
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


 2. This jet-powered missile was spotted attacking Donetsk on September 14. The fuselage appears to be more curved than the common cylinder shape. There are no obvious winglets. The tail is consistent with a dual tail (H-tail).
2. This jet-powered missile was spotted attacking Donetsk on September 14. The fuselage appears to be more curved than the common cylinder shape. There are no obvious winglets. The tail is consistent with a dual tail (H-tail). 

 2. The engine is mounted on a pylon but there are no markings to work with. It is hard to even be sure if this a Ukrainian or a russian drone. It is common for drones to have been cut up to remove the warhead & useful components.
2. The engine is mounted on a pylon but there are no markings to work with. It is hard to even be sure if this a Ukrainian or a russian drone. It is common for drones to have been cut up to remove the warhead & useful components. 

 2. At the start of the war, Ukraine obtain several Penguin-C military drones made in Latvia by UAV Factory (now called, Edge Autonomy).
2. At the start of the war, Ukraine obtain several Penguin-C military drones made in Latvia by UAV Factory (now called, Edge Autonomy). 

 2. For reference, here is a Z137T in its tradition role of applying chemicals to a crop. A maximum cruise speed of 252 km/h will be a constraint as a drone hunter.
2. For reference, here is a Z137T in its tradition role of applying chemicals to a crop. A maximum cruise speed of 252 km/h will be a constraint as a drone hunter. 

 2. Importantly, one video showed several drones attacking, one after the other. Oddly, there was remarkably little air defence heard as each drone approached over a lake. What happened to russia’s air defence?
2. Importantly, one video showed several drones attacking, one after the other. Oddly, there was remarkably little air defence heard as each drone approached over a lake. What happened to russia’s air defence? 

 2. Here are two fibre optics kits made by the Chinese company, Skywalker. Opening the boxes is the likely owner of PGI Technology, which operates in China but is effectively russian. Initially, this photo was confusing. Was Skywalker collaborating with PGI Technology? Nope.
2. Here are two fibre optics kits made by the Chinese company, Skywalker. Opening the boxes is the likely owner of PGI Technology, which operates in China but is effectively russian. Initially, this photo was confusing. Was Skywalker collaborating with PGI Technology? Nope.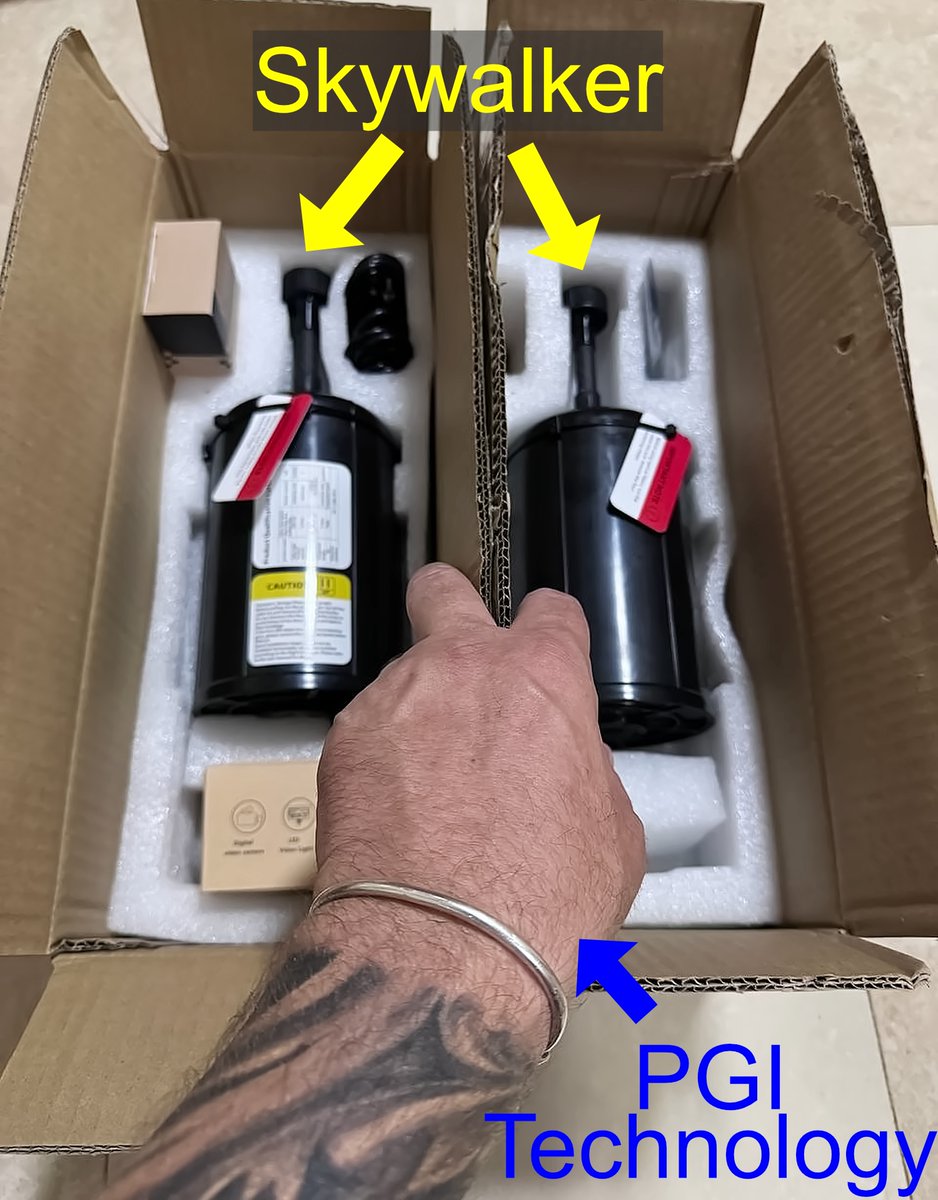 

 2. PGI Technology showed this photo of equipment being prepared to ship from China to russia. The packing tape has a company name & phone number on it. Note the Wallace restaurant and #24 bus across the street.
2. PGI Technology showed this photo of equipment being prepared to ship from China to russia. The packing tape has a company name & phone number on it. Note the Wallace restaurant and #24 bus across the street. 

 2. It currently calls itself “PGI Technology” but there are also references to “Dongguan PGI Technology”. Its location is murky but a now-defunct website gave an address in Tangxia Town in Dongguan.
2. It currently calls itself “PGI Technology” but there are also references to “Dongguan PGI Technology”. Its location is murky but a now-defunct website gave an address in Tangxia Town in Dongguan. 

 2. Skywalker posted several videos while developing fibre optics for drones. The first was a short-range, e.g. 100 metres, test in June 12, 2024. The spool of fibre optic was not on the drone but remained on the ground. A rod prevented the fibre from tangling in the propellers.
2. Skywalker posted several videos while developing fibre optics for drones. The first was a short-range, e.g. 100 metres, test in June 12, 2024. The spool of fibre optic was not on the drone but remained on the ground. A rod prevented the fibre from tangling in the propellers. 

 2. Skywalker posted a video showing how to attach a bomb release to a pricey (€13500) DJI Matrice 300 drone. It holds two rounds under the drone with a control module mounted on the top of the drone. There is also an excellent view from the office windows.
2. Skywalker posted a video showing how to attach a bomb release to a pricey (€13500) DJI Matrice 300 drone. It holds two rounds under the drone with a control module mounted on the top of the drone. There is also an excellent view from the office windows. 

 2. Now that the company with three names (DSI Drone System Innos, DSTech UAS, Dongshengtai Technology) has been introduced, let’s look at what they are up to. They make their own fixed-wing drones starting with moulds.
2. Now that the company with three names (DSI Drone System Innos, DSTech UAS, Dongshengtai Technology) has been introduced, let’s look at what they are up to. They make their own fixed-wing drones starting with moulds. 

 1. The Chinese company Skywalker Technology sells kits for controlling drones using fibre optics. Shown here is a quadrotor with a spool holding a few km of optical fibre. The fibre leads to a base station so control signals can be sent to the drone and video sent back.
1. The Chinese company Skywalker Technology sells kits for controlling drones using fibre optics. Shown here is a quadrotor with a spool holding a few km of optical fibre. The fibre leads to a base station so control signals can be sent to the drone and video sent back. 

 2. When triggered, four springs eject four weights that are attached to the net. The net simply hangs below this launcher. The release is a ring that slides upwards when moved by a servo.
2. When triggered, four springs eject four weights that are attached to the net. The net simply hangs below this launcher. The release is a ring that slides upwards when moved by a servo. 

 2. This photo gives a good idea of its size. Range is reported as over 700 km so this drone must hold a very large fuel tank. The size of the warhead will likely depend on the required range. Speed is reported as over 700 km/h (435 mph).
2. This photo gives a good idea of its size. Range is reported as over 700 km so this drone must hold a very large fuel tank. The size of the warhead will likely depend on the required range. Speed is reported as over 700 km/h (435 mph). 

 2. Here is a closer view of this object. The trouble is that most jet engines used in drones do not look like this. If not an engine, what is this? The following photographs will (partially) explain what this is.
2. Here is a closer view of this object. The trouble is that most jet engines used in drones do not look like this. If not an engine, what is this? The following photographs will (partially) explain what this is.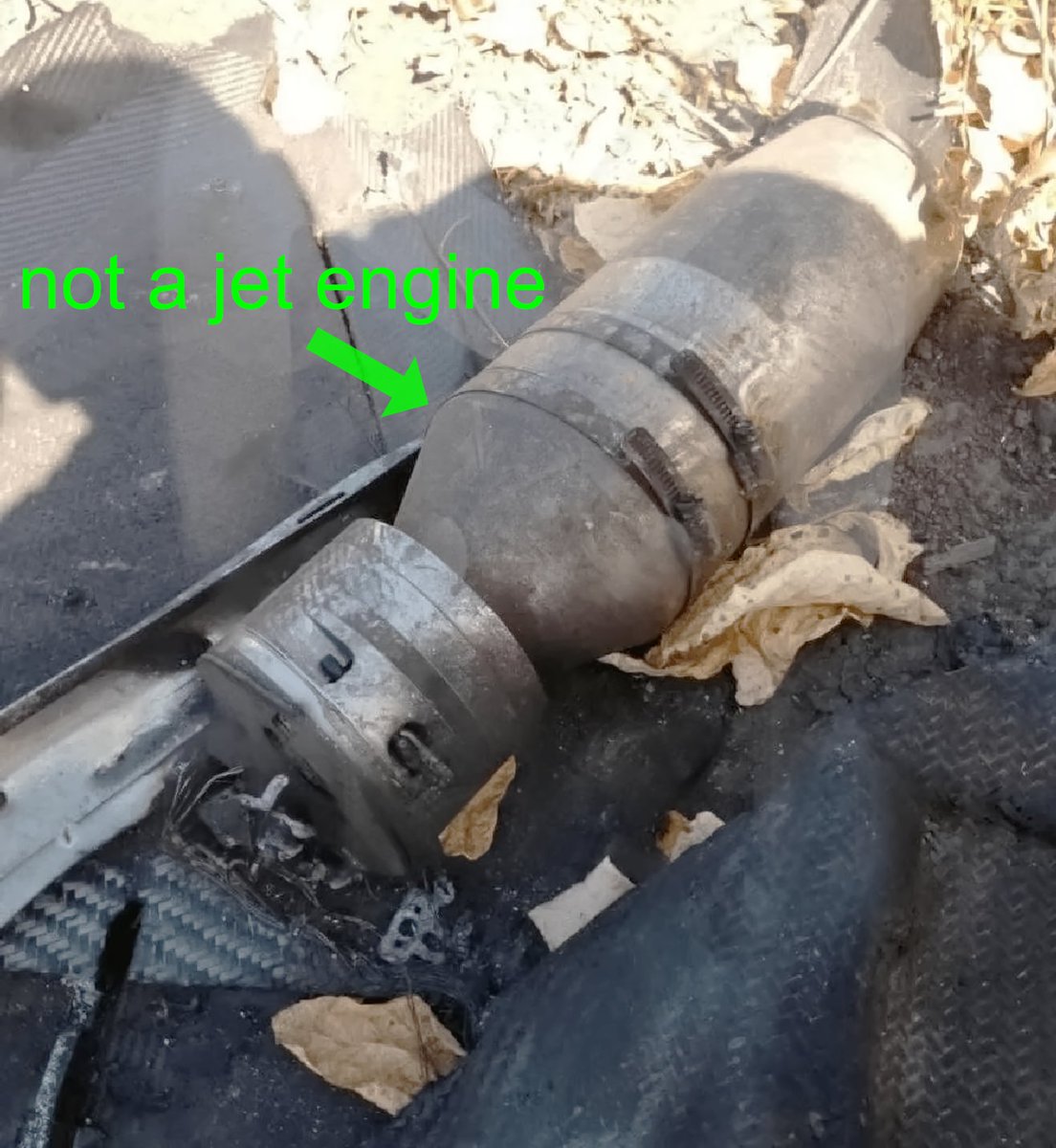 

 2. It’s not a secret but it is an interesting design. The fuselage is a carbon-fibre cylinder with fancy aluminum bulkheads. Wings and V-tail are composite construction with foam and wood internal structures. This is an expensive airframe compared to some other drones.
2. It’s not a secret but it is an interesting design. The fuselage is a carbon-fibre cylinder with fancy aluminum bulkheads. Wings and V-tail are composite construction with foam and wood internal structures. This is an expensive airframe compared to some other drones. 

 2. There is no single good photo of this drone so I made this rough sketch to give an idea what it looks like. Conceptually, it is very similar to the Shahed-136. The Ukrainian drone may have a larger diameter fuselage and be a bit shorter but it is hard to be certain.
2. There is no single good photo of this drone so I made this rough sketch to give an idea what it looks like. Conceptually, it is very similar to the Shahed-136. The Ukrainian drone may have a larger diameter fuselage and be a bit shorter but it is hard to be certain. 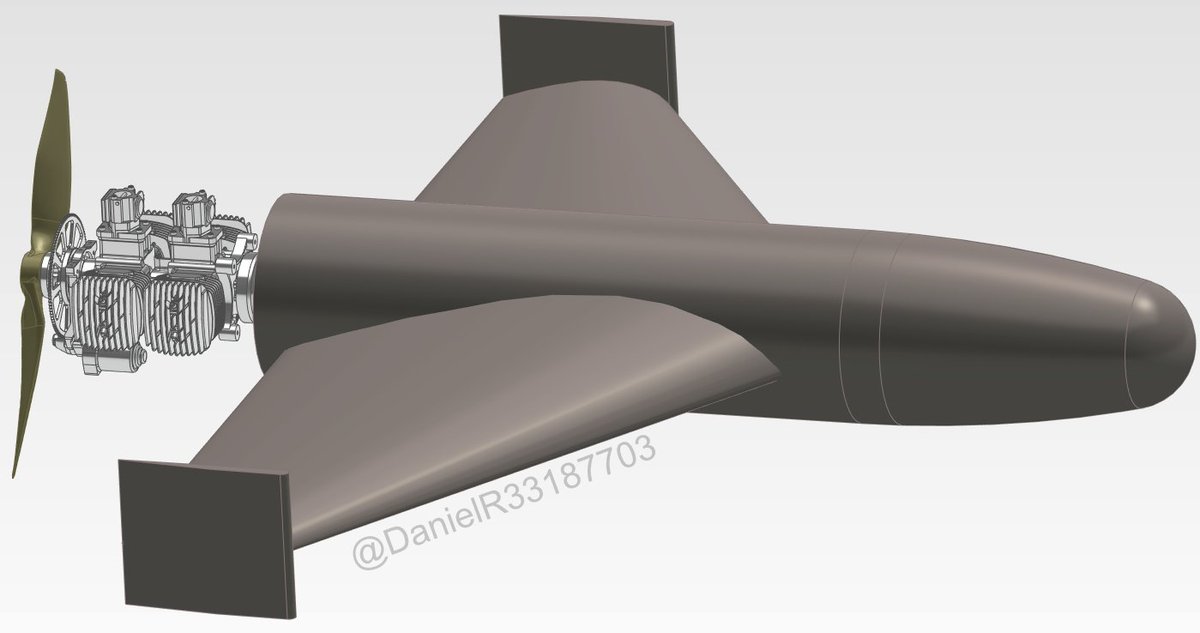

 2. This hinge appears to be well designed, likely after several iterations of refinement. The overall design is such that the left and right sides are identical or almost identical. This makes production easier as there are fewer unique components.
2. This hinge appears to be well designed, likely after several iterations of refinement. The overall design is such that the left and right sides are identical or almost identical. This makes production easier as there are fewer unique components. 

 2. The internal components are not shown but it appears to use a single cartridge as a source of propellant. To fire the cartridge, there is a spring-loaded hammer that is cocked by sliding a bolt into a slot. A servo motor fires the net by pushing the bolt out of the slot.
2. The internal components are not shown but it appears to use a single cartridge as a source of propellant. To fire the cartridge, there is a spring-loaded hammer that is cocked by sliding a bolt into a slot. A servo motor fires the net by pushing the bolt out of the slot. 

 2. This bomb is heavy and requires a large Baba Yaga multi-rotor drone to deliver it. Of note is the very large bomb release, which was probably also 3D-printed. Note that the bomb & release would require a very large-format 3D printer.
2. This bomb is heavy and requires a large Baba Yaga multi-rotor drone to deliver it. Of note is the very large bomb release, which was probably also 3D-printed. Note that the bomb & release would require a very large-format 3D printer. 