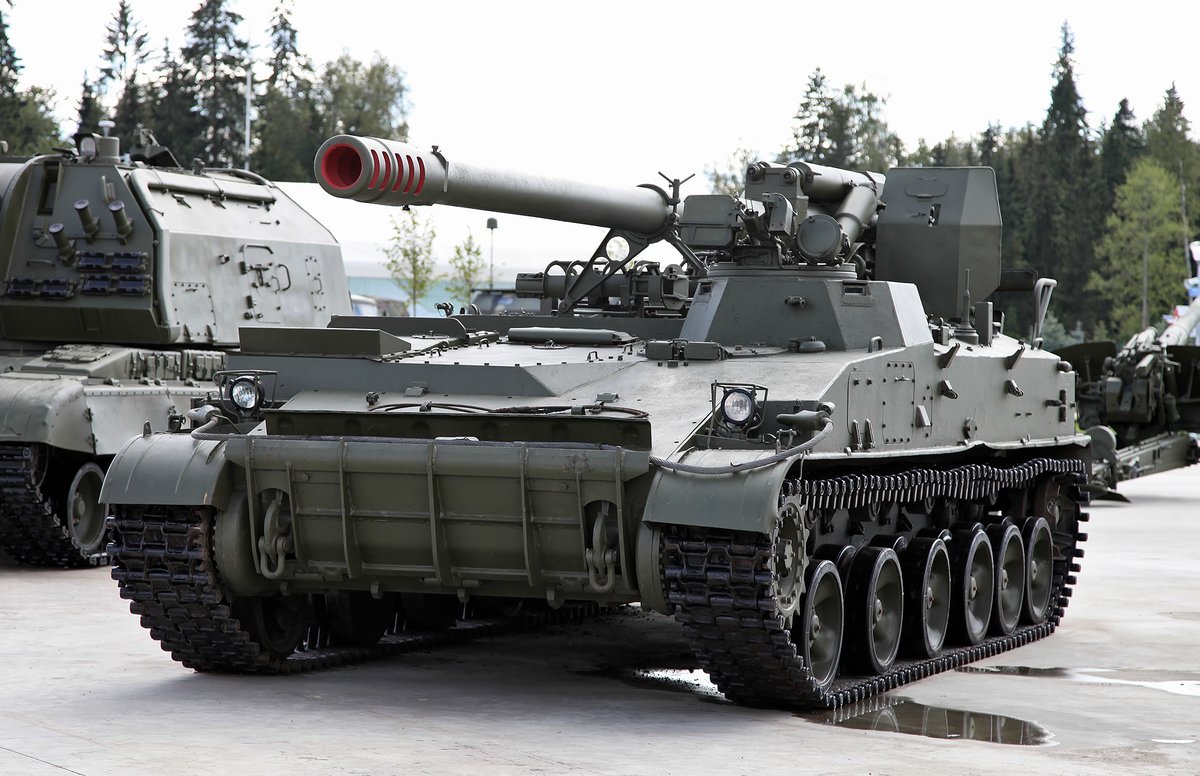
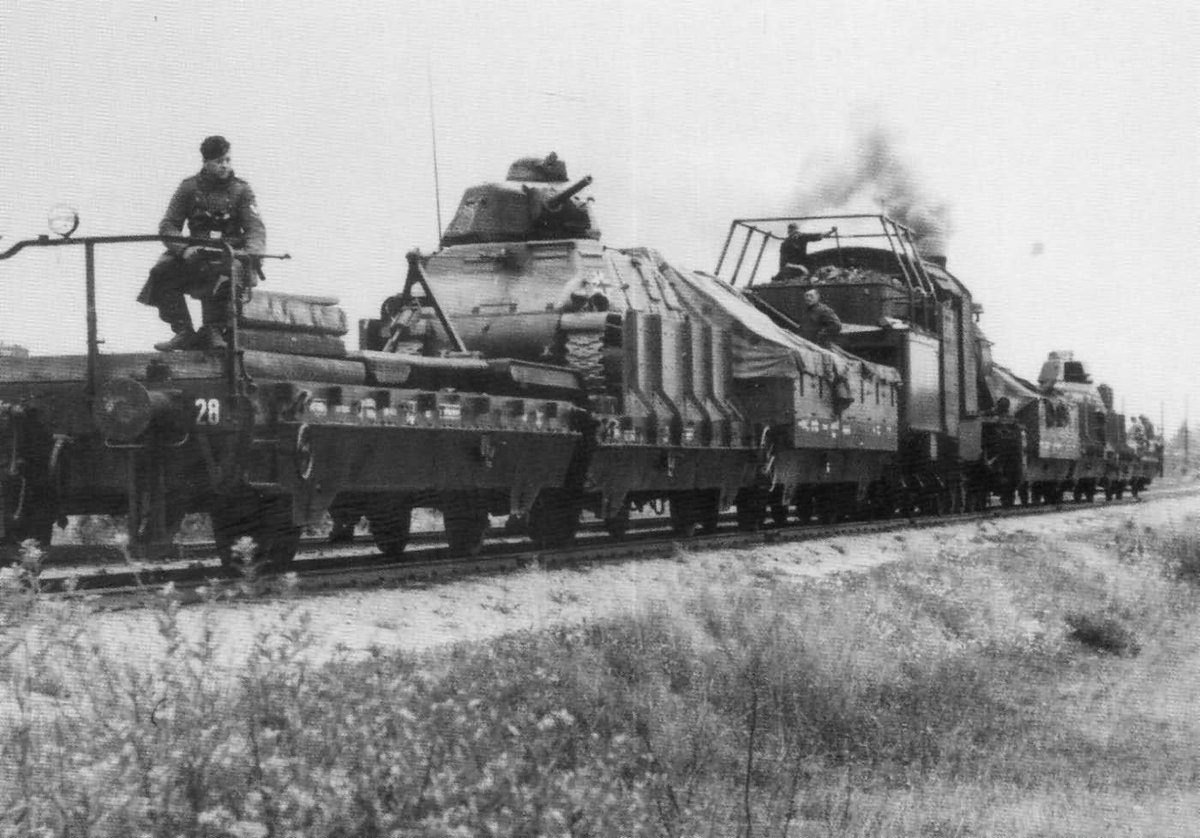
(2/25) By the end of WW2, the Soviets fielded considerable numbers of SPAs such as the ISU-152. But the ISU-152 was really mostly meant for direct fire and, with limited gun elevation (+20°), could only reach out to about 6 km. 

(3/25) In the immediate postwar years, SPAs were developed that could act as proper indirect-fire artillery. Among these were the SU-100P (obj.105) and SU-152G (obj.108). The latter had a 152 mm D-50 howitzer based on the 152 mm D-1.
kpopov.ru/military/kubin…



kpopov.ru/military/kubin…



(4/25) I've previously talked about the SU-100P in the context of the 2S5 Giatsint-S, but it and the SU-152G became victims of Khrushchev's enthusiasm for missiles, and neither entered full service. However, the chassis would live on in many other roles.

https://twitter.com/CalamineW/status/1689372334673530882

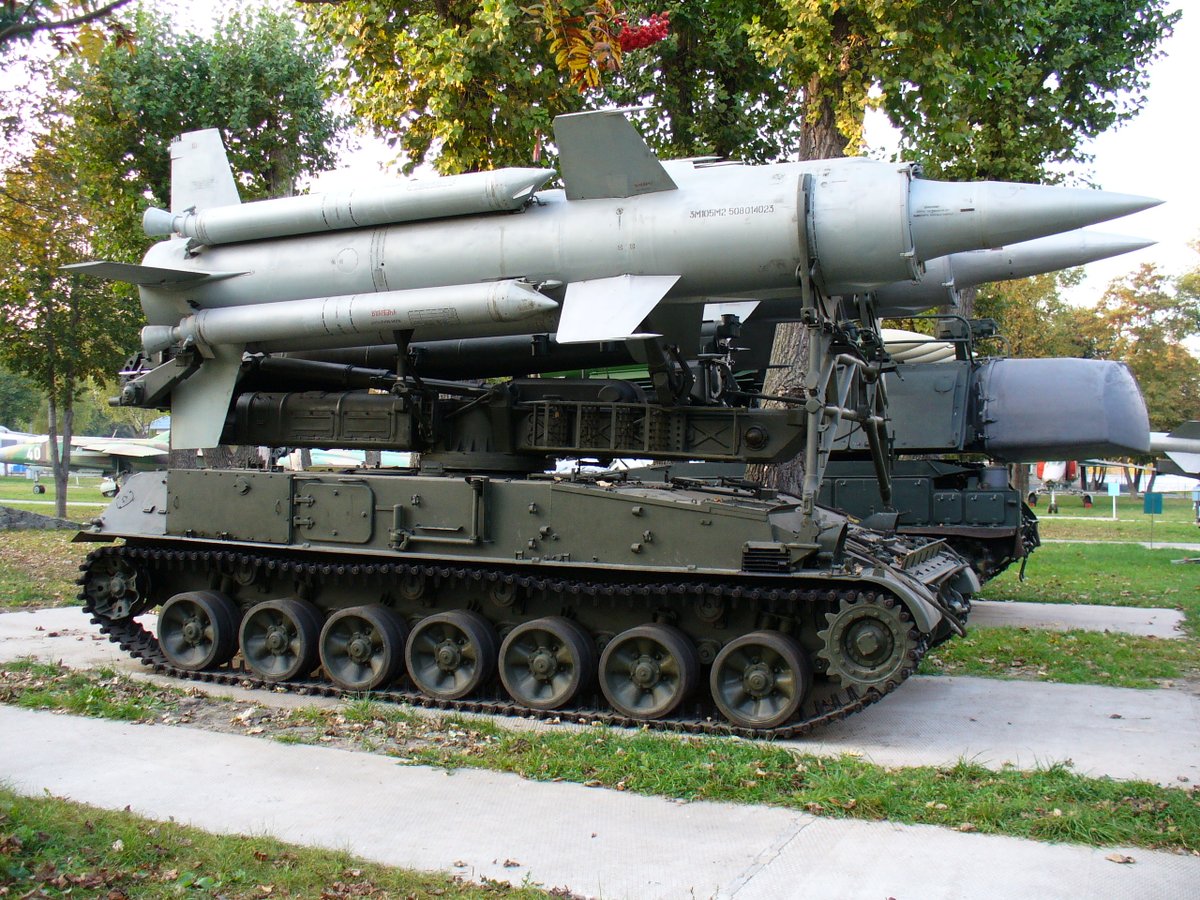
(5/25) One was the 2P24 TEL (obj.123) for the Krug SAM system. It is this chassis that would be the immediate precursor for the next generation of Soviet SPAs, Akatsiya, Giatsint-S, and Tyulpan.




(6/25) After Khrushchev was removed from power in 1964, the Soviets realised that they needed SPAs to keep up with mechanised forces. The Americans had introduced the M109 in 1963, and in time it would become NATO's standard SPA.
(7/25) In 1967, work began on the 'Akatsiya' ('Acacia') project. Uraltransmash, under Georgiy Yefimov, was responsible for the vehicle, while Motovilikha created the gun, once again under Fyodor Petrov (who else?). The 2S3 Akatsiya entered service in 1971.






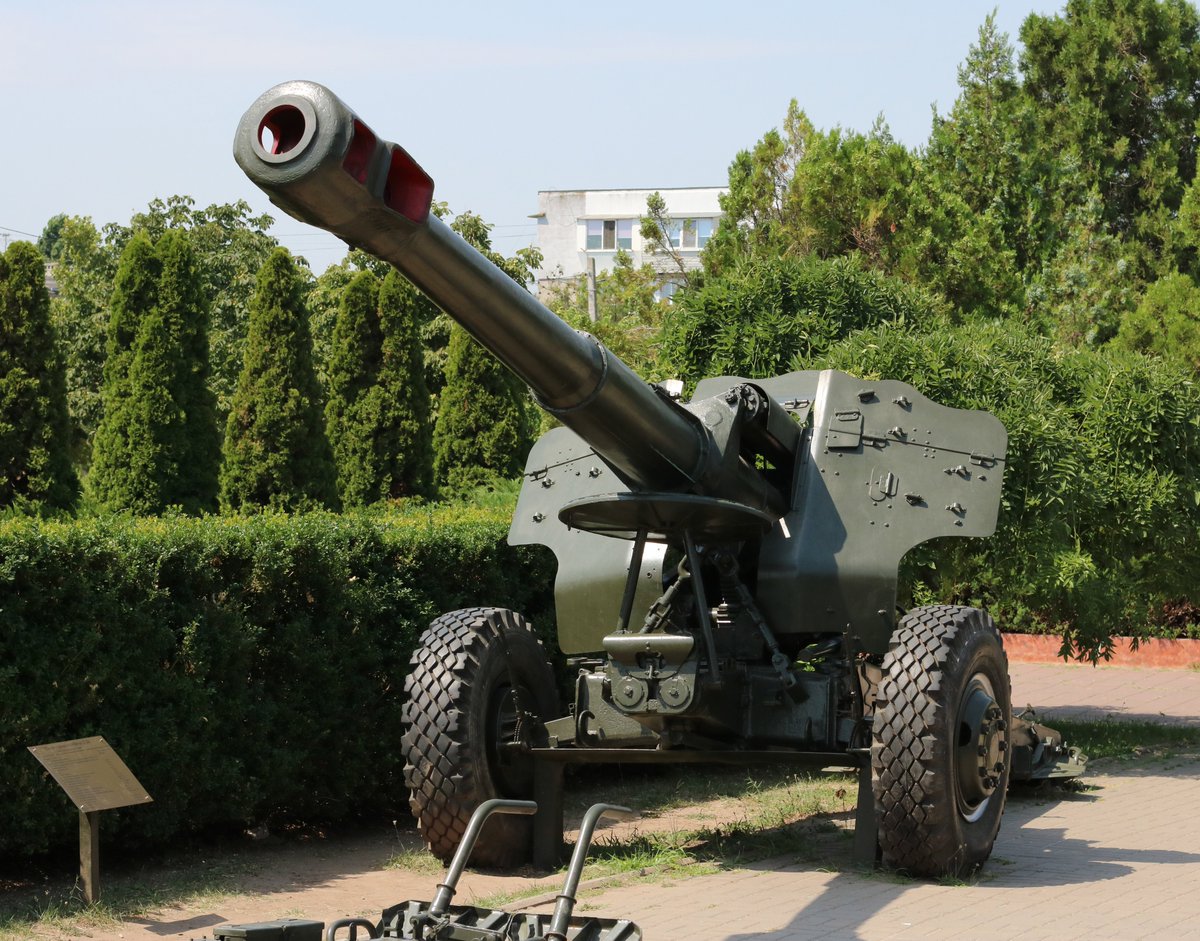
(8/25) The Akatsiya's 152-mm 2A33 gun is based on the 152-mm D-20 howitzer, which I have already talked about. It was planned that the Akatsiya would replace ALL towed 152 mm howitzers (ML-20, D-1, D-20) in Soviet tank and mechanised divisions.


https://twitter.com/CalamineW/status/1683166673342197761
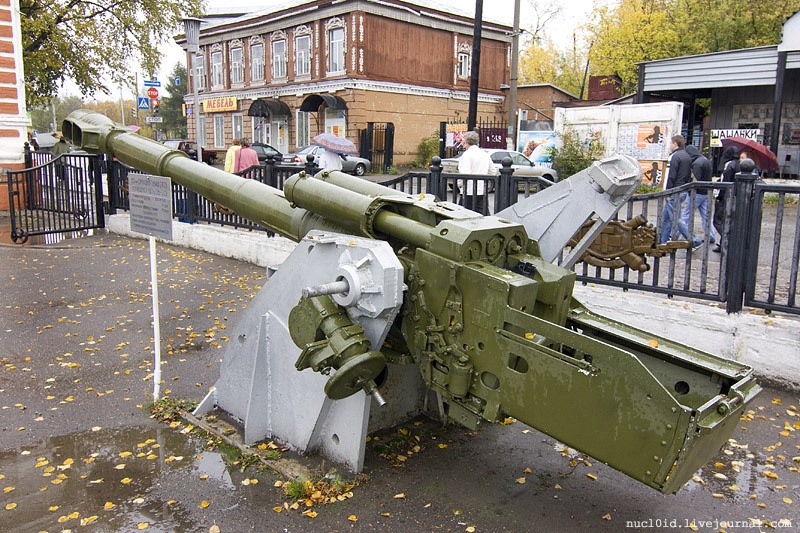


(9/25) The most significant external difference between the 2A33 (2A33M on 2S3M) and D-20 is the 2A33/33M has a fume extractor. The two guns are ballistically identical and use the same ammunition. The Akatsiya can also elevate higher (60°).






(10/25) The very earliest Akatsiyas effectively had the same hull as the Krug's 2P24 TEL, just with the rear half cut away and modified.




(11/25) This was soon changed to a different hull. About 200 2S3s were made before production switched to the 2S3M. It is difficult to distinguish them from the front, as most of the differences are in the rear hatches.
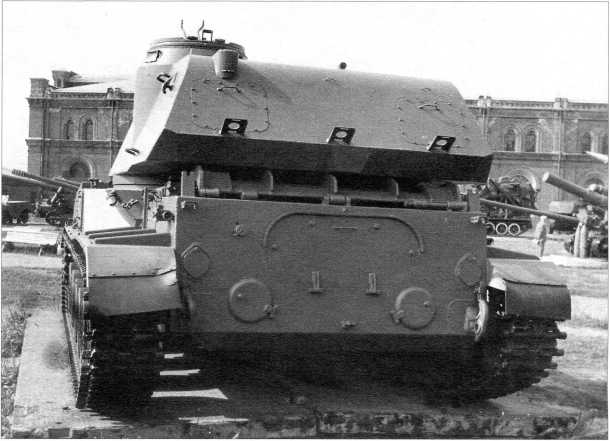








(12/25) The round hatches/hatch are used to pass ammunition into the Akatsiya from the ground, when firing from prepared positions.
(13/25) The original 2S3 had two mechanised ammo racks, one in the turret and one in the hull. In the 2S3M (shown) this was changed to a single 12-round mechanised rack for shells, and the total ammo increased from 40 to 46 rounds.






(14/25) A chain rammer is provided for the loader to make his life much easier. The nominal rate of fire is 3 rounds/minute
(15/25) This can increase to 3.5 rounds/minute in direct fire under certain circumstances. Thermal restrictions limit sustained intensive fire to 30 rounds in 10 minutes or 75 rounds in 60 minutes. Spent cartridges are ejected through the side hatch.
flibusta-club.translate.goog/b/497805/read?…


flibusta-club.translate.goog/b/497805/read?…


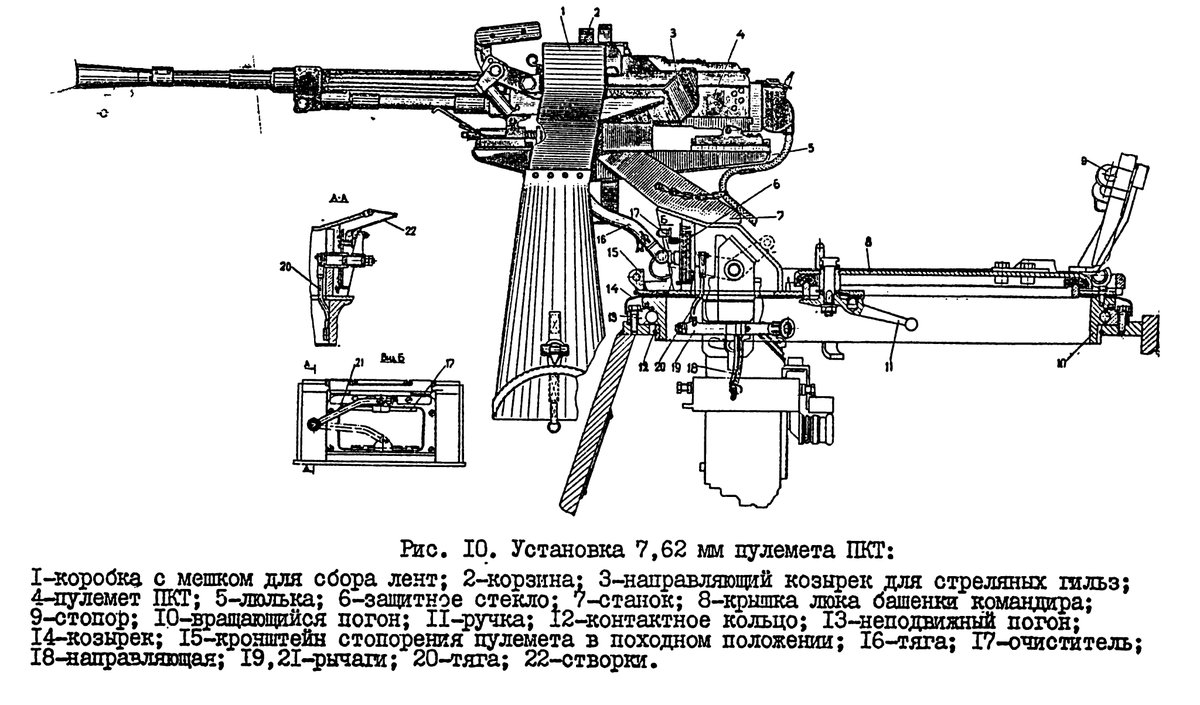
(16/25) The commander has a PKT machine gun in a remote-controlled mounting. It can be aimed and fired without opening his hatch.
(18/25) Automotively, the 27.5 t Akatsiya is fairly conventional. 520 hp V-59U V-12 engine, mechanical transmission with planetary gearbox (6+2 speeds), and torsion bar suspension. It'll do up to 60 km/h on a highway, 14 in reverse.








(19/25) In Soviet times, the Msta-S was to replace the Akatsiya as the backbone of the Soviet mechanised artillery, but this did not happen before the USSR collapsed. Thus, the Akatsiya serves on with both the Russian and Ukrainian forces. 

(20/25) For the Ukrainians, the Akatsiya is numerically their most important SPA. At the start of 2014, the 2S1 Gvozdika was being demobilised, and thus the mechanised units had to rely on the Akatsiya.
ukrmilitary.com/2016/01/2s3-ak…


ukrmilitary.com/2016/01/2s3-ak…
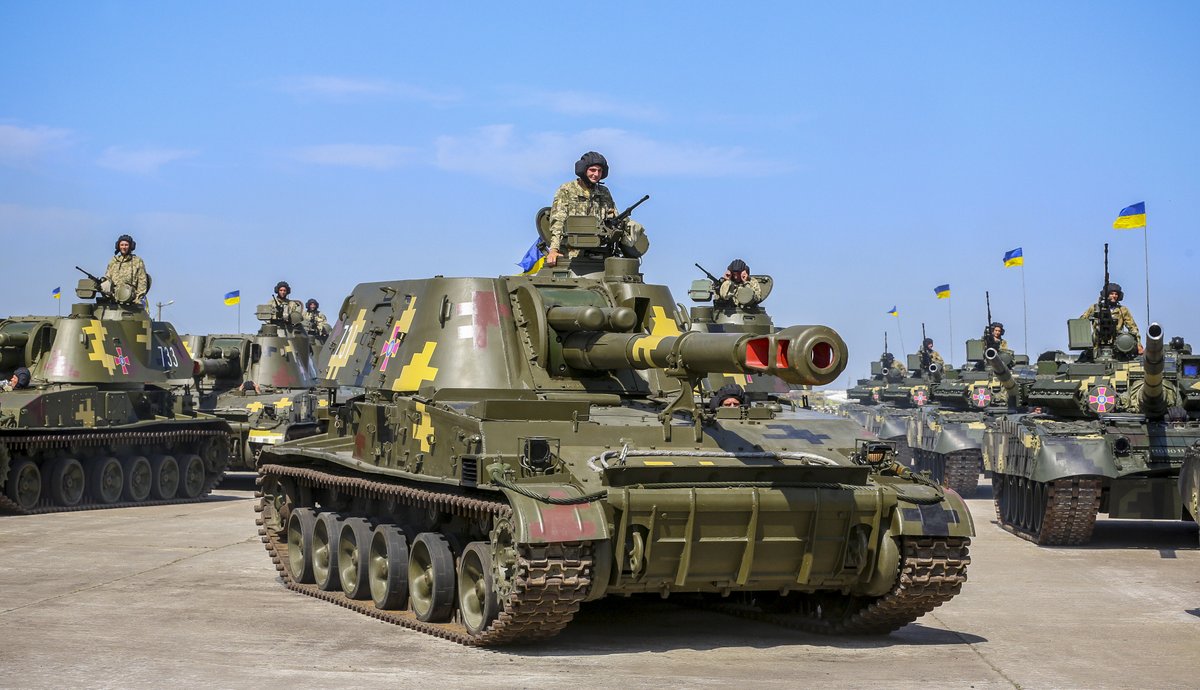
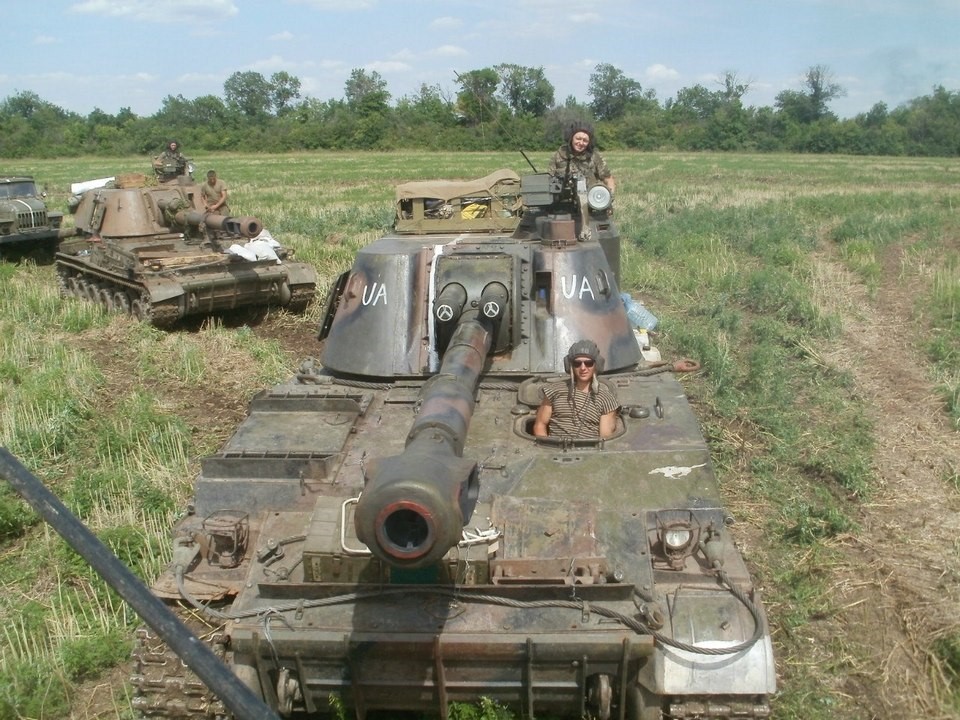


(21/25) In 2017, Ukrainian Akatsiyas and Gvozdikas began undergoing refurbishment to further strengthen the artillery arm.
en.ukrmilitary.com/2017/07/shepet…


en.ukrmilitary.com/2017/07/shepet…


(22/25) They don't get the attention of the M777s, Krabs, or CAESARs, but the Ukrainian Akatsiyas play their part as the war continues.
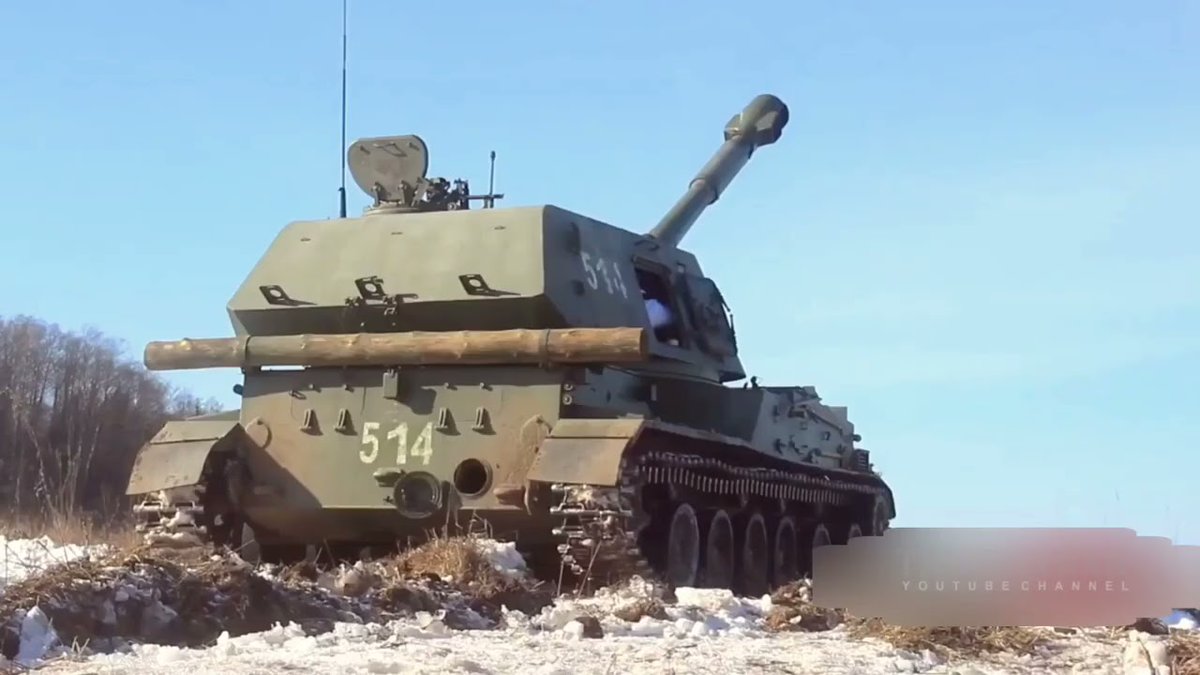
(23/25) Russia continues to use the Akatsiya, since they have not yet been able to replace it with the Msta-S on a 1-1 basis. They have implemented a few modernisations (2S3M1 and 2S3M2), mostly focused on improving fire control and comms.
en.topwar.ru/182938-pervaja…

en.topwar.ru/182938-pervaja…

(24/25) Certainly, they play an important role for the Russian forces in Ukraine today, and have suffered accordingly. They are currently second in losses (130) among SPAs only to the Msta-S (142), at least according to Oryx counting.
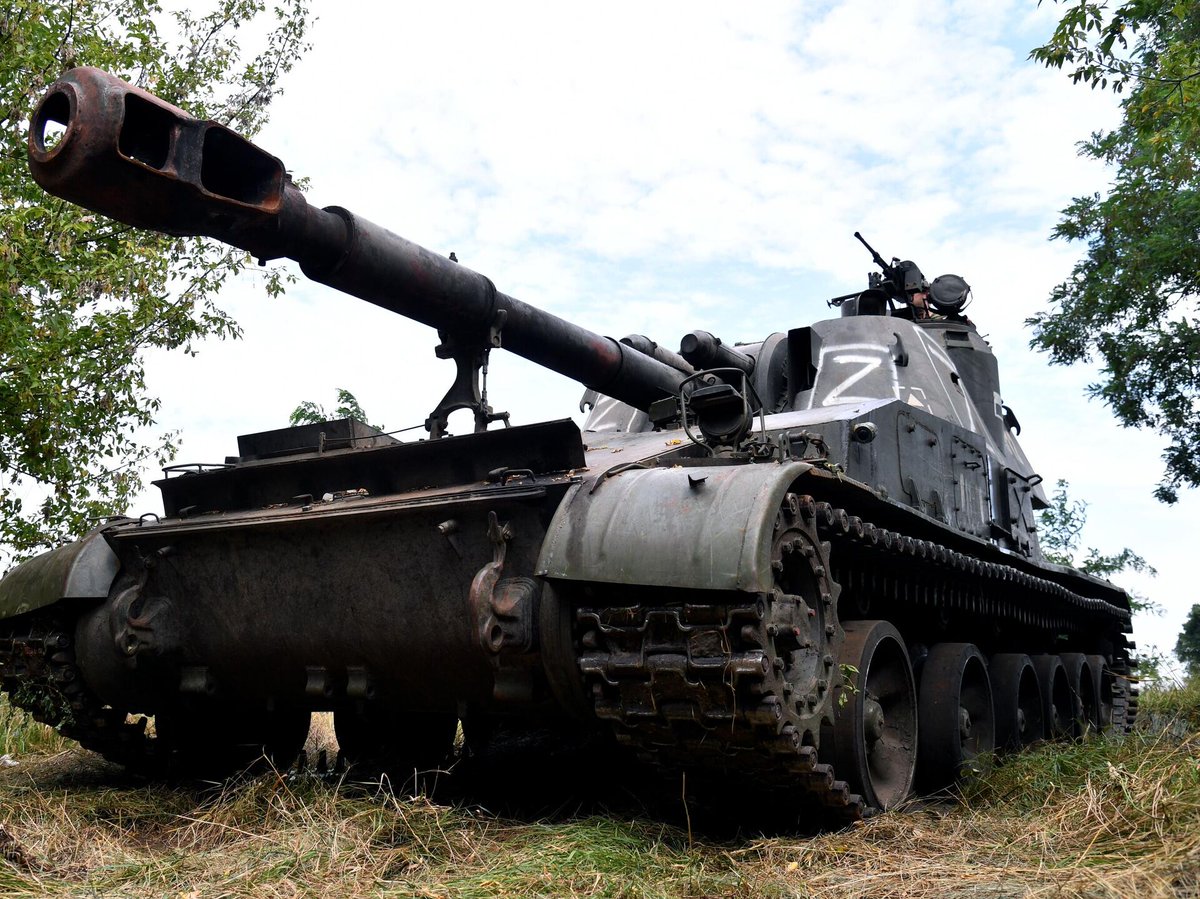
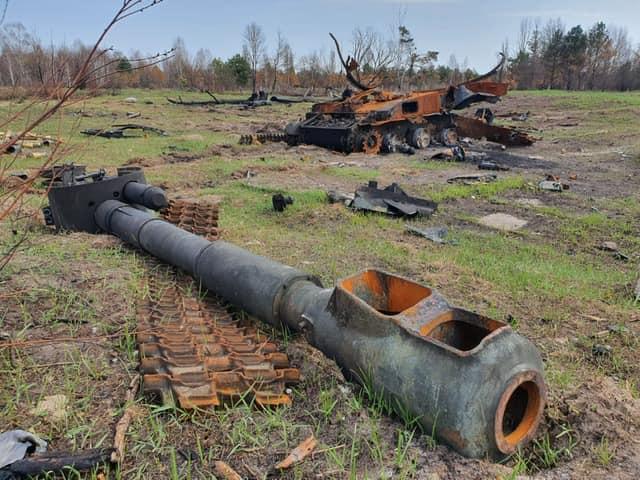
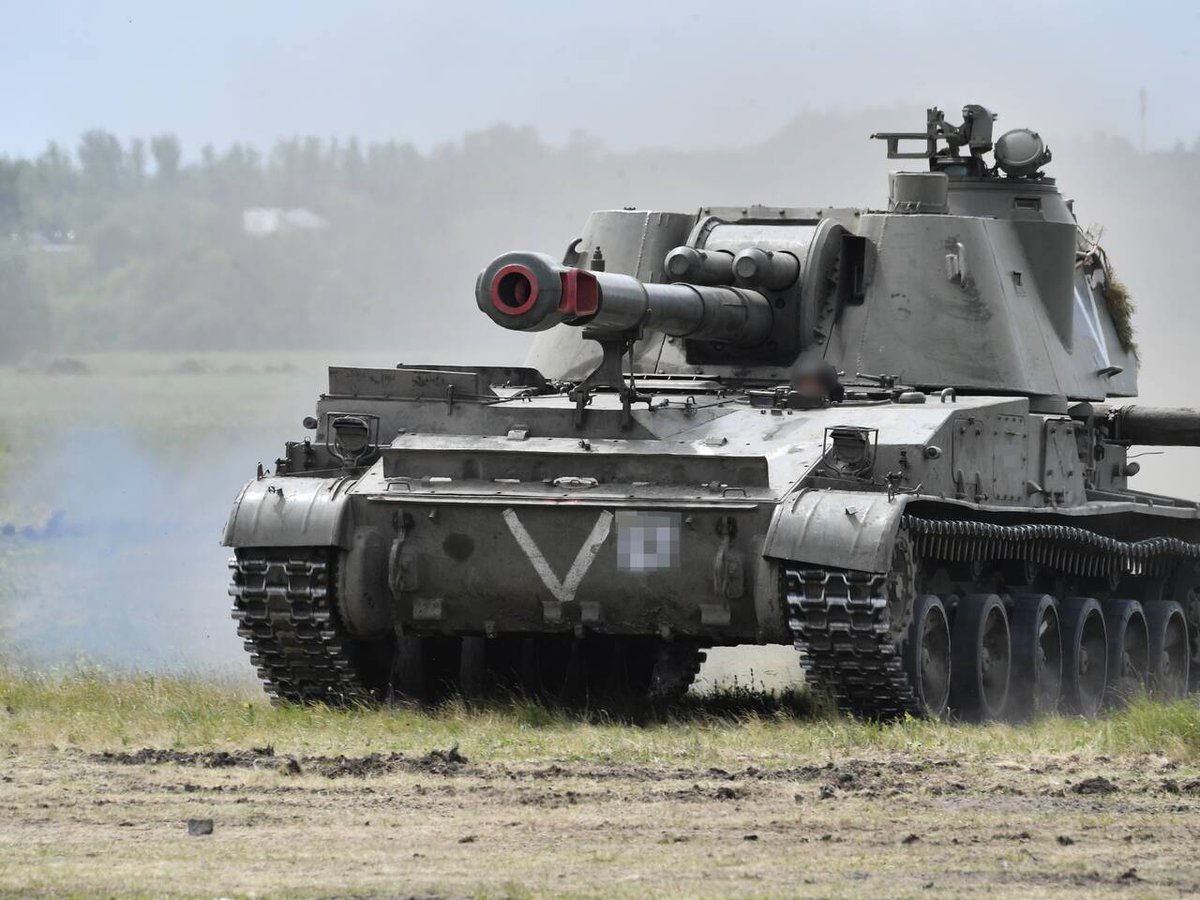








(25/25) It's over half a century old and it may lack the range of modern 155 and 152 mm pieces, but numerically the Akatsiya is one of the most important artillery pieces of a war dominated by artillery. Don't expect to see it go away any time soon. 
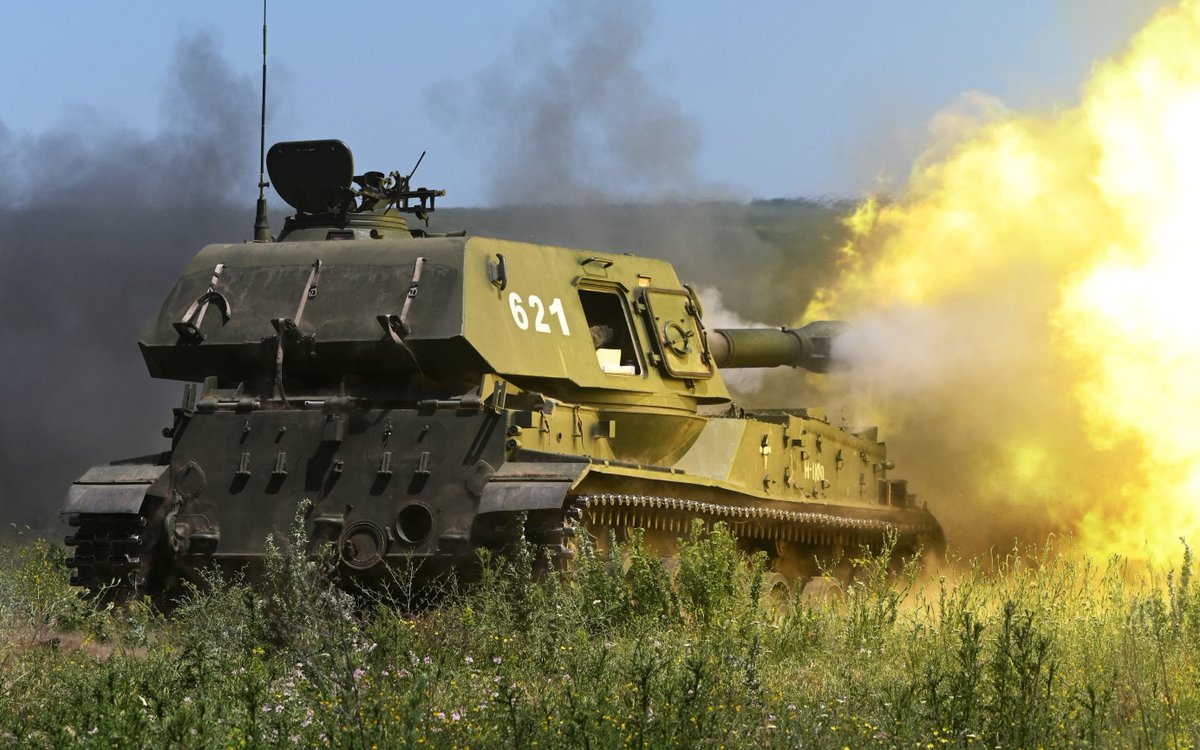

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh