one way to help curb the excesses of fast fashion is to encourage ppl to value the patina and wear-and-tear that good clothes develop. that way, they: 1) buy less, buy better; 2) buy vintage; 3) wear things. examples
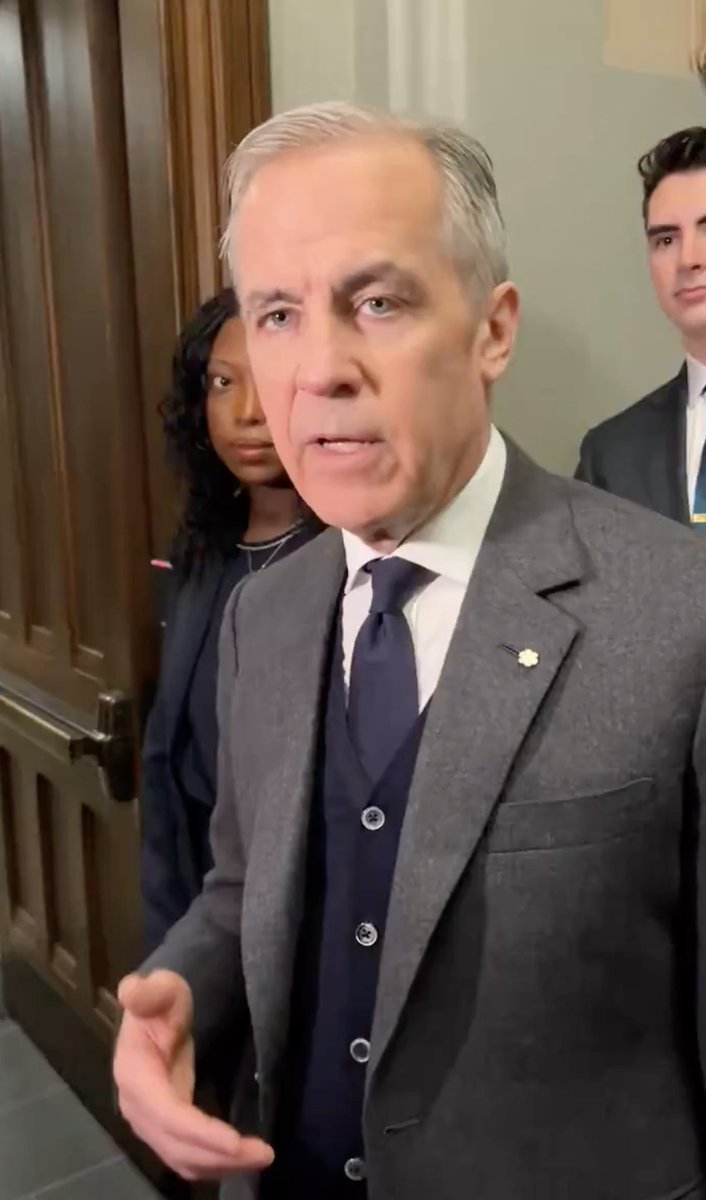
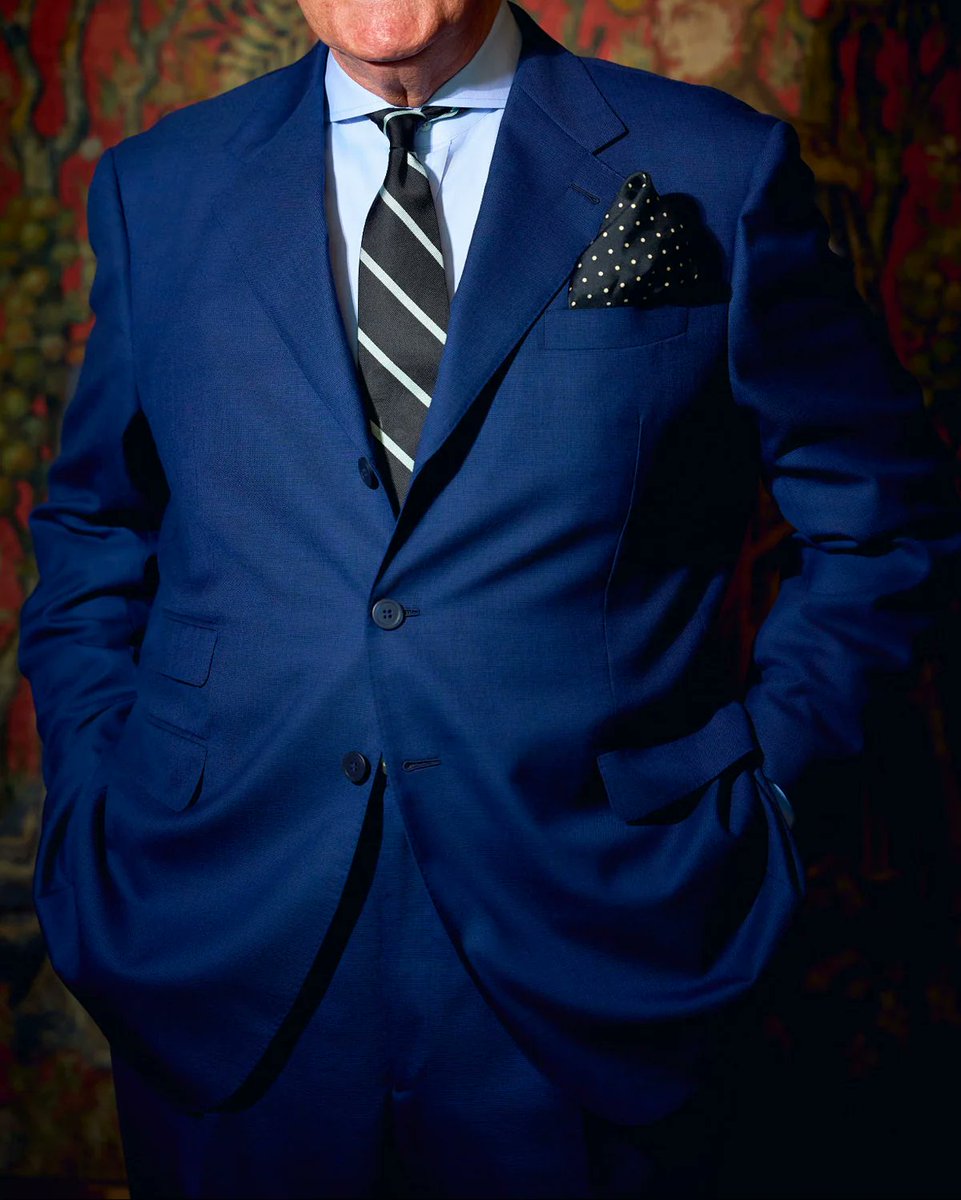
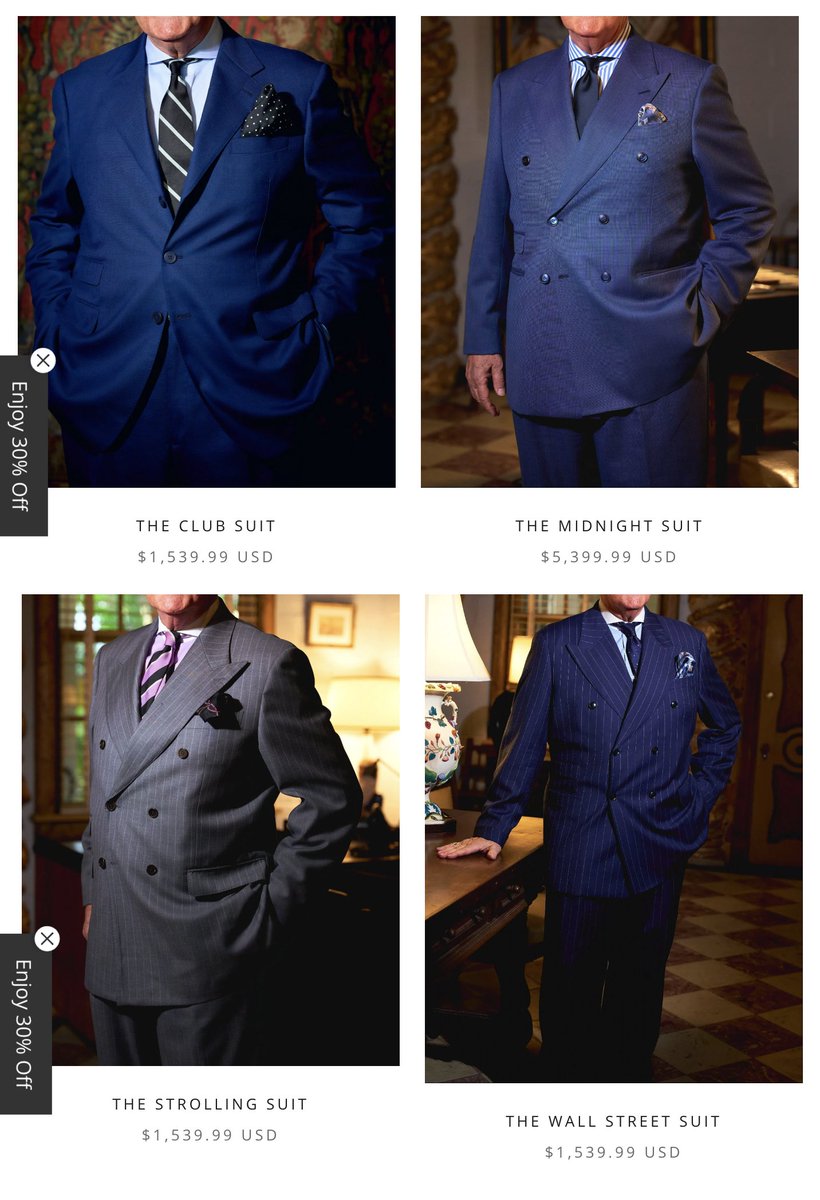
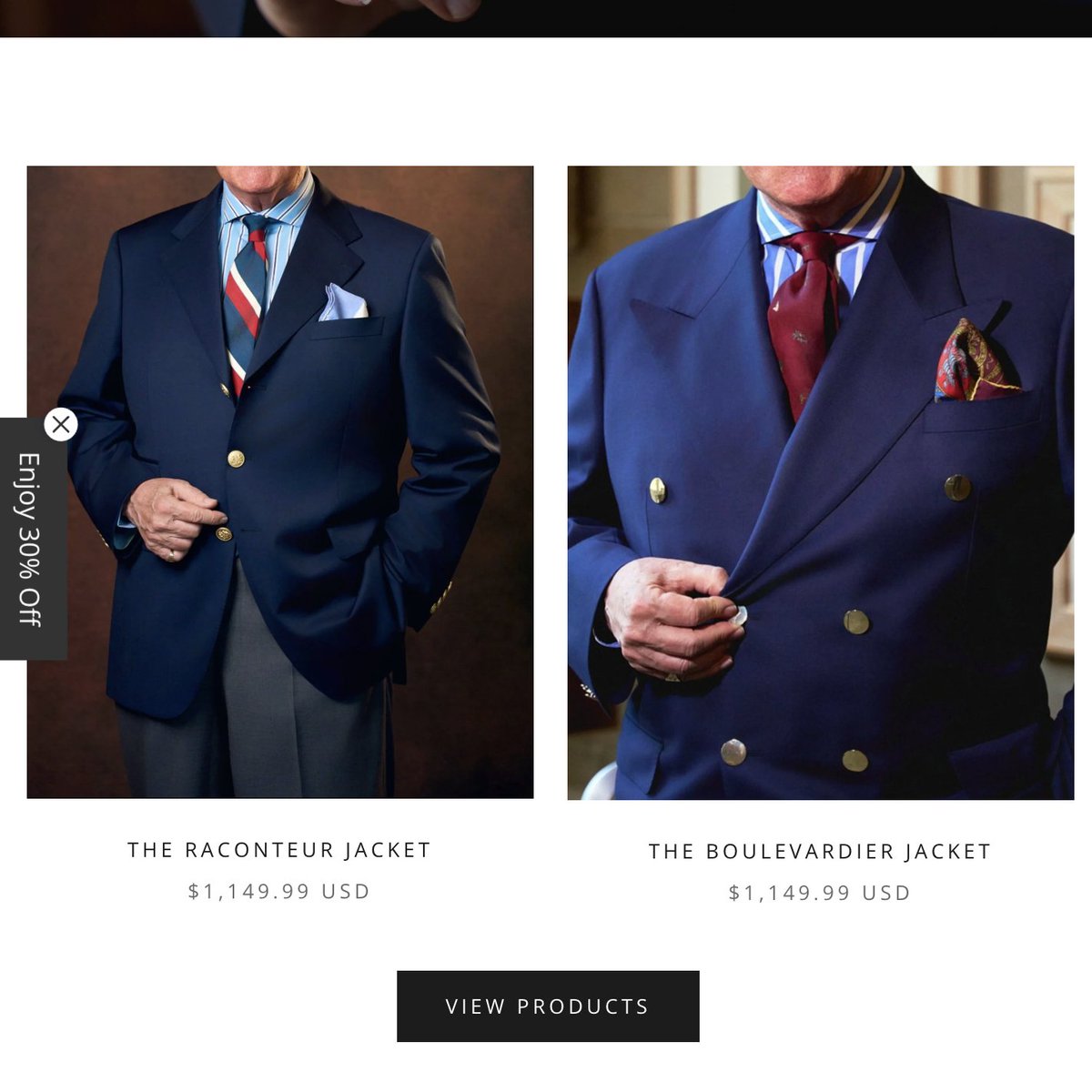
1. King Charles' patched-up suit (see hem)
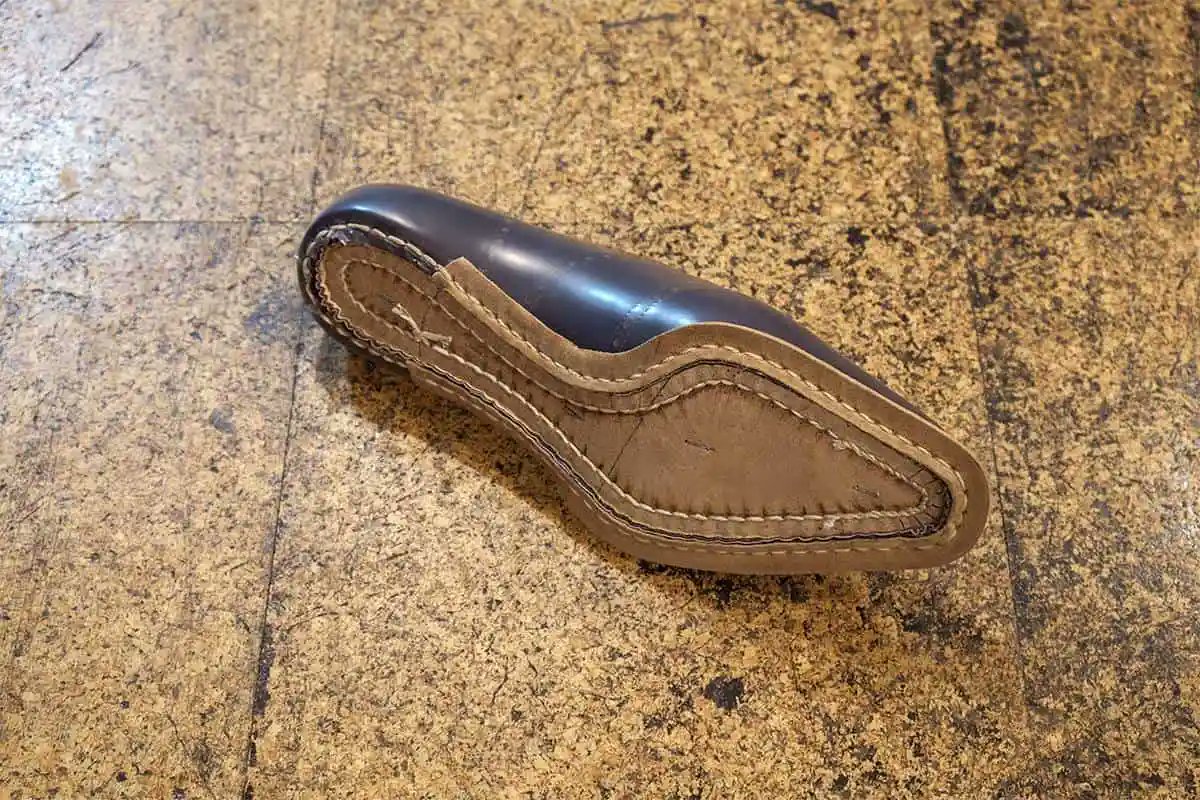
2. King Charles' patched-up shoes
3. Vintage Lee 101-J trucker jacket with a repaired collar (collar has been repaired by hand with a bit of oxford cloth). Vintage denim garments are also great in that they're softer and often have natural fades (rather than pre-distressed fades that don't always look very convincing)
4. Old sweatshirts (easy to find vintage; just search eBay and Etsy for vintage Russell Athletic). Looks great with old jeans and boots




1. King Charles' patched-up suit (see hem)
2. King Charles' patched-up shoes
3. Vintage Lee 101-J trucker jacket with a repaired collar (collar has been repaired by hand with a bit of oxford cloth). Vintage denim garments are also great in that they're softer and often have natural fades (rather than pre-distressed fades that don't always look very convincing)
4. Old sweatshirts (easy to find vintage; just search eBay and Etsy for vintage Russell Athletic). Looks great with old jeans and boots




the NYT had an article about this earlier this year about how old beat-up Birkins are a bigger status symbol than new Birkins. this is a very old concept—people who signal generational wealth are considered "higher status" than nouveau riche
nytimes.com/2023/03/04/sty…
nytimes.com/2023/03/04/sty…
the idea of aping the signals of the upper-most class seems kind of crass, but ... whatever gets you there is fine IMO. valuing quality things as they age is good. the wear-and-tear becomes part of the item's beauty, like the Japanese concept of kintsugi 

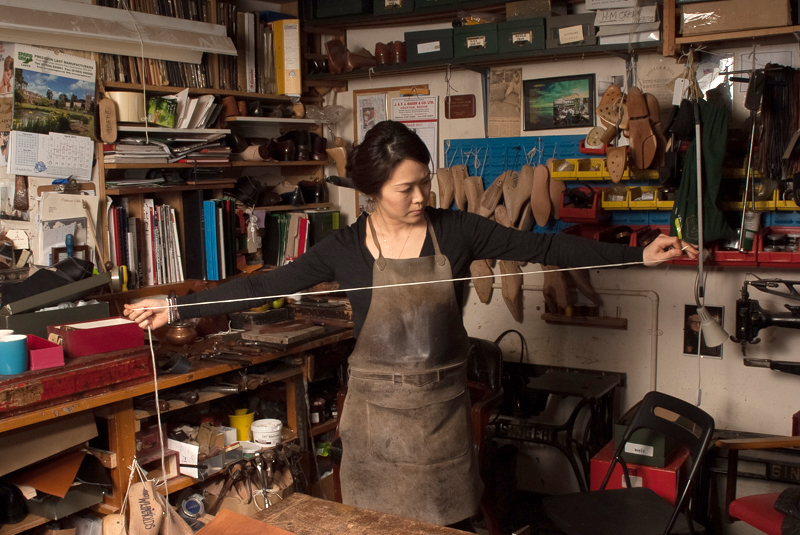
repair them. you can
1. darn old jeans
2. use invisible mending on knits and wovens
3. patch up holes
4. there are services for all these things. but if you can't afford them, you can easily do some of them yourself




1. darn old jeans
2. use invisible mending on knits and wovens
3. patch up holes
4. there are services for all these things. but if you can't afford them, you can easily do some of them yourself
https://twitter.com/DomainJulian/status/1699246641692430473




• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh