THIS might just be causing your gut problems.
The FDA has swept these under the rug for decades.
We’re now waking up to the harms of these so-called “safe” ingredients, added to nearly every commercial food.
Let’s talk about it⬇️
The FDA has swept these under the rug for decades.
We’re now waking up to the harms of these so-called “safe” ingredients, added to nearly every commercial food.
Let’s talk about it⬇️

The intimate link between food additives and gut health is a complex web we're only just beginning to unravel.
As our diets have evolved to include a myriad of packaged foods, these substances have woven their way into the fabric of our daily consumption.
As our diets have evolved to include a myriad of packaged foods, these substances have woven their way into the fabric of our daily consumption.

The FDA classifies most of these ingredients as “generally recognized as safe,” a nice way of saying they get put into the food based on expert opinion with minimal study.
While food additives have long played a role in enhancing flavor, prolonging shelf life, and improving texture, recent studies suggest they may be double agents with hidden agendas in our gut's ecosystem.
While food additives have long played a role in enhancing flavor, prolonging shelf life, and improving texture, recent studies suggest they may be double agents with hidden agendas in our gut's ecosystem.

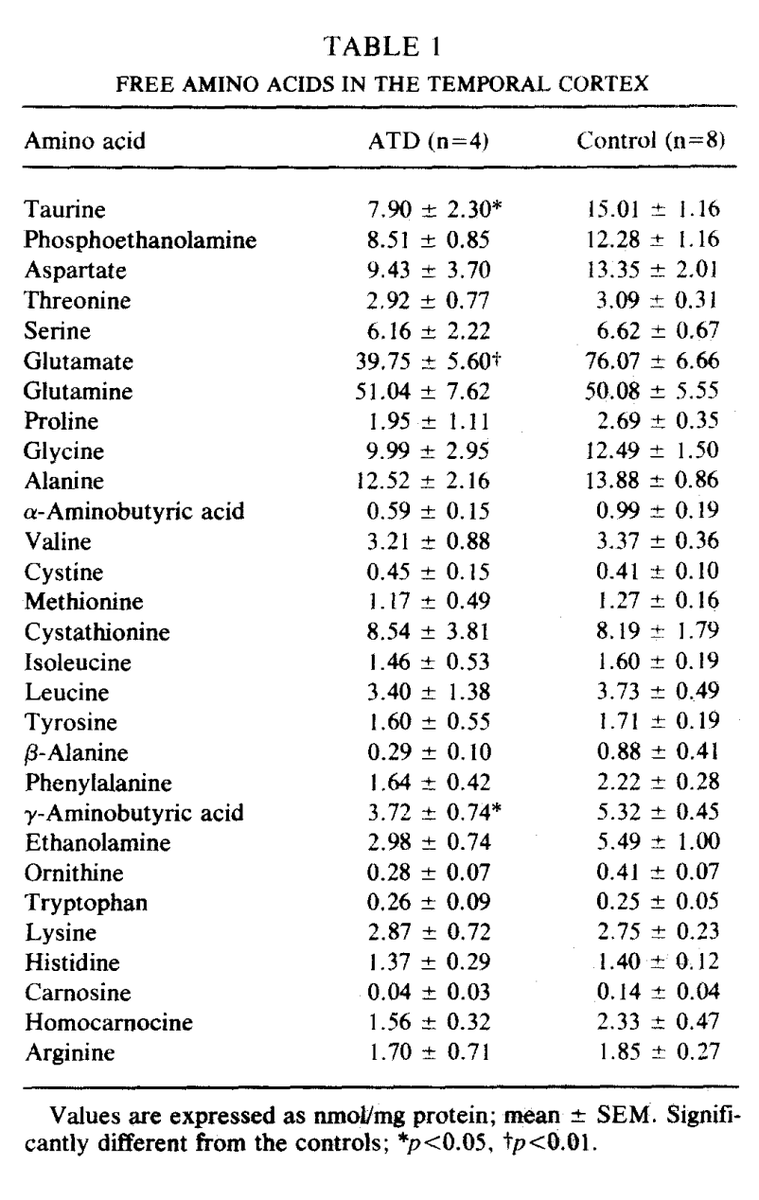
Polysorbate 80 and carboxymethylcellulose are absolutely ubiquitous in foods and supplements.
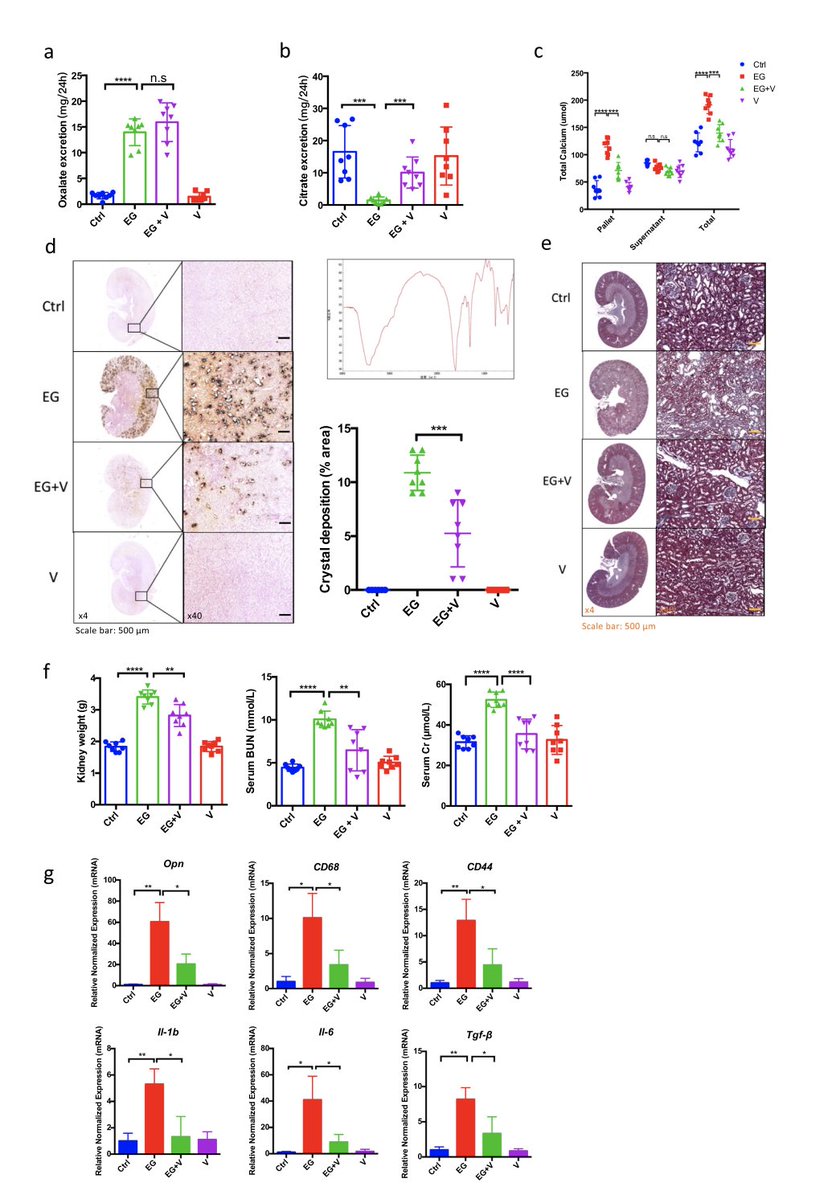
In rodent studies, these emulsifiers cause dysbiotic bacterial overgrowth and support the genesis of COLITIS, i.e inflammatory bowel disease.
In rodent studies, these emulsifiers cause dysbiotic bacterial overgrowth and support the genesis of COLITIS, i.e inflammatory bowel disease.

Specifically, Polysorbate 80 and carboxymethylcellulose seem to foster an environment ripe for mucus-degrading bacteria, degrading this layer of critical protection and paving the way for conditions like colitis and metabolic syndrome in animals.
Germ-free mice receiving fecal transplants from P80 and CMC-treated counterparts displayed similar microbial disruptions, demonstrating the cause and effect relationship.
Germ-free mice receiving fecal transplants from P80 and CMC-treated counterparts displayed similar microbial disruptions, demonstrating the cause and effect relationship.
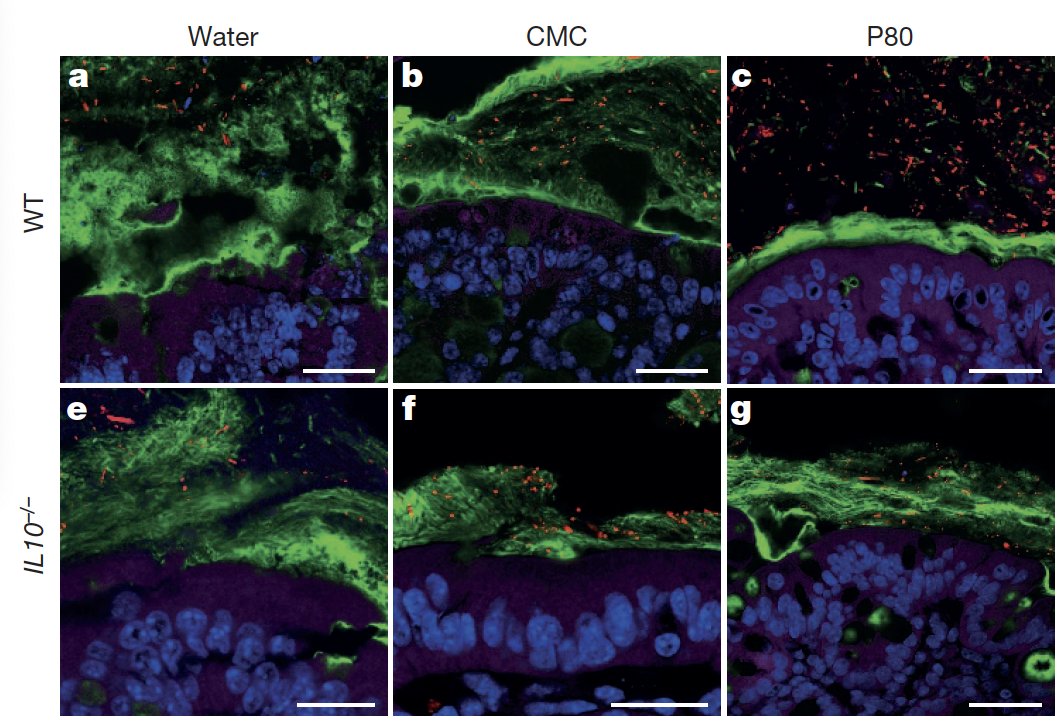
Additionally, these substances have been demonstrated to drive a proliferation of inflammation-related pathogenic bacteria when direct contact with human-derived microbial communities is made, with the bacteria invading our mucus layer.

The detrimental effects extend beyond physical health.
P80 and CMC are implicated in altering behaviors.
Female mice, for instance, exhibited antisocial tendencies, while their male counterparts showed increased anxiety levels.
These behavioral changes align with identifiable shifts in the gut bacteria and levels of specific neuropeptides.
This should come as no surprise, the mental health connection to poor gut health is obvious and well understood at this point.
P80 and CMC are implicated in altering behaviors.
Female mice, for instance, exhibited antisocial tendencies, while their male counterparts showed increased anxiety levels.
These behavioral changes align with identifiable shifts in the gut bacteria and levels of specific neuropeptides.
This should come as no surprise, the mental health connection to poor gut health is obvious and well understood at this point.

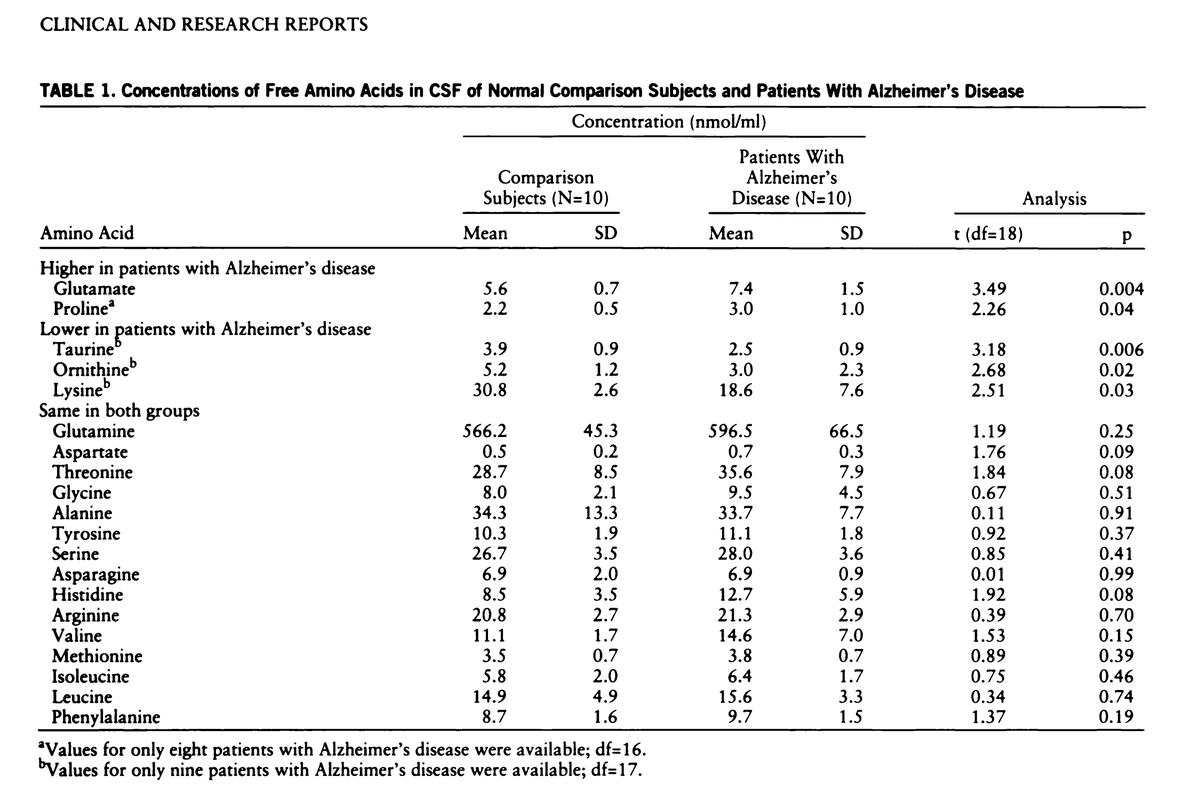
Another familiar food additive, maltodextrin, a thickening agent derived from starch, raises its own red flags.
It has been implicated in impairing gut homeostasis and promoting intestinal disorders, again by promoting the pathogenicity of certain gut bacteria.

It has been implicated in impairing gut homeostasis and promoting intestinal disorders, again by promoting the pathogenicity of certain gut bacteria.

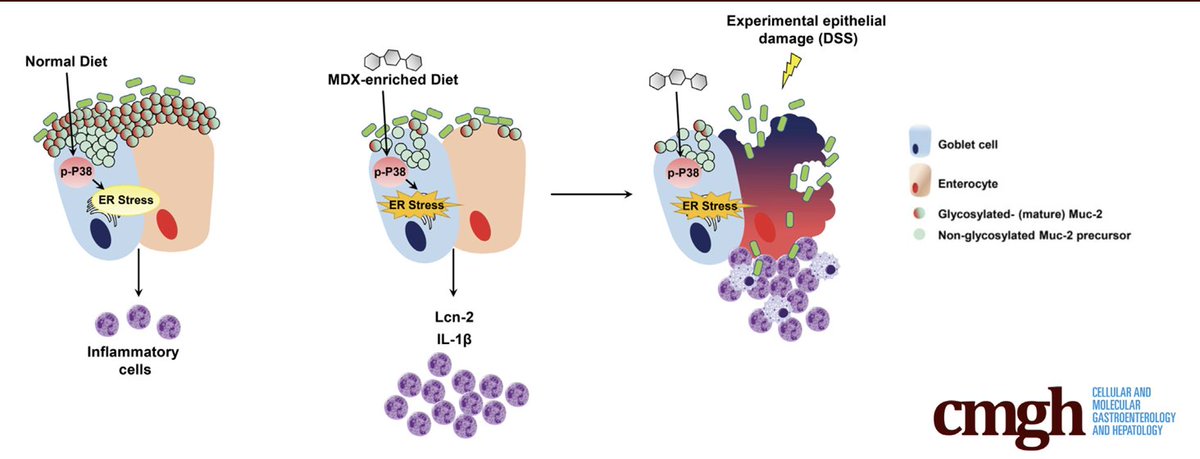
Alarmingly, maltodextrin administration in a preterm pig model heightened the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis, a nasty and severe intestinal inflammatory condition, indicating a potential risk in the most vulnerable patients—newborns.
This is in your baby formula.
This is in your baby formula.

More disturbingly, maltodextrin (MDX) triggers a stress response in intestinal goblet cells, diminishing our intestinal mucus production, and sensitizes to inflammatory stimuli.
This paints a worrying picture of its impact on the gut's protective mechanisms.
This paints a worrying picture of its impact on the gut's protective mechanisms.

Artificial sweeteners also don't spare the gut.
These sweeteners, found in numerous diet foods and beverages, are linked to glucose intolerance and gut dysbiosis in animal models.
One study highlighted that prolonged saccharin intake led to glucose intolerance and changes in the fecal metabolites of mice, suggesting that these sweeteners might instigate metabolic disorders through inducing gut bacterial overgrowth.
These sweeteners, found in numerous diet foods and beverages, are linked to glucose intolerance and gut dysbiosis in animal models.
One study highlighted that prolonged saccharin intake led to glucose intolerance and changes in the fecal metabolites of mice, suggesting that these sweeteners might instigate metabolic disorders through inducing gut bacterial overgrowth.

Concerns extend to sucralose, another artificial sweetener.
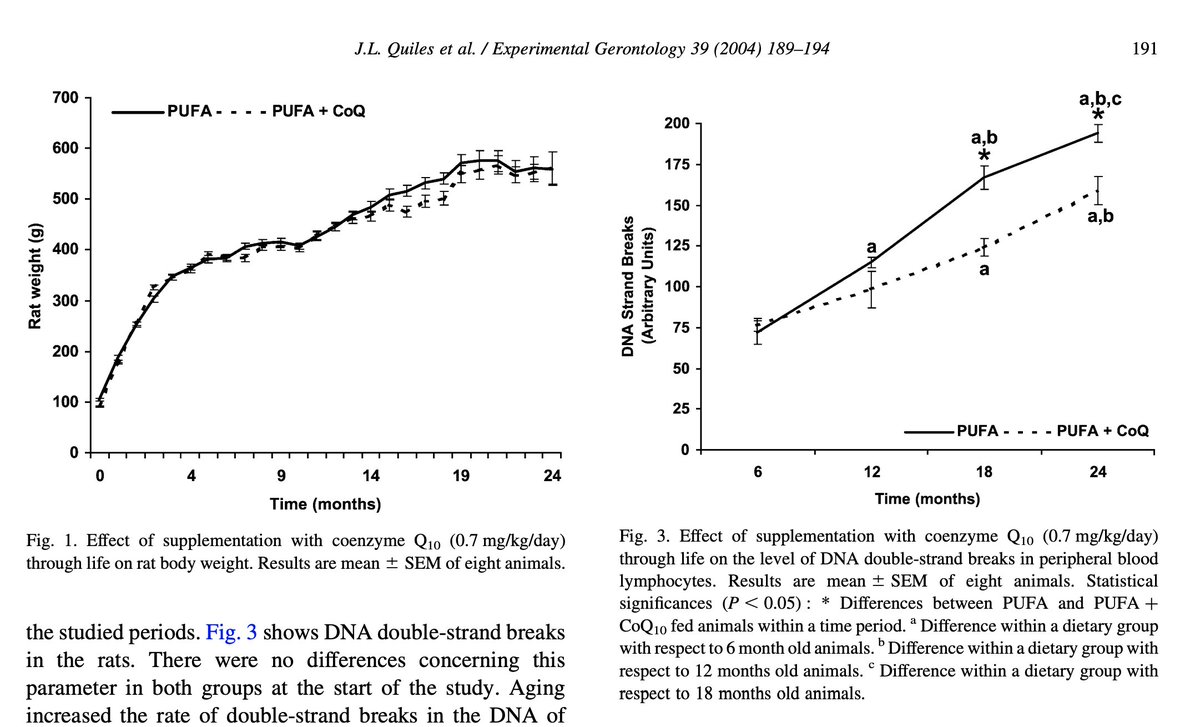
Six-month consumption once again induced dysbiosis in mice, contributing to the formation of endotoxin and subsequent liver inflammation, bringing attention to their broader systemic effects.
Six-month consumption once again induced dysbiosis in mice, contributing to the formation of endotoxin and subsequent liver inflammation, bringing attention to their broader systemic effects.

Disturbingly, artificial sweetener-induced bacterial disruptions correlate with impaired hepatic detoxification mechanisms in prenatally exposed mouse pups, raising serious questions about sweetener’s impact for future generations.

Food colorants, particularly titanium dioxide, are another culprit.
Used widely for aesthetic appeal, their ingestion can cause intestinal inflammation and contribute to dysbiosis, a critical root cause if you’re dealing with any type of lingering gut issue.
Used widely for aesthetic appeal, their ingestion can cause intestinal inflammation and contribute to dysbiosis, a critical root cause if you’re dealing with any type of lingering gut issue.

The damage from titanium dioxide manifests through altered epithelial barrier permeability, creating unwanted bacterial translocation across the gut into systemic circulation, making this a problem for the entire body.
IBD sufferers also have increased titanium in their blood.

IBD sufferers also have increased titanium in their blood.


Alarmingly, evidence points toward titanium dioxide's role in the facilitation of colon carcinogenesis upon prolonged exposure, as seen in animal models, signaling a red flag for its presence in our diet.

This is far from a comprehensive look.
Other sweeteners like Splenda, additives like Silica and emulsifiers like the various gums, have shown similar effects.
There are literally hundreds if not thousands of these “safe” food ingredients out there just flying under the radar.

Other sweeteners like Splenda, additives like Silica and emulsifiers like the various gums, have shown similar effects.
There are literally hundreds if not thousands of these “safe” food ingredients out there just flying under the radar.


It’s also recently been shown that the ubiquitous food dye, red 40 or Allura Red AC, can cause inflammatory bowel disease outright, you guessed it, by increasing gut serotonin.
This was mediated by inducing dysbiosis and subsequent inflammation in the gut, along with increasing intestinal permeability.
This was mediated by inducing dysbiosis and subsequent inflammation in the gut, along with increasing intestinal permeability.

You can read more about serotonin’s impact on your gut here:
https://x.com/Outdoctrination/status/1678072420190547968?s=20
In regulatory circles, the FDA and EFSA have been basing food additive approvals on outdated safety testing from the 70s and 80s.
The increasing evidence of food additives’ negative impact on gut health cannot be ignored, with the FDA responding by calculating dietary exposure to emulsifiers and assessing their safety anew.
However, this FDA study has its limitations, looking retrospectively only up to 2010.
The quick pace at which the food industry and additive use are growing means regulations will likely never keep up.
The increasing evidence of food additives’ negative impact on gut health cannot be ignored, with the FDA responding by calculating dietary exposure to emulsifiers and assessing their safety anew.
However, this FDA study has its limitations, looking retrospectively only up to 2010.
The quick pace at which the food industry and additive use are growing means regulations will likely never keep up.
It’s up to you to protect yourself.
If you’re going to buy food with ingredients, at the very least check the label. If something seems like it shouldn’t be in your food, it probably shouldn’t. Better safe than sorry.
Additionally, some of these don’t even make it onto the label at all!
For example, in skim milk, vitamins A and D are added, but they’re fat soluble so they require the addition of emulsifiers, but you won’t find them on the label at all!

If you’re going to buy food with ingredients, at the very least check the label. If something seems like it shouldn’t be in your food, it probably shouldn’t. Better safe than sorry.
Additionally, some of these don’t even make it onto the label at all!
For example, in skim milk, vitamins A and D are added, but they’re fat soluble so they require the addition of emulsifiers, but you won’t find them on the label at all!


This may not seem like a big deal since they are in small quantities, but if you can avoid them I think it is optimal for your long term health.
Throughout my own experience and working with several others with gut problems, this can be a major cause of unexplained problems.
Be careful out there.
Throughout my own experience and working with several others with gut problems, this can be a major cause of unexplained problems.
Be careful out there.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh