🧵Thread:
I have recently obtained a valuable russian document titled "Recommendations for countering an enemy operating as tank and mechanized columns." This thread will include analysis of select section of the manual, extracting insights from its contents.
I have recently obtained a valuable russian document titled "Recommendations for countering an enemy operating as tank and mechanized columns." This thread will include analysis of select section of the manual, extracting insights from its contents.

2/ The manual highlights utilization of combined-arms units and formations by the Armed Forces of Ukraine. According to them, AFU tactics are based on NATO strategy, adapted for local conditions, and implemented by AFU commanders through memorized "NATO combat algorithms”. 
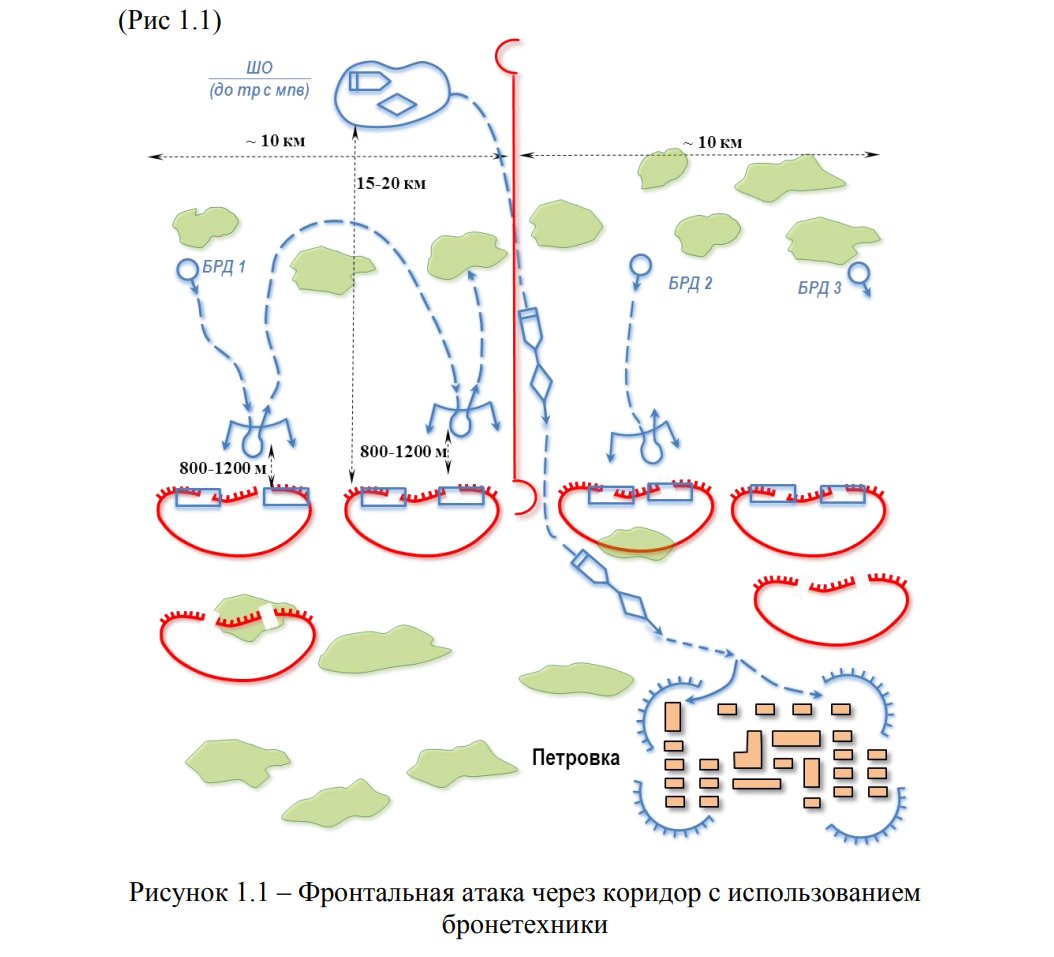
3/ The discussed section is titled "Frontal Attack via 'Pierced' Corridor with Armored Vehicles."To enhance clarity, I will blend book visuals with my original graphics.
As per the manual, AFU units initiate the first stage by conducting reconnaissance with small recon groups.
As per the manual, AFU units initiate the first stage by conducting reconnaissance with small recon groups.
4/ These groups typically consist of a platoon-sized unit (30 personnel), reinforced with 1-2 tanks and 2-3 BMPs. Notably, alternative vehicles like pickups with mounted firearms have been mentioned. Each group operates within a 5-10 km front. 

5/ In the subsequent stage, following the identification of a vulnerable point in the defense by the recon team, the assault unit rapidly progresses towards the designated breakthrough location. Two distinct compositions of AFU assault columns have been noted: 

6/
- A tank column comprising 8-10 tanks, with infantry positioned on the armored vehicles, commencing from the 4th or 5th tank.
- A mixed column, featuring the initial 5-9 tanks, followed by IFVs.
- A tank column comprising 8-10 tanks, with infantry positioned on the armored vehicles, commencing from the 4th or 5th tank.
- A mixed column, featuring the initial 5-9 tanks, followed by IFVs.

7/ During the advance towards the breakthrough area, artillery engages in preparatory fire, targeting entire width of the defense line. The objective is twofold: to obscure the main direction of the attack and to hinder the defending forces' ability to maneuver 

8/ The AFU operates as a column without deploying into a battle formation or dismounting infantry. AFU swiftly advances in a march order, following the best route through open terrain. The objective is to rapidly breach troops' frontline, anticipating collapse of defenders 

9/ Subsequently, the AFU assault unit bypasses russian second echelon units, aiming to capture the nearest town. During the approach, Ukrainian vehicles increase speed and heavily shell the outskirts, forcing defending unit to retreat deeper into a town, allowing safe dismounting
10/ The russians analyze the strengths of this tactic and propose countermeasures. Per their analysis, AFU objective is to overpower Russian units and disrupt coordinated defense. The direction of attack is determined based on weak points identified by reconnaissance groups.
11/ Mentioned weaknesses: well-established recon allows to detect the Ukrainian assault column's movement beforehand. Additionally, the advancing assault unit has limited firepower and striking capabilities, with only the first 2-3 tanks (BMPs) able to engage in combat. 

12/ They also note that the rapid selection of the breakthrough point may not always uncover the presence of minefields. Furthermore, the loss of communication with command or supporting artillery is seen as a factor that can result in the abandonment of further assault.
13/ To counter this tactic, authors emphasize that recon operations should be conducted to detect assault column movements within a range of 5 km. AT minefields should have at least three rows. There should be designated responsible commanders for each junction between units.
14/ Artillery fire should be prepared on likely paths of the assault unit movements to slow down advance. Commanders should prepare anti-tank reserves, and form tank destroyer groups in motorized infantry platoons. 

15/ Additionally, they should plan airstrikes by air force on call, utilizing helicopters equipped with ATGMs and NARs. Authors put emphasis on maximizing concealment and camouflage of other assets as well.
16/ As the AFU approaches the 2000-1000 m range, tanks and MT-12 guns engage in direct fire, supported by anti-tank guided missile systems. Once the AFU breaches the minefield or reaches the 250-300 m range in front of russian positions, tank destroyer groups come into action.
17/ In the event of a breakthrough, AT assets are deployed from cut-off positions. If the AFU successfully breaches positions, measures are taken to close the gap by launching flank attacks from units stationed in unaffected areas, preventing the enemy's reserves from advancing. 

18/ In summary, it should be noted that this represents their perspective on AFU actions. However, the battlefield often unfolds in unpredictable ways, deviating from established plans and algorithms, particularly in relation to the armament and actions of the assault unit.
19/ Their counter-actions rely heavily on multiple components, such as the air force, minefields, reconnaissance, artillery, and anti-tank assets. Effective implementation of this defense requires a certain level of coordination among units to ensure an efficient defense. 

20/ Please be advised that this thread specifically addresses a particular tactical element from the manual and does not provide an exhaustive analysis of the entire document. Subsequent threads will analyze other sections covering various tactics and proposed counter-measures.
21/ If you found this content valuable, please support by liking, retweeting, or by donating via Buy Me a Coffee, which is linked in my bio description. Your engagement enables me to provide better materials. Follow for upcoming threads with further analysis.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh