🧵Thread
Mines pose a significant challenge for our army during the counter-offensive. As I've highlighted months ago, the difficulty lies in effectively tackling this issue while dealing with the constant threat of fire from enemy aircraft, AT weaponry, and artillery.
Mines pose a significant challenge for our army during the counter-offensive. As I've highlighted months ago, the difficulty lies in effectively tackling this issue while dealing with the constant threat of fire from enemy aircraft, AT weaponry, and artillery.

2/ Based on my knowledge about the current situation, russian forces continue mining vast expanses, spanning dozens and hundreds of square kilometers. Even the deployment of Mine Clearing Line Charges (MICLIC) does not provide a foolproof solution, given the scale of the problem. 
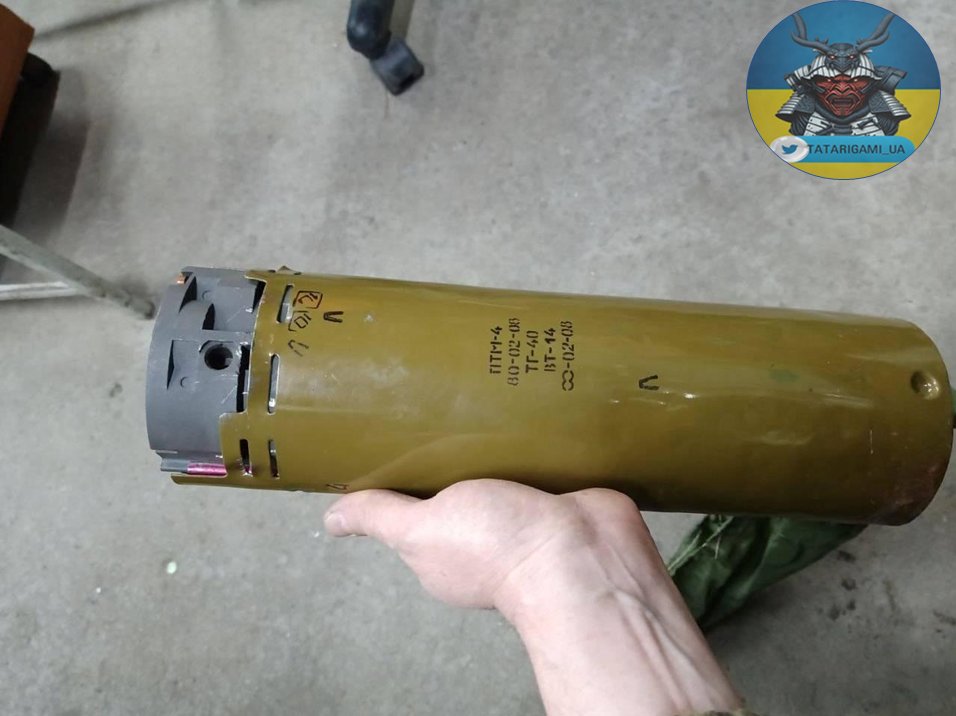

3/ Russian forces persistently employ both anti-tank and anti-personnel mines to fortify the area. Additionally, it appears that they are utilizing a significant number of remote-mining machinery, such as the Zemledeliye system. 

4/ In the specific case, provided to me from the field, the identified mine was likely deployed via remote mining, possibly utilizing the BM-27 Uragan launcher. The Uragan launcher, equipped with 16 rockets containing 9 mines each, enables the simultaneous deployment of 144 mines 
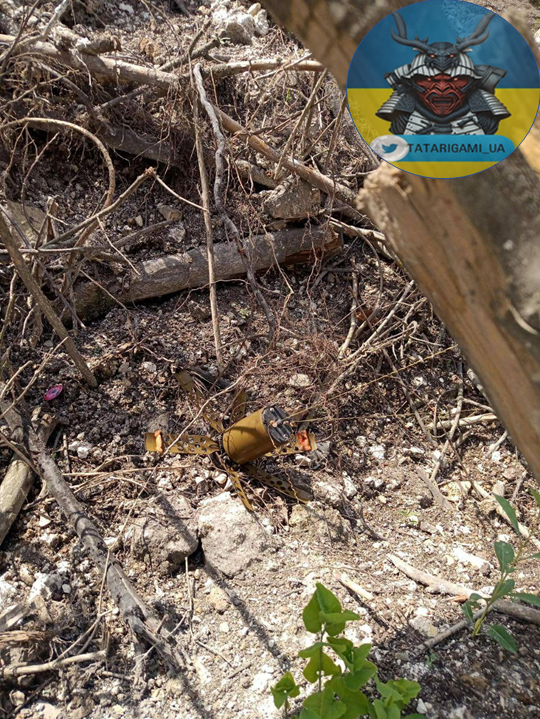

5/ The civilian population is endangered by this situation. Numerous reports have emerged about incidents of both domestic animals and people falling victim to mines. Similar incidents occurred before; however, the scale of the current mining is far larger. 

6/ The limited supply of engineering equipment, SHORAD, and long-range artillery poses a challenge in breaking through the rigid minefield. While it remains possible to breach the defense line, achieving this objective will demand significant time and resources.
7/ Modern Western armies haven't faced similar challenges with extensive minefields recently. This is primarily due to their aerial supremacy, which enables the elimination or neutralization of threats long before mine-clearing equipment is deployed in the operational area. 

8/
The core emphasis of the Russian military doctrine and strategic thinking on defense and active defense measures was designed to resist more technologically advanced enemy than russia itself
The core emphasis of the Russian military doctrine and strategic thinking on defense and active defense measures was designed to resist more technologically advanced enemy than russia itself
9/
In summary, the task of breaching defenses and minefields, particularly in the presence of hostile artillery and air support, is a high-risk task that needs significant time and effort. Let us not forget the formidable challenge that our officers and soldiers are confronting.
In summary, the task of breaching defenses and minefields, particularly in the presence of hostile artillery and air support, is a high-risk task that needs significant time and effort. Let us not forget the formidable challenge that our officers and soldiers are confronting.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh