1/ The destruction of the Kakhovka dam will cause calamitous economic, social and humanitarian impacts across southern Ukraine, including the loss of much of the region's agriculture, industry and the drinking water of hundreds of thousands of people. ⬇️
2/ Ihor Pylypenko, the Dean of Kherson State University's Faculty of Biology, Geography and Ecology, has given an interview setting out the likely impacts of the dam's destruction. He's previously written about the risks in the German journal 'Osteuropa'. 

3/ Pylypenko notes that the dam was toppled at the worst possible time – just before midsummer and when the Kakhovka reservoir was at a near-record high. Its destruction now is peculiarly self-defeating given that the flooding affects the Russian-held side particularly badly.
4/ "The left bank suffers more than the right; the right bank is high and relatively steep. Relatively speaking, every 10 centimetre increase in the water level of the Dnipro means 15 metres of flooding on the left bank and only 3 metres on the right bank."
5/ He notes that the volume of water released by the breach has been enormous – between 4.5 to 5 cubic kilometres of water a day (1.3 trillion gallons / 5 trillion litres). This is already causing huge ecological effects downstream and is likely to badly affect the Black Sea.
6/ Pylypenko also provides a detailed analysis of the economic impacts, particularly on agriculture (on which see also the threads linked below). The reservoir supplied water to more than 12,000 kilometers of canals. 
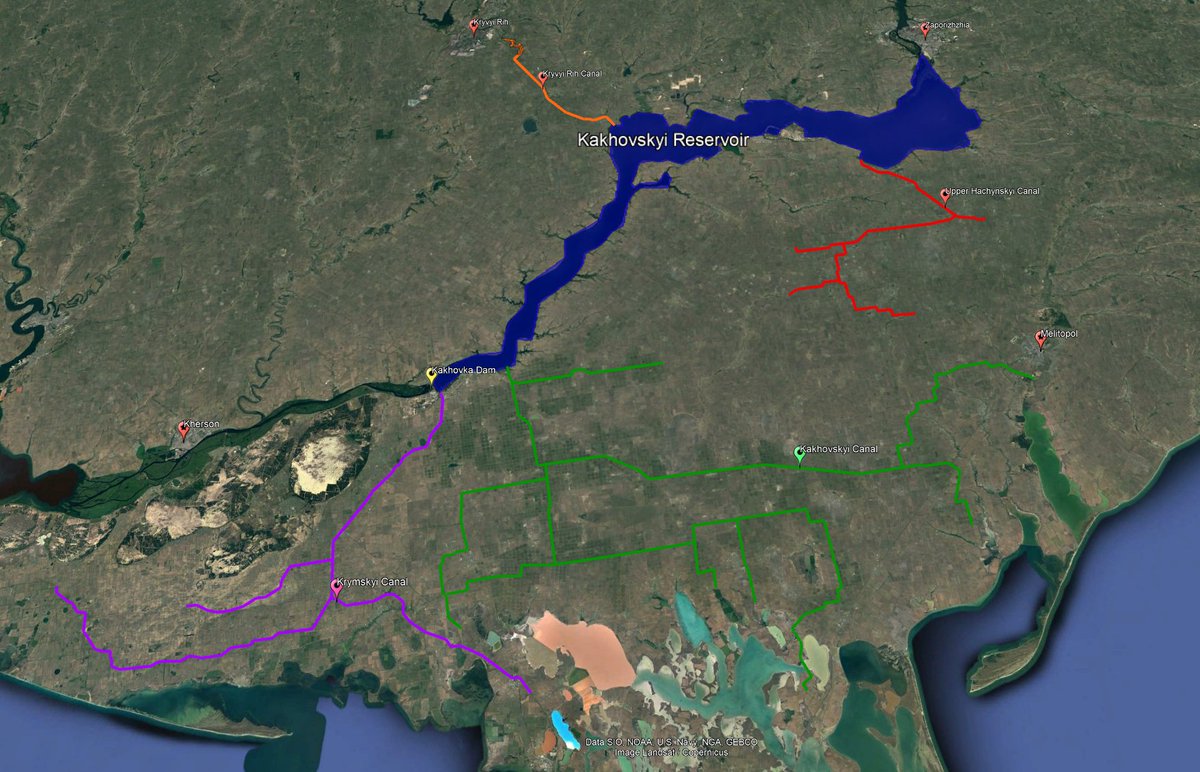
7/ The Russian-occupied Azov region depends for its water supply on canals leading from the Dnipro. They will cease to flow when the water falls too low to supply them, which is already happening (see thread below).
https://twitter.com/ChrisO_wiki/status/1666896908311224325
8/ The Kakhovka canal, which relied on pumps lifting water from the reservoir to a height of 30m, is no longer functioning. This has cut the water supply to cities such as Melitopol and Berdyansk, as well as all the settlements between them, affecting 400,000 people. 
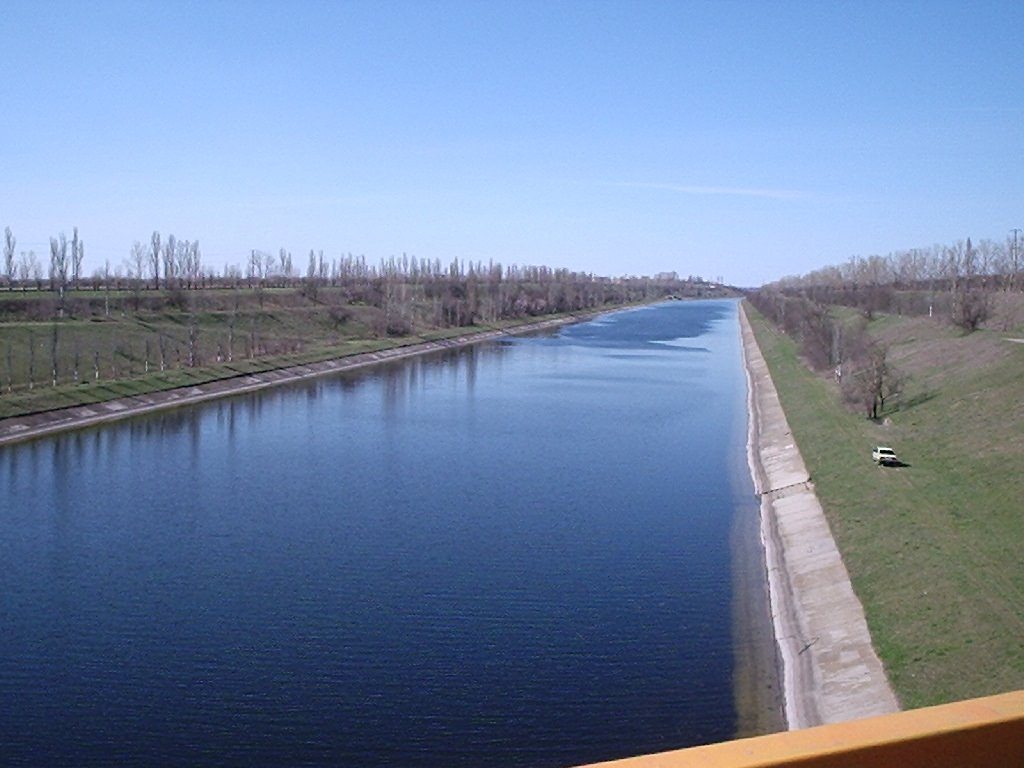

9/ This canal alone supported the irrigation of about 220,000 hectares of land – 190,000 in the Kherson region and 30,000 in the south-west of the Zaporizhia region – and the livelihoods of hundreds of thousands of people in the agricultural sector.
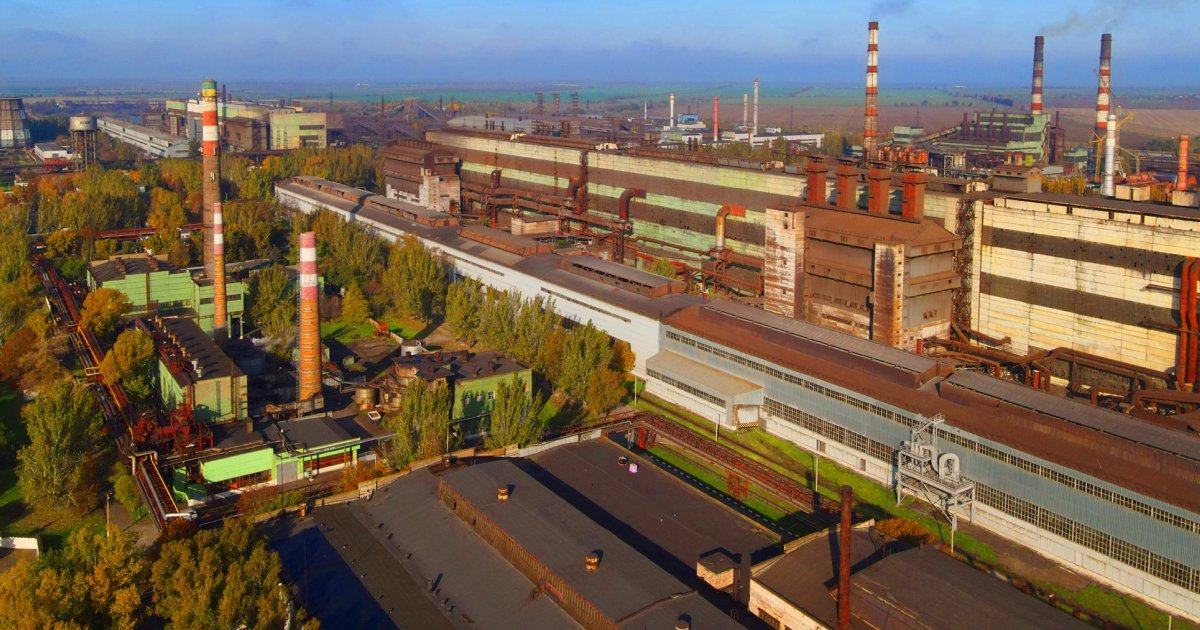
10/ As well as cutting off drinking water supplies, the loss of the reservoir may shut down water-hungry industries such as the metallurgical facilities at Nikopol, which are on the Ukrainian side of the Dnipro. 

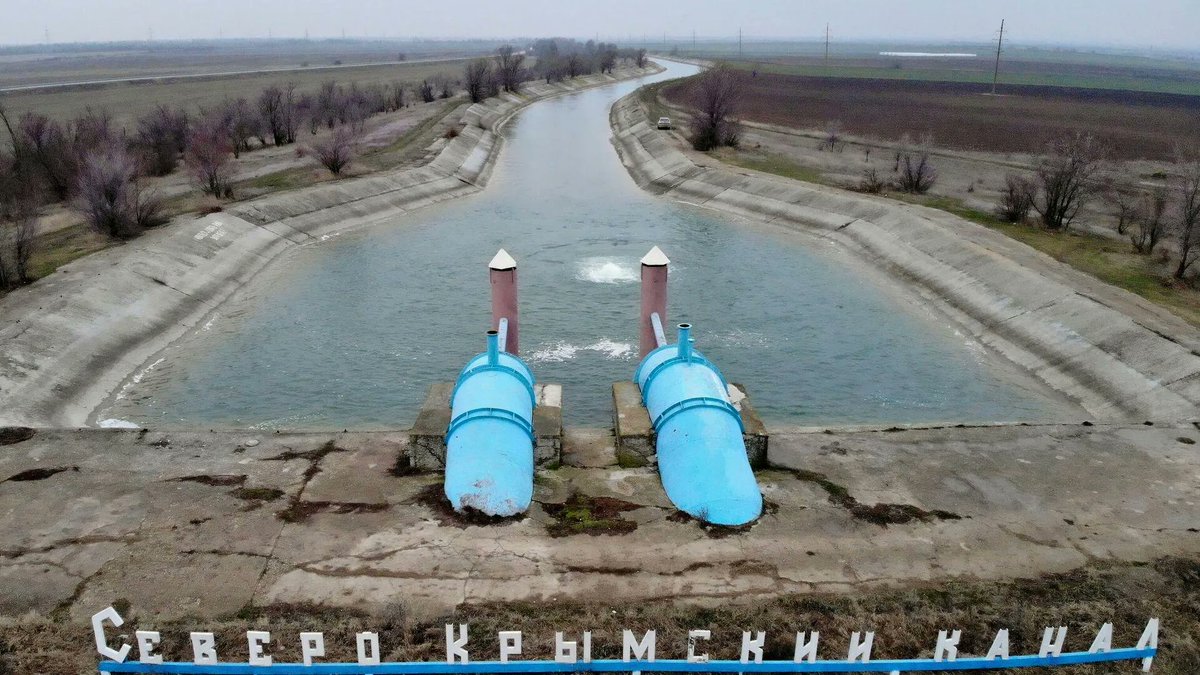
11/ The North Crimean Canal, which supplies 85 percent of Crimea's water, will not function when the water level falls below about 10 metres – at current outflow rates, this will happen by Sunday. Apart from some aquifers in the Oleshky Sands area, the region is otherwise arid. 

12/ Pylypenko notes that annual rainfall in the Azov region is only 350 millimeters while evaporation amounts to 1000-1100 mm. It'll dry out very quickly, within a single season. Crops grown for livestock feed and export such as soybeans and onions will no longer be viable.
13/ This has grave effects for the human population. 150,000 to 200,000 people are forecast to lose their jobs in the Kherson region alone. Many towns and villages will no longer be economically viable. Up to 420,000 agricultural jobs are potentially at risk.
14/ The region's population grew by 340% after the canals were built between the 1950s and 1980s, due to the increased water supply and agricultural opportunities. Pylypenko estimates that a population of only half as much is now sustainable.
15/ The right-bank region around the city of Kherson will be less affected, as it depends primarily on locally supplied but poor-quality water from the Inhulets river, rather than the Dnipro. That said, Dnipro water was used to irrigate a radius of around 40 km from Kherson.
16/ Crimea will be very severely affected, as it was before when Ukraine cut off the water supply in 2014. In February 2021, the Simferopol reservoir was only 7% full. Arable land fell from 130,000 hectares in 2013 — a fraction of Soviet-era levels — to 14,000 in 2017. 

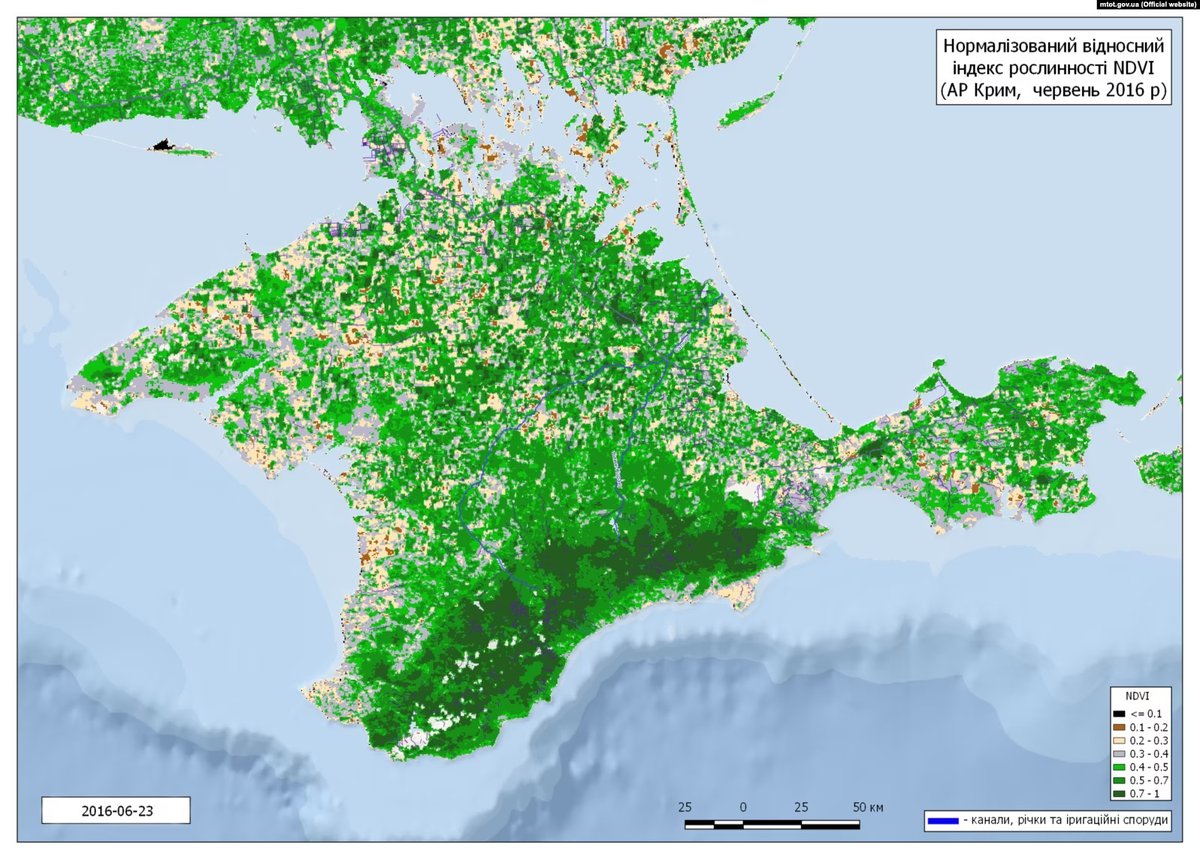
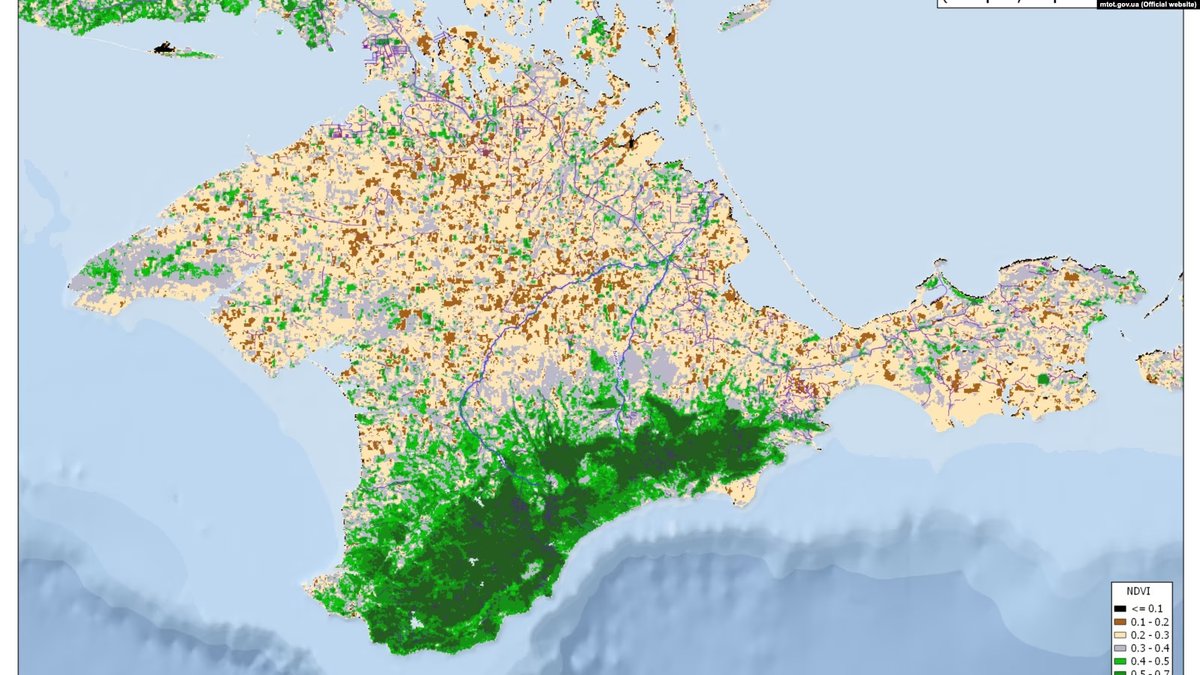
17/ Unlike the concrete-lined Kakhovka canal, the North Crimean Canal – which was built in a much simpler (and therefore cheaper) fashion in the Khrushchev era – has a bed of earth. It drains completely by the end of the irrigation season, so it will be empty in a few weeks. 
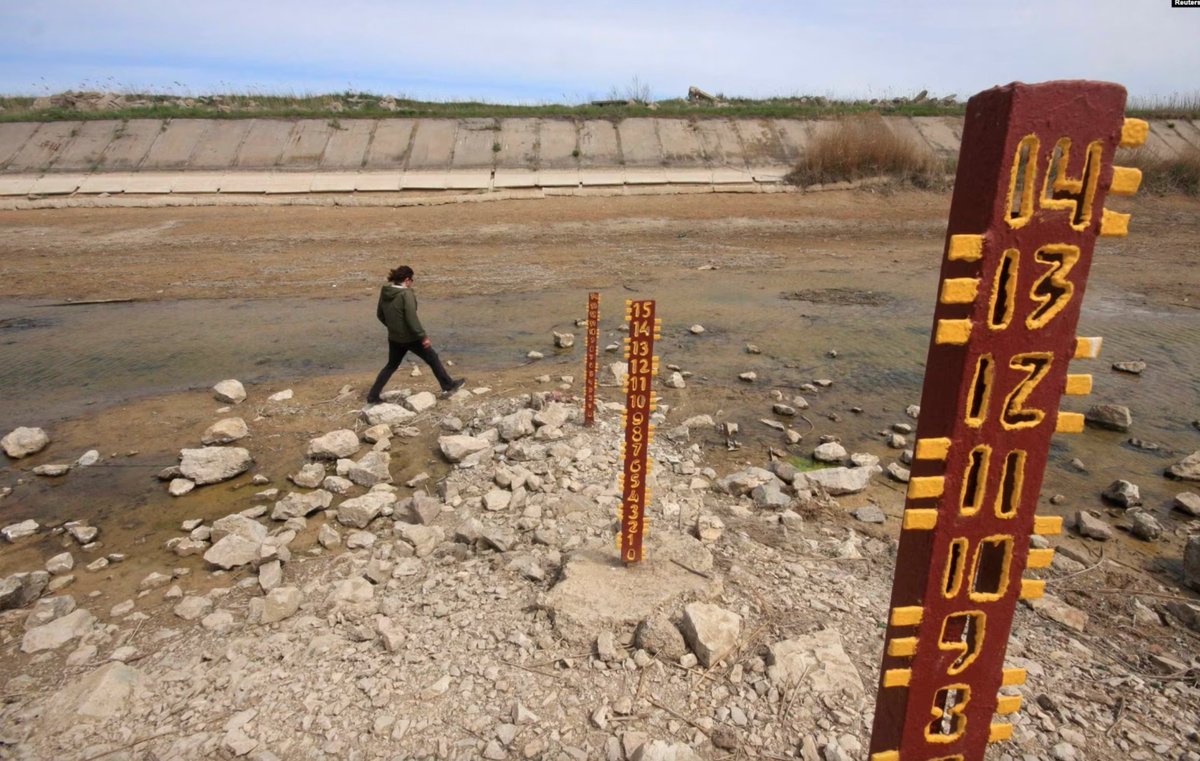

18/ Before 2014, Crimea used over 700 million cubic litres of water during the relatively short irrigation period (spring and summer). When Russia launched the February 2022 invasion of Ukraine, it unblocked the North Crimean Canal almost immediately to restore the water flow.
19/ Nonetheless, despite a high-profile relaunch of irrigation by Crimea's governor Sergey Aksyonov in April 2022, the water flow was only restored to 80 million cubic litres and the amount of arable land increased only to 25,000 hectares. 

20/ During the years of drought, the irrigation infrastructure in Crimea was reportedly "almost completely lost, plundered" and required the expenditure of 14.5 billion ($177 million) rubles to restore. 

21/ This year, Crimea planned to increase the area under cultivation to 40,000 hectares and to bring more than 300 million cubic metres through the canal. Now the water has been cut off entirely, plunging Crimean farmers into long-term crisis.
22/ Pylypenko is hopeful that the dam can be restored within three years (the Soviets took five years to build it), due to improved construction technology. The reservoir itself will take a year to refill. But this will depend on peace being restored.
23/ "In case of a negative scenario, of course, nothing can be restored ... Without irrigation there will be no supply of drinking water. There will again be the situation of the 1930s-50s of the last century: a sparse, small population, sparse villages, imported water." /end
Sources:
🔹 svoboda.org/a/my-vernemsya…
🔹 bloomberg.com/opinion/articl…
🔹 vk.com/wall535871340_…
🔹 zeitschrift-osteuropa.de/hefte/2023/1-2…
🔹 svoboda.org/a/my-vernemsya…
🔹 bloomberg.com/opinion/articl…
🔹 vk.com/wall535871340_…
🔹 zeitschrift-osteuropa.de/hefte/2023/1-2…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh









