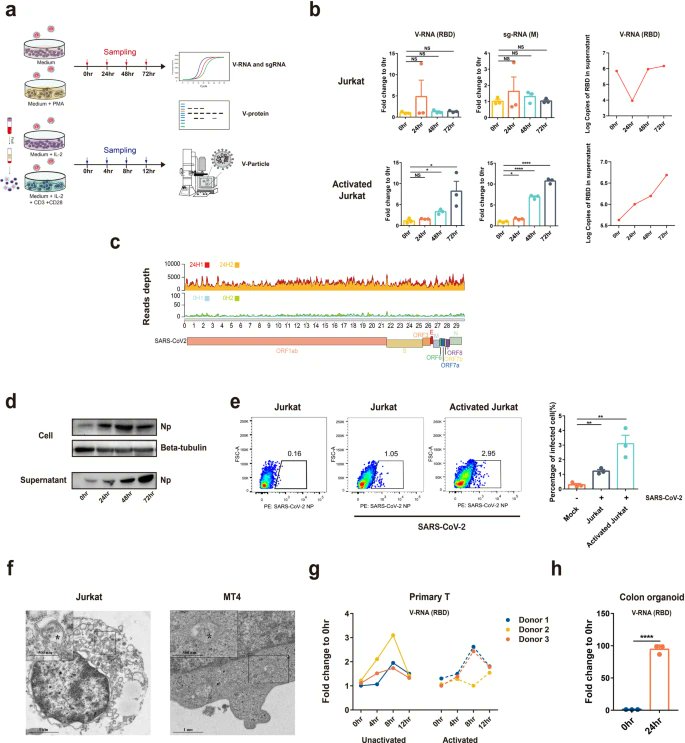
Fig. Peripheral blood lymphocytes are infected by SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients.
Fig. Peripheral blood lymphocytes are infected by SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients.

6) DISCUSSION
"Here, we showed that SARS-CoV-2 infected T lymphocytes, mainly CD4 + T cells, in an ACE2-independent manner. SARS-CoV-2 infection triggered pronounced T-cell death, which potentially contributed to lymphopenia in patients with COVID-19."
"Here, we showed that SARS-CoV-2 infected T lymphocytes, mainly CD4 + T cells, in an ACE2-independent manner. SARS-CoV-2 infection triggered pronounced T-cell death, which potentially contributed to lymphopenia in patients with COVID-19."
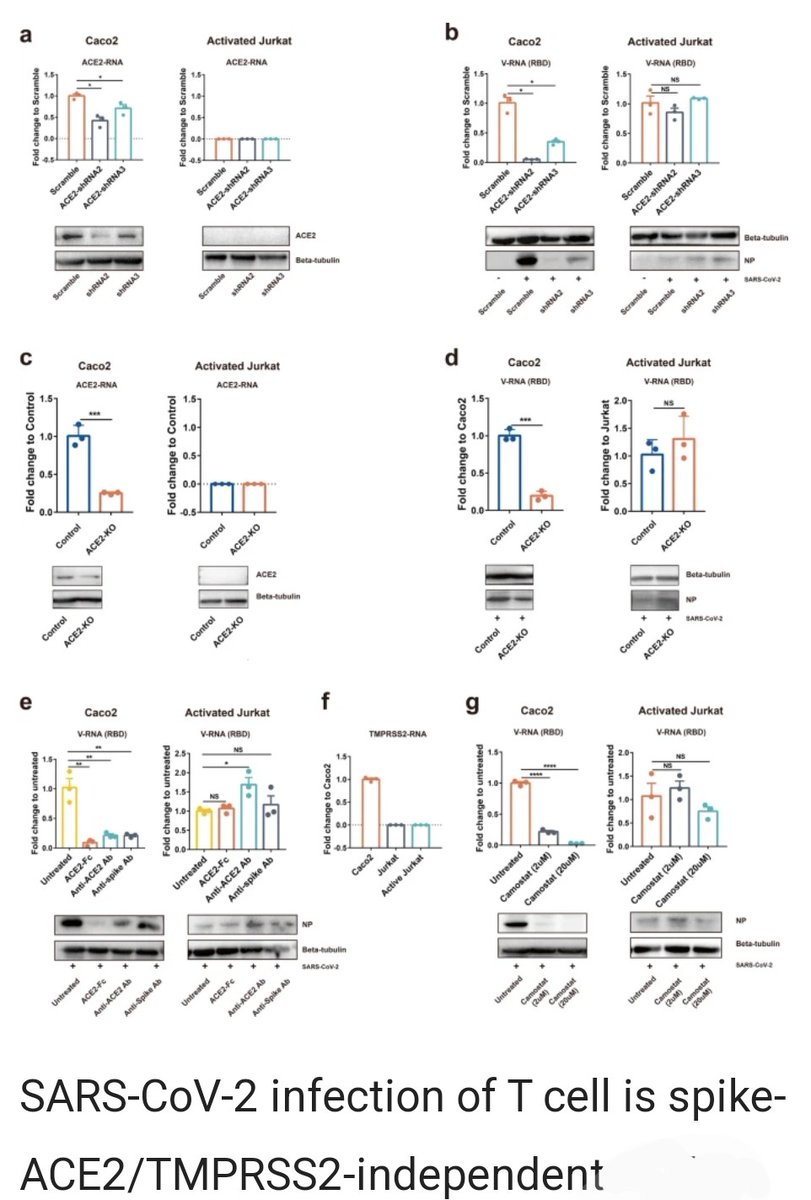
7) "T-cell infection may also pose profound influences on patients. Infected T lymphocytes not only lost the ability to control viral infection but may also carry viruses to other parts of the body through blood circulation."
Thanks for reading
Thanks for reading

8) FYI
@MeetJess @white_bite @DavidJoffe64 @xabitron1 @HarrySpoelstra @1goodtern @C_A_Gustave @T_Brautigan @Antonio_Caramia @TRyanGregory @arijitchakrav @_ppmv @fitterhappierAJ
@MeetJess @white_bite @DavidJoffe64 @xabitron1 @HarrySpoelstra @1goodtern @C_A_Gustave @T_Brautigan @Antonio_Caramia @TRyanGregory @arijitchakrav @_ppmv @fitterhappierAJ
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh