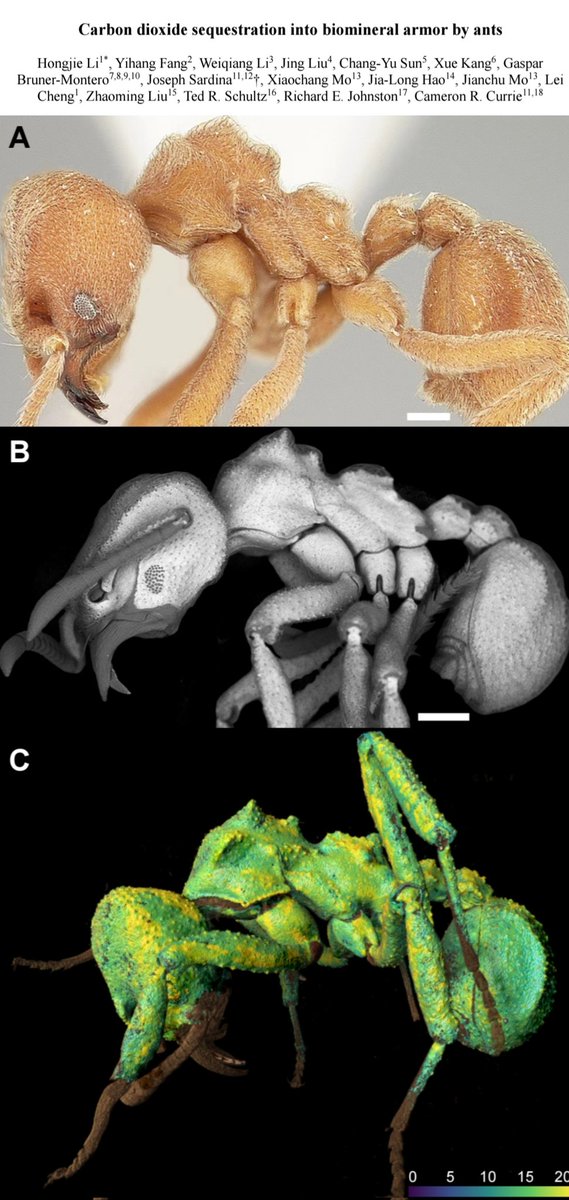
Rewind "restore the earth's carbon balance by storing #OrganicCarbon in anoxic water."
#CarbonDioxideRemoval
Details in a 🧵 below ⬇️
1/6
#CarbonDioxideRemoval
Details in a 🧵 below ⬇️
1/6

Plants are the best option for capturing CO2
"They naturally extract CO2 from the air and use it as feed. The more CO2 plants absorb, the less CO2 remains trapped in the atmosphere."
2/6
"They naturally extract CO2 from the air and use it as feed. The more CO2 plants absorb, the less CO2 remains trapped in the atmosphere."
2/6

As plants decompose, CO2
is released back to the air
"If left alone, plants are eaten by other organisms and releasing the carbon back to the carbon cycle within months."
3/6
is released back to the air
"If left alone, plants are eaten by other organisms and releasing the carbon back to the carbon cycle within months."
3/6
Anoxic conditions slow decomposition
"In anoxic waters, plants decompose extremely slowly, effectively storing the carbon much longer."
4/6
"In anoxic waters, plants decompose extremely slowly, effectively storing the carbon much longer."
4/6

The Black Sea is the ideal location
"It is the largest anoxic body of water on earth, 2km deep, surrounded by fertile lands. The Black Sea is the optimal environment allowing affordable, environmentally safe, gigaton scale #CarbonRemoval in this decade."
5/6
"It is the largest anoxic body of water on earth, 2km deep, surrounded by fertile lands. The Black Sea is the optimal environment allowing affordable, environmentally safe, gigaton scale #CarbonRemoval in this decade."
5/6

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh