
Biomolecular Engineer. Helping people virtually worldwide with a personalized approach. Book a free call here to work with us: https://t.co/zanpmphTQB
69 subscribers
How to get URL link on X (Twitter) App


https://x.com/Outdoctrination/status/1972277835591999550
 I stumbled across this study a few months ago.
I stumbled across this study a few months ago.

https://x.com/Outdoctrination/status/1762946202889490517
 This was an animal study done in a classic model of heart disease, the high cholesterol diet in rabbits.
This was an animal study done in a classic model of heart disease, the high cholesterol diet in rabbits.
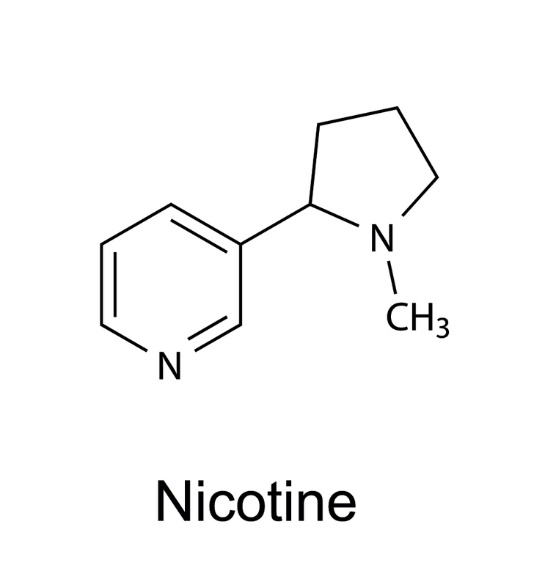
 More than a few studies have shown that nicotine consumers have lower rates of inflammatory conditions.
More than a few studies have shown that nicotine consumers have lower rates of inflammatory conditions.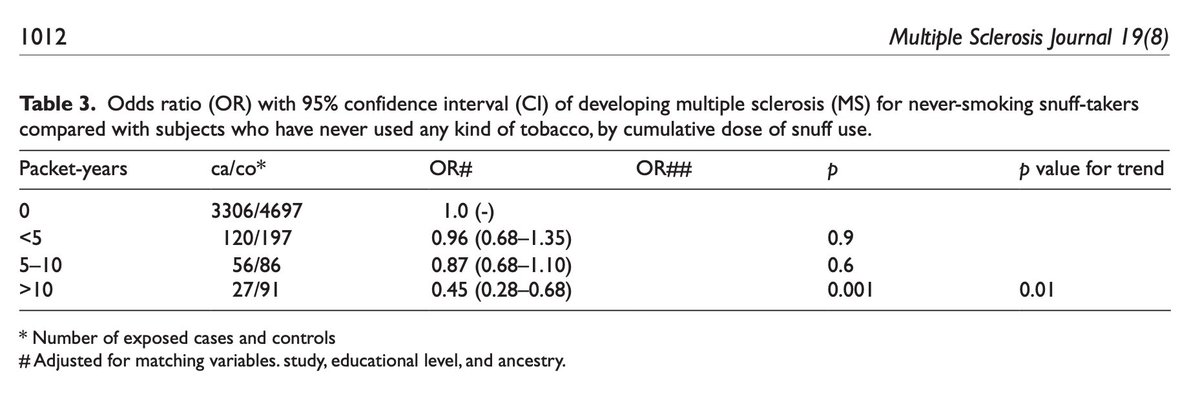

 There are a few chemical mediators that induce the symptoms of allergies:
There are a few chemical mediators that induce the symptoms of allergies: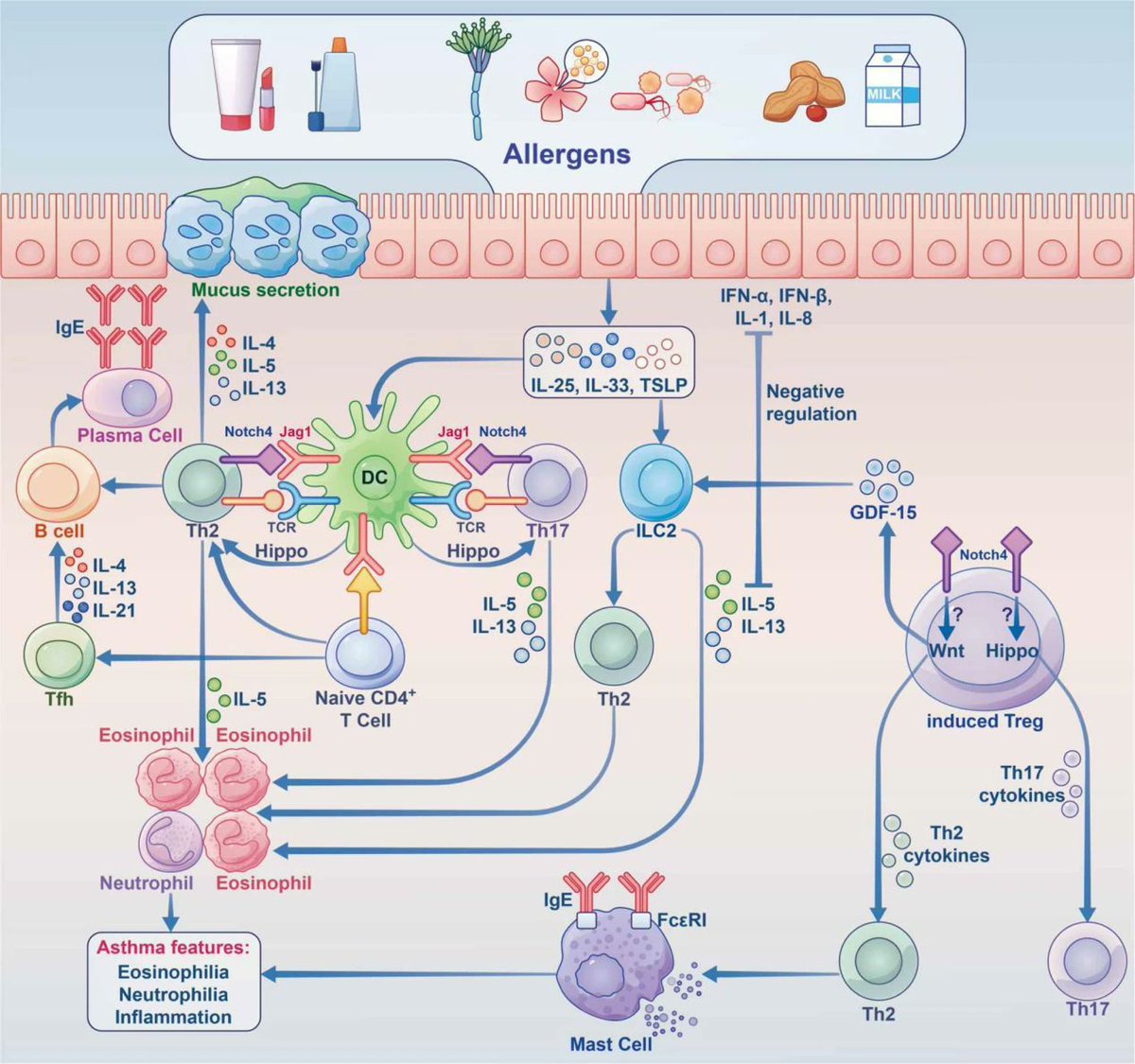


 I was surprised to find out that taurine is actually the second most abundant amino acid in the central nervous system, behind glutamate.
I was surprised to find out that taurine is actually the second most abundant amino acid in the central nervous system, behind glutamate.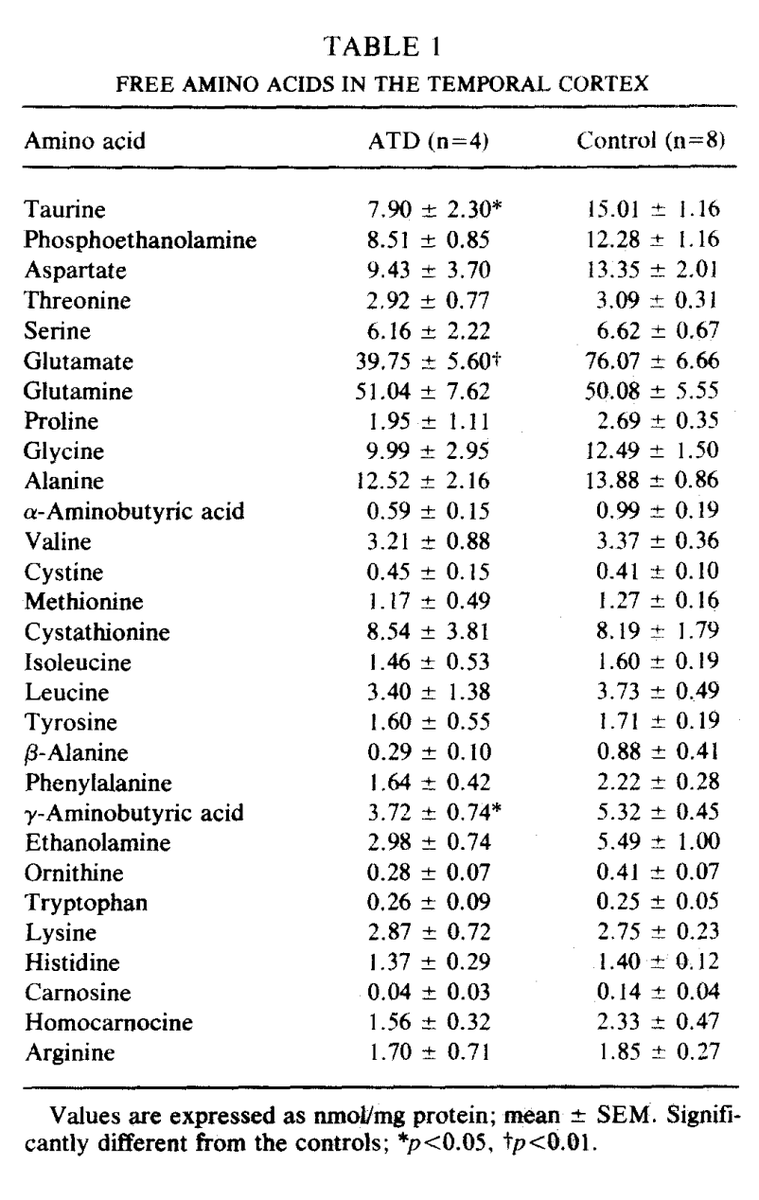
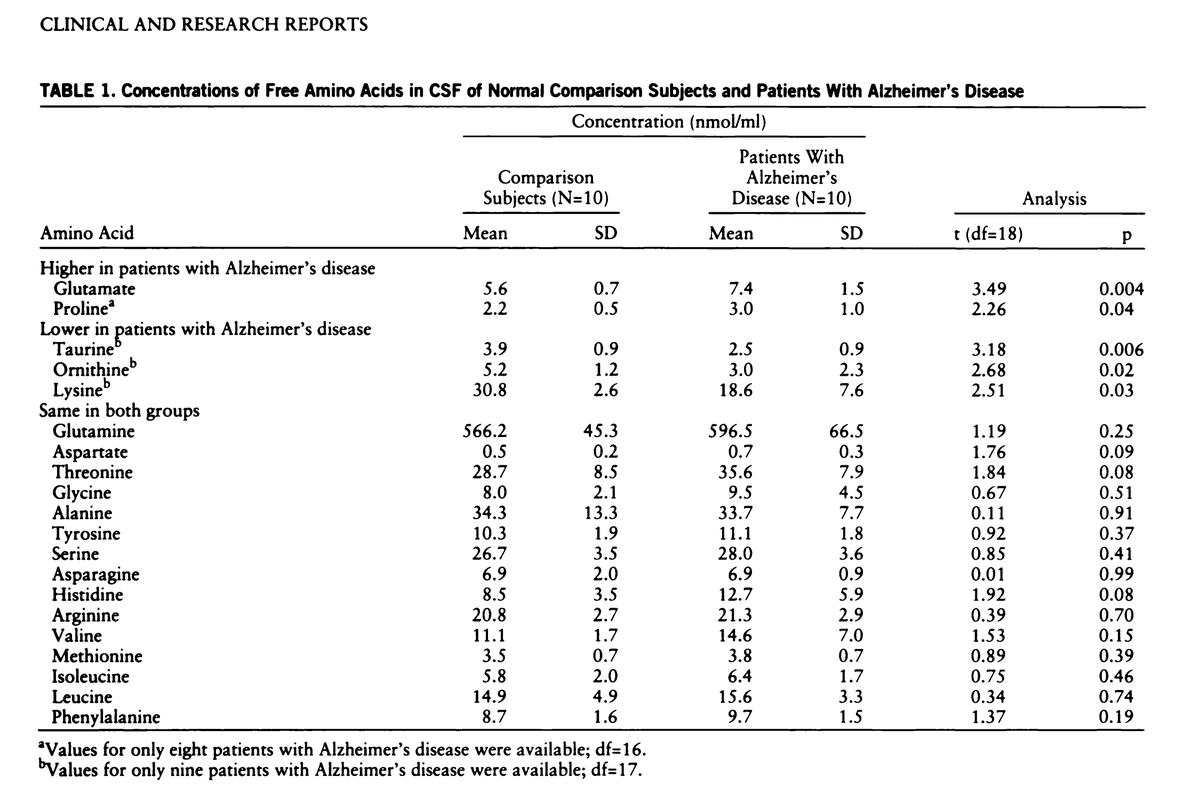

 This study was published in 2018.
This study was published in 2018.
 Your gut is connected directly to your mouth.
Your gut is connected directly to your mouth.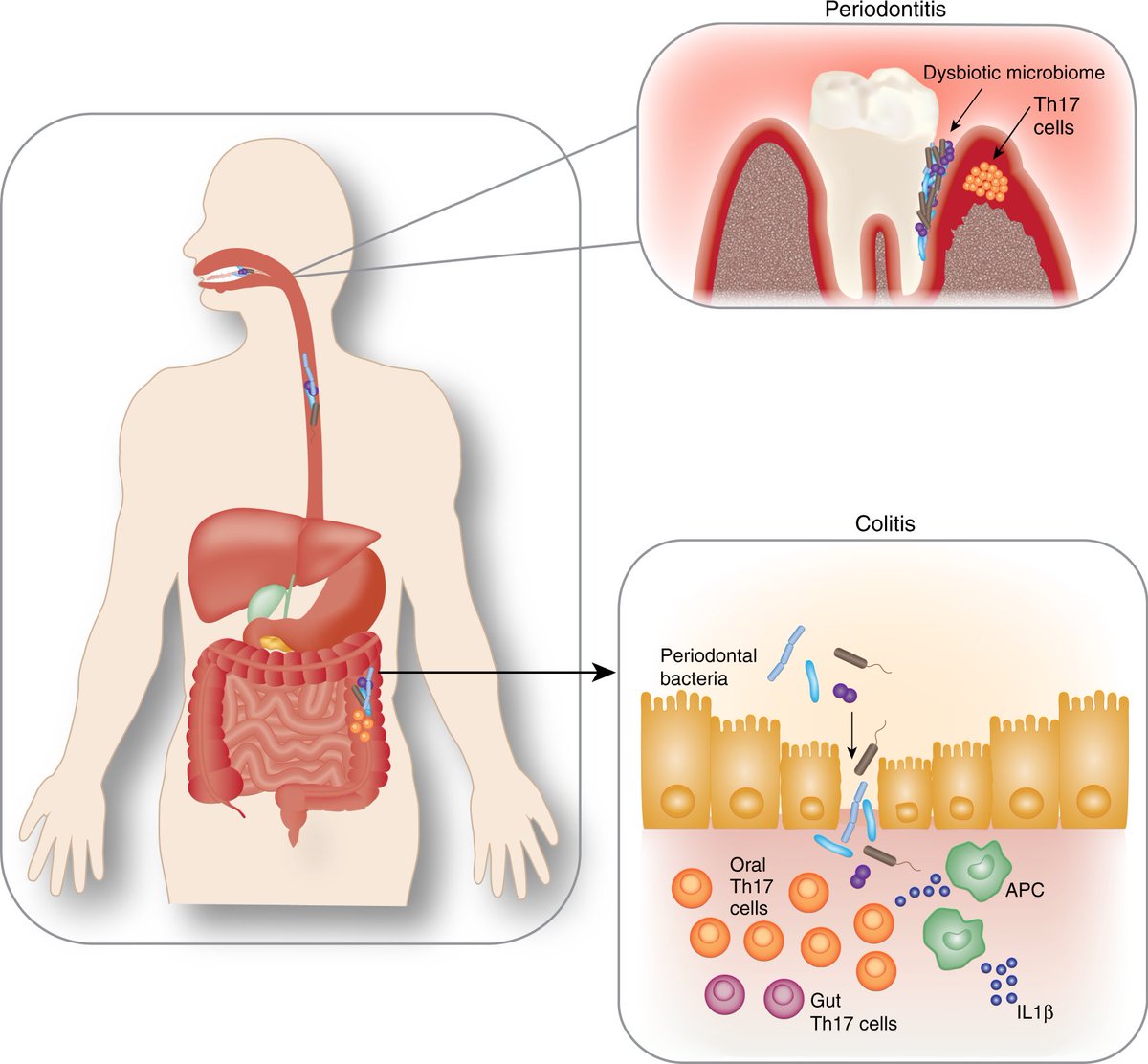

https://x.com/Outdoctrination/status/1877384078619554207
 The inability to pay attention in ADHD is not just a feeling, it's a well characterized system in the brain.
The inability to pay attention in ADHD is not just a feeling, it's a well characterized system in the brain.

https://x.com/Outdoctrination/status/1952777425932148765

 This study came out in 2021.
This study came out in 2021.

 This first study came out in 2008.
This first study came out in 2008.

https://x.com/Outdoctrination/status/2020490038870433827
 The narrative that most doctors / public health agencies say around this topic is that:
The narrative that most doctors / public health agencies say around this topic is that:
 This first study came out in 2004 in JAMA.
This first study came out in 2004 in JAMA.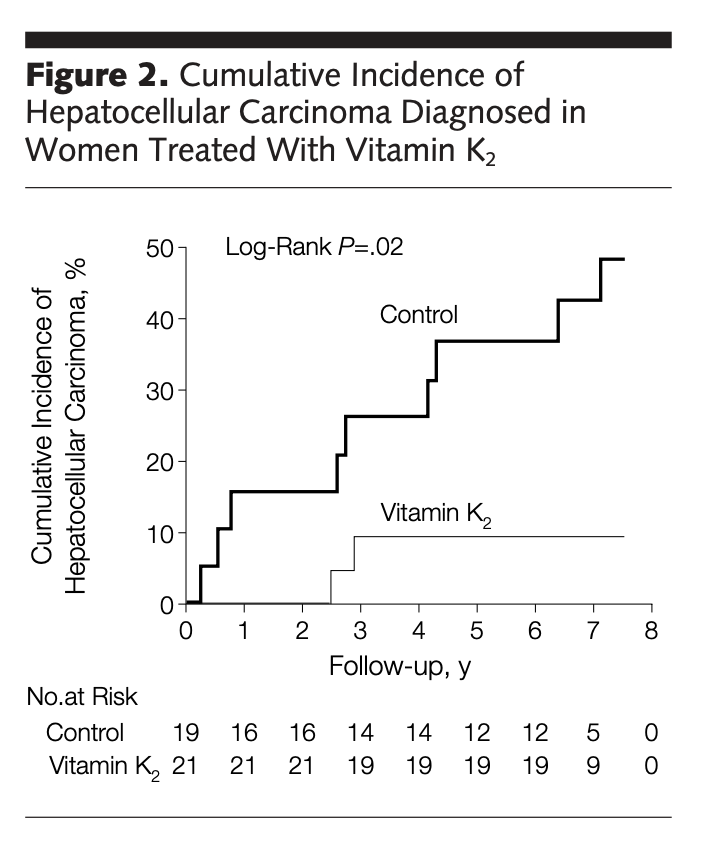

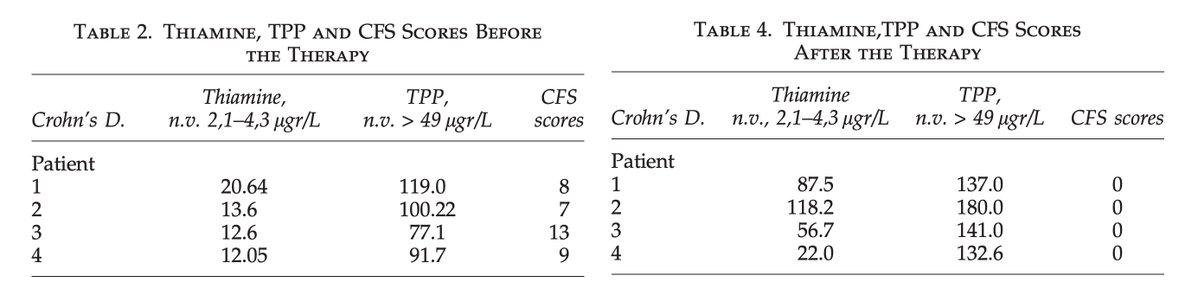
 This first study was a small pilot study conducted about a decade ago.
This first study was a small pilot study conducted about a decade ago.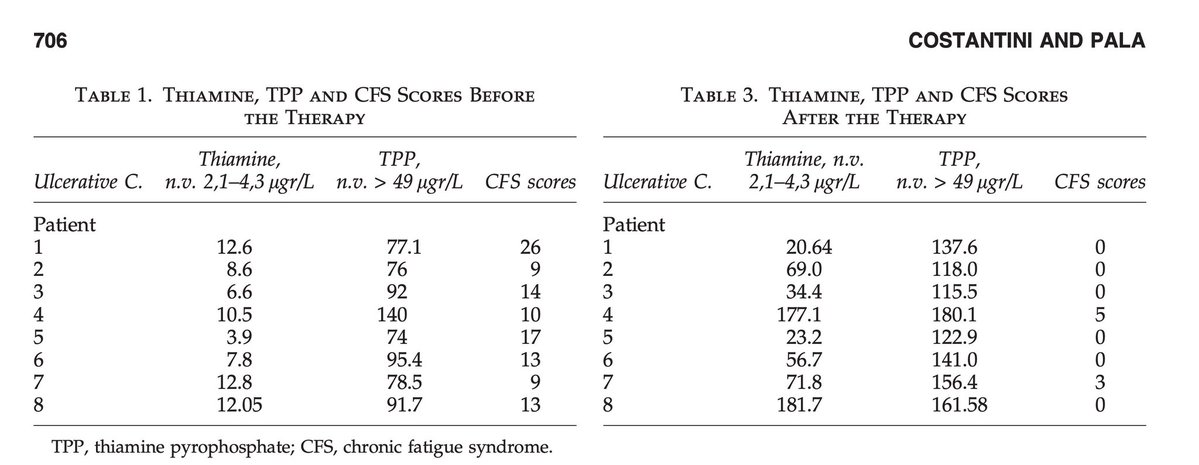

 Vitamin E does a few things that make it so powerful:
Vitamin E does a few things that make it so powerful:
 This study was published in 2024, investigating the effects of iron chelation on age related parameters.
This study was published in 2024, investigating the effects of iron chelation on age related parameters.
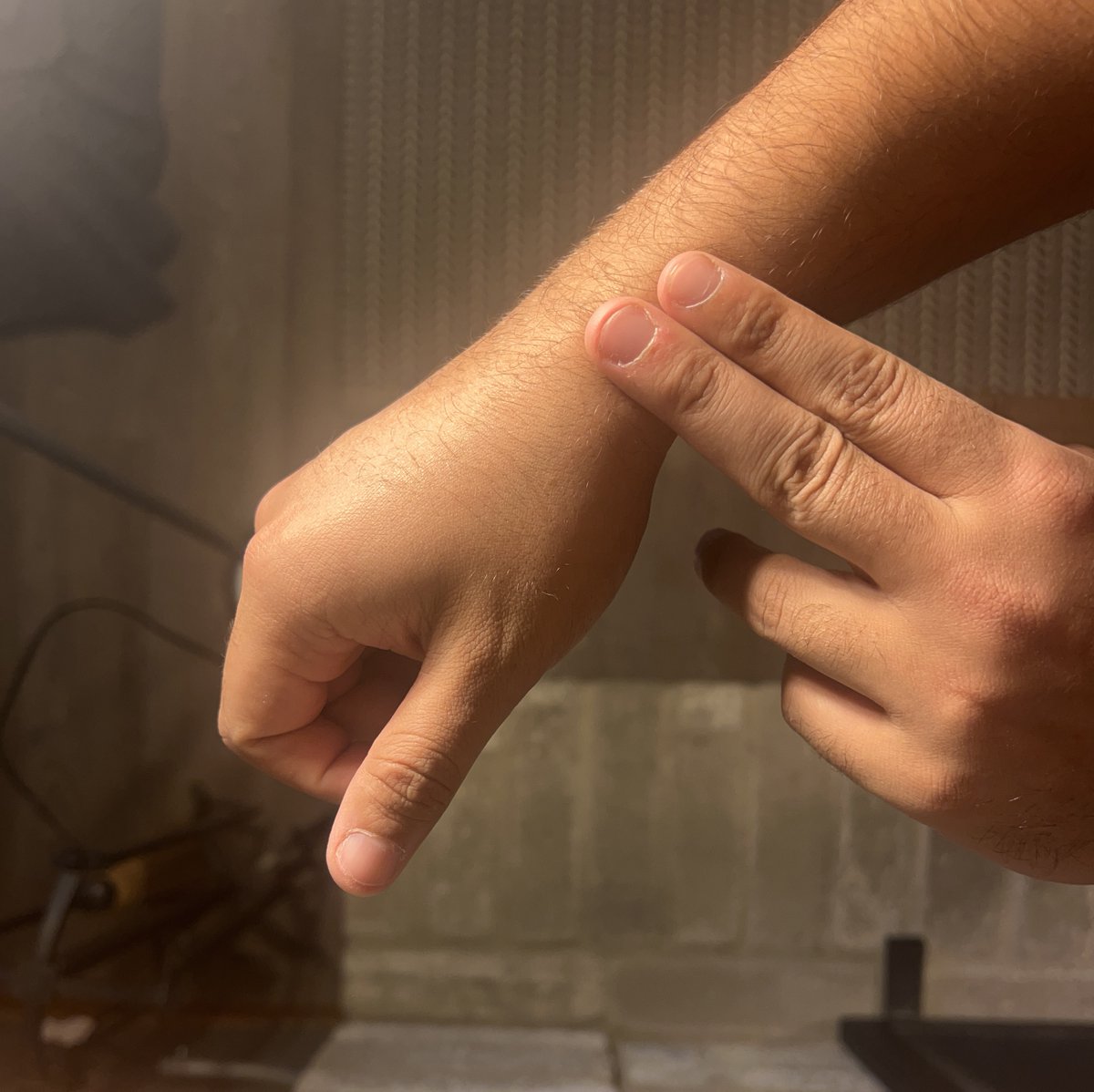

 What you are feeling is your radial artery in your wrist area.
What you are feeling is your radial artery in your wrist area.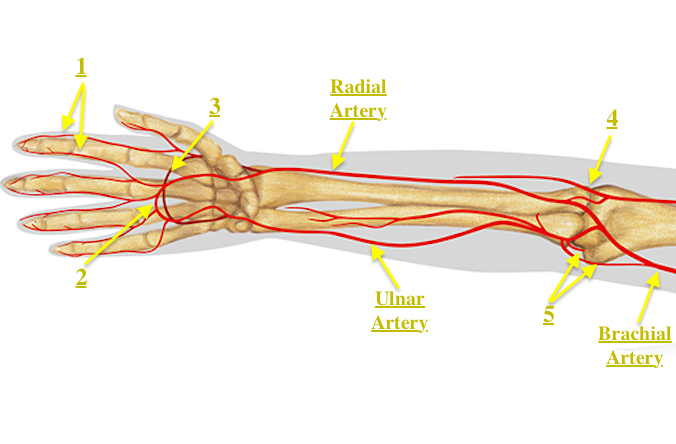

https://x.com/Outdoctrination/status/1988009439228502109

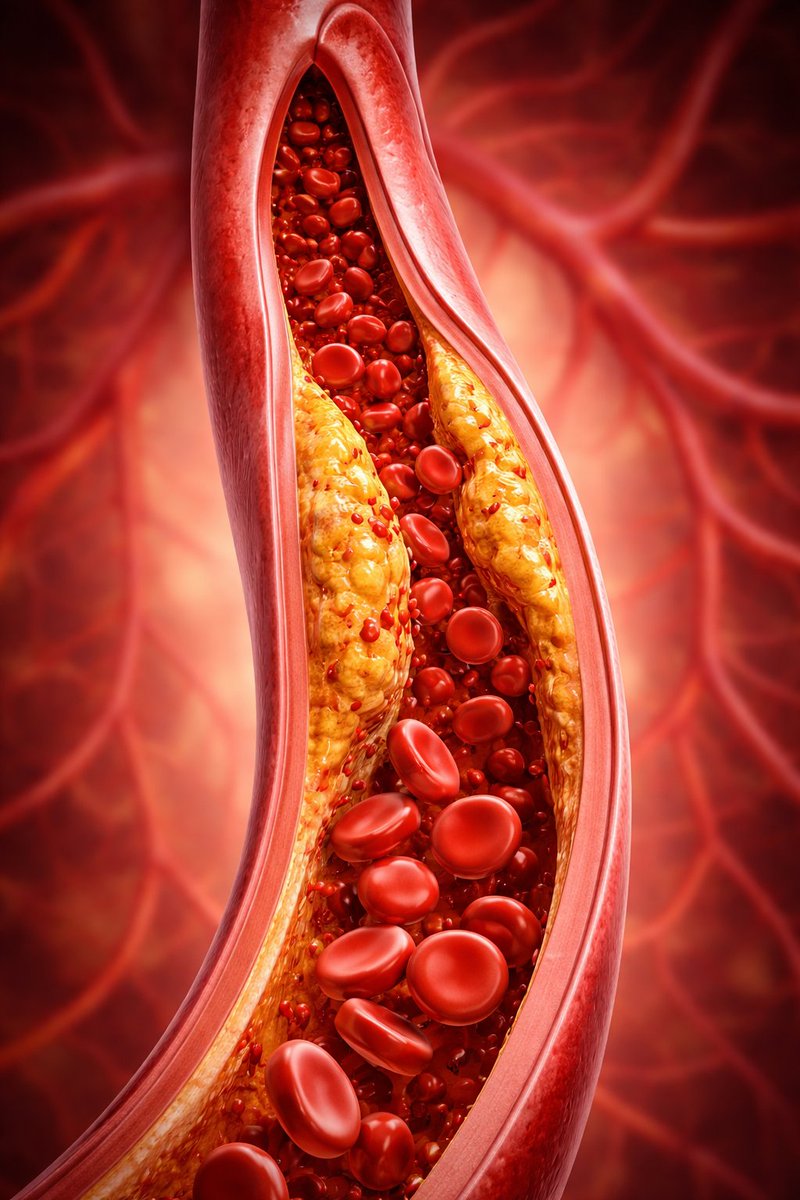 This study was published in 2019, examining people with diabetes with plaque in the coronary artery.
This study was published in 2019, examining people with diabetes with plaque in the coronary artery.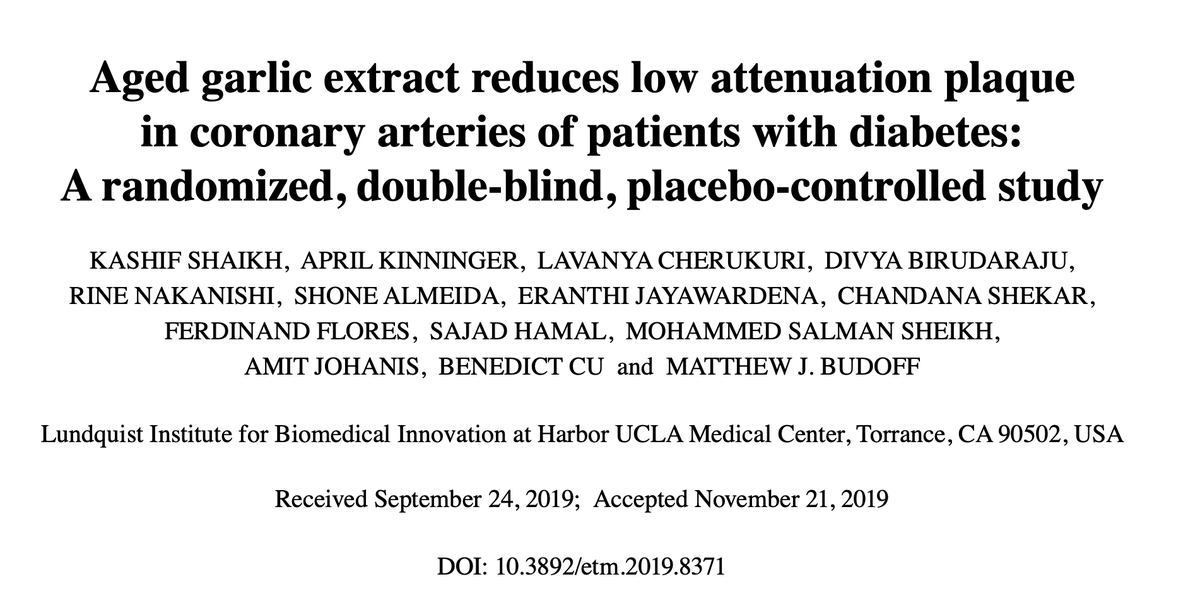

 Animals were put into 6 groups - either getting aluminum or NAC or both.
Animals were put into 6 groups - either getting aluminum or NAC or both.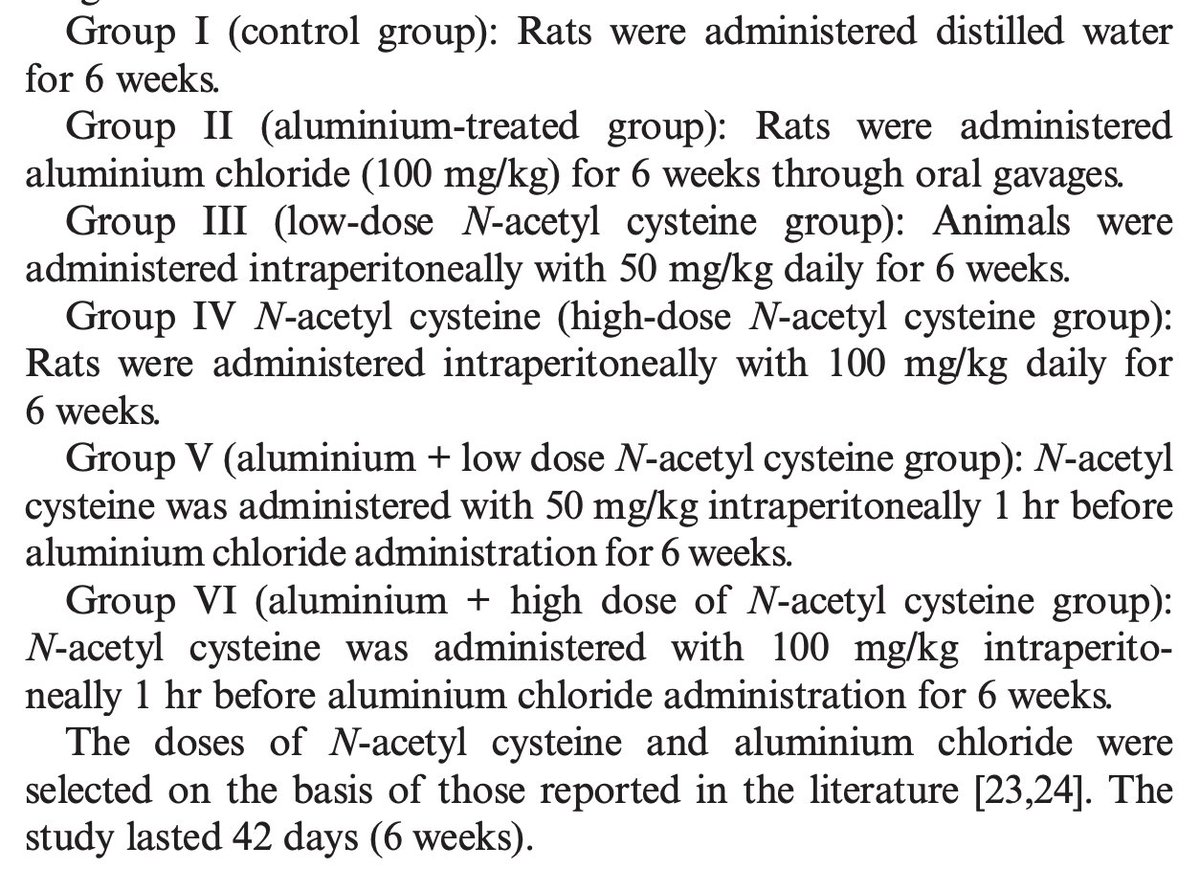

 This first paper is a review article from 2017.
This first paper is a review article from 2017.

 The idea that vitamin C supplementation can cause kidney stones is not completely baseless, but it does lack context.
The idea that vitamin C supplementation can cause kidney stones is not completely baseless, but it does lack context.


 In 2024 a massive review of studies was done on the effects of fluoride exposure and markers of thyroid health.
In 2024 a massive review of studies was done on the effects of fluoride exposure and markers of thyroid health.