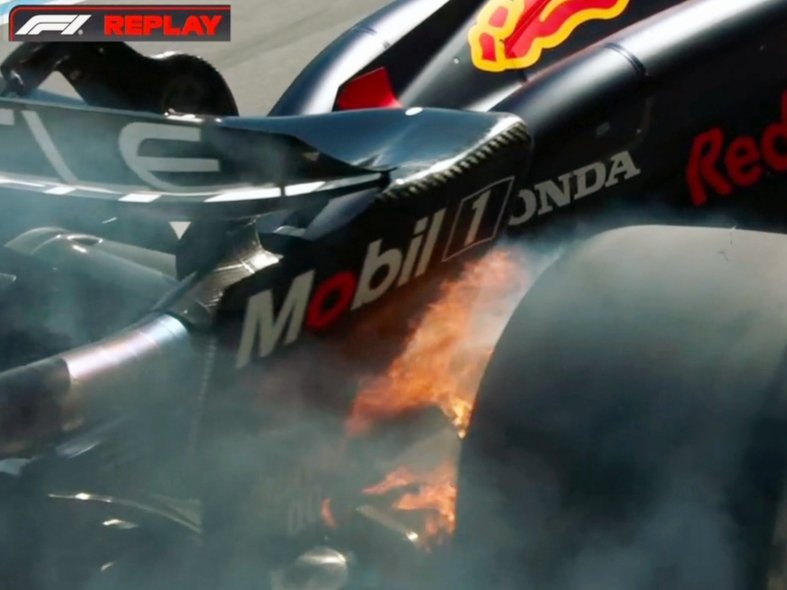
Williams are another team bringing a big update to their car.
The FW45 has had a thorough aero review, with one set of bodywork readied for #AA22 at the #CanadianGP.
#F1 #F1Tech

The FW45 has had a thorough aero review, with one set of bodywork readied for #AA22 at the #CanadianGP.
#F1 #F1Tech


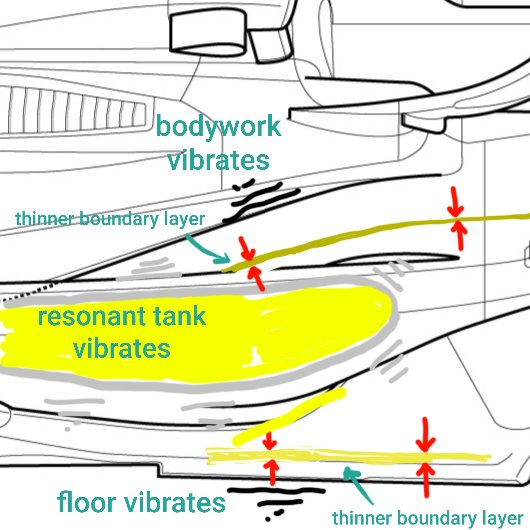
The floor is the key change. Mostly the underside, but the inlet fences, floor edge and diffuser are more visible changes. The rear brake ducts are reworked accordingly.
#F1 #F1Tech

#F1 #F1Tech


Also the sidepods, feature new inlets and a deeper scallop to the waterslide. Directing more flow to the diffuser.
#F1 #F1Tech



#F1 #F1Tech




• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh