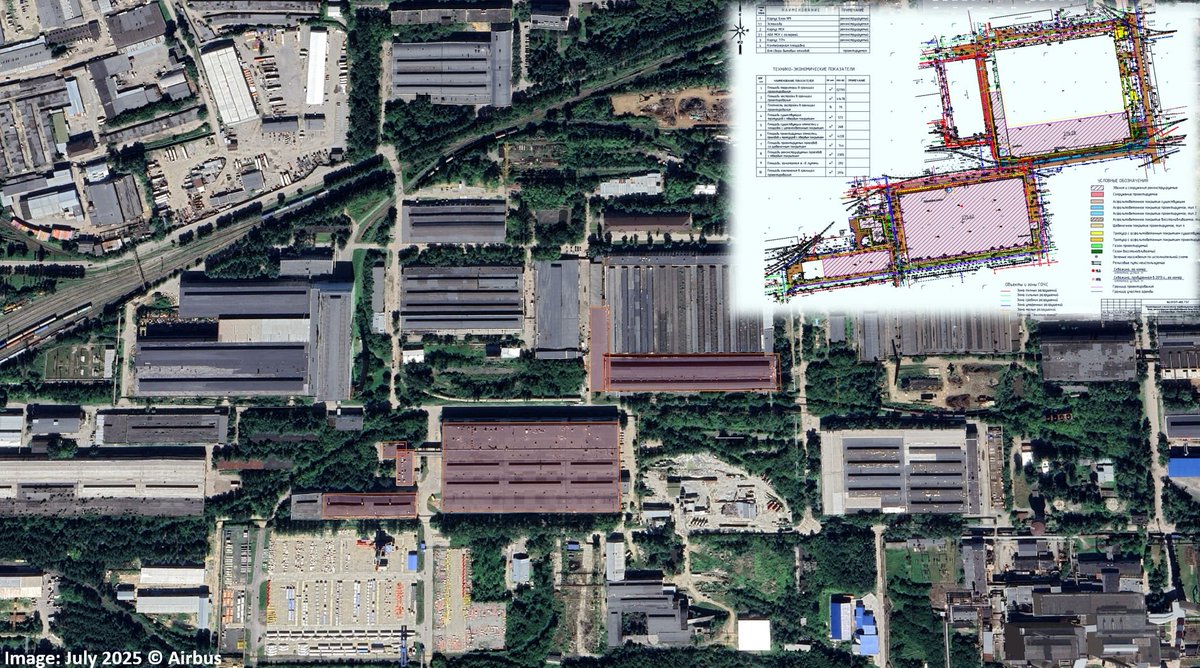
Geospatial Analysis: Railroad Construction on Occupied Territories. 🧵Updated Thread:
1/ Frontelligence Insight examined satellite imagery of railroad constructions in occupied territories, specifically south of Donetsk and in Mariupol. Here is what we know:
1/ Frontelligence Insight examined satellite imagery of railroad constructions in occupied territories, specifically south of Donetsk and in Mariupol. Here is what we know:

2/Burne - Malovodne branch
To enhance logistics between Russia, Donetsk, and Mariupol, Russians are actively constructing a new railroad branch to the south of Donetsk. This branch aims to bypass a risky section of the frontline near Mariinka and Vuhledar.
To enhance logistics between Russia, Donetsk, and Mariupol, Russians are actively constructing a new railroad branch to the south of Donetsk. This branch aims to bypass a risky section of the frontline near Mariinka and Vuhledar.

3/ The new branch starts in the village of Burne and links up with the existing railroad at Malovodne. Based on satellite imagery, significant progress is evident in the construction of this railroad branch, making our team believe that it might be completed in 2024. 

4/ Comparative analysis highlights a slowdown due to the construction of a bridge over the Kal'mius River. While composing this analysis, reports from the adviser to the Mariupol mayor suggested that Ukrainian forces had targeted the bridge while still under construction
5/ The vulnerability of this single point of failure to Ukrainian weaponry increases the likelihood of future strikes even after completion, impacting the functionality of the entire railroad branch. 

6/ Taganrog - Crimea
Russians are also working on the railroad connecting Taganrog with Mariupol and Crimea to the rest of Russia. This serves as an alternative to the Crimean Bridge, aiming to shorten travel time. Frontelligence Insight has identified early construction stages
Russians are also working on the railroad connecting Taganrog with Mariupol and Crimea to the rest of Russia. This serves as an alternative to the Crimean Bridge, aiming to shorten travel time. Frontelligence Insight has identified early construction stages
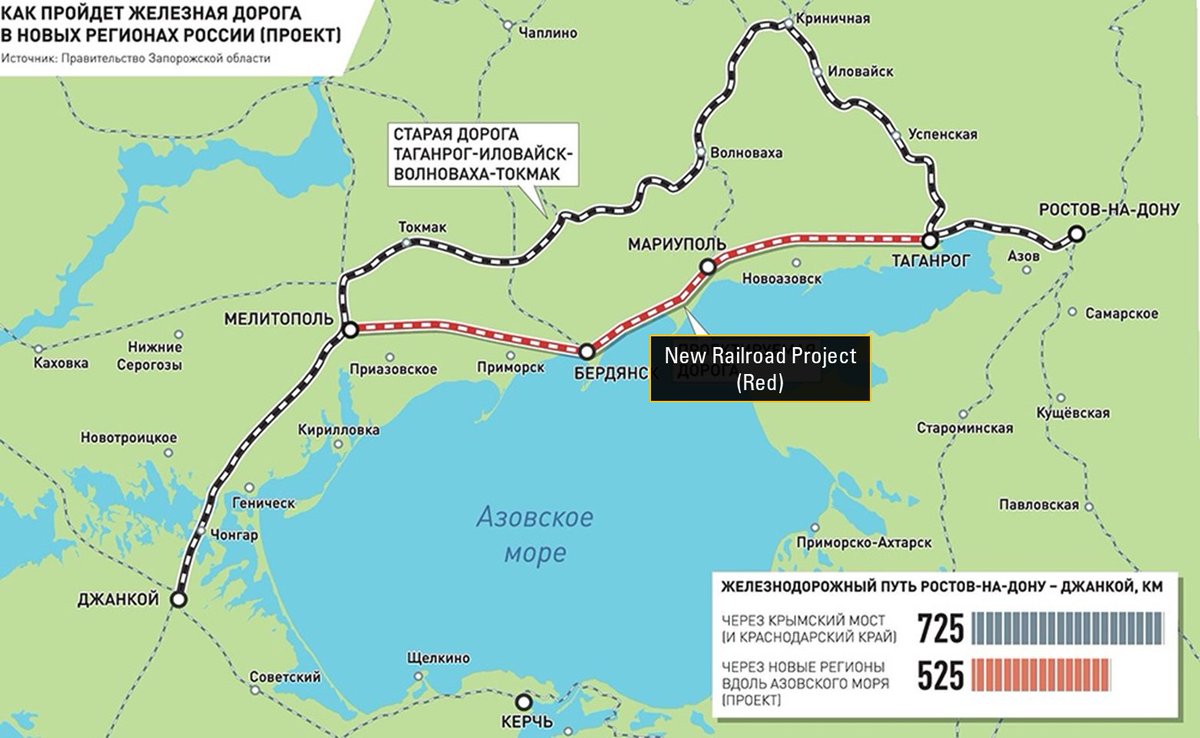
7/ In contrast to the previously mentioned railroad between Burne and Malovodne, this railroad branch is much longer and is still in the early stage of construction. Consequently, we assume that Russia won’t be able to complete this project by the end of 2024.
8/ Sattelite imagery shows that Russians also successfully restored the gas pump station and worked on the restoration of a gas pipeline between Mariupol and the broader continental region of Russia. 
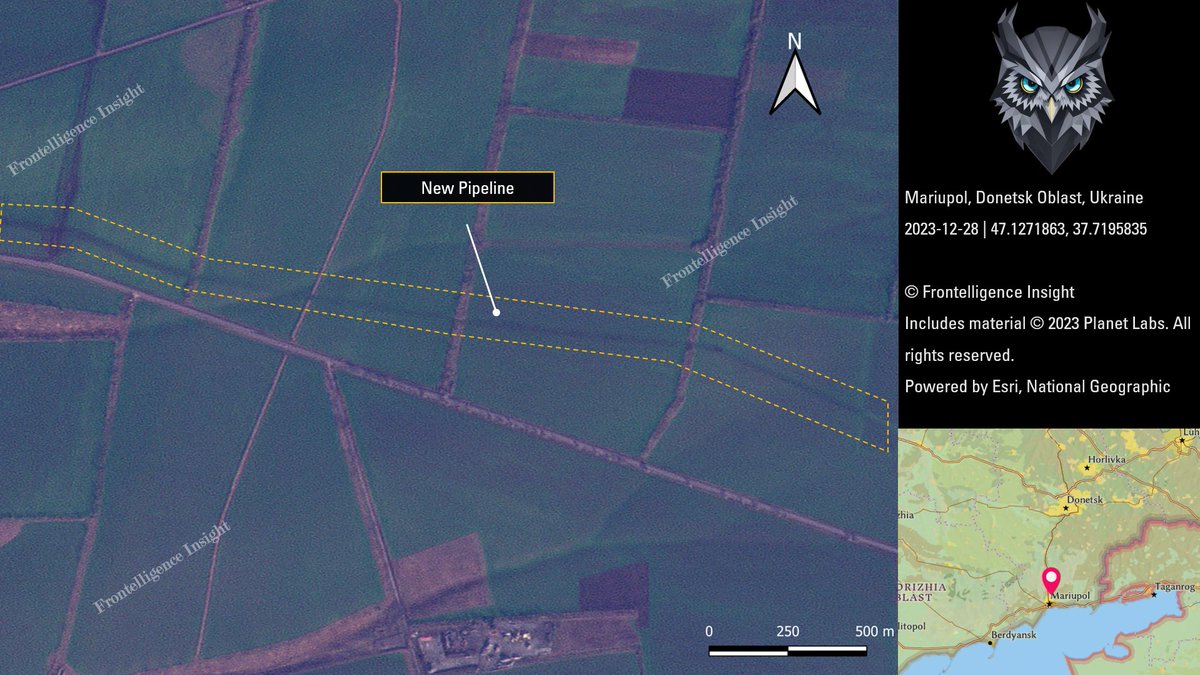
9/ This pipeline is likely a component of the Mariupol-Taganrog natural gas system. The significant investment in infrastructure suggests that the Russians are intending to transform the region into a fortified frontline stronghold with a robust military presence. 

10/ To effectively target railroad bridges, Ukraine would require more powerful missiles designed for bridge destruction, like the German Taurus missiles. Overall, Russia is anticipated to improve and expand its military infrastructure on occupied territories in 2024 

11/ With Ukraine facing challenges such as ammo shortages, undermanned units, and limited assistance from the US in 2024, a defensive approach will likely be adopted. Concurrently, Russian forces are expected to intensify their efforts in expanding their military infrastructure. 

12/ The full analysis is accessible on the website listed in my bio. Kindly consider supporting us through BuyMeaCoffee, as our expenses rely solely on your public support, and maintaining quality without financing is still challenging for us. Don't forget to share and like!
13/ This is an updated thread to address inaccuracies and incorporate additional imagery. In the previous version, an image near Mariupol was mislabeled as a railroad instead of a pipeline, which is now corrected. We apologize for any confusion.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh