Through visual analysis of satellite imagery, our team found Russian military vehicle losses in Avdiivka between October 10 and October 20. The total number exceeded 109, indicating a significant loss of approximately aligning to a brigade-sized force in just ten days.🧵Thread: 

2/ The actual count of destroyed vehicles is notably higher. We excluded about a dozen vehicles with low to medium confidence due to inconsistent imagery coverage. In some cases, it was impossible to determine if a vehicle had remained in place for a while or was in motion 

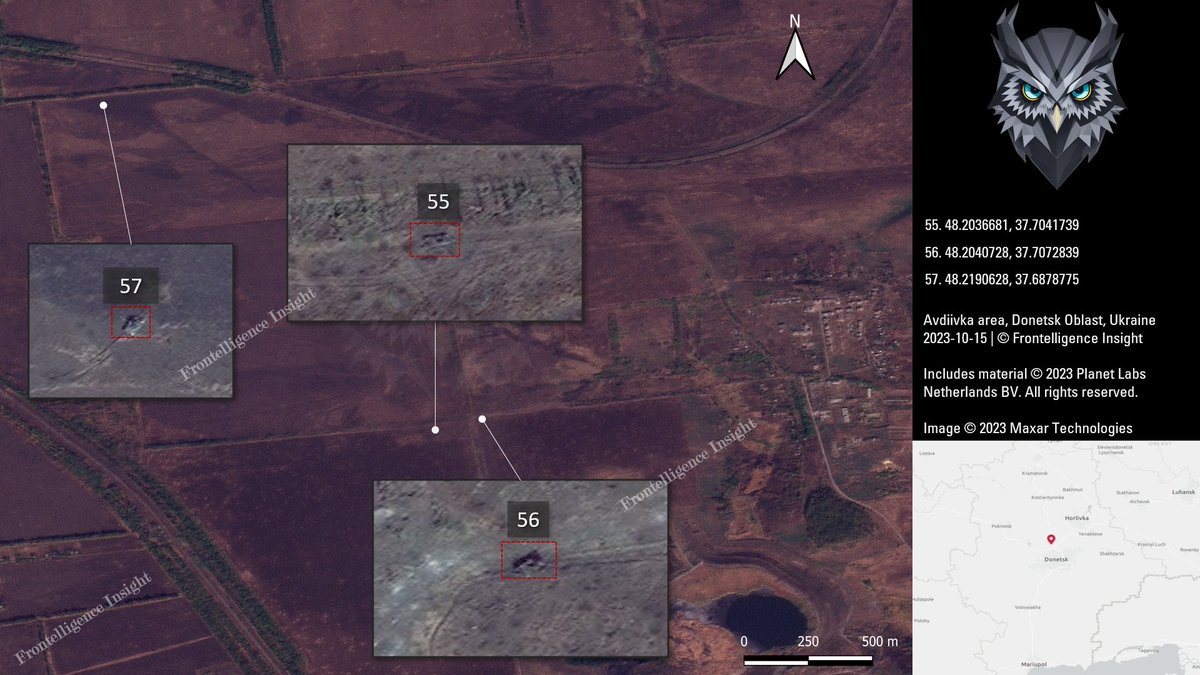
3/ All new lost vehicles are indicated by a red square on the imagery, while old losses that were already present at the end of September are marked with a white square. 

4/ The overwhelming majority of losses were primarily Armored Fighting Vehicles, including BMP-1 and BMP-2 of various configurations, T-72, T-64, and T-80 tanks in different variations, MT-LB, BTRs, and transport vehicles. In total, these losses amount to 109 vehicles. 

5/ The operation's scale and the involvement of multiple brigades strongly indicate that it is being conducted at the army level. We also see some evidence about additional reinforcements being deployed to the Avdiivka area, but further details cannot be disclosed at this time. 

6/ Despite reports of old equipment use, our team identified a significant presence of modern vehicles and equipment in coordinated battalion-level assaults, further underscoring the operation's importance for Russian command. 

7/ Upon analyzing the initial phase, our team concluded it was a long-planned, not a reactionary, operation. The observed patterns suggest Russians invested substantial time and resources, expecting significant losses to achieve their objective 

8/ Despite large losses, the enemy persisted in employing more mechanized forces to develop the limited success they had achieved, with the aim of securing dominant positions, disrupting logistics, and controlling waste heaps. 
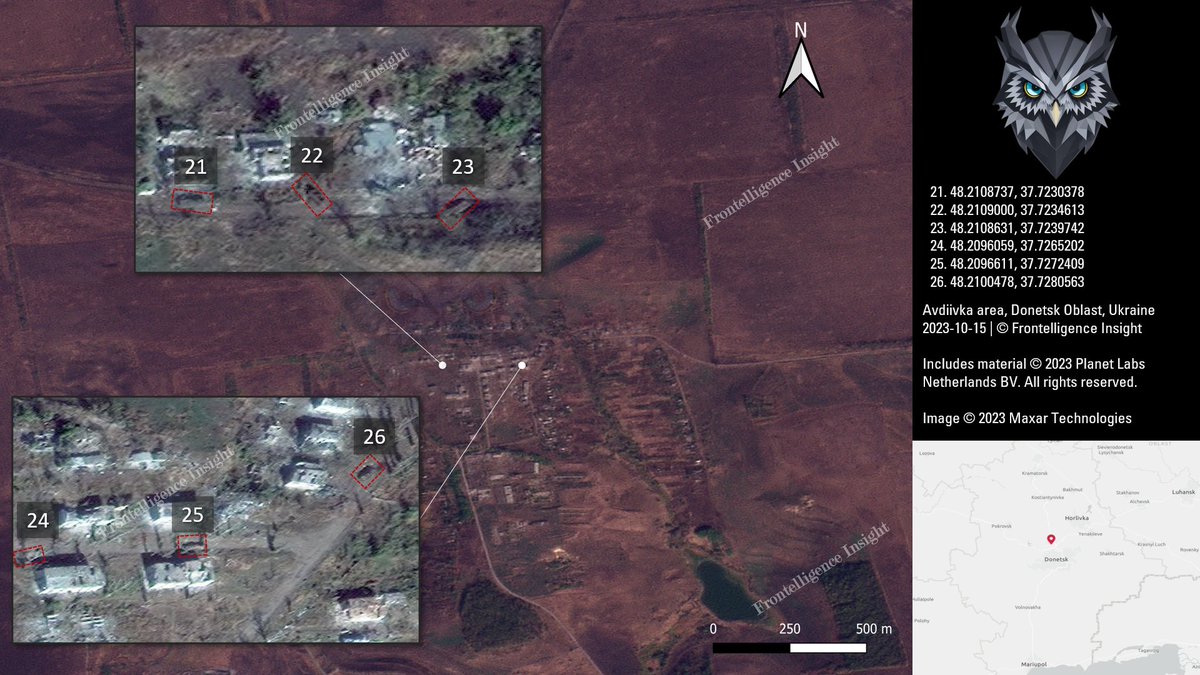

9/ The Russian vehicle losses have now surpassed those incurred during the Siversky Donets crossing in 2022. It's likely that these losses have already exceeded or will surpass the vehicle losses sustained by the Russians in the Vuheldar area between November 2022 and April 2023. 

10/ Two independent sources on the ground estimate Russian vehicle losses at around 200. Our current assessment is primarily focused on geospatial evidence, hence, we have chosen not to include this number, as we currently lack supporting satellite imagery for it. 

11/ However, the situation is far from stable. Russian forces continue to extensively use guided air-dropped bombs and artillery strikes, along with deploying LMUR (Light Multipurpose Guided Rockets). Multiple indicators point to active efforts to sustain the operation. 

12/ In conclusion, we want to emphasize several key points. This army-level operation, conducted through battalion or battalion-tactical groups, signifies not only the gravity of the operation but also shows an attempt to shift the strategic initiative to the Russian side. 

13/ The sustainability of these losses is in question, although this approach mirrors what we've observed in previous battles like Mariupol, Vuhledar, and Bakhmut when the Russians committed significant human and material resources and were willing to accept enormous losses 

14/ The operation originally aimed for a faster outcome and the advancement of Avdiivka through its flanks, but the resistance and skills exhibited by Ukrainian defenders have proven to be far more formidable than the Russians had anticipated in their plans. 
15/ To access the complete set of imagery, additional information, and a detailed methodology for this assessment, please visit our website:
frontelligence.substack.com/p/avdiivka-rus…

frontelligence.substack.com/p/avdiivka-rus…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh