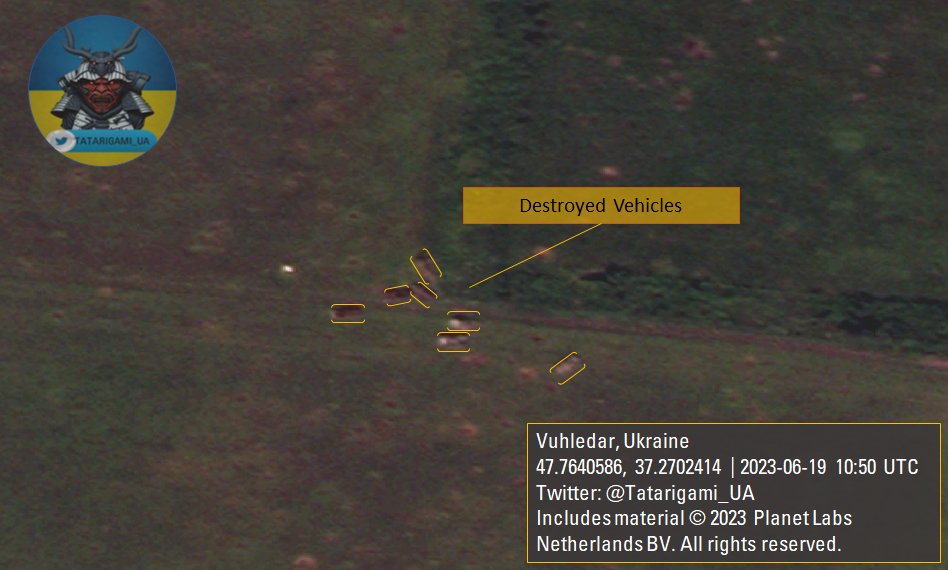
🧵With new satellite imagery from Vuhledar revealing the extent of the catastrophe experienced by the Russian army during the winter, as well as the ongoing counter-offensive, it is crucial to explore the role of minefields and operational planning in shaping assault operations. 

2/ The objective of a minefield extends beyond causing harm; it also aims to impose a specific mindset and tactical approach on the opponent, compelling them to act in a manner most advantageous for the party laying the minefield. Minefields limit the enemy's maneuvering options 
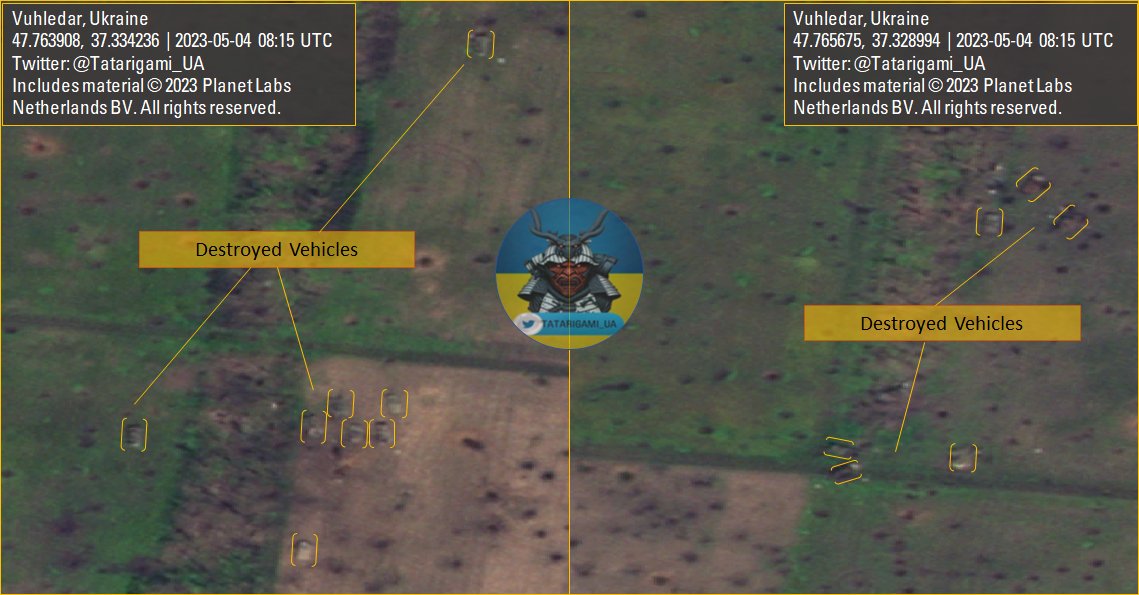
3/ Mechanized units are used for maneuvering, executing assaults, bypassing enemy positions, and launching flanking maneuvers. Their firepower and off-road speed make them ideal for such operations. However, minefields restrict maneuvering space, hampering the assault's tempo. 
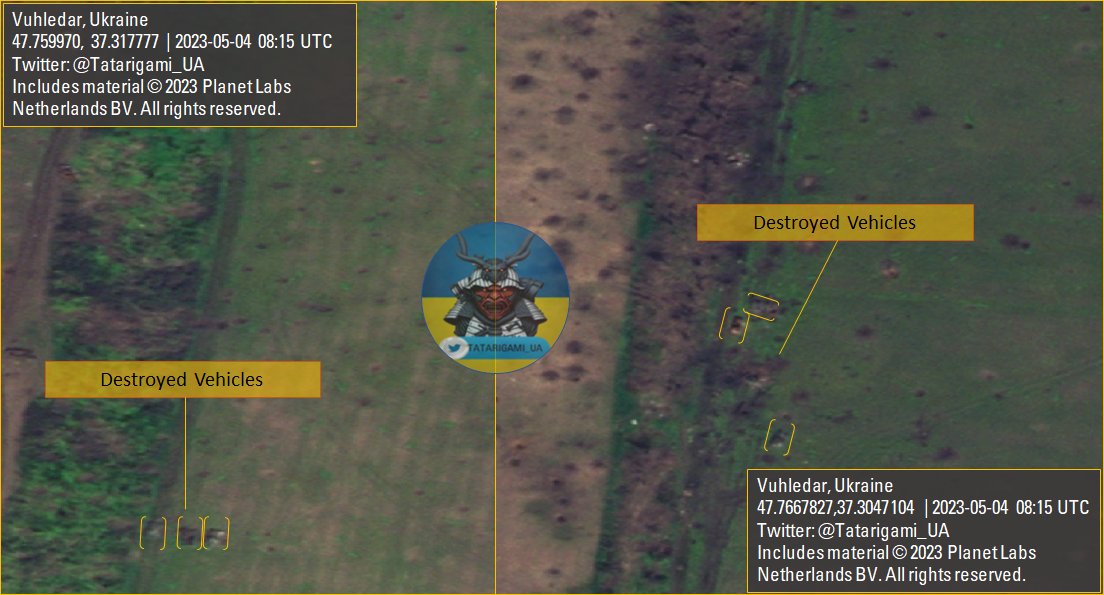
4/ When encountering minefields, the enemy must allocate extra resources for mine clearance, including engineering vehicles. Yet, even after clearance, the available path remains narrow, compelling large forces to move predictably along a confined route 

5/ It is often mistakenly assumed by observers that russians and Ukrainians are not utilizing tank plows to clear paths. However, this is inaccurate as both sides employ tank plows. It's important to note, though, that tank plows are not a universal solution to all the challenges 

6/ While not a widely adopted tactic, the utilization of off-route mines, such as the TM-83, is not uncommon. It enables the engagement of tanks from the flank once they are detected by mine sensors, rather than relying on the pressure exerted by the tank's weight itself. 
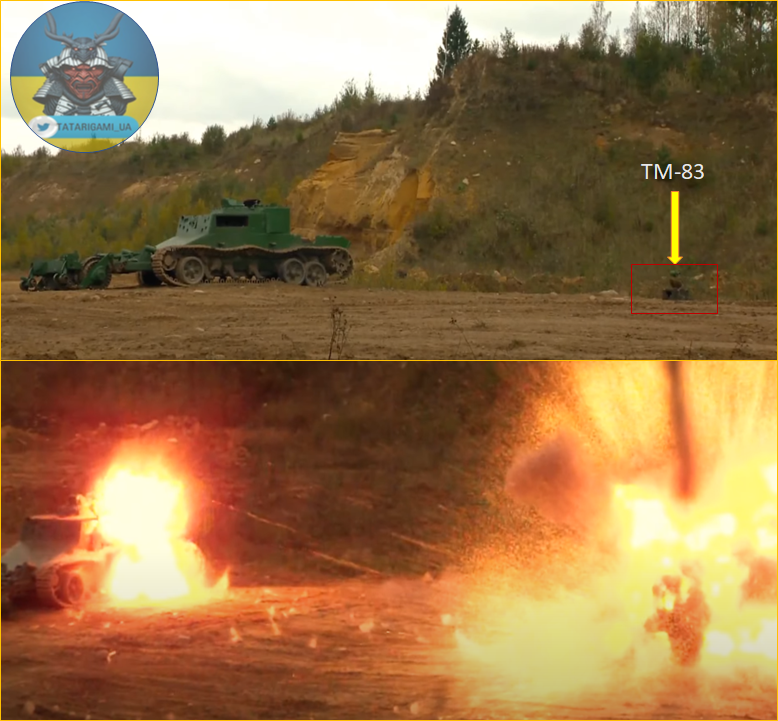

7/ Another alternative is the use of modified mine setups that are designed to resist mine plows. In this specific case, the mine is configured to detonate approximately 1.5 to 2 meters after encountering the plow. 
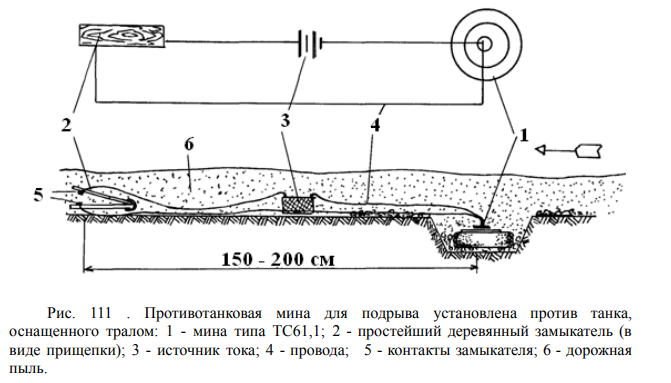
8/ As troops follow the narrow-cleared path, if the clearing tank is immobilized, it significantly hampers or even blocks the movement of the column. This situation presents a perfect opportunity for artillery to target and inflict damage on the immobilized or slowed-down forces. 
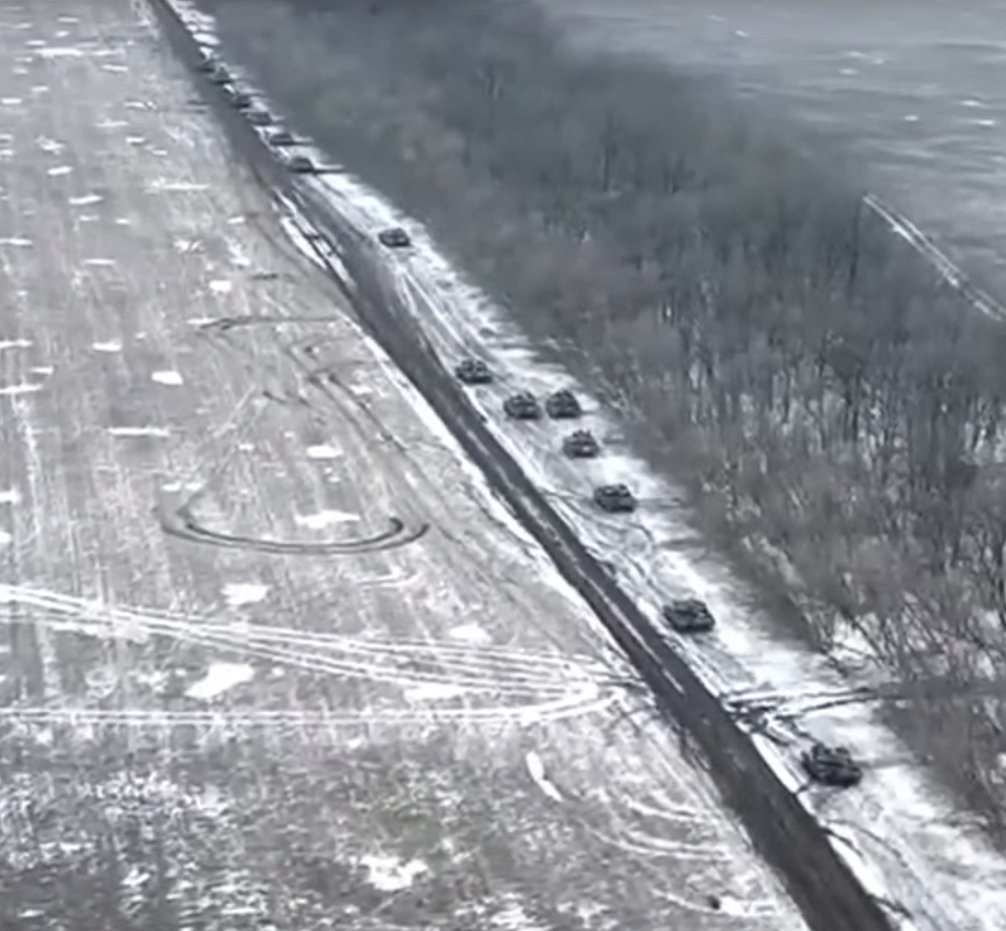

9/ Reinstalling mines after their detonation or removal by the enemy is a critical factor. This introduces an additional layer of complexity that the assaulting side must plan for, prepare, and counteract.
10/ Insufficient preparation results in a reduction of mechanized firepower advantage in assaulting forces, shifting the battlefield dynamics to artillery duels and infantry assaults. This restricts and challenges maneuverability for the assaulting side. 
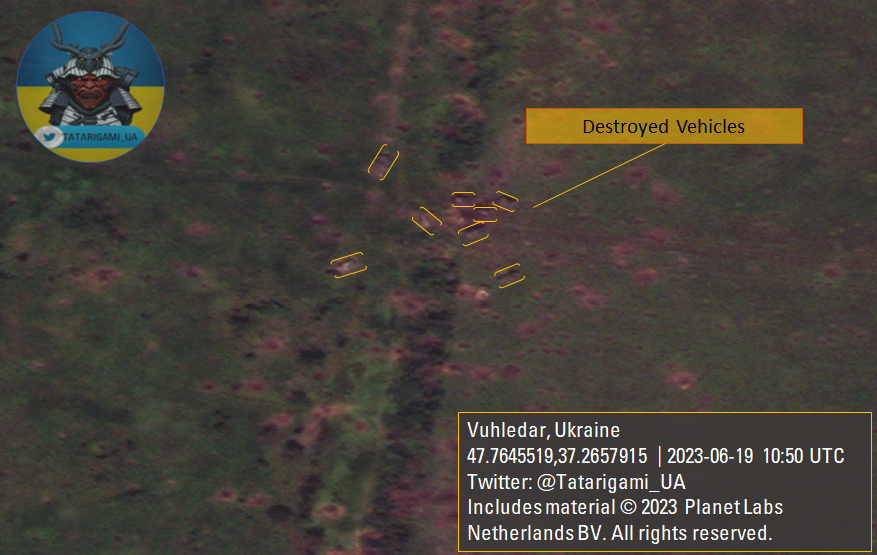
11/ In summary, the critical role of minefields and AT measures in limiting enemy maneuverability and impeding their mechanized forces from achieving a breakthrough is evident. However, the root cause of this failure lies in the absence of proper planning and bad intelligence.
12/ Minefields add complexity, but with effective planning, they are not detrimental. If planners on the assaulting side fail to allocate resources properly, make incorrect decisions based on bad intel, or order assault despite insufficient resources, they are bound to fail. 
If you found this content valuable, please support by liking, retweeting or following. Your engagement enables me to provide more and better materials.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh