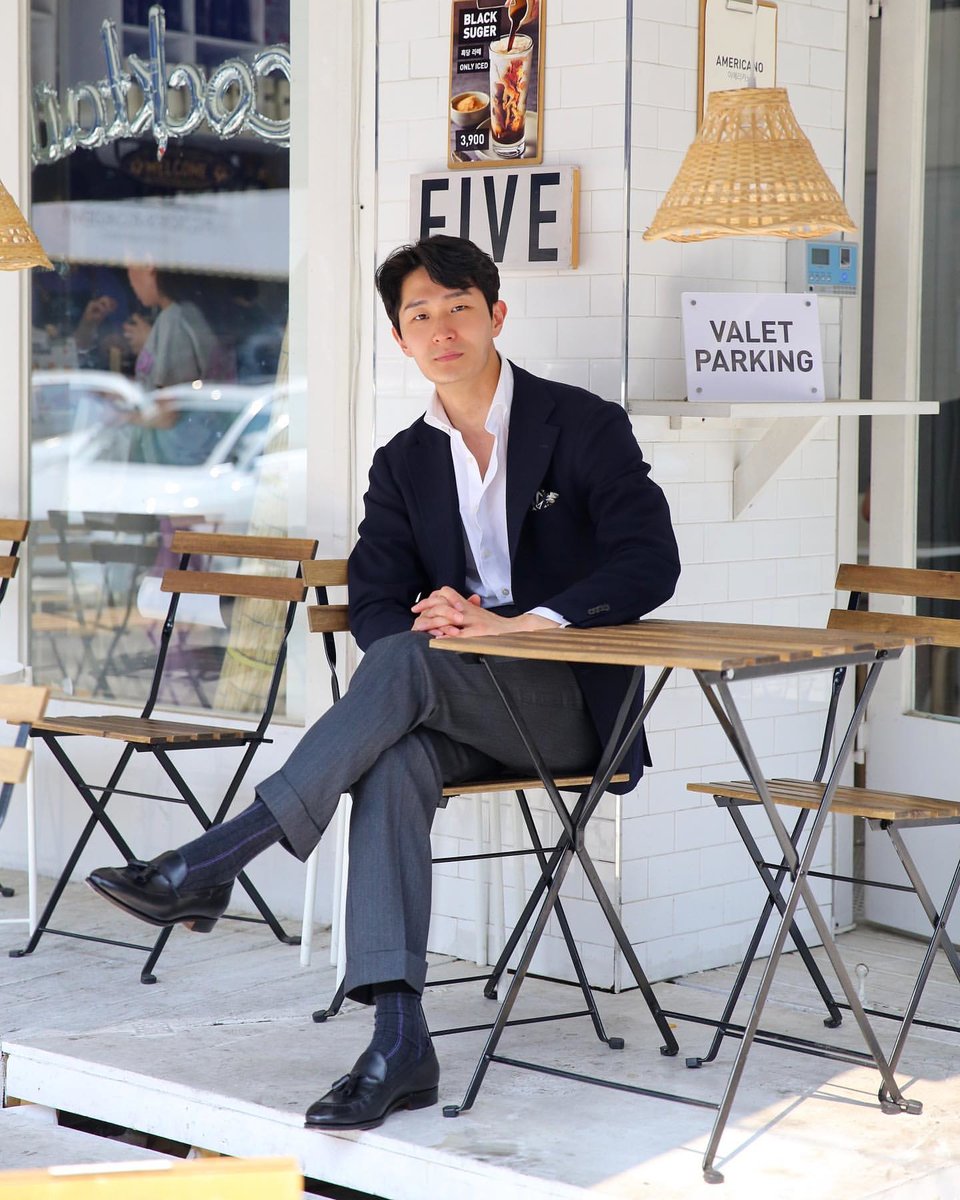
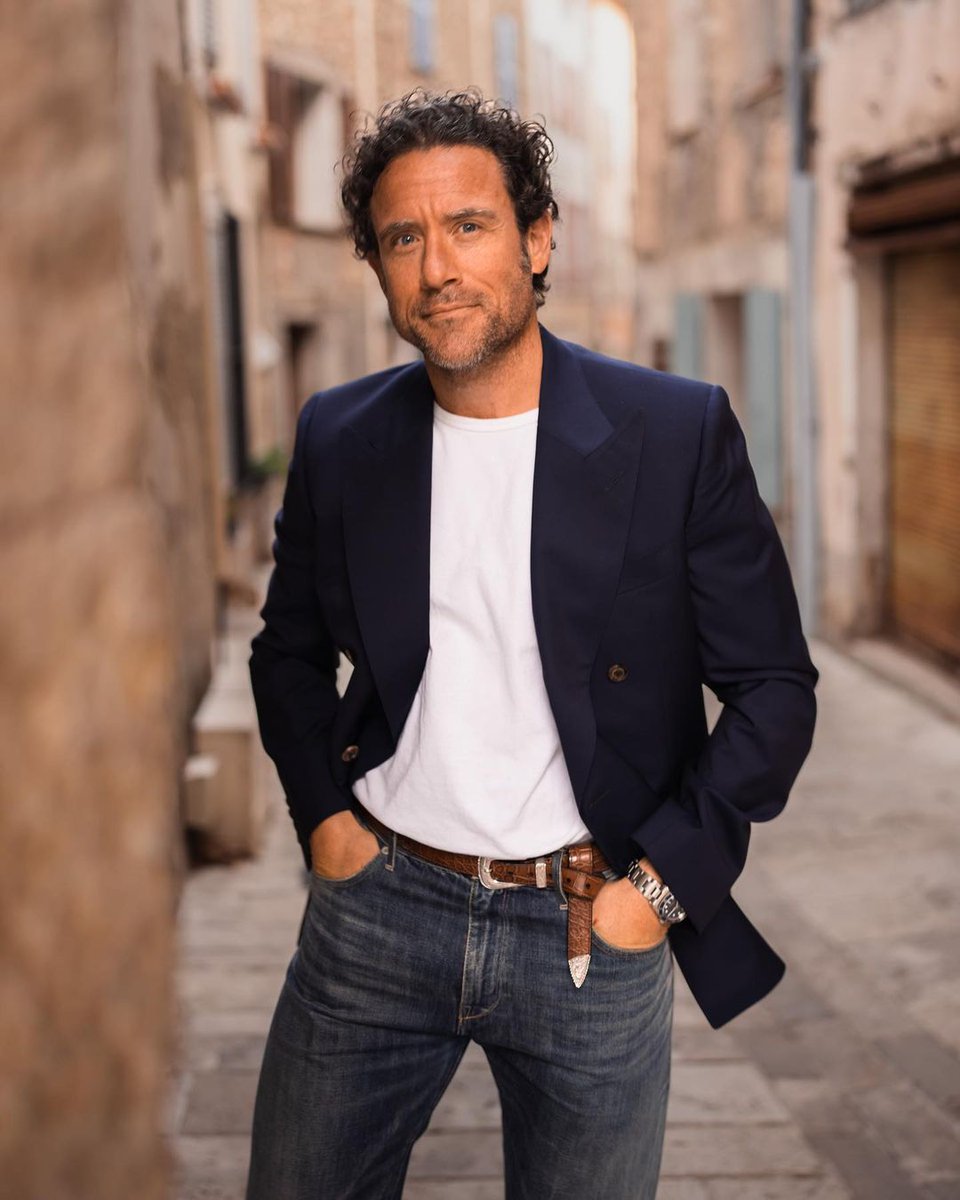
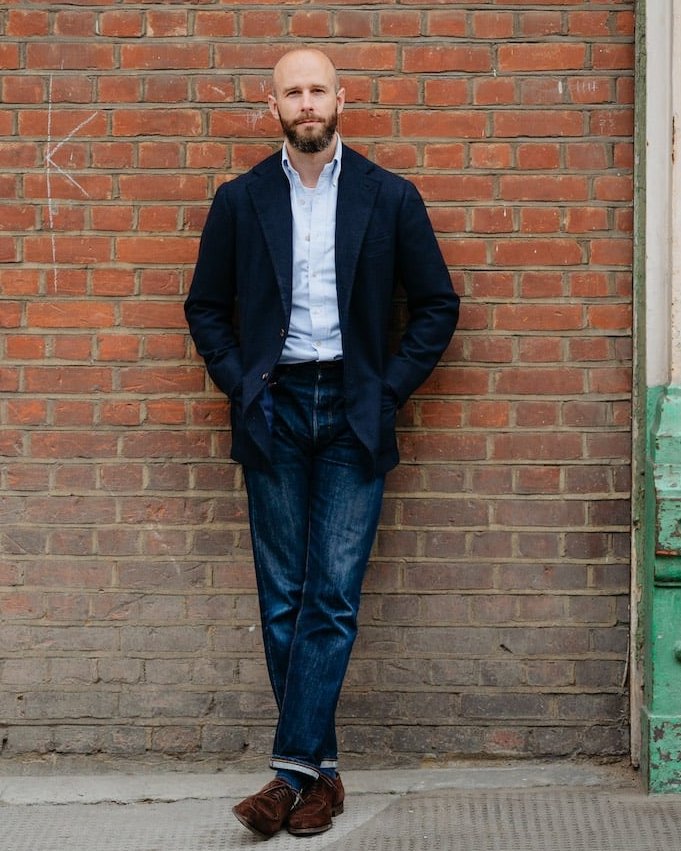
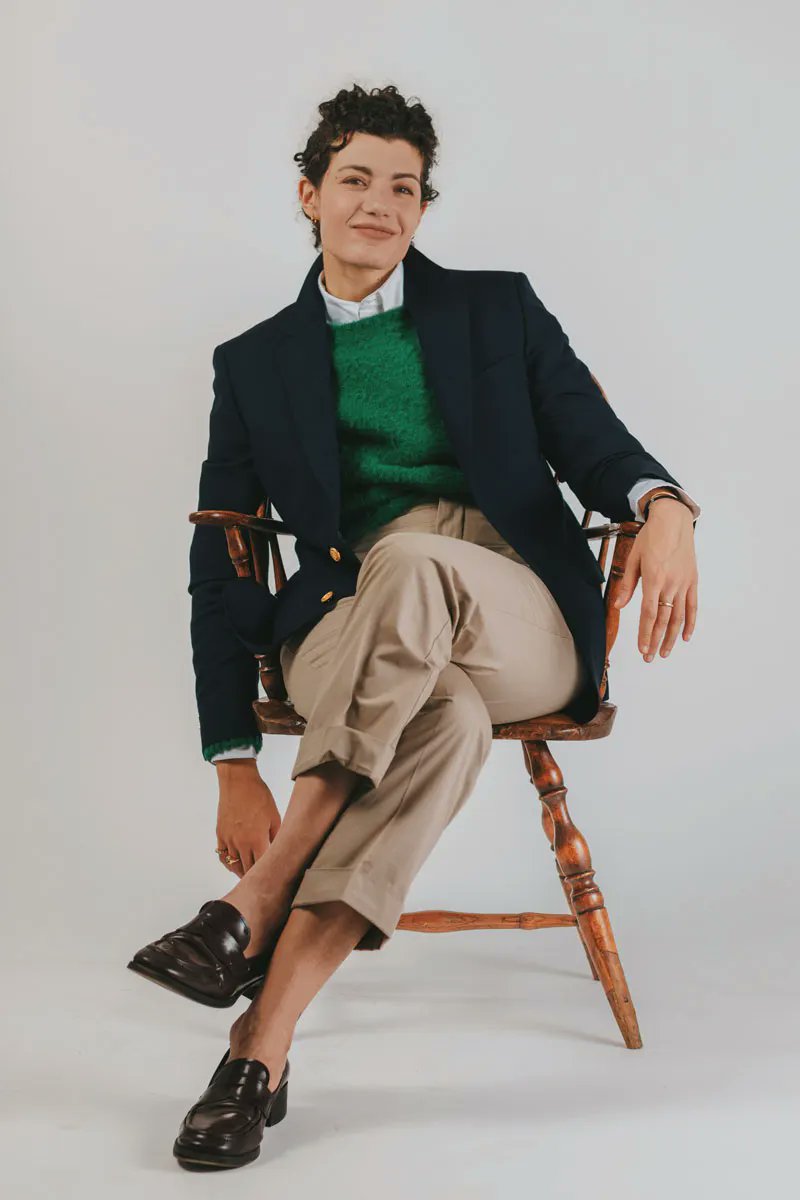
WHY ARE SUITS SO EXPENSIVE?
Whenever I post a link to a suit or sport coat, many people respond in shock bc of the price. Let's break down why tailored clothing costs so much money. 🧵
Whenever I post a link to a suit or sport coat, many people respond in shock bc of the price. Let's break down why tailored clothing costs so much money. 🧵

For this, I'm going to assume that the suit was made in the United States, largely because I'm relying on information given to me by a friend who works at a high level in the US suit manufacturing industry. These are simplified numbers but are generally reflective of reality.
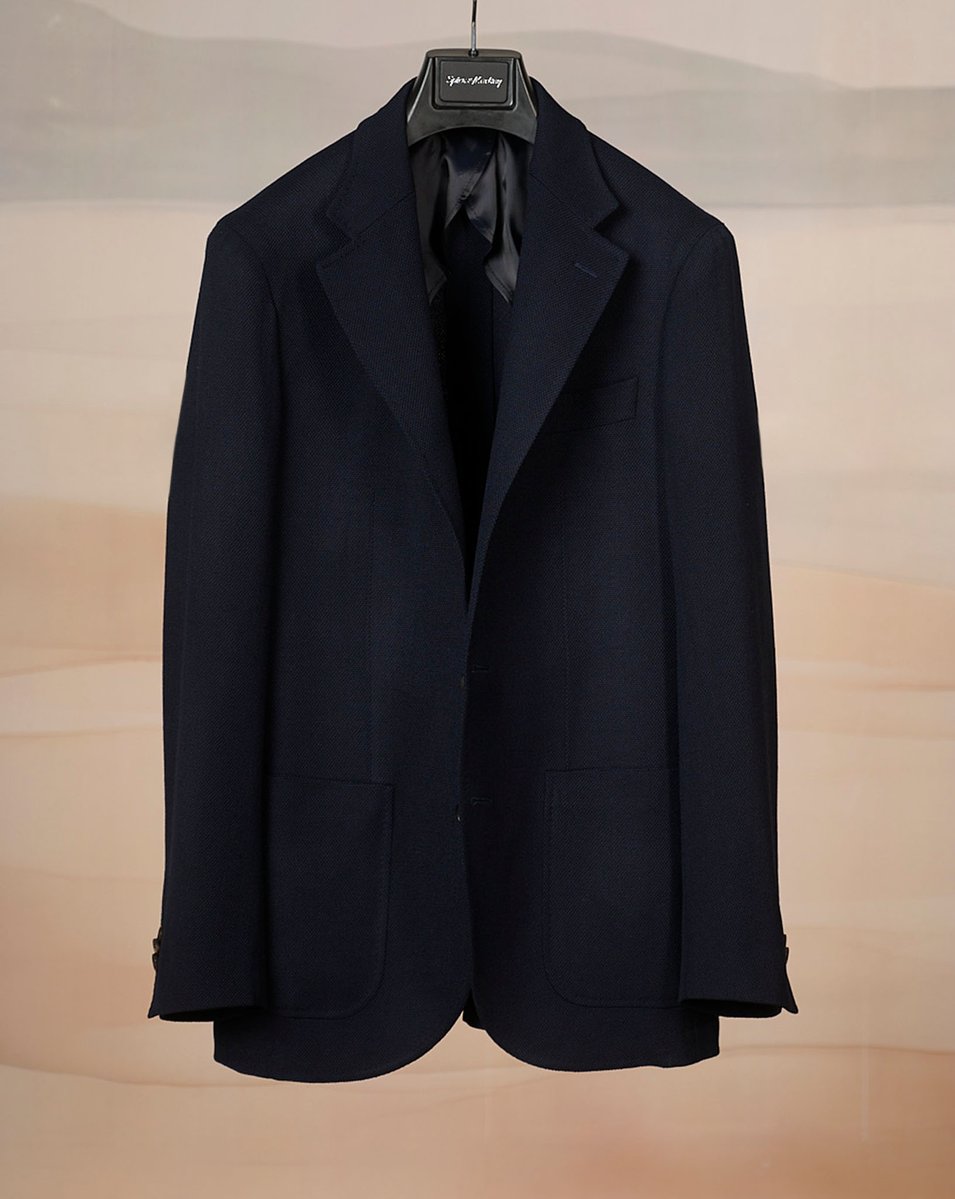
The first thing to understand is that suits and sport coats are not made like casualwear. They are built up from many layers of haircloth, canvassing, and padding, which are carefully sewn together using either specialized machines or human hands (needle and thread) 

Let's break down the cost of making a suit.
A garment worker at a US suit factory makes about $15/hr. The total number of minutes spent on making that suit (in terms of actual operations) will be about 260 mins.
A garment worker at a US suit factory makes about $15/hr. The total number of minutes spent on making that suit (in terms of actual operations) will be about 260 mins.

The factory also has to pay for worker benefits, which, spread across the total production, adds about $23 per suit. And then there's the cost of overhead (e.g., warehousing, administration, etc.). That adds an additional $26 per suit.
So now we have spent $114.
So now we have spent $114.
There is also the cost of materials. A factory may spend about $30/meter for fabric. They need 3.5 meters to make a suit, which brings the price per suit to $105. Now add $30 worth of trims (haircloth, padding, canvas, buttons, and such).
So now we have a total cost of $249.
So now we have a total cost of $249.

$249 is how much it costs the factory to make a suit. To make a profit, they do a gross margin markup of 40%. That means they sell it to a brand for $415. The brand has to pay for a bunch of other expenses (e.g., marketing, administration, etc). 

The brand also has to make a profit. So they sell the suit to a store at a gross margin markup of 60%. (This store, too, has its own expenses, such as sales staff, warehousing, marketing, etc.).
Now, we have a retail price of $1,037.
Now, we have a retail price of $1,037.

The above is a rough sketch of what it would cost to make a fully machine-made, fully canvassed suit in the United States. The price could go up on a host of factors. The factory could spend more on nicer fabric. Or they can include some hand-tailoring details. 

Alternatively, the price can go down. The suit could be made in China, where the avg garment worker in a suit factory makes just under $4/hr. They could buy cheaper fabric. Or they can do a fully fused or half-canvassed construction, which may be less durable or not hang as well.
One of the ways to cut costs is in the patternmaking stage. Remember, a suit is made from many layers of material. Each of these layers has to be cut according to a pattern, which is a term for the architectural blueprint for the garment.




If a factory is taking the time and care to make a good suit, they will draft the pattern a little larger than what they need, then lay those internal pieces—haircloth, canvas, padding—on and carefully stitch. Then, they trim away the excess material—trim, adjust, trim, adjust. 

However, if they're trying to cut costs, the components of the suit are cut exactly as they're supposed to be, laid on top of each other, and just sewn. There is no trimming or basting, you just sew everything together and hope for the best.
The problem is, cloth moves and linings shift. So things, sometimes, these lower-end garments don't come out quite right. Everyone along the stage is trying to maximize money, so the garment goes out to the sales floor as-is, and you hope a customer doesn't notice.
However, even at the lowest level—garment made in China, cheaper fabrics (but still natural fibers), fully fused or half-canvassed construction, no trimming or adjusting during the manufacturing process, etc.—you are looking at a retail price of about $500.
So, the answer to the original question: Why are suits expensive? They are more complicated to make than casualwear. They often require more expensive fabrics. If they are made in the UK, Italy, or the US, there are wage and labor laws.
There are many ways to look good; you don't have to buy tailored clothing. But tailoring is a beautiful thing, and the price paid goes towards supporting workers who are skilled in a special area of manufacturing. You can also end up with a garment you love and look good in. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh