1/8: Hey folks! Today, let's talk about Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and their significance in the online world.
🌍 CDN stands for Content Delivery Network, and it plays a vital role in ensuring fast and reliable content delivery to users around the globe. Let's dive in!
🌍 CDN stands for Content Delivery Network, and it plays a vital role in ensuring fast and reliable content delivery to users around the globe. Let's dive in!
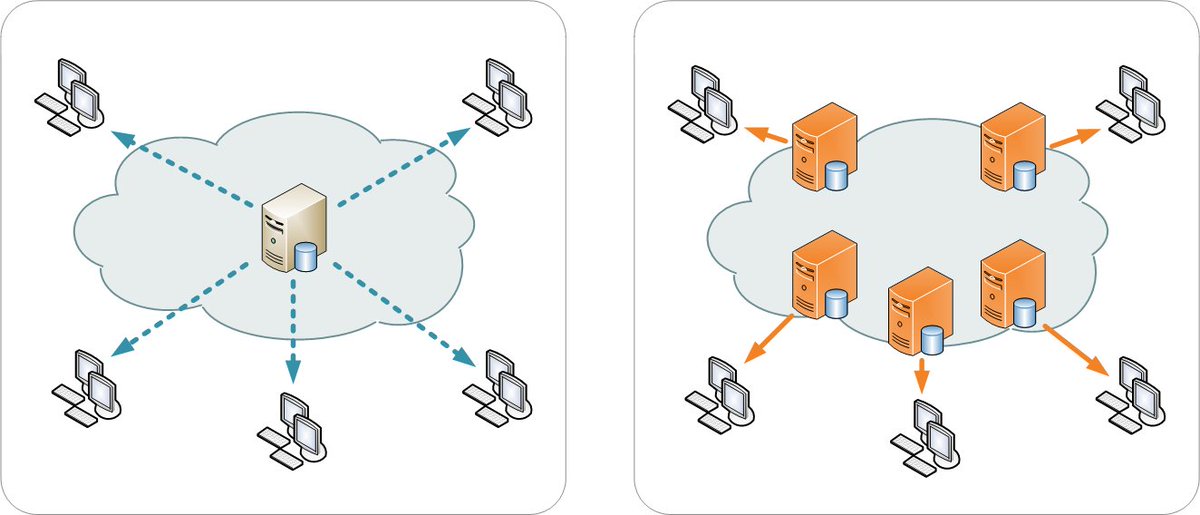
2/8: In simple terms, a CDN is a nw of servers strategically distributed across various locations worldwide. These servers store copies of websites, images, videos, and other web content. When a user requests this content, the CDN delivers it from the server closest to the user.
3/8: The main objective of CDNs is to minimize latency, reduce server load, and enhance the overall user experience. By serving content from a nearby server, CDNs significantly reduce the time it takes for the content to reach the user's device, resulting in faster load times.
4/8: Imagine a website hosted on a server in US. W/o a CDN, users accessing it from India would experience significant delays due to the long distance data has to travel. But with a CDN, the website's content can be cached on servers in India, ensuring faster access 4 local users
5/8: CDNs work by employing a technique called caching. When a user requests some content, d CDN checks if it has a cached copy. If it does, d CDN delivers d content directly from its server, avoiding d need to fetch it from d origin server. This saves time, reduces server load.
6/8: Additionally, CDNs utilize load balancing techniques to distribute user req's across multiple servers. By doing so, CDNs can handle large amt of traffic efficiently, preventing any single server from becoming overwhelmed. This ensures a more stable & reliable user experience
7/8: Popular examples of CDNs include Cloudflare, Akamai, and Fastly.
These providers have extensive networks of servers worldwide, making it possible for websites and applications to deliver content quickly to users, regardless of their location.
These providers have extensive networks of servers worldwide, making it possible for websites and applications to deliver content quickly to users, regardless of their location.
8/8: In conclusion, CDNs are a crucial component of today's internet infra. They improve content delivery speed, reduce latency, & ensure a smooth user experience. By caching content & distributing it across a network of servers, CDNs revolutionize how we access online content.🚀
1/8: Hey folks! Today, let's explore the concept of Edge Locations and their significance in content delivery. Edge Locations play a crucial role in bringing content closer to users, reducing latency, and improving overall performance. Let's dive in!
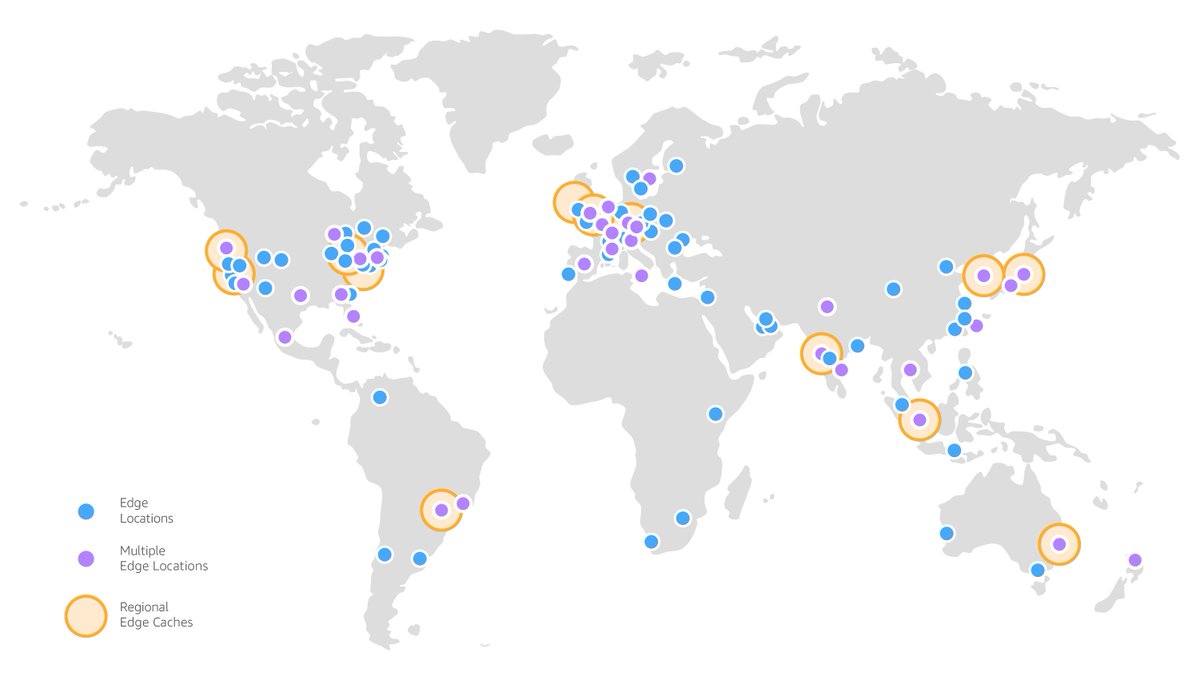
2/8: Edge Locations are physical points of presence (PoPs) strategically distributed worldwide. These locations are part of a broader infra, often associated with Content Delivery Networks (CDNs). The primary purpose of edge locations is to bring content closer to the end user.
3/8: Imagine a user accessing a website from a distant location. W/o edge locations, the user's req would have to travel a long distance to reach d website's origin server, resulting in slower load times. Edge locations solve dis by caching content in closer proximity to the user
4/8: When a user req content, CDN routes d req to d nearest edge location based on d user's geographical location. The edge location acts as an intermediary, retrieving & delivering the content from its cache. This process significantly reduces d time it takes to access d content
5/8: Edge locations r equipped wid caching servers dat store frequently accessed content. For eg, if a user in London req's an image dat hs already been accessed by someone in Paris, d image may already be cached in d edge location closest to London, resulting in faster delivery.
6/8: By strategically deploying edge locations across s globe, CDNs can optimize content delivery based on user proximity. This means that regardless of d user's location, the content can be served from an edge location nearby, minimizing latency & providing a smoother user expr.
7/8: Popular CDN providers, such as Cloudflare and Akamai, have extensive nw of edge locations spread across multiple continents. These locations ensure that content is stored and delivered efficiently, reducing the reliance on the origin server and improving overall performance.
8/8: In conclusion, edge locations are key components of content delivery infrastructure. By caching content closer to users, they enable faster access, reduced latency, and improved user experience. They work hand-in-hand with CDNs to bring content closer to where it's needed.🚀
Edge Location vs. CDN 🌐
1/8: Let's clarify the difference between Edge Locations and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs). While they are related, they serve distinct roles in the world of content delivery. Let's delve into it!
2/8: Edge Locations refer to physical points of presence (PoPs) strategically located in various cities or regions around the world. These locations are part of a broader Content Delivery Network infrastructure and act as caching endpoints to bring content closer to users.
3/8: CDNs, on the other hand, are the overarching networks that consist of multiple edge locations. A CDN is a system of interconnected servers, spread across various locations, designed to optimize content delivery by storing and distributing cached copies of web content.
4/8: Edge Locations serve as the points where CDN servers are deployed. They act as intermediaries between the user and the content, ensuring faster and more efficient delivery. These locations are typically equipped with caching servers that store frequently accessed content.
5/8: When a user requests content, the CDN routes the request to the nearest edge location based on the user's location. The edge location then retrieves the content from the CDN's central servers or the origin server if it's not already cached.
6/8: The primary purpose of edge locations is to bring the content closer to d end user, reducing latency & improving response times. By having multiple edge locations spread across different regions, CDNs can serve content from d location dat offers d lowest latency for d user.
7/8: CDNs ensure that content is distributed efficiently across their network of edge locations. They manage caching, load balancing, and content delivery processes to optimize performance and enhance the user experience, all while reducing the load on the origin server.
8/8: In summary, Edge Locations are specific physical points within a CDN's infrastructure, acting as caching endpoints closer to users. CDNs, on d other hand, r e dentire nw's that encompass multiple edge locations, responsible for content caching, distribution, & optimization.
Both work together to improve content delivery globally. 🌍
Hope this makes everything clear about these two technologies.
Hope this makes everything clear about these two technologies.
Retweet the thread if you find it useful. Thanks!
https://twitter.com/devops_tech/status/1670645328759119873?s=20
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter