In 1955 the M42 Duster entered service with the German Army, under the name "Flakpanzer M42 Duster“. Germany integrated 500 M42 Duster vehicles into the Bundeswehr. 

in 1966 the Germans needed a new vehicle to replace the M42 and they had a long list of requirements to meet. 

weight requirements, sensors and Radiation Protection:
* day, night and all-weather combat capability
* engagement range of 3000 m
* engagement altitude of 2000m
* maximum weight of 42 t (total weight) / 12 t (turret)
* full NBC protection
* wading capability+
* day, night and all-weather combat capability
* engagement range of 3000 m
* engagement altitude of 2000m
* maximum weight of 42 t (total weight) / 12 t (turret)
* full NBC protection
* wading capability+
* pulse Doppler search radar and tracking radar with 4000 m range
* identification friend or foe (IFF) systems
* power supply system in the chassis and vehicle navigation system.
* identification friend or foe (IFF) systems
* power supply system in the chassis and vehicle navigation system.
The weapon system:
* elevation range of -10° to +85°
* lateral range of 360°
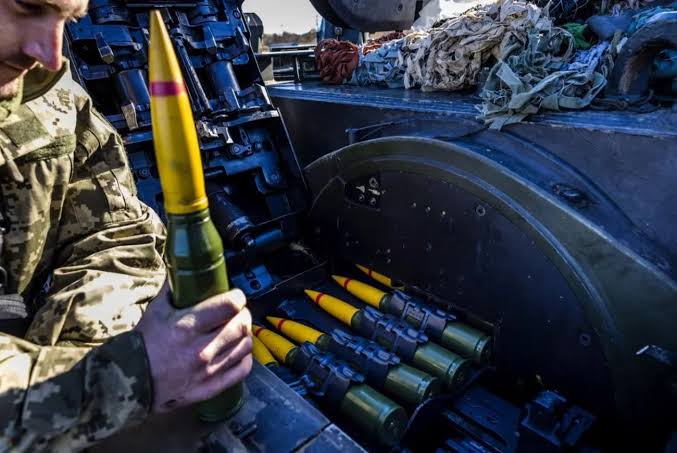
* 1000 rounds of ammunition
* optical and ground sights
* short reaction time
* elevation range of -10° to +85°
* lateral range of 360°
* 1000 rounds of ammunition
* optical and ground sights
* short reaction time
Still in 1966 2 prototypes were presented: Rheinmetall, AEG, Siemens and Krauss-Maffei's "Matador" as well as Oerlikon's 5PFZ-A. At the end of the competition, the Germans decided that the 5PFZ-A was the better vehicle and put it into production.
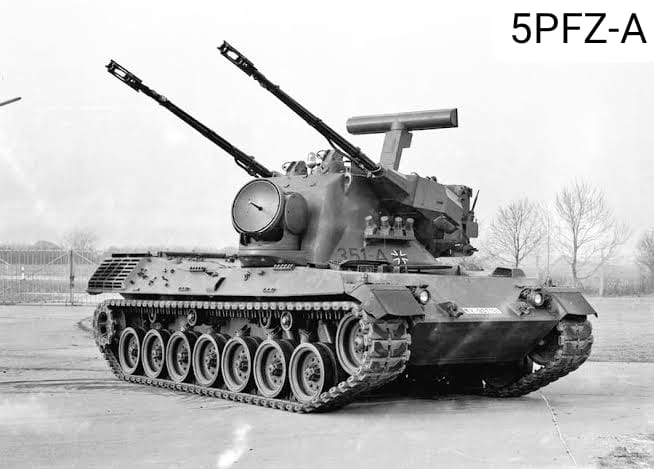
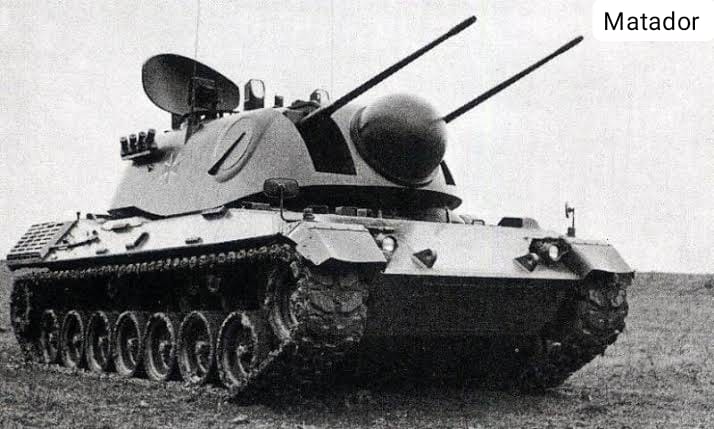




Initially 2 batches were delivered, one of 4 test vehicles in 1971 and 12 pre-production vehicles in 1973. Also in 1973 the vehicle was given the name Flugabwehrkanonenpanzer Gepard, abbreviated to "Flakpanzer Gepard". 
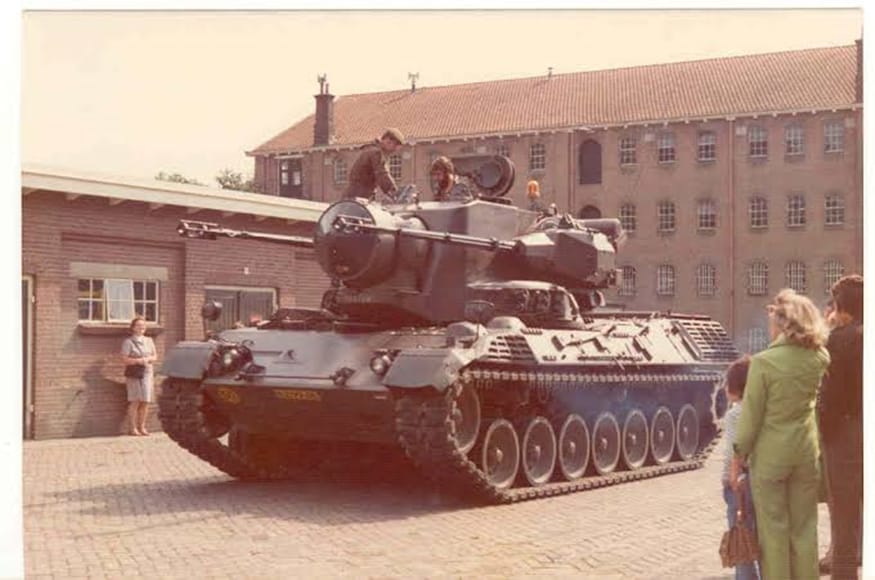

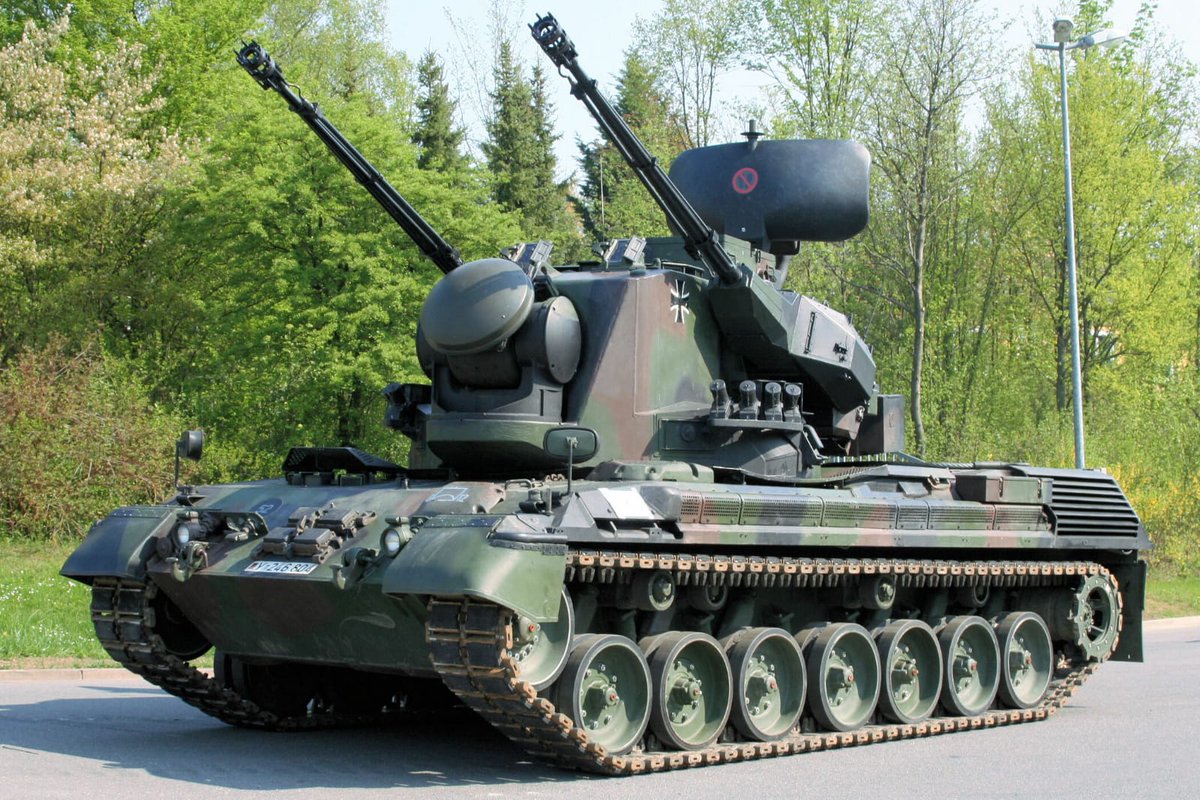
The Bundeswehr started to retire its Gepard vehicles in 2010, at which time the Gepard 1A2 version already existed. This version will be the subject of this thread. 
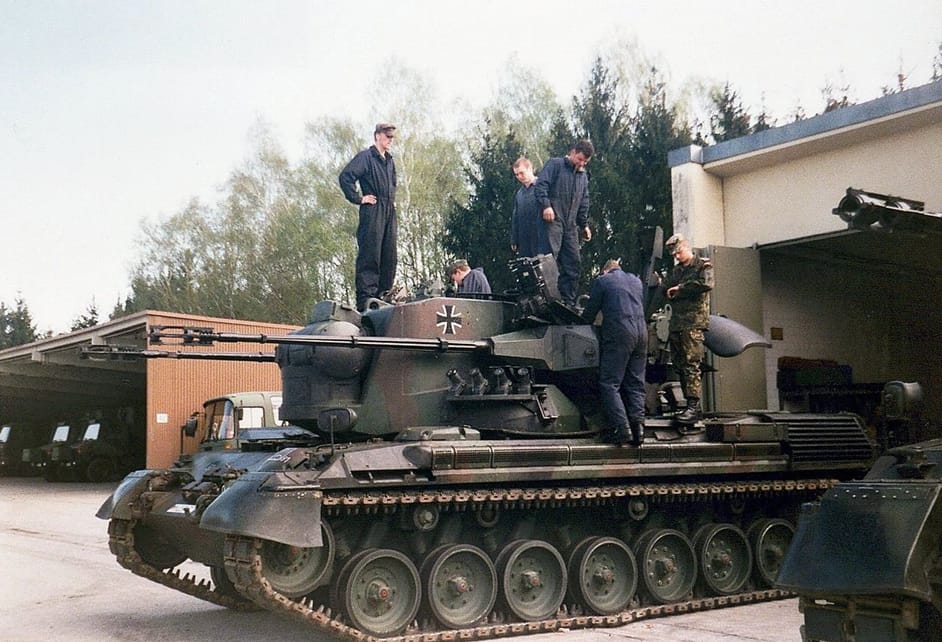

To save resources, the Gepard was built in the same hull as the Leopard 1, with a few modifications. One of them is the space between the third and fourth wheels, which increases the size of the hull a little, but not too significantly. 
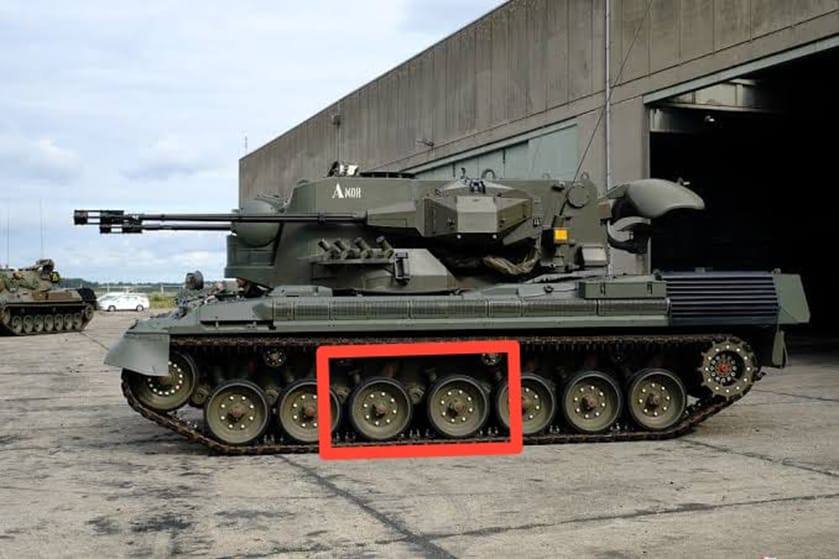

A 4-cylinder Daimler-Benz OM 314 diesel engine was fitted to the front of the hull to supply the vehicle's electrical systems, providing power for the traverse, gun lift and radars. 
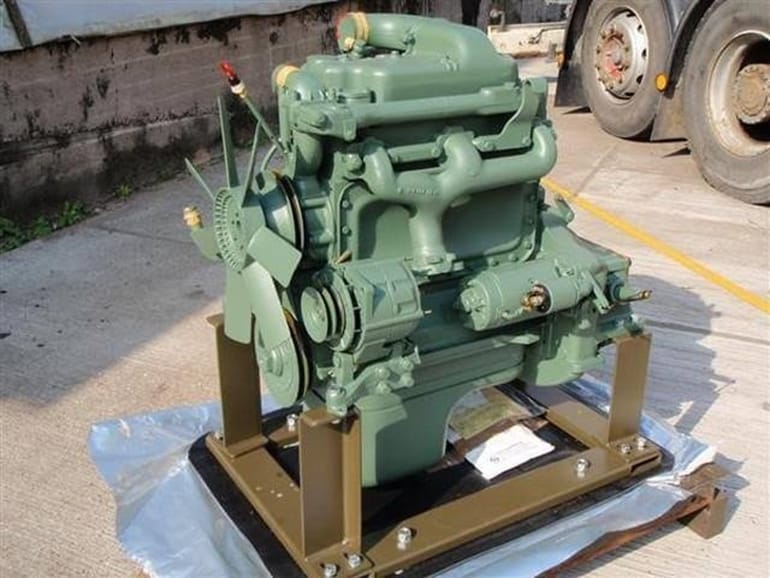

You can see that the exhaust of this engine is mounted on the left-hand side of the car and that it extends to the rear. 
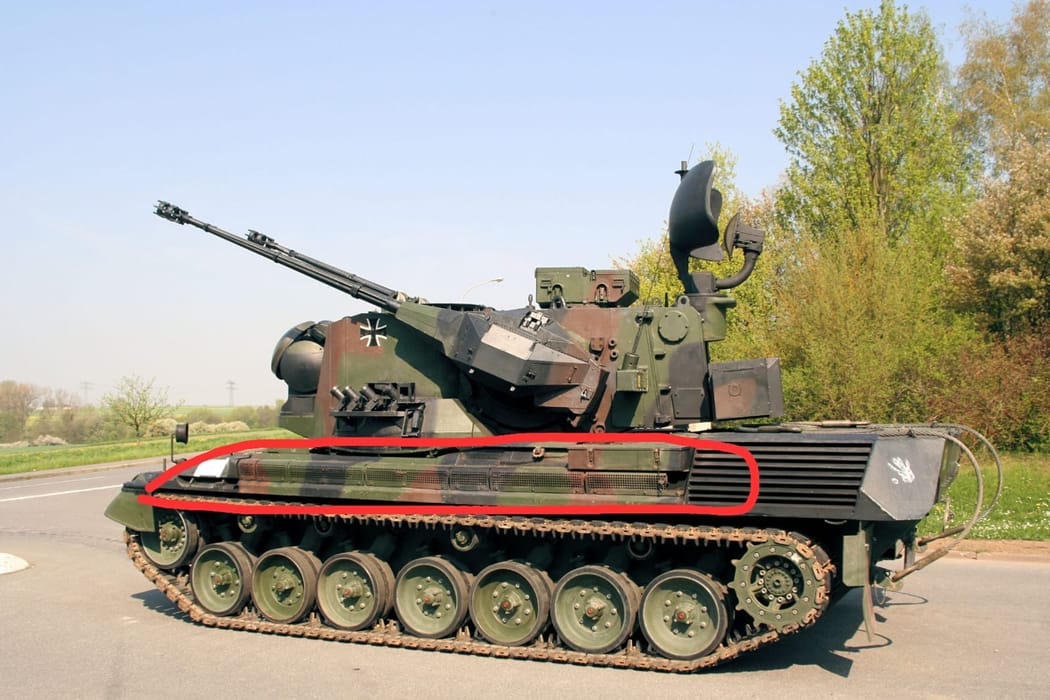

The engine compartment was enlarged to make room for 6x 24 volt batteries. Unfortunately I could not find photos of the batteries or identify them in this picture. 
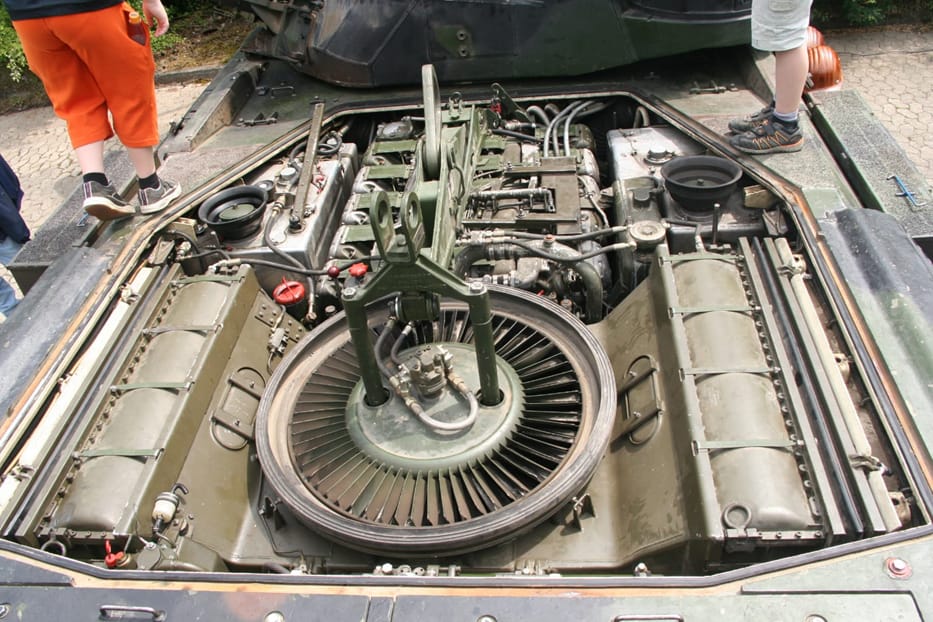

The vehicle has the same engine as the Leopard 1, the 830hp MTU MB CA M500, which gives the vehicle a road top speed of 65km/h (40mp/h). 
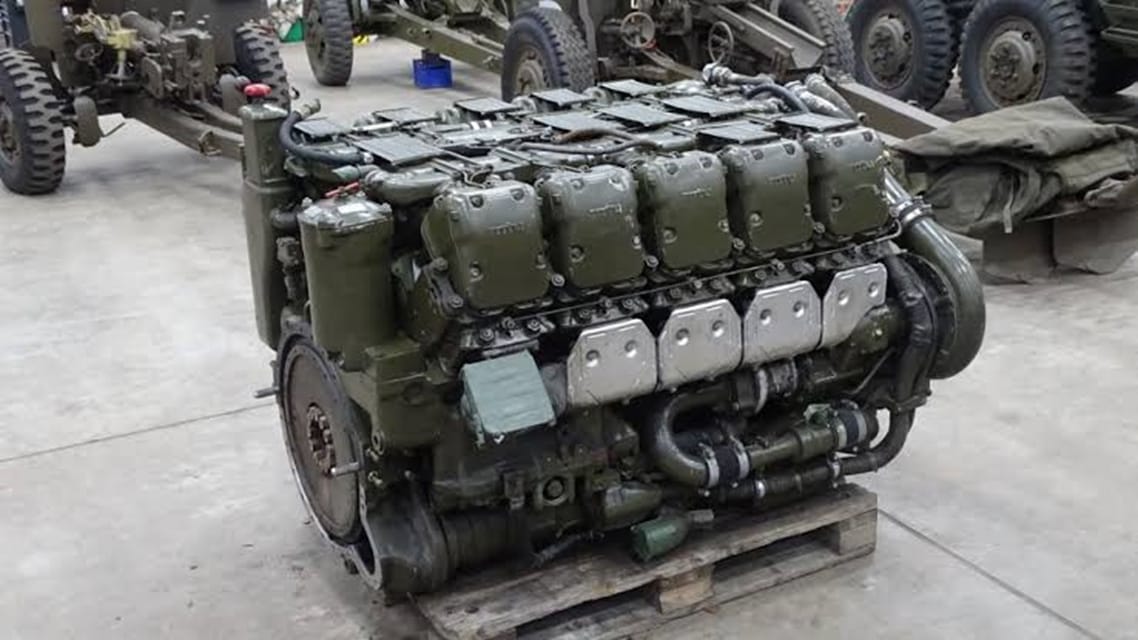

The Leopard 1A5 weighs 42 tons. The Gepard 1A2, on the contrary, weighs 47 tons, mainly due to the turret, the radars and the additional engine. However it should be noted that the turret and the front radar of the vehicle have received reinforced armor. 
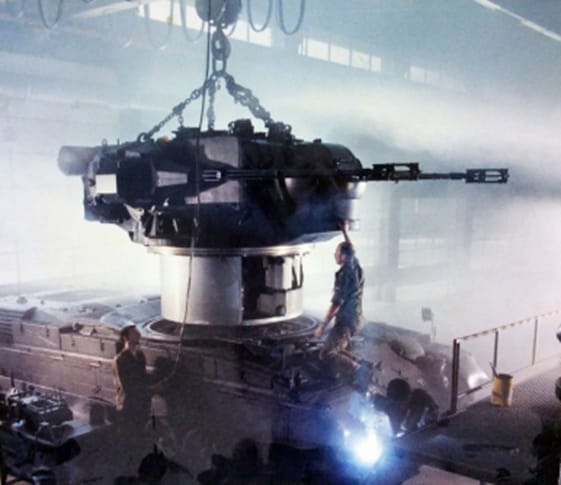

The commander and gunner have their own stabilized panoramic vision systems, that sit next to each other on top of the turret. These stabilized systems help acquire targets even when the vehicle is moving. The system is binocular and has a zoom of 1.5x to 6x.
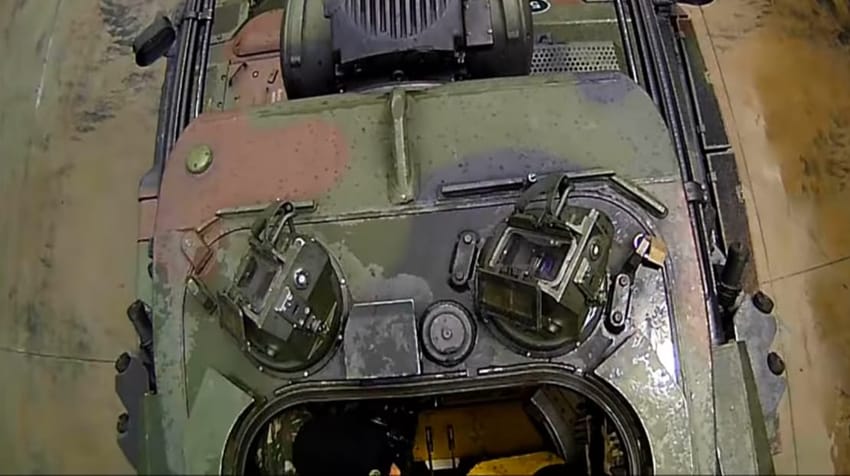
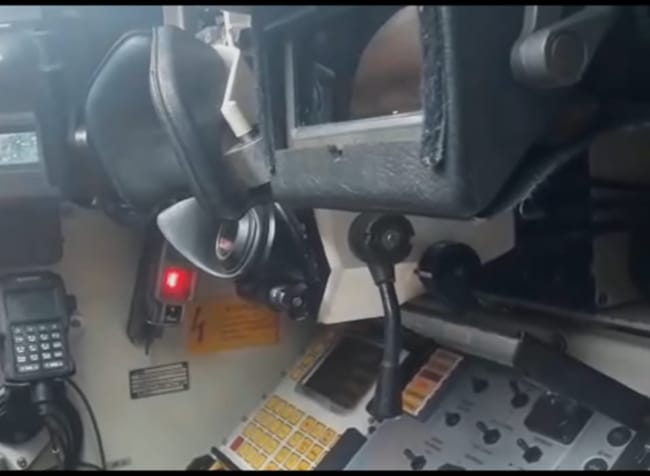




The turret is manned by the commander and gunner. The inside front is covered with 5 panels displaying important vehicle information. 
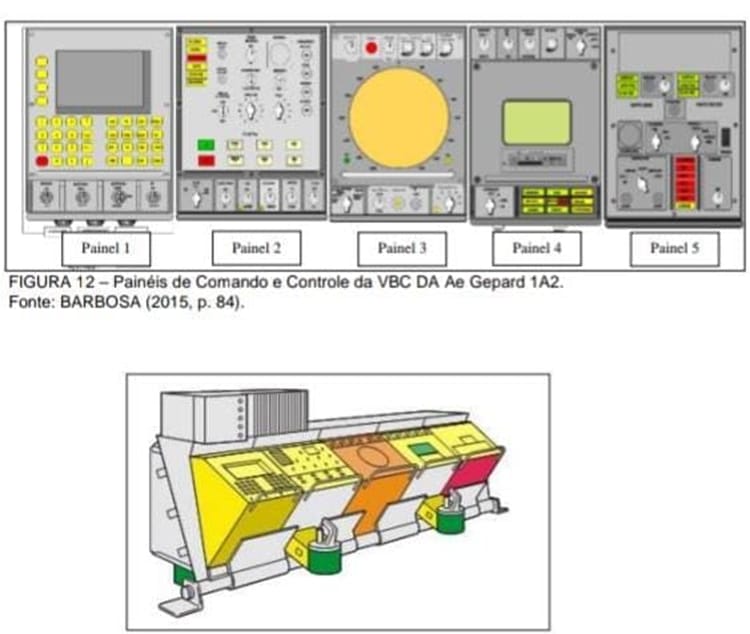
The first panel is a computer for many uses: the computer calculates the amount of ammunition needed for the target and its expected future position. Additionally, the computer also contains navigation data. 

The main functions of the second panel are to select the type of target (either ground or air), the type of ammunition, and to trigger the search radar. (There are, of course, other functions on the panel as well, but they are classified) 

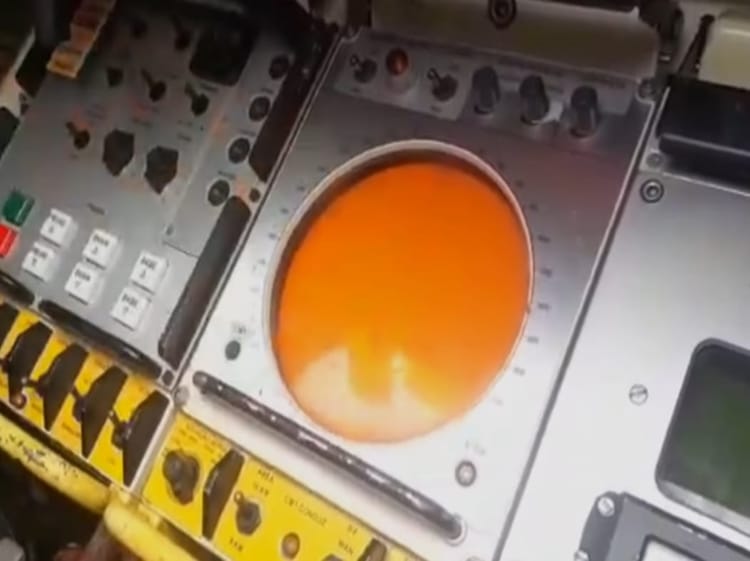
The third panel shows the aircraft picked up by the tracking radar. All detected aircraft within a radius of 15km (9,3mi) appear on this screen. 

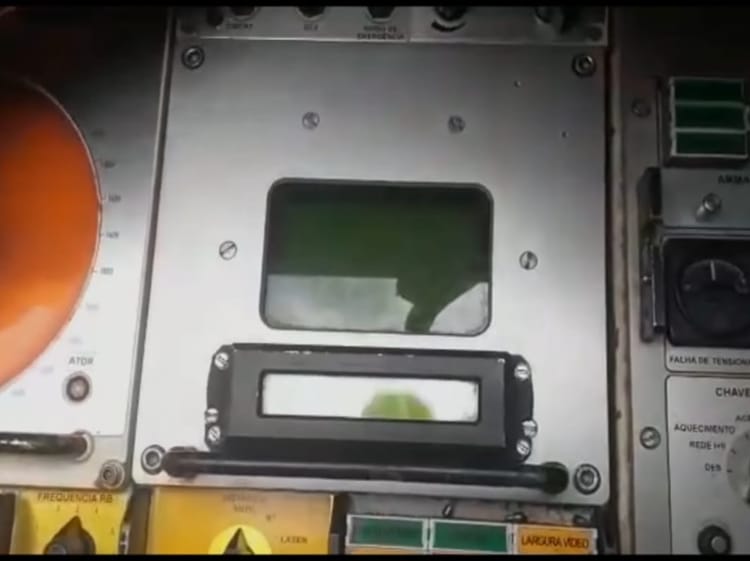
The fourth panel receives information from the fire control radar, calculates distance and speed, and automatically locks on the target so the crew only has to pull the trigger. This panel also contains all the safety devices. 

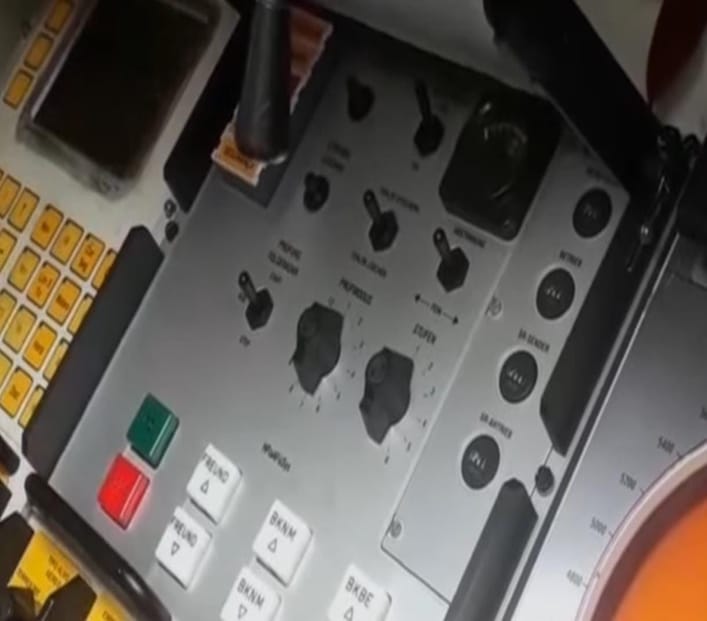
The fifth panel has more safety options and other features including test firing (to see if any ammunition is still in the breech), the option to load ammunition into the breech and to switch firing mode (Burst, Intermittent or Single). 

The search radar is located behind the turret of the vehicle, while the fire control radar is located in the front. Both radars can track a target at a distance of 15km (9,3mi) The search radar operates in the S-band (2–4 GHz) and the fire control radar in the Ku-band (12–18 GHz)






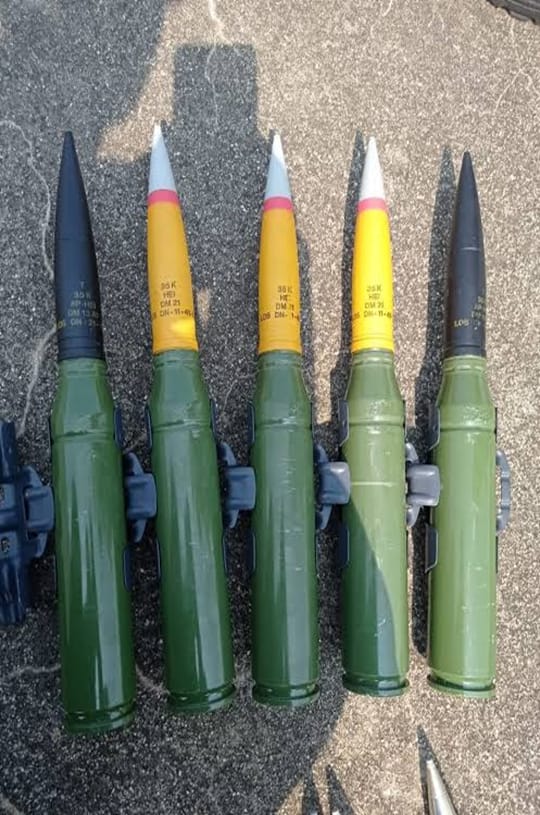
The main armament of the vehicle consists of 2x stabilized Oerlikon KDA 35mm guns with each gun having a projectile velocity sensor in the muzzle. One gun has a rate of 550 rounds per minute (combined rate of 1,100 rpm) and a muzzle velocity of 1400 m/s.


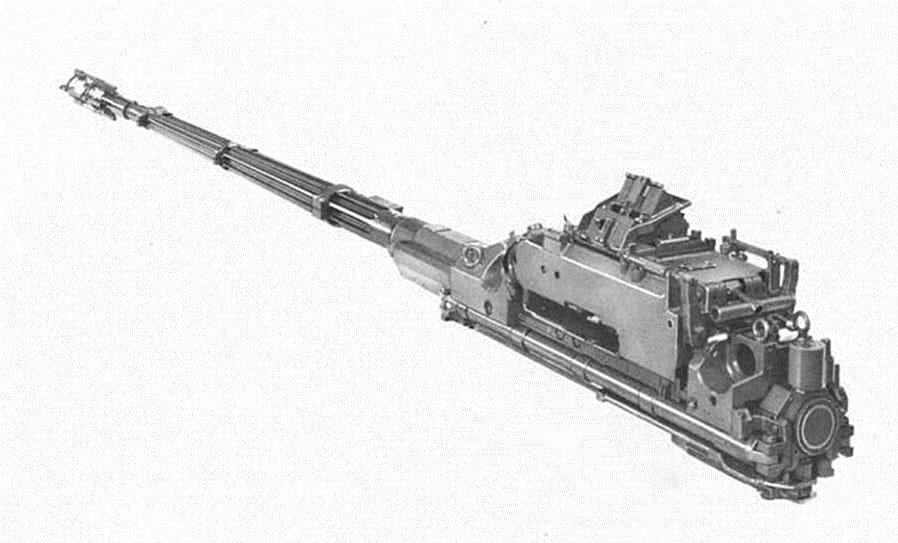

These cannons can fire:
* SAPHEI (Semi-Armor-Piercing High-Explosive Incendiary; also known as HEIAP)
* HEI (High-Explosive Incendiary)
* FAPDS (Frangible Armor-Piercing Discarding Sabot)
* HVAPDS-T (High-Velocity Armor-Piercing Discarding Sabot-Tracer)
* SAPHEI (Semi-Armor-Piercing High-Explosive Incendiary; also known as HEIAP)
* HEI (High-Explosive Incendiary)
* FAPDS (Frangible Armor-Piercing Discarding Sabot)
* HVAPDS-T (High-Velocity Armor-Piercing Discarding Sabot-Tracer)

I would like to thank @beto_caiafa For letting me use the photos from inside the vehicle's turret and periscopes, he also sent me exclusive images but unfortunately my cell phone was not compatible with the files (some shit like that)
@beto_caiafa I will thank you immensely my friend @dunkelkult By reviewing the Texts and modifying it so it made sense (English is not my native language so I make a lot of typing errors) he also added small but very important Information that made this thread really cool.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




















