Radiant Energy Group recently published a massive international survey of opinions on nuclear energy.
It's full of some things you might already know, but it also contains some surprises🧵
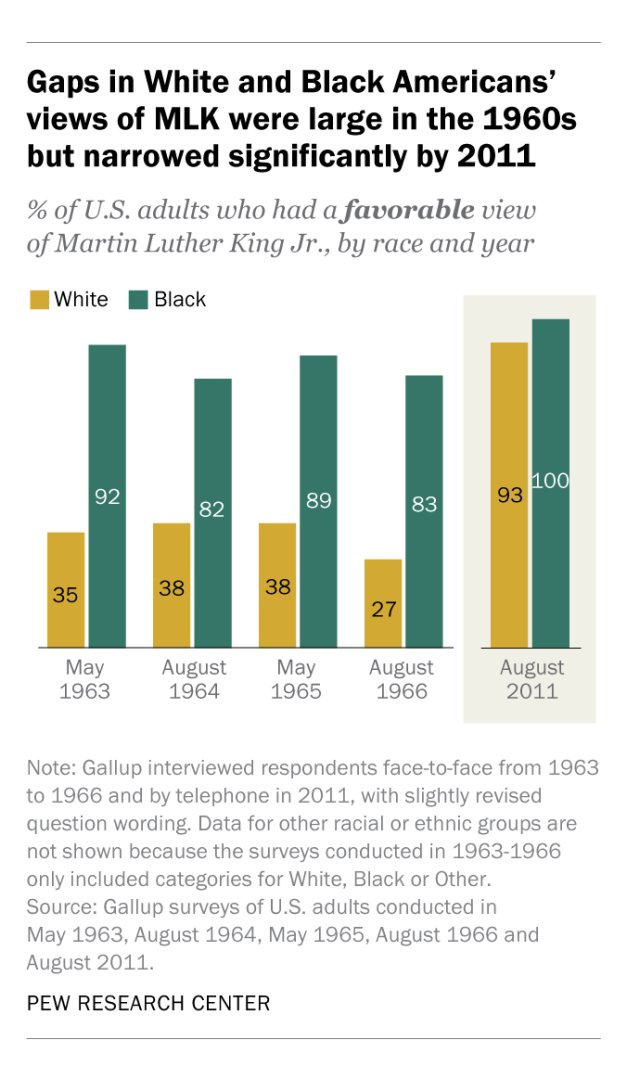
For example, did you know French and German nuclear support isn't that different?
It's full of some things you might already know, but it also contains some surprises🧵
For example, did you know French and German nuclear support isn't that different?

Nuclear does have less support than other green technologies, but in most places, it still receives net support. 

This apparently low level of support looks higher when survey participants are asked about their ranked supported for different energy sources. 

This support increases further if you subset to people who are techno-optimists or tech-neutral when it comes to fighting against climate change. 

Unfortunately, most people aren't aware about nuclear is exceptionally clean. Even larger numbers think nuclear waste is a major point of worry.
The Simpsons has done incredible damage to the reputation of our best energy source.
The Simpsons has done incredible damage to the reputation of our best energy source.

Onto the demographics!
In some countries, the old are the most supportive of nuclear. In others, it's the young.
In some countries, the old are the most supportive of nuclear. In others, it's the young.
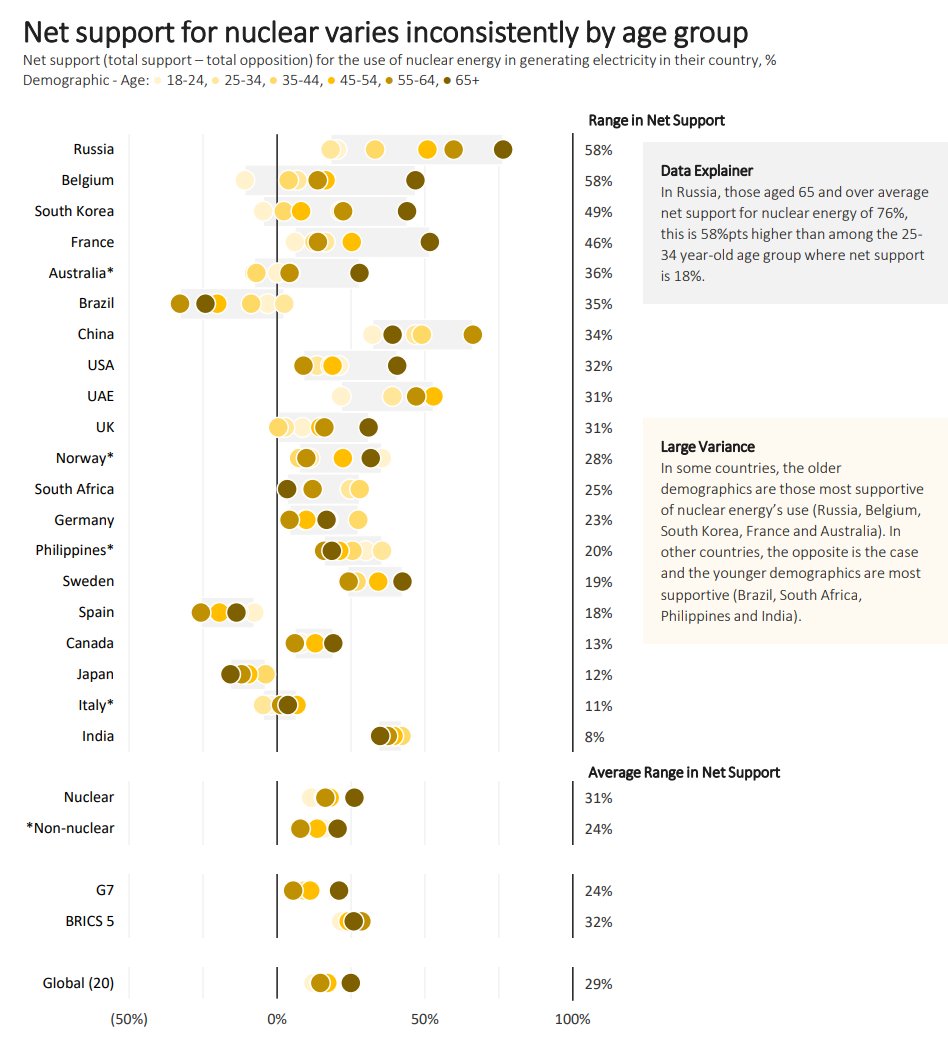
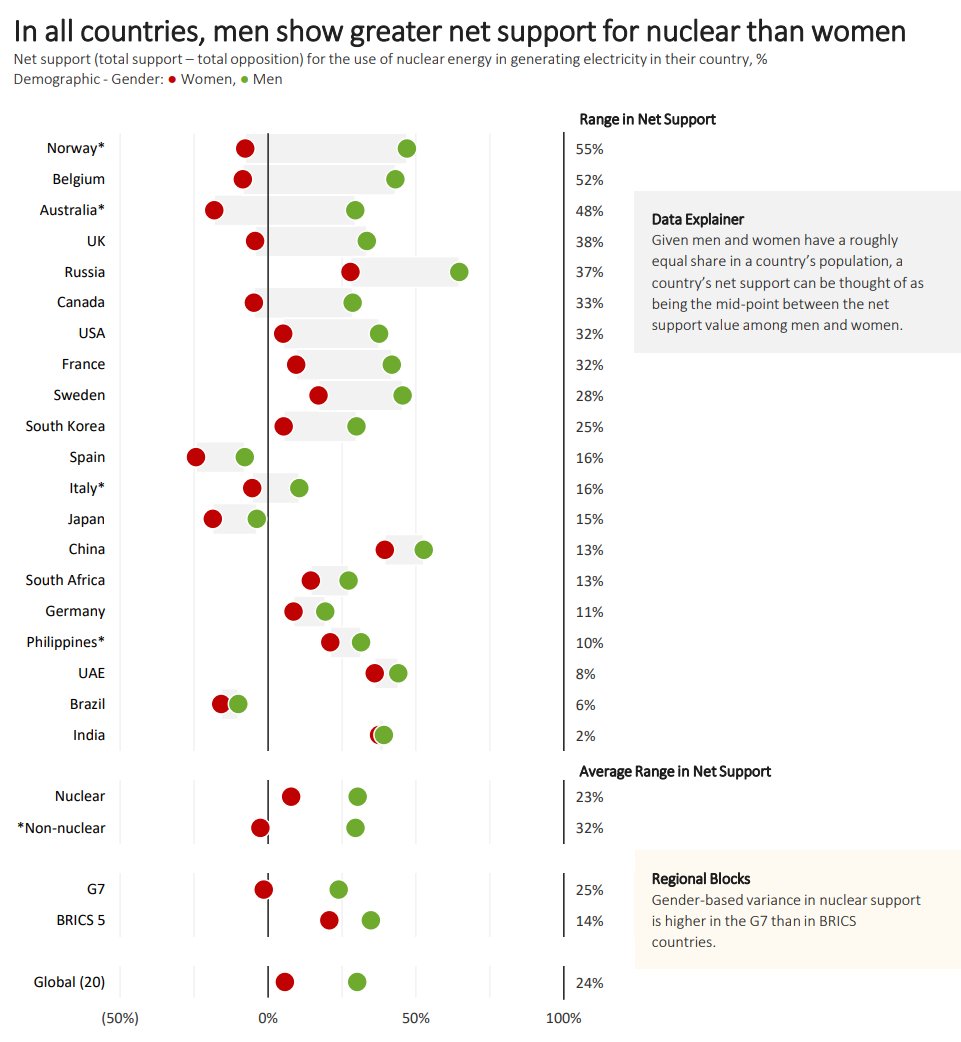
If you've seen other surveys on the demographics of nuclear support this one won't surprise you: men are universally more supportive of nuclear. 
If you've seen other surveys on the relationship between science knowledge and nuclear support, this won't surprise you either: the most knowledgeable are (almost) universally the most supportive of nuclear. 

Despite being the current best option for providing reliable, low-cost, and clean energy, being concerned about the climate generally predicts less support for nuclear.
When climate concern is represented by nonprofit membership, there's a similar result.

When climate concern is represented by nonprofit membership, there's a similar result.


Despite the nuclear industry being aligned with numerous (typically) left-wing goals from protecting the environment to supporting labor unionization and high employee safety standards, it's the economically right wing that's more supportive of nuclear. 

There's more in the report, but I'll end this thread on a happy note: globally, there's more support for additional nuclear builds than for additional nuclear shutdowns. 

Give the whole report a read, here: radiantenergygroup.com/reports/public…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh