Colchicine
An ancient remedy with anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, anti-amyloid, anti-cancer, anti-vascular inflammation properties.
And “may interfere with the efficacy of the adenoviral vector–based vaccine for COVID-19.”
A THREAD 🧵

An ancient remedy with anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, anti-amyloid, anti-cancer, anti-vascular inflammation properties.
And “may interfere with the efficacy of the adenoviral vector–based vaccine for COVID-19.”
A THREAD 🧵
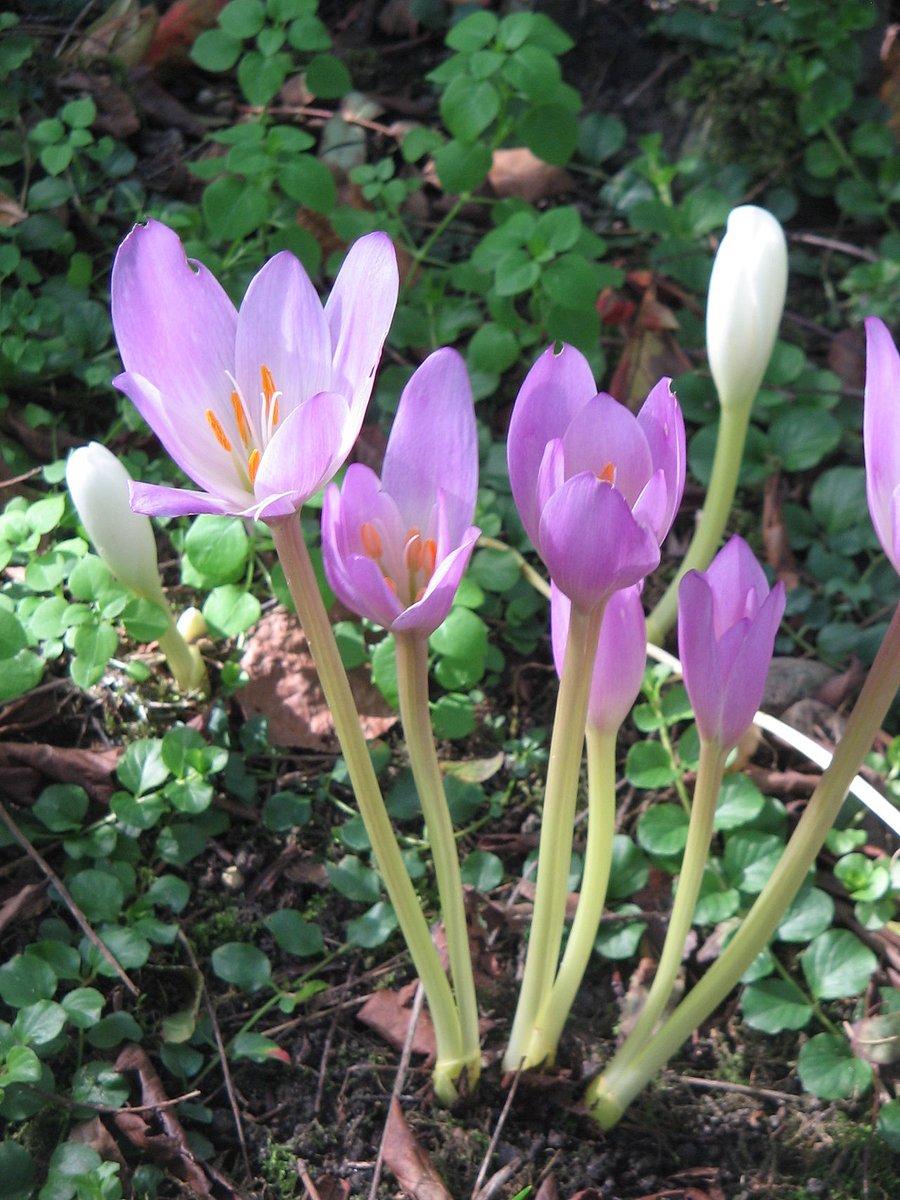


Colchicum autumnale is a flowering plant, of which the bulb-like corms contain colchicine, a historic medication for gout.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
Colchicine is one of the oldest remedies still in use today. Its history as an herbal remedy for joint pain goes back at least to the 1500 BCE Egyptian manuscript, the Ebers Papyrus.
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
Despite its use for thousands of years, colchicine’s mechanism of action is still not fully known.
Microtubules are polymers of proteins called tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to certain cells.
Microtubules are polymers of proteins called tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to certain cells.
Colchicine seems to induce microtubule destabilisation, thus affecting the cytoskeleton of certain cells. 

Colchicine also impairs neutrophil function by impacting inflammatory pathways and mediators of neutrophil activation; as well as being able to both decrease TNF-α receptor expression on macrophages (preventing activation)
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
Mast cells are integral to allergic and anaphylactic reactions and are involved in conditions like autism and mast cell activation syndrome.
Colchicine is known to interrupt granule release in mast cells, thus preventing degranulation.
jimmunol.org/content/174/8/…
Colchicine is known to interrupt granule release in mast cells, thus preventing degranulation.
jimmunol.org/content/174/8/…
Other than being used as a treatment for gout, colchicine has been the treatment of choice for Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) and the prophylactic treatment of secondary amyloidosis, a disorder in which abnormal proteins build up in tissues and organs.
It has been shown that colchicine not only prevents or considerably reduces the frequency of FMF attacks in 90–95% of patients when taken daily in doses of 1–2 mg, but almost always delays the onset of amyloidosis.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
Other than this, colchicine is looking promising at treating various other disorders, including acute and recurrent pericarditis, coronary artery disease, stroke, certain forms of vasculitis, and skin disorders, ranging from chronic urticaria to actinic keratosis.
Colchicine use has also been associated with lower rates of cancer (especially prostate and colorectal cancers).
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
A significantly lower risk of cardiovascular events (especially in inflammatory cardiac conditions such as pericardial diseases, coronary artery disease, and atrial fibrillation).
And has even been shown to be associated with a 73% reduction in all-cause mortality.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
If you like my threads, then you may find if of interest to know that I source the information for it from my recently released book.
People are seeming to enjoy it!
Click on the link to find out more 👇🏾 callingouttheshots.xyz
People are seeming to enjoy it!
Click on the link to find out more 👇🏾 callingouttheshots.xyz

Due to its anti-inflammatory potential, colchicine has been researched as an agent to help target the cytokine storm post-SARS-CoV-2 invasion.
One study showed that colchicine treatment decreased CRP levels and COVID-19 severity, but others haven’t been so promising. More studies are needed.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35381033/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35381033/
Interestingly, it has been hypothesised that amyloidosis may be a factor causing systemic complications after coronavirus disease,
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
And another paper noted that the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein showed the ability to form amyloid proteins in vitro.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
Colchicine’s anti-amyloid properties haven’t been researched in this regard, however.
Another researcher warned that colchicine may interfere with the efficacy of the adenoviral vector–based jabs for COVID-19 (ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 - Oxford, AstraZeneca vaccine).
This claim has not been followed up.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
This claim has not been followed up.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
Colchicine in the low doses used in most trials (≤ 1 mg/d) has been generally safe and well-tolerated.
The most common side effect is diarrhoea (approximately 10%), which may be due to colchicine’s ability to increase intestinal permeability and alter the gut microbiome.
The most common side effect is diarrhoea (approximately 10%), which may be due to colchicine’s ability to increase intestinal permeability and alter the gut microbiome.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter