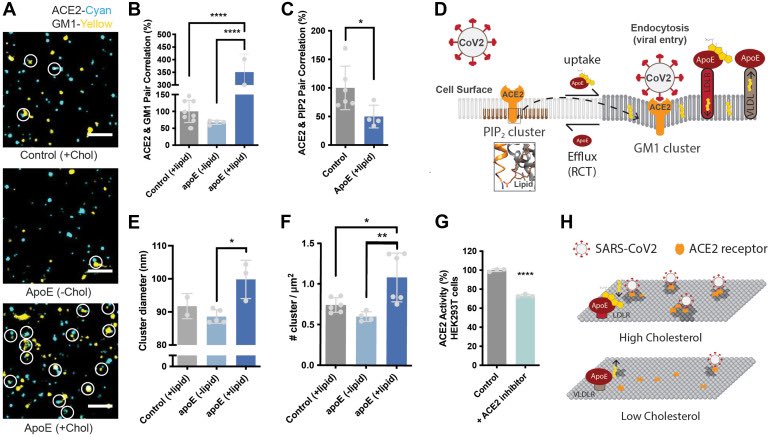
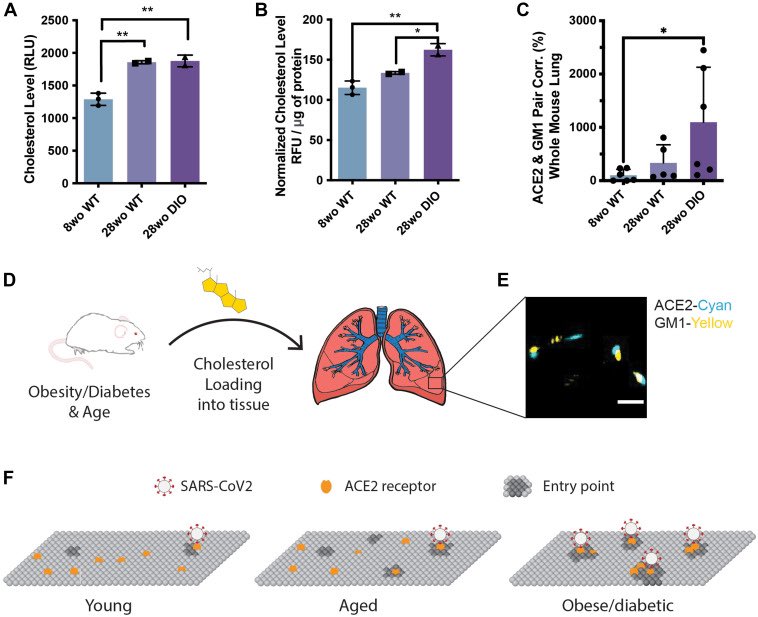
Knowledge about how genomes change over time is key for our understanding of evolution. Though fission & fusion rearrangements represent just a small fraction of the ways in which genomes can change, we know little about how these mutations become fixed in populations 1/
Rearrangements could fix by genetic drift if they are weakly deleterious or neutral, or they may instead be favoured by positive natural selection. 2/
To address this, a team of #Spanish researchers analysed genome wide variation in butterflies to infer past demography and natural selection in relation to chromosome rearrangements. 3/
Here are the main findings:
1-drift is a stronger force than overall diversity would suggest.
2-drift is not strong enough to fix considerably underdominant rearrangements. 4/
1-drift is a stronger force than overall diversity would suggest.
2-drift is not strong enough to fix considerably underdominant rearrangements. 4/

3-there is only weak evidence that chromosomes fusions fixed through positive natural selection or meiotic drive.
We need similar investigations in other organisms which together will illuminate how genomes evolve across the tree of life. 5/
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
We need similar investigations in other organisms which together will illuminate how genomes evolve across the tree of life. 5/
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter