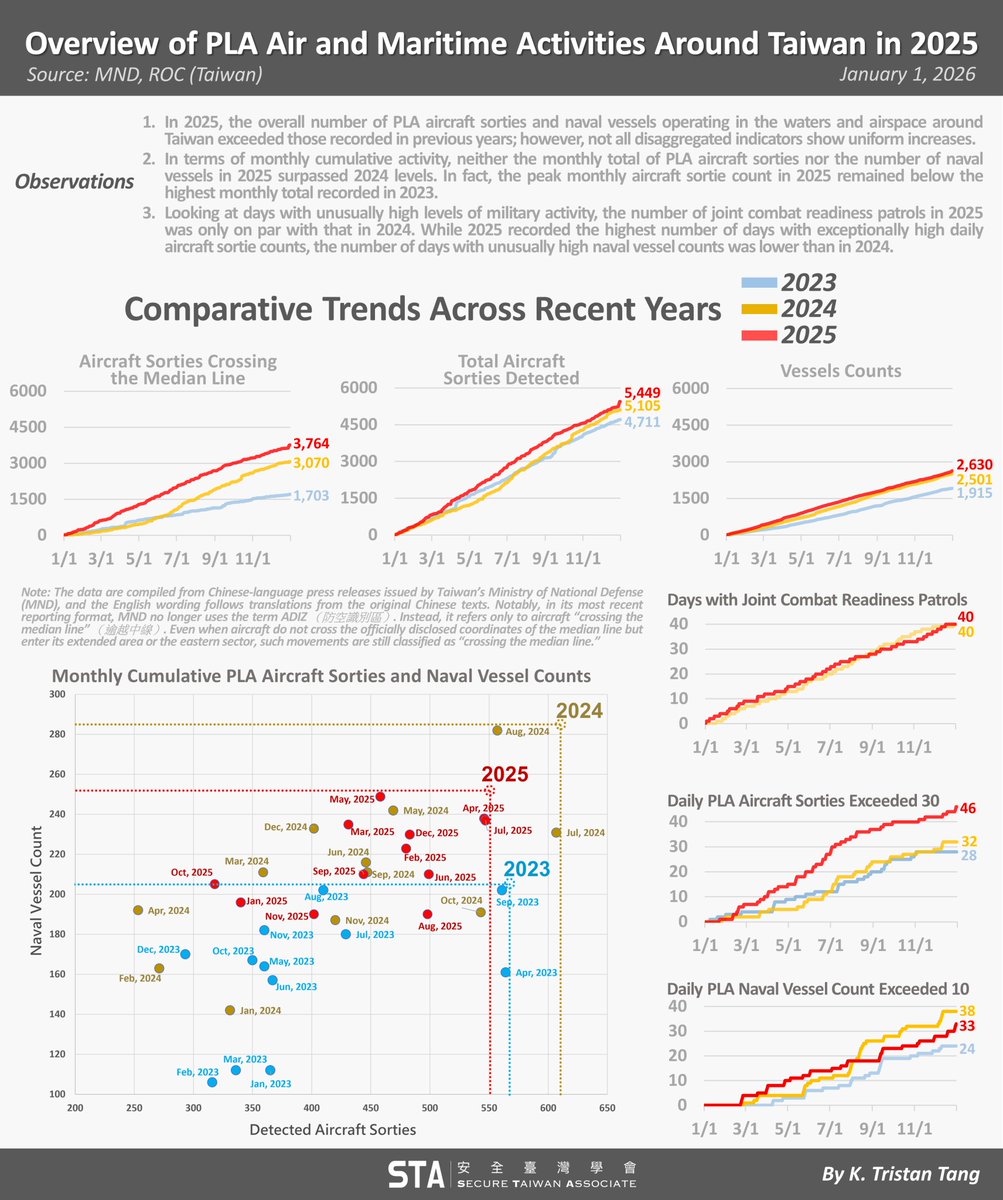
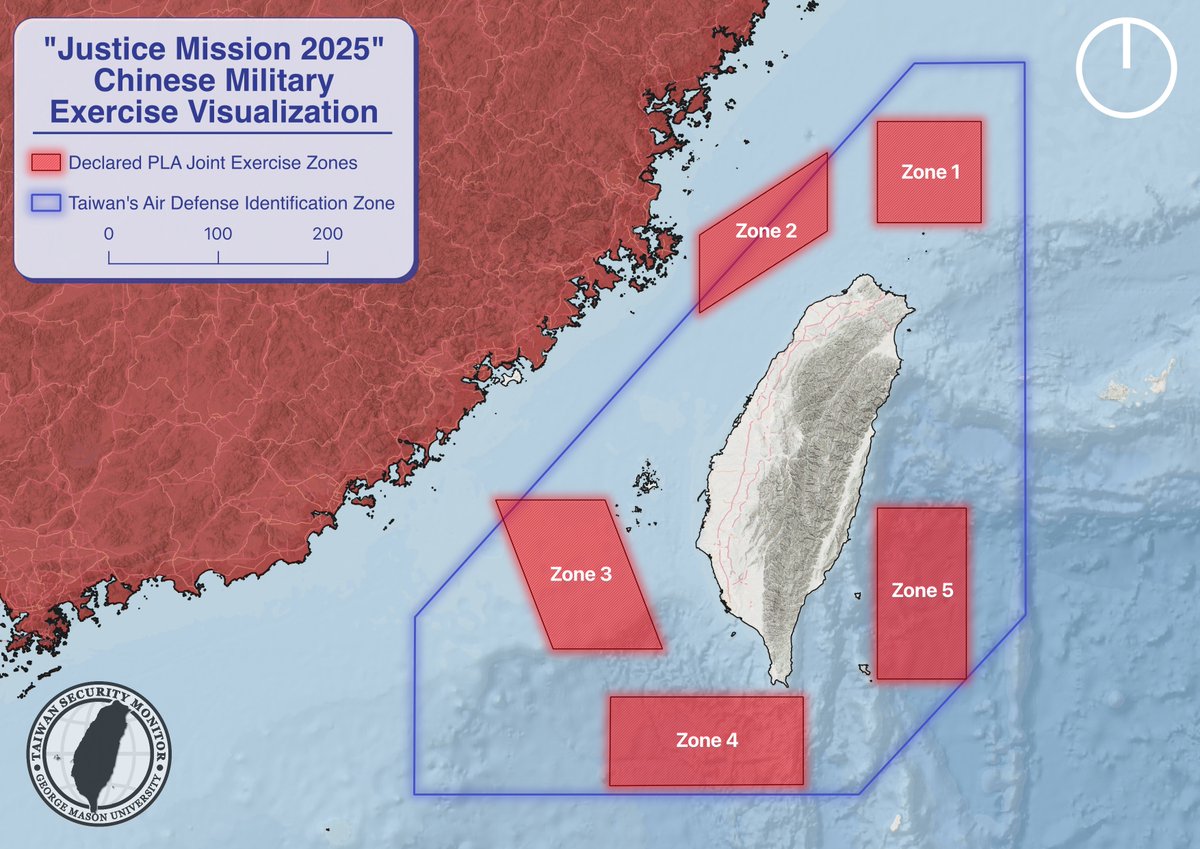
Lots of recent discussion about the ‘slow’ Ukrainian offensives. What is actually occurring now is a steady, deliberate taking down of the Russian 'operational system'. This takes time. 1/25 🧵 

2/ What is this operational system? To understand what it is, and how Ukraine is ‘taking down’ the Russian operational system, two foundational concepts are important to understand: the operational art; and, systems destruction warfare.
3/ In war, we talk about strategy (the link of purpose with high level resource allocation & action) & tactics (involving attacks & conduct of specific combat ops). Because of the complexity of modern war, strategy and tactics are linked through what we call Operational Art.
4/ Operational Art is the planning, orchestration, sustainment and adaptation of tactical actions over long period of time and, often, across a large geographic area as well. It ensures military forces are in a good position for tactical activity that achieves strategic outcomes.
5/ One element of the operational art that is debated is whether there is an operational ‘level’ of war. Critics argue that the operational level undermines strategy & relegates tactics to a less important aspect of war. Perhpas, but most nations recognise this level in doctrine.
6/ Systems Destruction Warfare. A RAND report notes that: “thinking about systems pervades virtually every aspect of the PLA’s approach to training, organizing, and equipping for warfare… the system-of-systems construct is the mode of modern fighting for the PLA."
7/ PLA theorists view modern war as a confrontation between opposing systems in a multidomain battlespace. As such, the Chinese seek to build their own systems to attack enemy systems. An important component of this is degrading and destroying the enemy ‘operational system’.
8/ An operational system is the components of a military force – above units and brigades – that binds a force together, allows for concurrent and sequential tactical activities, and underpin its ability to conduct operational level maneuver that achieve strategic objectives.
9/ For the Russians in #Ukraine, there are 6 key elements of their operational system: the command system, the firepower-strike system, the information system, the reconnaissance-intelligence system, the support system (logistics etc); and, the learning and adaptation system.
10/ In essence, this is the brain and nervous system of the Russian forces in Ukraine. This operational system will have been a first-order target when planning and executing military campaigns.
11/ The reason for this is that if the Ukrainians can attack the Russian brain (such as it is) and nervous system, the limbs are unable to be coordinated, and can be isolated and destroyed.
12/ Therefore, when the Ukrainians have asked for modern fighters, long range strike (and probably classified cyber and IW capabilities as well), they have been requesting the capabilities to attack, degrade and destroy the Russian operational system.
13/ All six elements of the Russian operational system have been attacked in the lead up to the Ukrainian offensive beginning in June, and they continue to be attacked. The cumulative effect of Ukrainian attacks on the Russian system will be aggregated & measured regularly.
14/ There will be a time when Ukraine assesses the Russian operational system has been sufficiently degraded, its ability to support tactical forces damaged & the ability to move reserves has been limited. This decision point will inform when large-scale ground combat begins.
15/ Unfortunately, in the west, the only model we have for taking down an enemy operational system is the US in the 1991 Gulf War. A 42-day campaign using thousands of aircraft was needed. We then have to look back further into history to see a campaign of this complexity. 
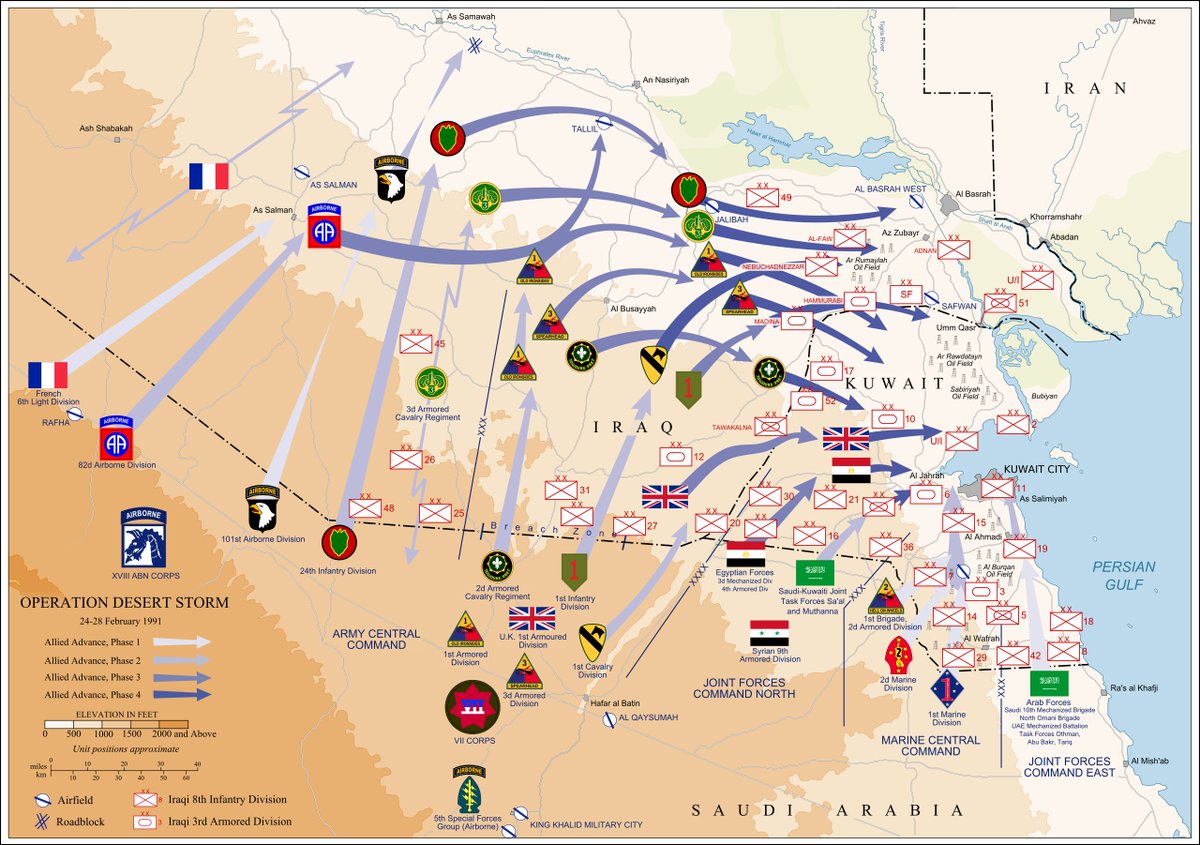
16/ So, in short, there is no modern comparator for what Ukraine is trying to do. It lacks control of the air, and western nations have failed to provide the kinds of modern fighters, or the quantity of long range attack systems (eg. ATACMS), needed.
17/ Therefore, Ukraine has had to think & plan creatively for a different way to take down the Russian operational system. This has involved HUMINT in rear areas, use of civil and military intelligence collection, and selective tactical actions to prompt Russian responses. 

18/ Russian responses aren't just tactical. Ukraine will be hoping to also see how Russian operational level C2 makes decisions & how its communication networks work. They will also want to find key reserve units, assess triggers for their deployment, and how long it takes.
19/ Other objectives of this current phase of degrading the Russian system including finding & destroying logistics / engineers (who lay minefields) as well as fire support units. Given the size of the Russian force in Ukraine, this is a considerable undertaking & takes time. 

20/ While this is occurring, information & lessons are being fed back into the Ukrainian system to improve targeting and their knowledge of the Russian operational system. And, it provides time for Ukrainian units to be raised, trained and rehearsed for their roles in later ops.
21/ That time will come. But before then, #Ukraine will do everything it can to make these ground combat operations as uneven as possible in their favour. That means they must steadily, methodically take down the Russian operational system over the coming weeks.
22/ One final element of this approach is important. In holding back most of their tactical forces, the Ukrainians have a lot of flexibility about where they eventually make their main effort in subsequent phases.
23/ This Russian system, perhaps the most complex multi-domain system ever constructed, includes EW, air defence, long range fires, multiple protected N2 nodes, etc. No country on earth, besides the US, could attack and degrade such a system. Except #Ukraine.
24/ When they do, the Ukrainians will have disconnected tactical units from achieving Russia’s strategic objectives in Ukraine. They will have given their soldiers the best chance of breaking through the Russia defensive lines & unhinging their operational scheme of defence. End 

25/ For those who are interested, I will be publishing a longer piece at my substack that explores this topic. . Thank you to the following whose images were used in this thread: @Militarylandnet @combined2forcesmickryan.substack.com
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh