Mechanisms of long COVID: An updated review: most common symptoms include fatigue, dyspnea, and other symptoms involving multiple organs. Vaccination results in lower rates of long COVID. sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
Symptoms and symptom proportions in long COVID. A longitudinal study among patients in Wuhan with the original SARS-CoV-2 strain reported symptoms and the changing proportion of symptoms of long COVID at different follow-up time. 

Common symptoms and possible mechanisms of long COVID. POTS: Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome; PTSD: Post-traumatic stress disorder. 
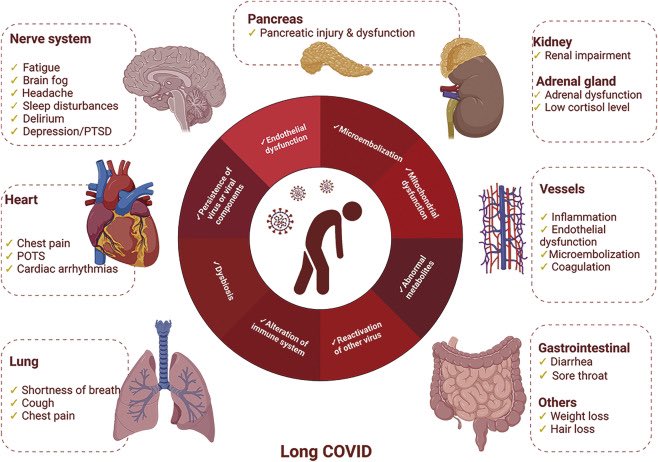
mech of LC:alteration of immune system,persist of residual viral component-chronic inflam,endothelial dysfunctn-activ, microembolization,mitochondrial dysfunction,abnormal metabolites,reactiv of pre-exist chronic viral infection,dysbiosis of microbiota,unrepaired tissue damage
female sex,obesity, severe COVID19 disease-as main risk factors. LC is not limited to only severe forms of COVID19. OPDs mild symptoms in acute phase hv LC, infection with diff SARSCoV2 variants is asso with varying LC phenotypes,owing to diff in viral–host interactions.
Among patients infected with original virus strain, ⬆️ % of them had long COVID than did patients infected with alpha or delta SARS-CoV-2 variants. The omicron variant is associated with⬇️risk of long COVID in comparison with delta variant
adaptive humoral & cellular immune response against SARSCoV2 functions in viral clearance. Immune memory persists after infection to further protect host, virus-specific NAbs & Tcell responses up to 12mth post infection,compromise immune resp lead to prolong chronic immune activ
⬇️perforin expression in CD8 + T lymphocytes in acute phase of severe SARSCoV2 predict LC;
Alteration of adaptive immune response persists in recovery from acute infection. COVID19, Tcell subsets exhib diff severity- time-dependent dynamic; exhausted (PD-1-expressing)/senescent
Alteration of adaptive immune response persists in recovery from acute infection. COVID19, Tcell subsets exhib diff severity- time-dependent dynamic; exhausted (PD-1-expressing)/senescent
CD57-expressing) state in CD4+ & CD8+ Tcells; perturbance in CD4+ regulatory Tcells in CP with LC at 3mth
recovery from severe. exhausted/senescent state was still in CD8+ Tcells upto 6mth after severe infection.⬇️ naïve cell popul, augmented granzyme B & (IFN-γ) production,
recovery from severe. exhausted/senescent state was still in CD8+ Tcells upto 6mth after severe infection.⬇️ naïve cell popul, augmented granzyme B & (IFN-γ) production,
unresolved inflammation in LC;⬆️antiviral cytotoxicity in CD8+ Tcells &⬆️ expression of exhaustion marker PD-1 with LC, vs who had completely recovered-state of chronic inflammation; spike-specific clonal CD4+ Tcell receptor β depth was signif asso with dyspnea & no of symptoms
at 12mth, infection-induced SARSCoV2-specif immune resp influence LC; immunopathological of LC in children differ adults; children LC had⬇️ability to switch from innate to adaptive immune,(children hv contraction of naïve & switched Bcell compart & unstable balance reg T lympho
frequency & function of innate immune cells relate to LC. Monocytes have signif⬆️ in frequency with severe infection vs mild-to-moderate infection at 1–3mth post recovery,& exhib⬆️activ, (HLA) class II marker HLA-DR was signif⬇️, suppressed Ag-presenting function in post COVID
⬆️monocytes be asso with worse disease severity,subsets of monocytes differ slightly. (NK) cells in controlling viral infection primarily via cytotoxicity & secretion of IFN-γ cytokine. NK cells signif⬆️ in peripheral blood with LC; CD59⬆️ NK cells are⬇️in subgroups severe;
asso with⬆️ pro-inflammatory cytokines, (IL-6), impairs expansion- function of NK cells. myelopoiesis cytokines granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor were⬆️in LC. At 1month after infection,⬆️serum IL-17 & IL-2;
⬇️serum of IL-4 and IL-10 : cytokine profile of LC; markers are potential targets for long COVID. Mast cell activ symptoms are⬆️ in long COVID. lung (CT) with COVID19, no signif diff in immune-related indexes compared with healthy at 1yr followup;in abnormal CT, C3 remain⬆️
autoimmune reactive inflam is one cause of LC; autoimmune response is asso with release of autoantigens by activated or dying neutrophils,⬆️ of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, neutrophil extracellular traps. Persistence of neutrophil extracellular traps &
anticardiolipin autoantibodies in post-acute phase of COVID19 infection.COVID19 for autoantibodies against 2770 extracellular & secreted proteins. exhibit⬆️in wide range autoantibody reactivities,vs uninfected controls.Abs against anti-melanoma differentiatn-asso gene 5 is COVID,
⬆️titer of Abs is correlated with severe disease unfavorable outcomes; antinuclear antibody (ANA) titers ≥1:160 in 43.6% at 12mth after COVID19 symptom onset,&⬆️% of neurocognitive symptoms.post-acute COVID19 symptoms common in COVID19 with rheumatic disease.
correlation between long COVID and autoimmunity. only 4.3% had higher ANA titers at 8mth after infection,< frequency of ANA positivity in general popul (5%). anti-calprotectin Abs asso with return to healthy at 8mth post infectn- protective role in pathology of long COVID.
IFN-specific autoantibodies in severe COVID-driver of persistent symptoms character LC; CP-with SARS-CoV-2 infection show persistent anti-IFN Ab were unlikely to contribute to LC symptoms.
signif⬆️cells in BALF samples from post COVID19 and that neutrophils, alveolar macrophages, Tcells, Bcells were signif⬆️in post COVID19, even 80d after primary infection. proteomes in BALF collected from patients post COVID19 were different from healthy,
Persisting platelet activ & hyperactivity in COVID19 survivors.⬆️ D-dime,TE in LC; The ⬆️anomalous (amyloid) deposits (microclots) in plasma from LC; microclots, various inflammatory molecules, α 2-antiplasmin, fibrinogen chains, serum amyloid A.
Heparin-induced extracorporeal low-density lipoprotein (HELP)/fibrinogen precipitation apheresis, for septic MOD, acute COVID19 or long COVID.
coagulation parameters as Ddimer (VWF), factor VIII (FVIII) as markers of endothelial activation. VWF antigen, VWF propeptide, FVIII are
coagulation parameters as Ddimer (VWF), factor VIII (FVIII) as markers of endothelial activation. VWF antigen, VWF propeptide, FVIII are
signif⬆️in LC, endothelial cells (ECs) are direct or indirect preferential target of SARSCoV2 & dysfunction of endothelium; Delayed thrombotic events, vascular injury, endothelial dysfunction in post-acute COVID. Endothelial dysfunction relationship with microvascular occlusion
signif⬇️in vascular density in LC effects of patient sera on ECs suggested a pro-angiogenic effect in serum from post-COVID19 syndrome compensatory mechanism for endothelial dysfunction, (absent in LC),, chronic endothelial dysfunction,(key symptoms involving multiple organs);
Blood biomarkers for vasculature transformation are signif⬆️, with angiogenesis markers (angiopoietin-1/P-selectin) yielding a classification accuracy for LC of 96%,87 for diagnostic & therapeutic applications. Endothelial biomarkers (endothelin 1, angiopoietin-2)
altered in post-COVID-19 syndrome.88 During long COVID, there is ongoing endothelial cell dysfunction, dysregulated angiogenesis, as well as imbalance of the VWF & disintegrin, metalloprotease with thrombospondin type 1 repeats, member 13 axis. Immunophenotyping:
signif⬆️ intermediate monocytes & activated CD4+& CD8+ Tcells in CP, correlated with thrombin generation & endotheliopathy markers, cross talk between ECs and immune cells. L-arginine and vitamin C can regulate endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress,
Occult viral persistence; CoV2 RNA found in feces, plasma, urine up to 7mth after infection. persistence of residual Ag & CoV2 RNA found in tissues (appendix, skin, breast) of LC; common set of autoantigens is recogn in post COVID19. Persistent circulating SARSCoV2 spike protein
detected in plasma with long COVID up to 12 months after infection, associated with long COVID.98 long-term level of anti-spike immunoglobulin G is associated with the breadth of autoreactivity post COVID19
Mitochondria:central in host response to viral infection, immunity, immune signaling by IFN system.Mitochondrial ds RNA triggers antiviral signalling;disruption of mitochondrial metabolic pathways;SARSCoV2 infection⬇️expr of nuclear-encoded genes related to mitochondrial complex,
dysfunction of mitochondria;⬇️mitochondrial membrane potential,in leukocytes from post COVID19. SARS-CoV-2 infection affected metabolism of small mitochondrial RNAs without altering overall mitochondrial transcription.
plasma metabolic phenotype show PASC plasma metabolites; altered fatty acid metabolism & dysfunctional mitochondria-dependent lipid catabolism. selective neuronal mitochondrial targeting in SARS-CoV-2 infection, which affects cognitive processes to induce "brain fog" in LC
gut dysbiosis in 78.7% of PASC had not fully recovered,(14-month follow-up);In gut microbiota analysis- cluster 1 (Ruminococcus gnavus, Klebsiella quasipneumoniae, Aspergillus flavus, Candida glabrata, Candida albicans), Mycobacterium phage MyraDee, Pseudomonas virus Pf1)
was signif asso with severe COVID19 & dev of PASC,altered gut microbiome in gut–brain axis; asso neurological sequalae,altered gut microbiota⬆️expr of various mediator;zonulin causes disruption of tight junctions & stim enteric NS, signals to (CNS), precipit neurol sequalae in LC
dyspnea in 13.4% of survivors 2yr pi, persistent⬇️PFT, abn lung CT survivors, (PET-CT)-abn metab lungs/brains,mech of persistent lung injury,asso⬇️endothelial function, lung fibrosis,activ of absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2)R in circulat cells,⬆️IL-1α,IFN-α,transforming growth F beta
myoendocarditis,prolonged persistence of coronavirus in cardiomyocytes,endothelium,macrophages (upto 18m),⬆️immune activity,Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome,Direct viral damage,autonomic nerve damage, brainstem injury;recovering cardiovascular (MRI)- cardiac invol (78%),
ongoing myocardial inflam (60%),highly prevalent regardless of pre-existing conditions, overall course severity of acute illness, time from original diagnosis, Arterial wall stiffening, endothelial dysfunction, persistently high oxidative burden cardiac dysfunction,⬆️HT,
⬆️mortality post disch. PROLUN (Patient-Related Outcomes Lung Function After Hosp for COVID19): RV & LV diastolic dysfunct in 50% post COVID; 27% arrhythmias 3m pi, Arrhythmogenic RV cardiomyopathy RV dysfunct- arrhythmias, asso with anti-desmoglein-2 (DSG2) Abs,⬆️anti-DSG2 Abs
⬆️expr (ACE2) in kidney > lung AKI RFT in recovery may not completely recover;GFR⬇️2yr pi WT; Lipid mediators in renal injury fibrosis; SARSCoV2 direct infect kidney cells,⬆️collagen 1 protein expression,asso with⬆️ tubule-interstitial kidney fibrosis;
⬆️CKD,multi-ligand receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) & its ligands contribut factors in CKD and COVID19,⬆️promote RAGE activity. downstream effects- inflammation, cellular dysfunction, tissue injury, fibrosis
SARSCoV2 spreads to brain via nasal cavity or blood stream, trigger neuroinflammation, remaining sequelae of LC occur due to acute neurologic complications as stroke, encephalitis, Guillain–Barré syndrome,delirium, pathophysiology of neurological symptoms,cognitive or
mental disorders, headache, olfactory/gustatory dysfunction, differ from acute phase. sustained neuroinflammation in onset of symptoms involve microglia activation, autoimmunity,local microthrombosis or mitochondrial dysfunction, persistent neuroinflammation, microglia activation
MRI in LC-structural alterations in brain,signif enlarged gray matter volume (GMV) in several clusters (spanning frontotemporal areas, insula, hippocampus, amygdala, basal ganglia, thalamus both hemispheres), GMV alterations in limbic, secondary olfactory areas,dynamic over time.
Brain MRI:changes to structure of brain,cannot show metabolic changes before structural changes occur,in PET. Brain 18F-FDG PET:OPDs post-COVID19 hv⬆️hypometabolic right frontotemporal cluster,(more no symptoms initial & longer duration symptoms at⬆️risk of persistent brain invol
brain PET hypometabolism in LC, olfactory gyrus, connected limbic/paralimbic regions,extended to brainstem, cerebellum. PET-CT in children infected with SARS show hypometabolism in left orbito-frontal region,explain neurocognitive symptoms in children with LC.
Clinical symptoms LC, fatigue, myalgia, insomnia, headache, depression, shortness of breath, explained by brainstem dysfunction induced by tropism of SARSCoV2 & chronic inflammation; Both direct & indirect virus damage is asso with brainstem dysfunction.
ACE2R is⬆️expressed in brainstem vs other brain regions, SARSCoV2 persist in brainstem. CoV2 RNA & proteins in brainstem, brainstem damage, pathological immune or vascular activation-brainstem damage.
SARSCoV2 infection⬆️gene expression profile for Alzheimer risk
SARSCoV2 infection⬆️gene expression profile for Alzheimer risk
Apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4) gene is risk factor for severe COVID19 & post-COVID mental fatigue; ε4 allele of APOE4 strongest genetic risk factor for sporadic Alzheimer disease, SARSCoV2 S1 spike proteins hv self-associating “prion-like” regions,& amyloid peptide-binding & domains
pathological “seeding” amyloid genesis in pro-inflammatory neurodegeneration, neural cell atrophy,neuronal cell death.
⬇️activity of autonomic nerves (vagal) in LC; psychiatric disorders, new onset psychiatric, suicide risk. Autonomic nervous system damage;anosmia, smell, taste.
⬇️activity of autonomic nerves (vagal) in LC; psychiatric disorders, new onset psychiatric, suicide risk. Autonomic nervous system damage;anosmia, smell, taste.
sudden loss of the sense of smell for > 4wk- 1yr, 52.6% abnormal baseline Brief Smell Test;82.8% had persistent parosmia;destruction of olfactory neuroepithelium or transmission of pathogens directly via olfactory nerve in olfactory disorders; prolonged inflammation in
olfactory system & various brain regions,striatum, cerebellum. inflam in abs of infectious virus,asso with behavioral changes.PASC anosmia-dysregulated axis immune cells, horizontal basal cells, sustentacular cells, olfactory sensory neurons in PASC hyposmia olfactory epithelium,
sensory dysfunction. Local lymphocyte populations expressing interferon-γ and γδ T cell markers in olfactory epithelium with PASC, interferon response and inflammation. Trace elements imbalance accelerate SARSCoV-2 neurovirulence,⬆️neurotoxicity,
Endocrine system:Adrenal dysfunction, chronic adrenal insufficiency,cortisol level in LC 50%⬇️,most significant predictor of LC,asso with adrenal gland dysfunction induced by viral infection & cellular damage; prediabetes asso with⬆️risk of severe COVID19;
⬆️serum levels of IL-6 in acute phase, without long-term worsening of sequelae, new-onset DM persist in post-acute phase of COVID19: virus-induced ß-cell cytotoxicity, insulin resistance, dysregulation of immune & RAS. ⬆️risk of DM in COVID19;critical illness asso with⬆️risk DM
Impaired lipid metabolism associated with long COVID, body composition and nutrition may also be related. Extreme obesity is strong predictor of long-COVID in severe COVID19 illness & (ARDS).obesity & lipid metabolism disorders risk for development of long COVID syndrome.
Musculoskeletal manifestations of COVID19: hyperinflammatory host response, prothrombotic state, otherapeutic effects than viral toxicity; Physical inactivity, poor nutrition, muscle dysfunction, malnutrition, sarcopenia, ambulatory or inpatient rehabilitation,. Geriatric rehab
Epigenetics, single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), other factors related to LC: signif changes in transcript abundance & DNA methylation of genes, transposable elements in recovered, 425 upregulated genes, 214 downregulated genes, 18,516 differentially methylated regions.
overactivated immune response, abnormal stress response, metabolic processes asso with LC. DNA methylation profiling analysis: accumulation of epigenetic aging is asso with LC, cannot be reversed at late clinical phase. ACE2 & type II (TMPRSS2)R of SARSCoV2.
spike protein (S) CoV2 viral envelope glycoprotein that binds to ACE2 after its cleavage at sites S1/S2 by TMPRSS2.; SNPs of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 are asso with LC. negative correlation btw loss of taste; ACE2 gene expression levels. 4 SNPs of ACE2 asso with COVID19 severity;
not predispose dev LC sympt after recovery; ACE2 SNPs rs2106809 G allele signif⬆️expr of ACE2,& ACE2 SNP rs2106809 functnl brain expr quantitative trait locus; Reactivation after infection with other viruses asso- EBV in throat(⬆️in LC fatigue) vs CP;EBV replication cofactor
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter