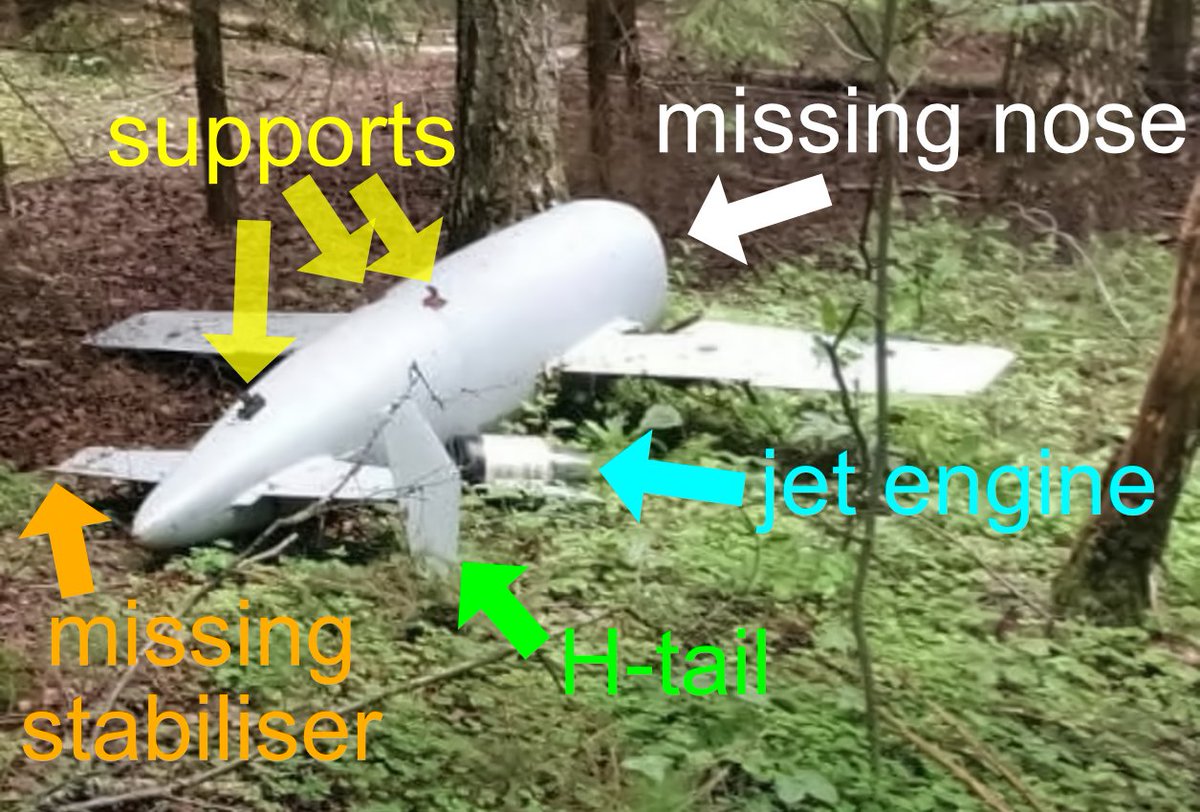
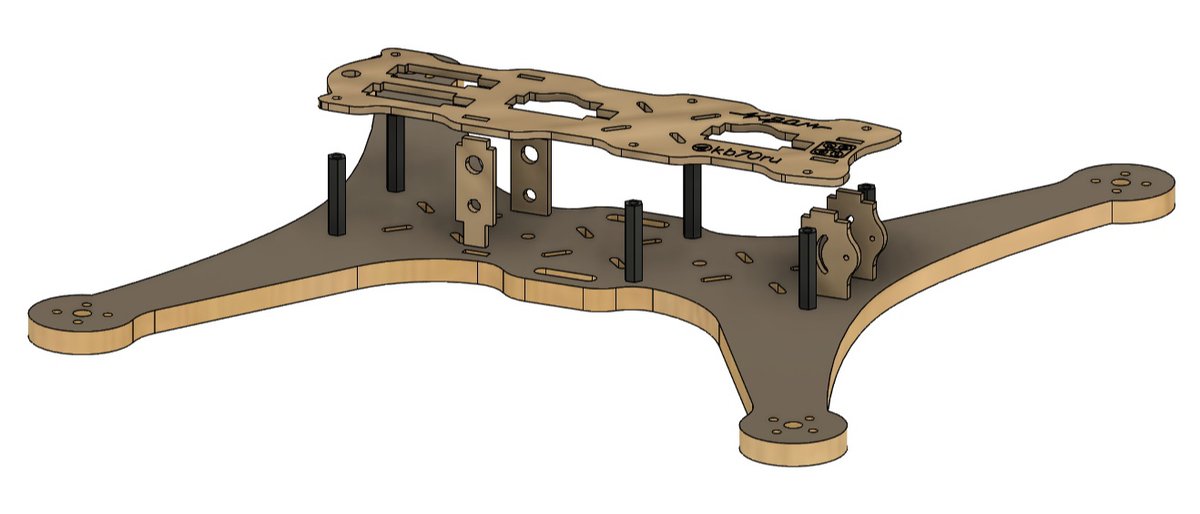
🧵1. In the #UkraineRussia war, volunteers assemble #drones for military use. Most components are imported from China but some are made locally. Russian volunteers (kb70ru Конструкторское дизайн бюро) designed a drone that uses a frame made from plywood.
vk.com/kb70ru
vk.com/kb70ru
2. A computer-controlled router is used to cut the drone frames out of 9mm thick plywood.
t.me/kb70ru/366

t.me/kb70ru/366

3. A laser cutter is used to cut parts out thinner plywood. The laser cutter is more accurate but is limited to cutting thinner materials. 

4. An advantage of this design is it's easy to make different size frames for different applications (the inch sizes refer to the propeller diameter):
5" Training (there is a large training program)
6" Reconnaissance
7" Kamikaze (attack)
9" Bomber
t.me/kb70talks/8924

5" Training (there is a large training program)
6" Reconnaissance
7" Kamikaze (attack)
9" Bomber
t.me/kb70talks/8924

5. Some interesting observations can be made. This project appears to be largely the initiative of one person (Alexey). The workshop used for development is not very big or fancy.
vk.com/mdciv
vk.com/kb70ru

vk.com/mdciv
vk.com/kb70ru

7. Keep in mind that there is a lot more to a drone than the frame. The frame needs to be assembled and 4 motors, 4 propellers, ELRS receiver, flight controller stack, camera, video transmitter, antennas & battery need to be installed.




8. Since all the drone parts are hobby-grade & made in China it is easy to determine the cost effectiveness of this home-made frame. At best, it reduces the cost of a drone by about 10 to 15%.
9.This cost estimate was verified in a post, “Six copters were paid for by concerned citizens. Production of one drone costs about 40,000 rubles and a month of waiting for the delivery of components.”
vk.com/kb70ru?w=wall-…

vk.com/kb70ru?w=wall-…
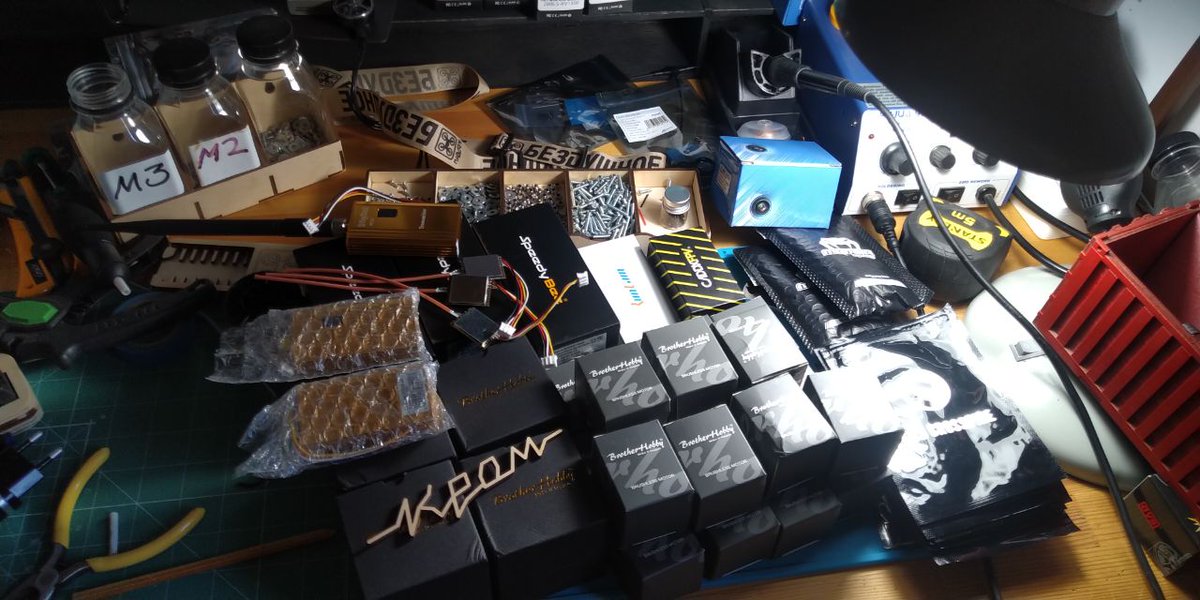

10. The frames are given to other groups to assemble. Photos confirm that many of these frames were used to make drones. But how many frames were made and how many resulted in a drone?




11. Apparently, these volunteers were not keeping track but instead estimated 500 frames from the number of nylon standoffs used (6 per drone). But no one knows how many of these frames were made into drones.
t.me/kb70talks/9099
t.me/kb70talks/9099
12. Keep in mind that to turn 500 frames into drones would require about US$200,000 worth of components. In a poor and corrupt country like Russia, it’s not clear how this would work out. Many frames were shipped and subsequently disappeared.
13. Some Russian sources claim that huge numbers of drones are being made each day. Because the volunteers are not keeping track of their own production, these (partially) official numbers cannot be accurate.
t.me/vatfor/8784
t.me/vatfor/8784
14. In spite of their efforts, this project was not approved for Russian government funding. “Ahaha plywood frames did not pass the selection of the high state commission))))” This rejection resulted in bitterness and may have dampened their enthusiasm.
t.me/kb70talks/7344


t.me/kb70talks/7344


15. In summary, this group of Russian volunteers worked very hard, made drones and had successes but still did not obtain government funding. Without serious money, it’s not clear how big their impact will be in a quickly evolving war.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh
























