1/Raise your hand if you’re confused by the BRACHIAL PLEXUS!
I could never seem to remember or understand it—but now I do & I’ll show you how
A thread so you will never fear brachial plexus anatomy again!
I could never seem to remember or understand it—but now I do & I’ll show you how
A thread so you will never fear brachial plexus anatomy again!

2/Everyone has a mnemonic to remember brachial plexus anatomy.
I’m a radiologist, so I remember one about Rad Techs.
But just remembering the names & their order isn’t enough. That is just the starting point--let’s really understand it
I’m a radiologist, so I remember one about Rad Techs.
But just remembering the names & their order isn’t enough. That is just the starting point--let’s really understand it

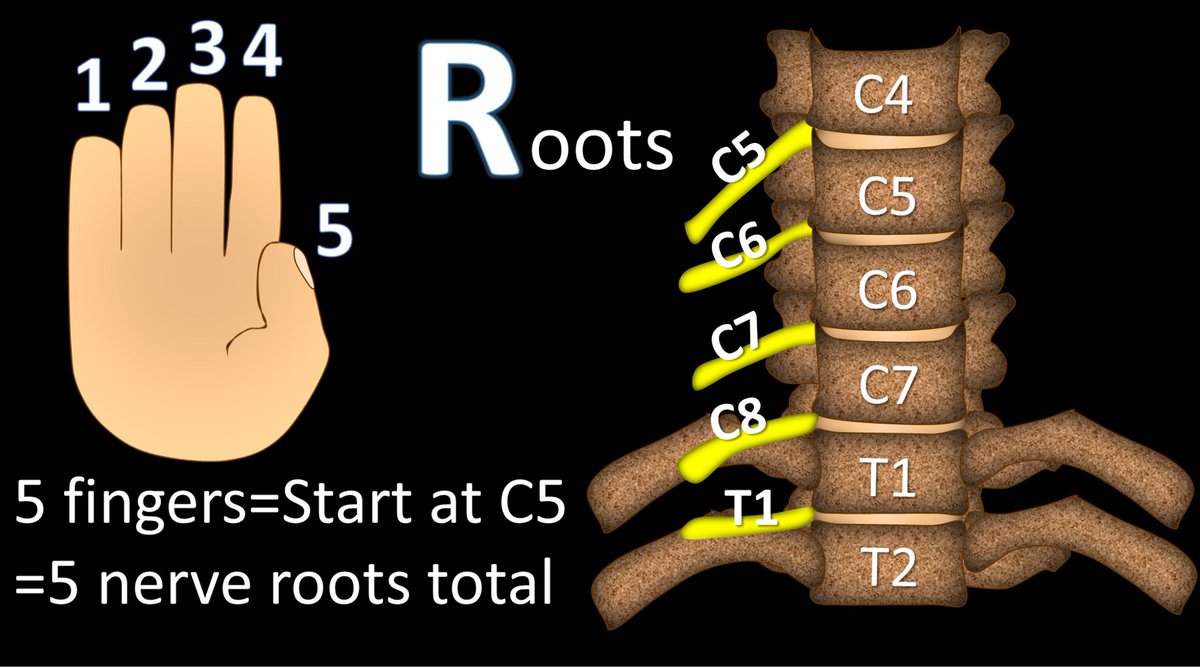
3/From the mnemonic, we start with the roots—the cervical nerve roots.
I remember which roots make up the brachial plexus by remembering that it supplies the hand.
You have 5 fingers on your hand so we start with C5 & we take 5 nerve roots (C5-T1).
I remember which roots make up the brachial plexus by remembering that it supplies the hand.
You have 5 fingers on your hand so we start with C5 & we take 5 nerve roots (C5-T1).
4/Next in the mnemonic are the Trunks.
Bc Trunks starts w/T, I can remember how they are named.
T is Top to bottom.
Trunks are named top to bottom: Superior, Middle, and Inferior.
But how to remember which nerve roots combine to give you which trunks?
Bc Trunks starts w/T, I can remember how they are named.
T is Top to bottom.
Trunks are named top to bottom: Superior, Middle, and Inferior.
But how to remember which nerve roots combine to give you which trunks?

5/Pairing of the nerve roots into the trunks is like pairing off at a dance when there is an odd number.
Everyone immediately turns to the person next to them & the person in the middle is left out.
For the roots, C7 is in the middle & has to go it alone as the middle trunk
Everyone immediately turns to the person next to them & the person in the middle is left out.
For the roots, C7 is in the middle & has to go it alone as the middle trunk

6/Next in the mnemonic are the Divisions
Divisions do what their name implies—they divide the trunks.
Each trunk is split or DIVIDED into an anterior & posterior division.
Divisions will look like scissors coming off the trunks, helping you to remember they are splitting
Divisions do what their name implies—they divide the trunks.
Each trunk is split or DIVIDED into an anterior & posterior division.
Divisions will look like scissors coming off the trunks, helping you to remember they are splitting

7/This division results in a fundamental change in the nerves—anterior divisions will supply flexors & posterior divisions will supply the extensors.
It's an important dividing line. Like rabid soccer fans, once they've chosen a team, they will never mix w/fans of the other team
It's an important dividing line. Like rabid soccer fans, once they've chosen a team, they will never mix w/fans of the other team

8/After the split of the divisions, the nerves come back together as the cords.
It is kind of like doing jumping jacks—they open up and then close back up again.
I remember that they come back together as the Cords bc Cords and Combine both start with C
It is kind of like doing jumping jacks—they open up and then close back up again.
I remember that they come back together as the Cords bc Cords and Combine both start with C

9/It’s like a toll road
The road widens to let more cars get to the toll booths. Once they have paid the toll, road narrows again
This is what happens w/the divisions—but instead of paying a toll, they are organizing into flexor & extensor groups & coming back together again.
The road widens to let more cars get to the toll booths. Once they have paid the toll, road narrows again
This is what happens w/the divisions—but instead of paying a toll, they are organizing into flexor & extensor groups & coming back together again.

10/But it’s more like going through a worm hole than toll booth
When you go through a wormhole, you are fundamentally changed when you come out the other side (or so I read on the internet)
Once cords emerge from divisions, they’re either team flexor or extensor & can’t go back
When you go through a wormhole, you are fundamentally changed when you come out the other side (or so I read on the internet)
Once cords emerge from divisions, they’re either team flexor or extensor & can’t go back

11/So when they form the cords, anterior divisions (team flexor) will only combine w/other anterior divisions that innervate flexors.
Similarly, posterior divisions (team extensor) will only combine with other posterior divisions (extensor group).
Similarly, posterior divisions (team extensor) will only combine with other posterior divisions (extensor group).

12/Divisions combine to form 2 ant. cords & 1 post. cord. Why the inequality?
Well, the fundamental purpose of the arm is to flex (pick up things), unlike the leg (which is to extend/stand up).
So bc it’s more important to flex, remember 2 cords to flexors & 1 to extensors
Well, the fundamental purpose of the arm is to flex (pick up things), unlike the leg (which is to extend/stand up).
So bc it’s more important to flex, remember 2 cords to flexors & 1 to extensors

13/All post divisions go to the 1 post cord. How do you remember which ant divisions go into which cord?
Remember, divisions come from the sup, middle, & inf trunks. Superior or even middle class don’t combine w/inferior things. So sup & mid combine. Poor inferior is left alone
Remember, divisions come from the sup, middle, & inf trunks. Superior or even middle class don’t combine w/inferior things. So sup & mid combine. Poor inferior is left alone

14/Names of the cords are based on their relationship to the axillary artery.
Posterior cord (extensors) is posterior to it. The flexor cord made of the superior & middle divisions is lateral. Flexor cord made from the lonely inferior division is medial
Posterior cord (extensors) is posterior to it. The flexor cord made of the superior & middle divisions is lateral. Flexor cord made from the lonely inferior division is medial

15/But this is hard to remember.
So I remember that the flexor cord made from the poor inf division is looked down upon, so it is given the worst seat—at the armpit.
In anatomic positioning, closest to the armpit is medial, so it's the medial cord.
So I remember that the flexor cord made from the poor inf division is looked down upon, so it is given the worst seat—at the armpit.
In anatomic positioning, closest to the armpit is medial, so it's the medial cord.

16/Now the final division into branches. Remember posterior cord only supplies extensors & is the only extensor cord. So when it branches, it needs to innervate extensors all along the arm (elbow, forearm, hand). So it gives off axillary to the upper arm & radial to the lower arm 

17/Now the branches of the flexor cords. As expected from their names, MEDIAL cord gives a branch for flexors/sensation to MEDIAL forearm/hand (in anatomic position = PINKY side, so ulnar nerve), & LATERAL cord gives a branch for motor/sensation to LAT. forearm (musculocutaneous) 

18/Usually superior/middle class look down on inferiors (why inf division travels alone as medial cord). But eventually the rich will have, ahem, liaisons w/inferiors. So it is w/cords. High-class lateral cord finally mingles w/low-class armpit medial cord, making median nerve 

19/Now move beyond mneumonics. Remember, brachial plexus splits & recombines like jumping jacks w/a very palindromic 5-3-6-3-5 pattern. The names tell you if they are splitting or combining (Trunk=Together, Division=Divide, Cord=Combine, Branch=break) 

20/Now all you need is to recall 1 fact @ each stage
Trunk: C7 left out
Div: Ant flexors don’t mix w/post extensors
Cord: Sup/mid class don’t mix w/inferiors
Br: Each cord gives a branch to region its name describes (post, med, lat) &rich give in to inferiors to form median nerve
Trunk: C7 left out
Div: Ant flexors don’t mix w/post extensors
Cord: Sup/mid class don’t mix w/inferiors
Br: Each cord gives a branch to region its name describes (post, med, lat) &rich give in to inferiors to form median nerve

21/Now you understand the anatomy of the brachial plexus.
Hopefully, the next time someone has a question about brachial plexus anatomy, you will be the first to raise your hand and BRACH it down for them!
Hopefully, the next time someone has a question about brachial plexus anatomy, you will be the first to raise your hand and BRACH it down for them!

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






















